Analytical method of phytoplankton particle size structure
A technology for phytoplankton and structure analysis, which is applied in the field of phytoplankton particle structure analysis, and can solve the problems of large consumption of reagents, inability to indicate the particle size of a single algal cell, and cumbersome processing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] A method for analyzing the particle size structure of seawater phytoplankton, comprising the following steps:
[0096] 1) In-situ measurement of seawater absorption spectrum:
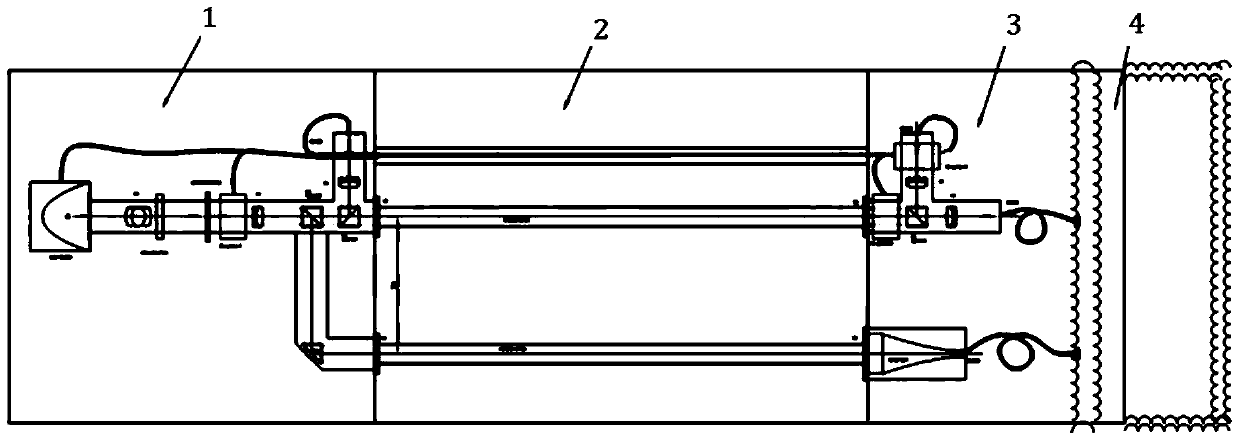
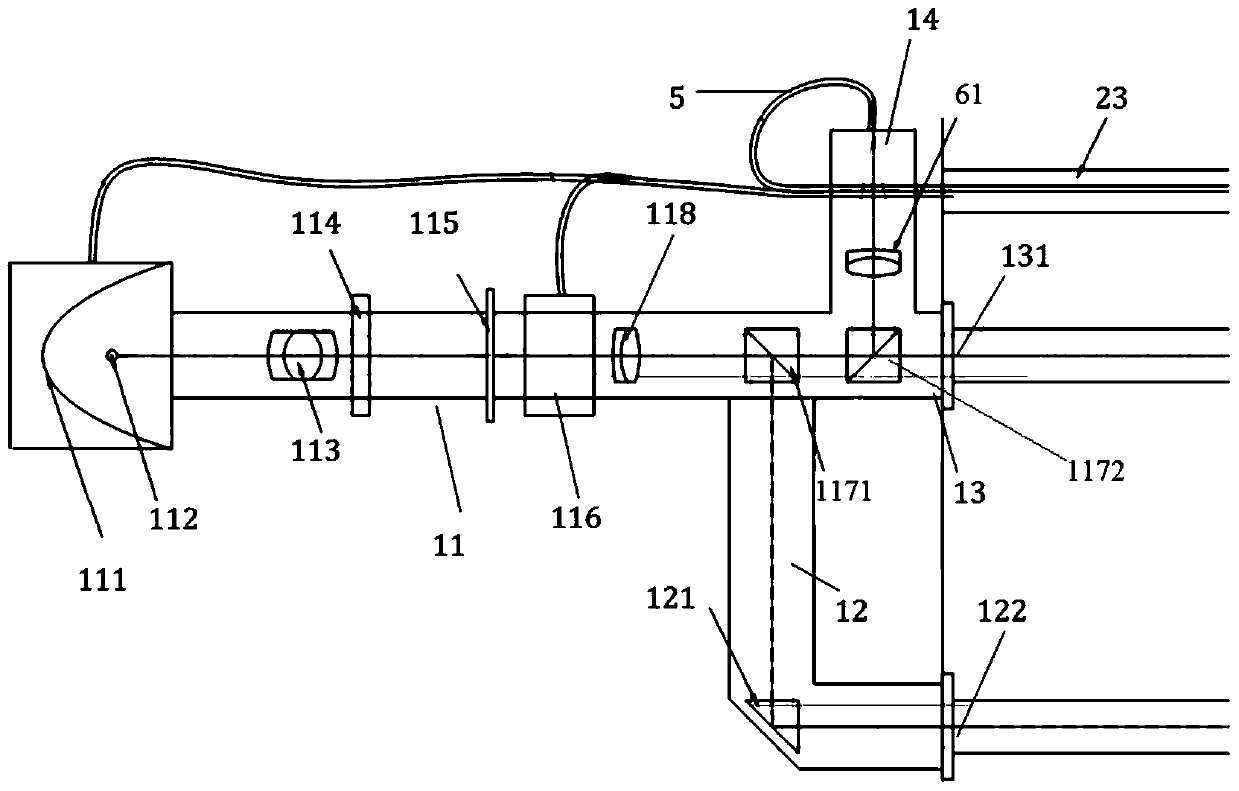
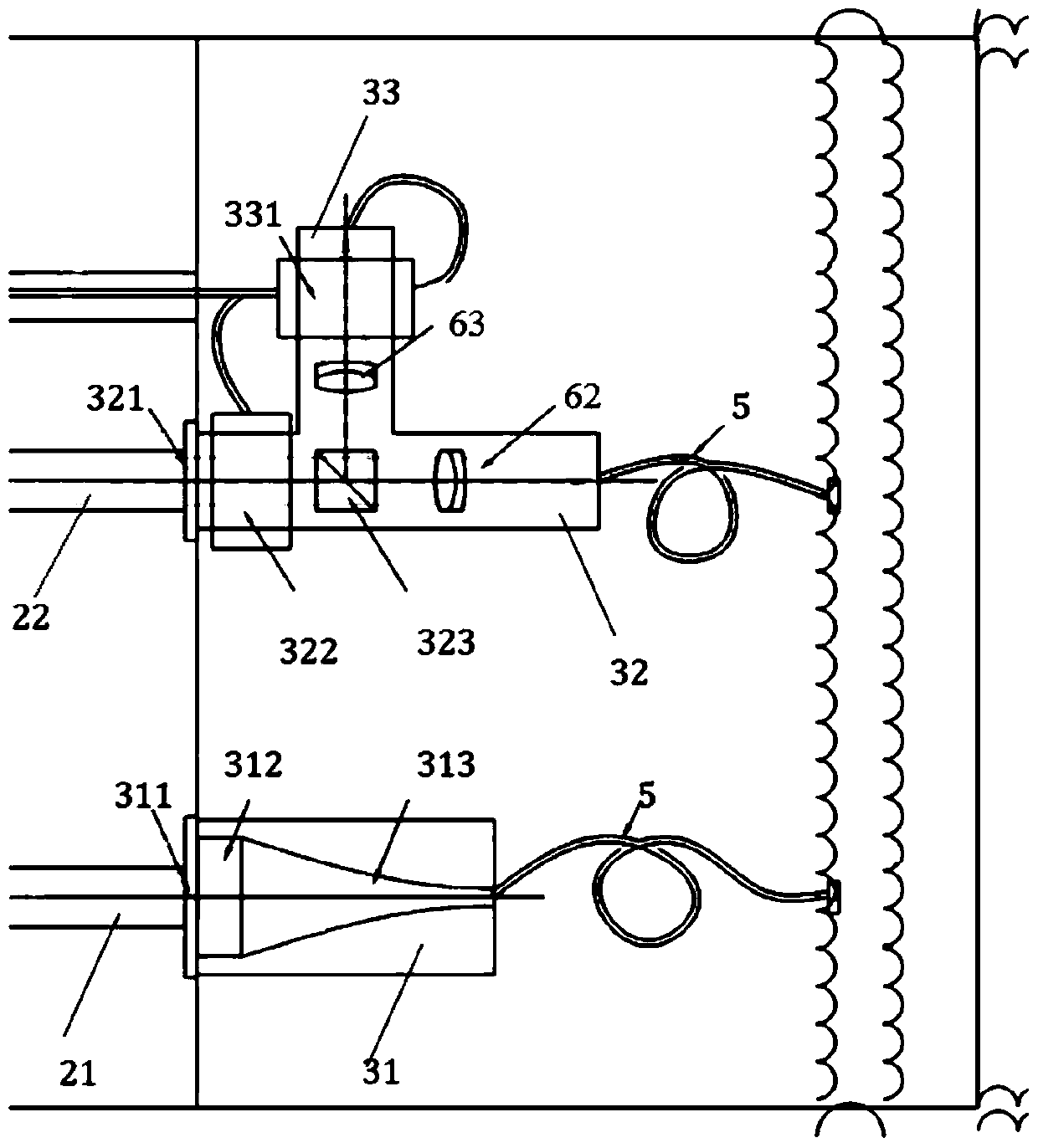
[0097] Use water body light attenuation and absorption parameter measuring instruments, such as figure 1 As shown, it is mainly composed of a light-emitting unit 1, a sampling unit 2, a detection unit 3, and a signal acquisition and analysis unit 4; the light-emitting unit 1 includes a main channel 11 and three sub-channels divided into one end of the main channel 11, which are respectively defined as absorption channels 12 , the attenuation channel 13 and the reference channel 14, the main channel 11 and the absorption channel 12 are directly connected, and the attenuation channel 13 is directly connected with the reference channel 14;
