Pulse width modulation switching-on method and system of LED display driving
A technology of pulse width modulation and display drive, which is applied to static indicators, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as small brightness unevenness, electromagnetic interference, and LED current instability in LED display systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
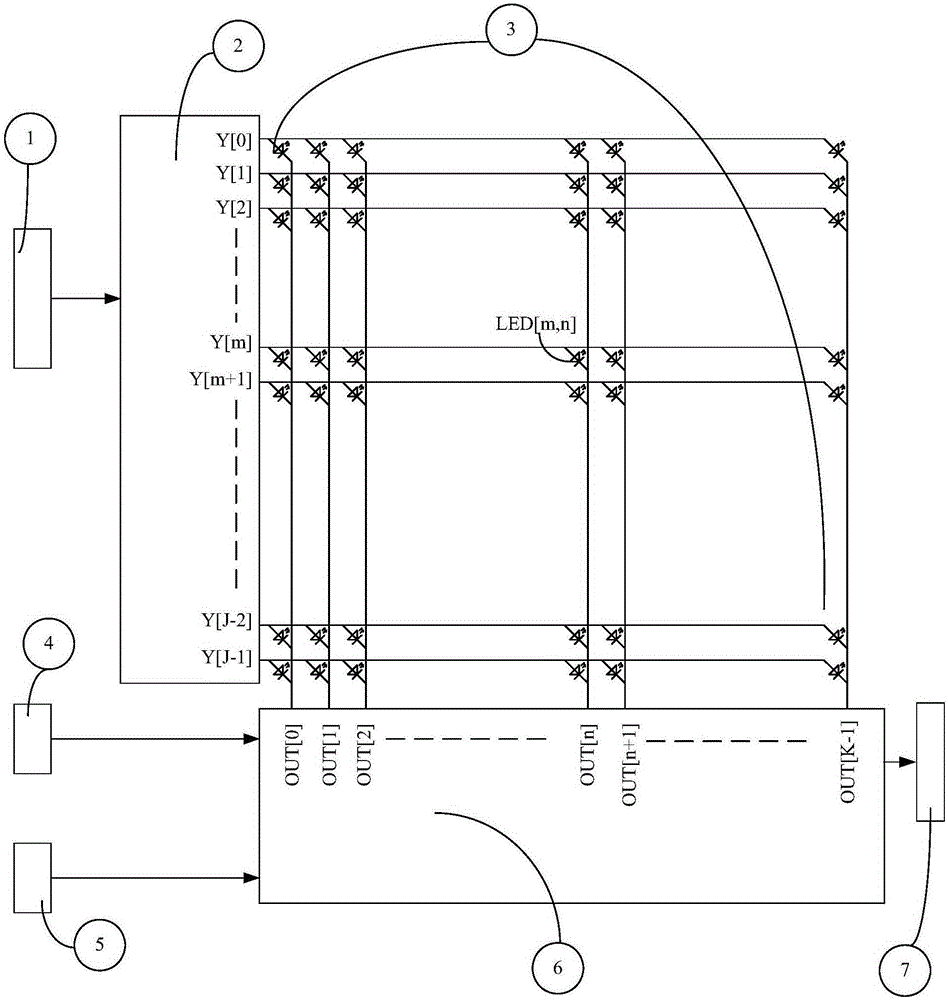
[0055] The present invention also provides a pulse width modulation conduction system for LED display drive. Embodiment 1 of the system of the present invention specifically includes:
[0056] PWM period register, PWM brightness register, subtractor, bias bit register, shifter, adder and conduction module;
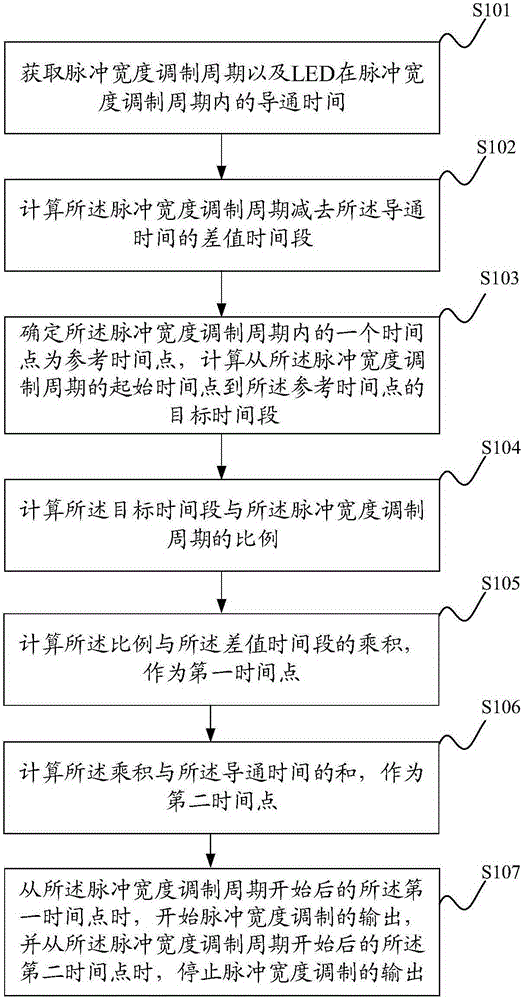
