A PCR primer for identifying codling moth cell lines and its identification method
A technology of codling moth and cell line, applied in the field of agricultural biology, can solve the problems of poor repeatability, low sensitivity and the like, and achieve the effect of stabilizing the enzyme cleavage identification method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Amplification and sequence analysis of COI gene fragments in codling moth cell lines and several other insect cell lines
[0029] The applicant analyzed the COI gene partial sequence (SEQ ID No: 5) of the amplified codling moth cell line and the COI gene partial sequence (SEQ ID No: 6) amplified from the codling moth egg genome; carried out in the NCBI database Blast comparison, using DNASTAR software to compare and analyze the COI gene fragments of codling moth and several other insects, found that the COI gene nucleotide identity of codling moth and black beetle was 81.6%, and the COI gene of beet armyworm was 81.6%. The nucleotide identity of the gene is 87.9%, and it is 83.9% nucleotide identity with the COI gene of Trichoplusia spp. There are obvious differences in the sequences.
[0030] According to the sequence analysis results, the applicant designed the following primers:
[0031] Forward primer LCO1490: 5'-GGTCAACAAATCATAAAGATATTGG-3' (SEQ ID NO:...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The PCR-RFLP pattern of embodiment 2 several codling moth cell lines
[0050] (1) Extraction of genomic DNA from several codling moth cell lines
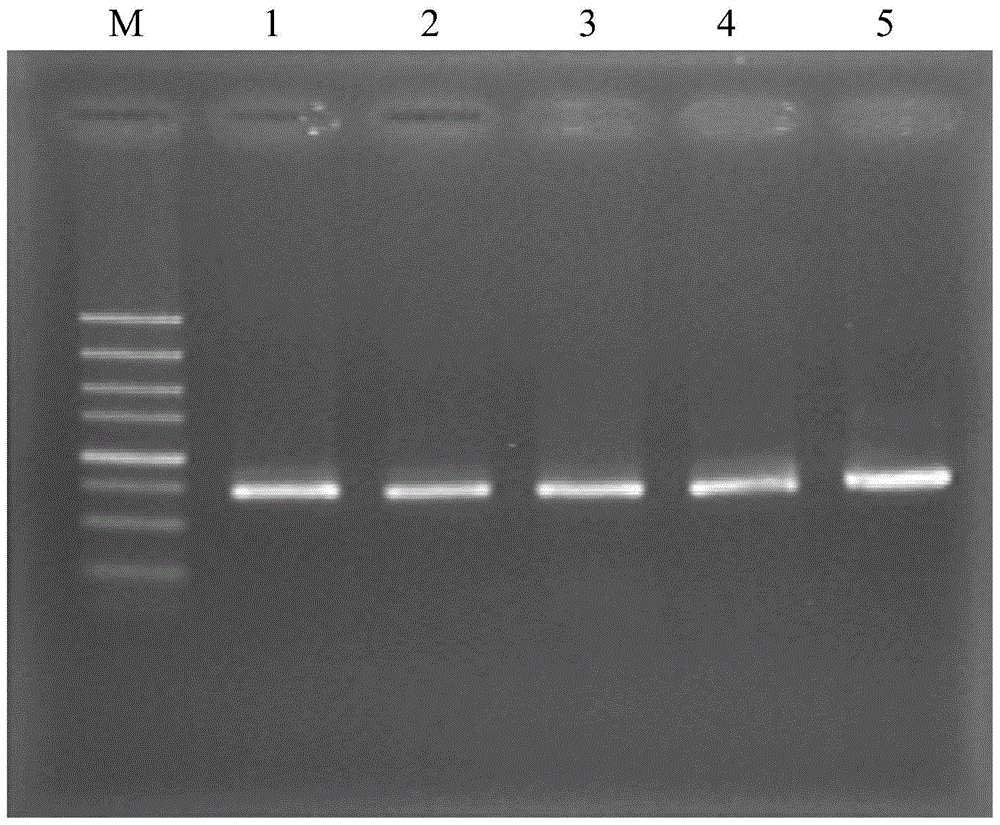
[0051] Seven codling moth cell lines Cp-E-4, Cp-E-6, Cp-E-9, Cp-E-10, Cp-E-11, Cp-E-12 and Cp - Genomic DNA was extracted from the cell suspension of E-13 with a MagExtractor-Genome kit to obtain genomic DNA solutions of each cell line of codling moth.