[0098] Such as figure 2 As shown, the main channel 11 is provided with a condenser cover 111, a light source 112 for sampling a high-stable tungsten halogen ...
Embodiment 2
[0125] A method for analyzing the particle size structure of seawater phytoplankton, comprising the following steps:
[0126] 1) In-situ measurement of seawater absorption spectrum:
[0127] Concrete measurement method is with embodiment 1;
[0128] 2) extract phytoplankton absorption coefficient from the spectral absorption coefficient a (λ) of described seawater by decomposition method:
[0129] According to the existing research, the spectral absorption coefficient a(λ) of seawater is expressed according to the composition of the water body as:
[0130] a(λ)=a w (λ)+a p (λ)+a CDOM (λ) (14)
[0131] Among them, a w (λ), a p (λ) and a CDOM (λ) represent the absorption coefficients of pure seawater (w), total particulate matter (p) and colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM), respectively;
[0132] The absorption coefficient of total particulate matter (p) can further decompose the absorption coefficient of phytoplankton (ph) a ph (λ) and non-algae particulate matter...
Embodiment 3
[0148] A method for analyzing the particle size structure of seawater phytoplankton, comprising the following steps:
[0149] 1) In-situ measurement of seawater absorption spectrum:
[0150] Concrete measurement method is with embodiment 1;
[0151] 2) extract phytoplankton absorption coefficient from the spectral absorption coefficient a (λ) of described seawater by decomposition method:
[0152] Concrete extraction method is with embodiment 2;
[0153] 3) Extract the size parameter S of phytoplankton based on the shape change of phytoplankton absorption spectrum :
[0154] First, according to the effect of algae particle size on the shape change of phytoplankton absorption spectrum, a hybrid spectral model is established, and the particle size parameter S :
[0155]
[0156] in: is the normalized absorption coefficient of phytoplankton, and represent the normalized absorption coefficients of picophytoplankton and microphytoplankton, respectively, and the pa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com