[0057] The PWM period register is used to obtain the pulse width modulation period;
[0058] The PWM brightness register is used to obtain the conduction time of the LED in the pulse width modulation cycle;
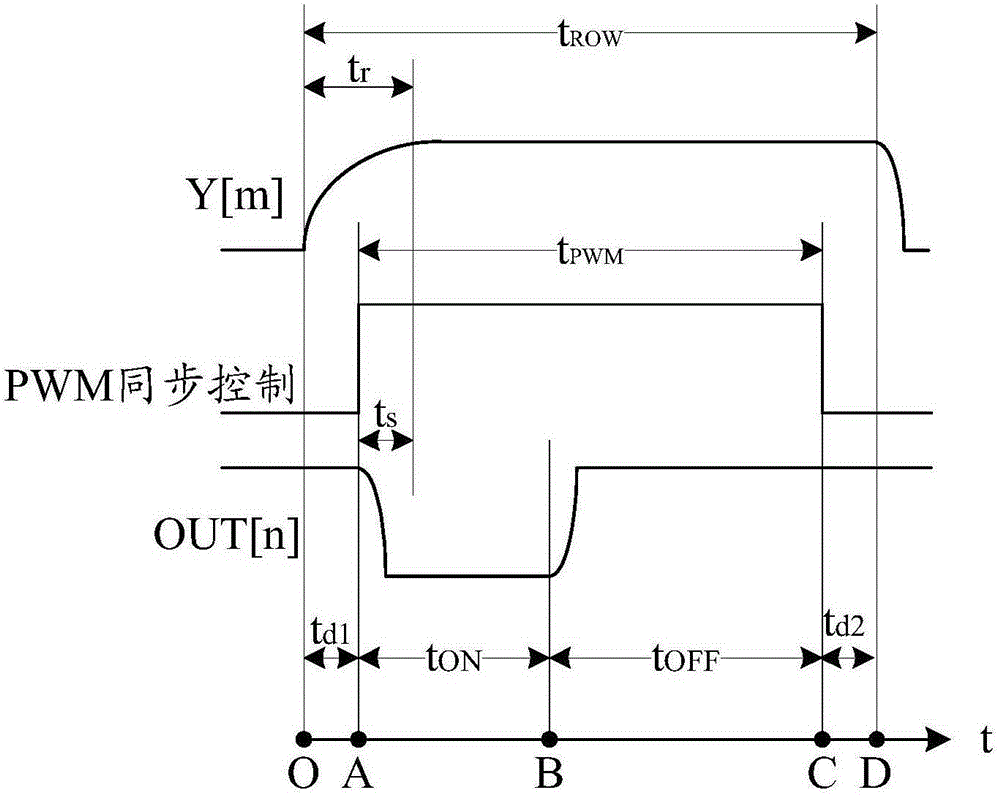
[0059] The subtractor is used to calculate the difference time period of the pulse width modulation period minus the conduction time;
[0060] The subtractor is used to determine a time point in the pulse width modulation cycle as a reference time point, calculate a target time period from the start time point of the pulse width modulation cycle to the reference time point, and calculate the the ratio of the target time period to the pulse width modulation period; ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com