A method for improving the tolerance and degradation rate of chlorella to phenol
A chlorella, degradation rate technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, methods of using microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of poor initial inoculation density phenol tolerance and low degradation rate, etc. Poor receptivity, low degradation rate, improved tolerance and degradation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
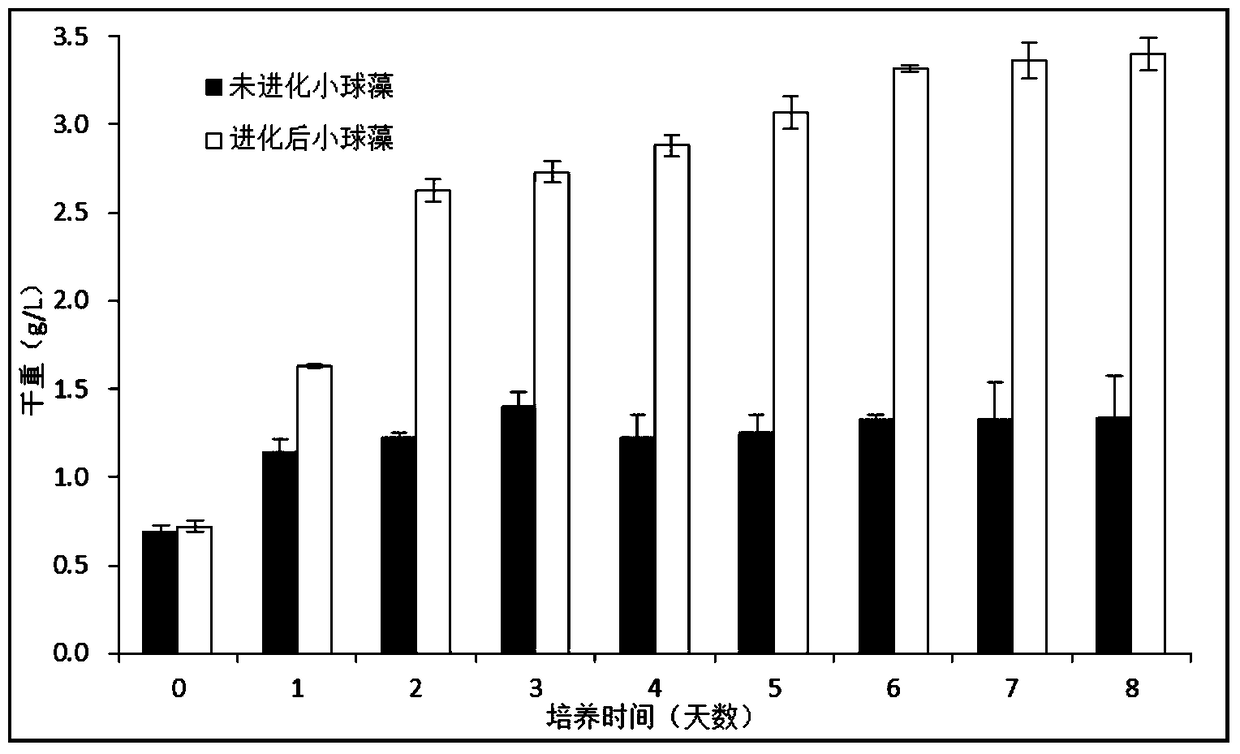
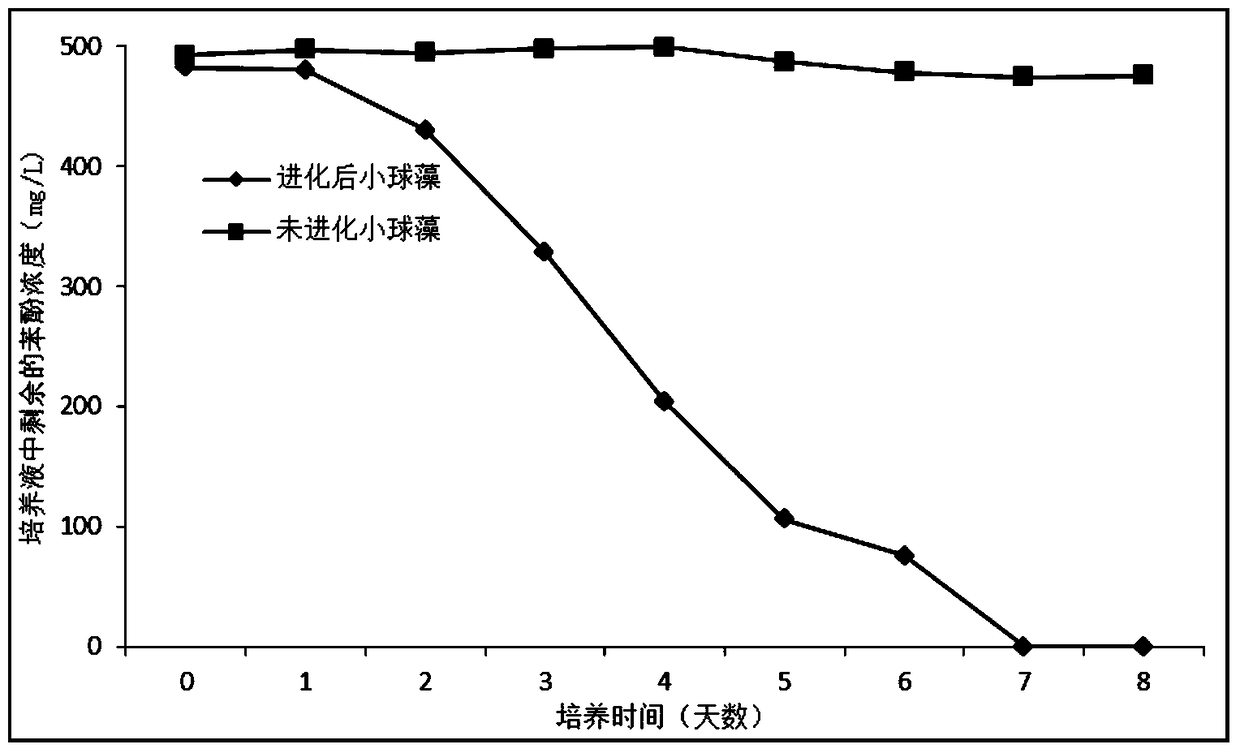
[0043] In this embodiment, Chlorella sp. whose initial concentration of 500 mg / L phenol cannot be degraded is taken as an example to illustrate the feasibility of the technical solution.
[0044] The basic medium of Chlorella is the above-mentioned TAP liquid medium, and the culture conditions: initial pH=6.0, temperature 29±0.8°C, light intensity 117.67±6.89μmol / m 2 / s, continuous light, 150rpm shaker shaking culture, the phenol concentration in the culture solution is 500mg / L.
[0045] The first generation of Chlorella was inoculated in 100mL TAP medium (250mL flask) with a phenol concentration of 500mg / L at an initial inoculation density of 0.6g / L. After 3 days of cultivation, the dry weight and liquid medium were measured. The remaining phenol concentration.
[0046] Next, dilute the first generation chlorella after 3 days of culture and continue to inoculate it with an initial inoculation density of 0.6 g / L in 100 mL of TAP liquid medium containing 500 mg / L of phenol (the medium...
Embodiment 2
[0062] The basal medium of Chlorella is the above-mentioned TAP liquid medium, and the culture conditions: initial pH=6.0, temperature 25℃, light intensity 100μmol / m 2 / s, continuous light, 100rpm shaker shaking culture, the phenol concentration in the culture solution is 450mg / L.
[0063] The first generation of Chlorella was inoculated in 100 mL of TAP medium (250 mL flask) with a phenol concentration of 450 mg / L at an initial inoculation density of 0.8 g / L, and measured its dry weight and liquid medium after 2 days of cultivation The remaining phenol concentration.
[0064] Next, dilute the first generation Chlorella after 2 days of culture and continue to inoculate it with an initial inoculation density of 0.8 g / L in 100 mL of TAP liquid medium containing 450 mg / L of phenol (the medium is re-formulated), and then culture for 2 days. Dry weight and concentration of phenol remaining in the culture medium. Repeat the above process and carry out 40 cycles of cyclic culture. The dr...