[0052] (2) PCR amplification of COI gene fragments in several codling moth cell lines
[0053] The genomic DNA solutions of several codling moth cell lines were respectively used as templates for PCR amplification to obtain PCR amplification products;
[0054] The PCR amplification system is:
[0055] Genomic DNA solution of codling moth cell line: 1 μL, 10 μmol / L forward primer: solution 1 μL, 10 μmol / L reverse primer solution: 1 μL, 5 U / μL Taq enzyme: 0.5 μL, 10×Taq buffer: 5 μL , 2.5mmol / L dNTP: 4μL, sterile pure water: 37.5μL.
[0056] The primer sequences are as fol...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3 The difference between codling moth cell lines and other several insect cell lines PCR-RFLP patterns
[0067] (1) Extraction of genomic DNA of codling moth, black gill beetle, beet armyworm and Trichoplusia spp.
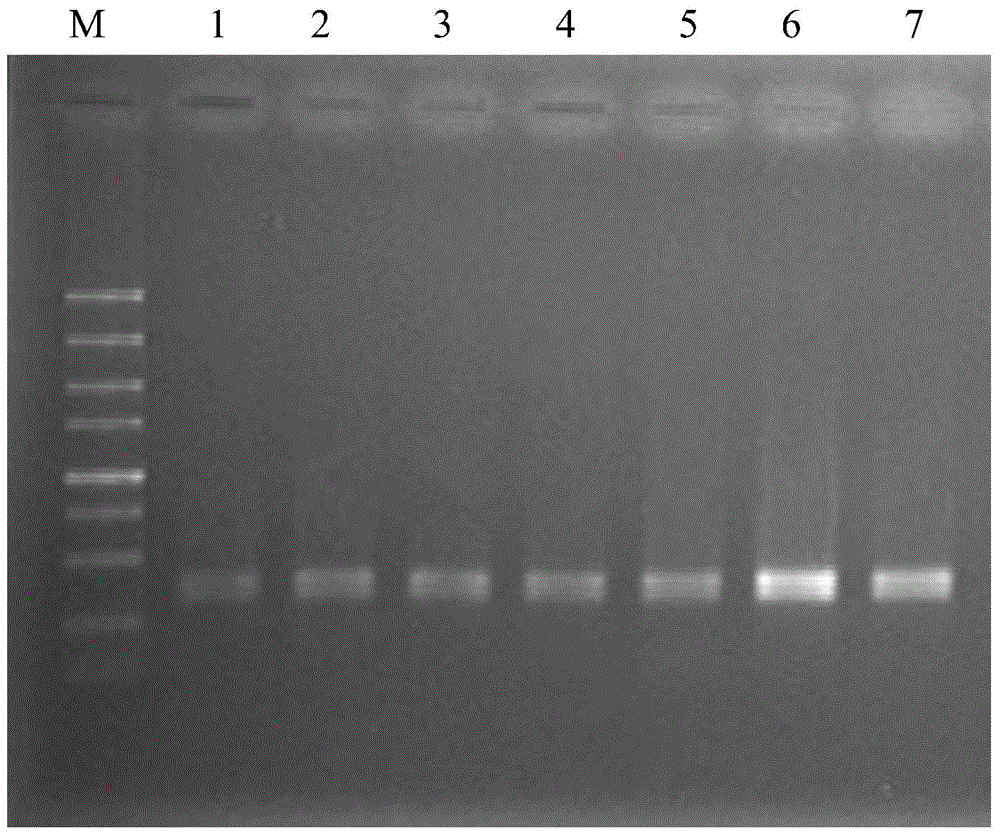
[0068] MagExtractor-Genome Reagent for Cell Suspensions of Codling Moth Cell Line Cp-E-10, Black Beetle Cell Line Hp-E-1, Beet Spodoptera Cell Line Se-1, and Trichoplusia Tn9-4s Genomic DNA was extracted using the cassette, and the genomic DNA solutions of the codling moth, black beetle, beet armyworm and Trichoplusiae cell lines were obtained.
[0069] (2) PCR amplification of COI gene fragments of codling moth, black gill beetle, beet armyworm and Trichoplusia spp.
[0070] The genomic DNA solution of codling moth and the genomic DNA solution of cell lines of beetle moth, beet armyworm and Trichoplusia spp. were respectively used as templates for PCR amplification to obtain PCR amplification products.
[0071] The PCR amplification system is:
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com