Embodiment 3
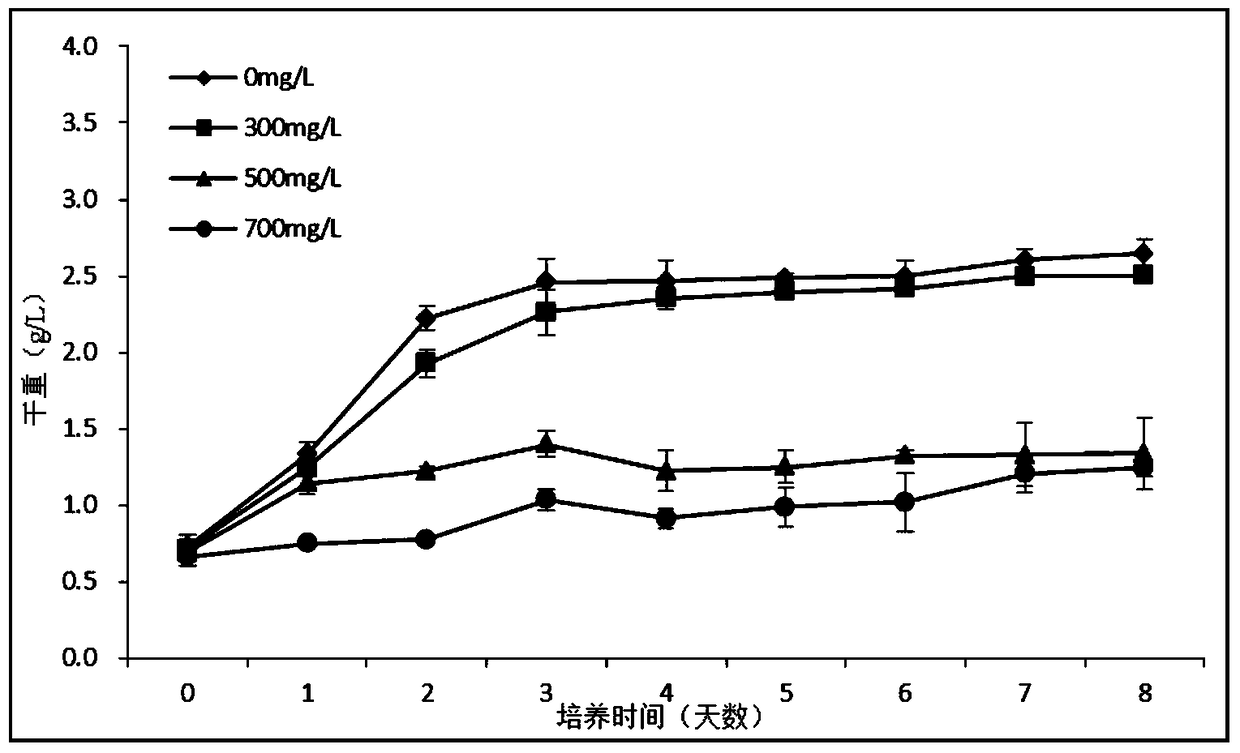
[0066] The basal medium of Chlorella is the above-mentioned TAP liquid medium, and the culture conditions: initial pH=7.0, temperature 35℃, light intensity 200μmol / m 2 / s, continuous light, 200rpm shaker shaking culture, the phenol concentration in the culture solution is 700mg / L.
[0067] The first generation of Chlorella was inoculated into 100mL TAP medium (250mL flask) with a phenol concentration of 700mg / L at an initial inoculation density of 1.0g / L. After 5 days of cultivation, the dry weight and liquid medium were measured. The remaining phenol concentration.
[0068] Next, dilute the first generation Chlorella after 5 days of cultivation and continue to inoculate it with an initial inoculation density of 1.0 g / L in 100 mL of TAP liquid medium containing 700 mg / L of phenol (the medium is re-prepared). Dry weight and concentration of phenol remaining in the culture liquid medium. Repeat the above process and carry out 50 cycles of cyclic culture. The dry weight of chlorella ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tolerance concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com