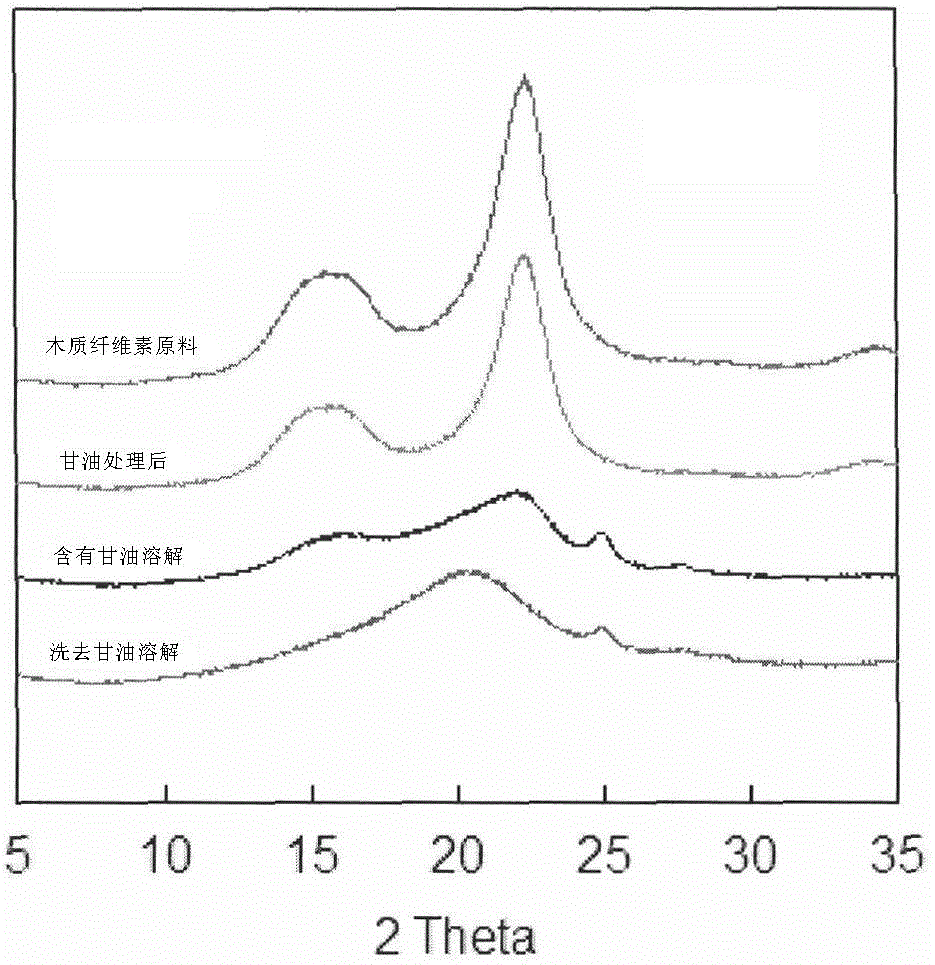
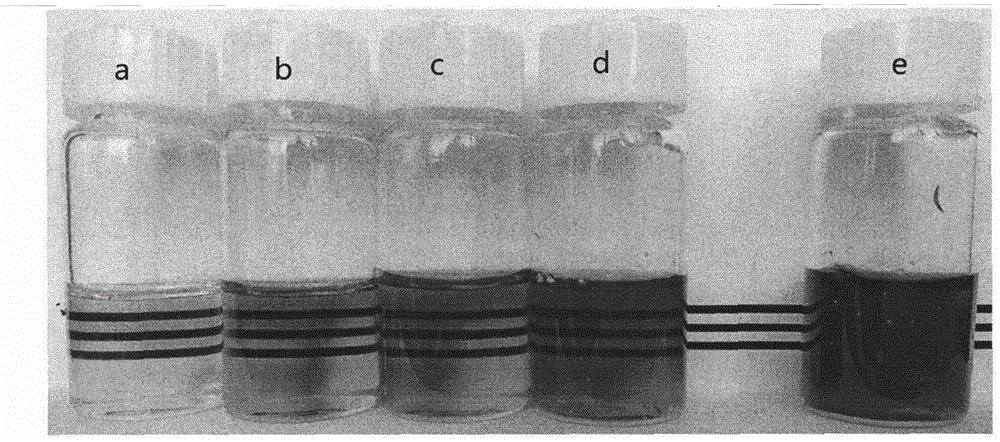
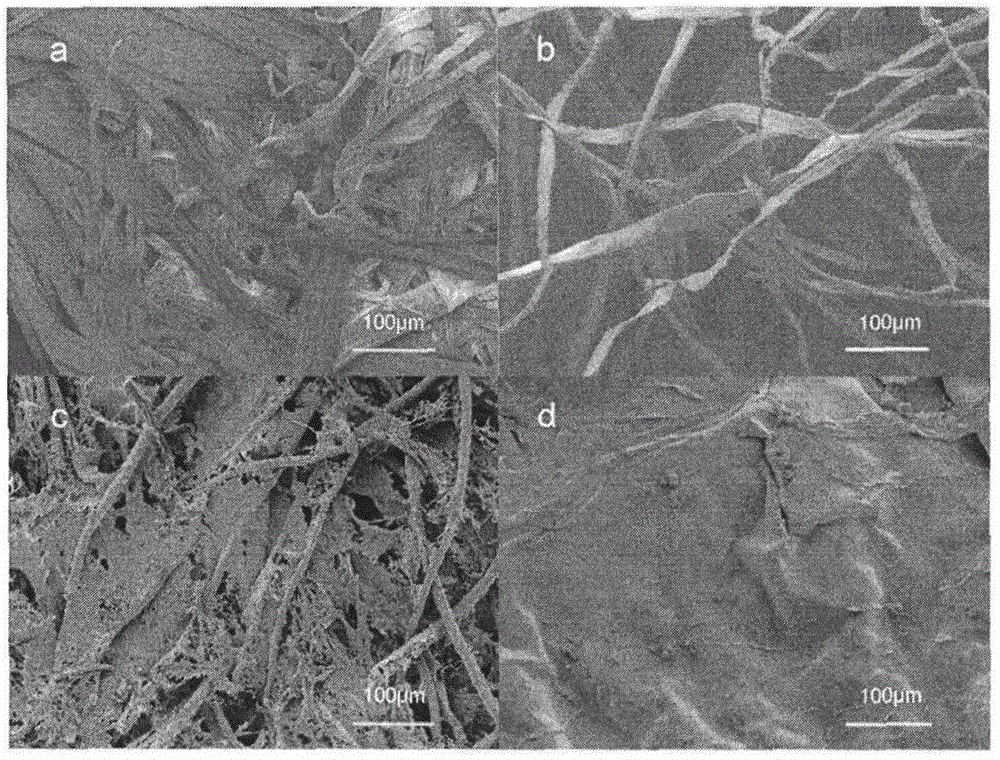
Dissolution method of lignocellulose
A technology of lignocellulose and solution, which is applied in the field of lignocellulose processing and application, to achieve the effects of increasing accessibility, improving dissolution efficiency, and reducing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Add 20 g of dry poplar bleached pulp to 160 g of glycerol, place it in an oil bath at 120°C for 2 hours, and transfer it to a screw press for extrusion and swelling. The obtained sample is ready for use;
[0031] Take 3.34g of the sample containing glycerol in the impregnating solution (glycerol content is 90.01%), add it to 30g of N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide monohydrate solution, place it in a water bath at 85°C and stir it mechanically for 1 hour at a speed of 400r / min, a lignocellulose solution with a concentration of 1% can be obtained. In the obtained lignocellulose solution, the lignocellulose content is 1%, the glycerol content is 9.02%, the N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide content is 78.01%, and the rest is water.
[0032] Take 10 g of the sample containing the impregnating solution and use centrifugal washing method to wash away the glycerol contained in the sample, and dry it for later use.
[0033] Take 0.30g of an absolute dry sample that does not contain glycerol...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Add 20 g of absolute dry poplar pulp with a lignin content of 3.03% to 160 g of glycerol, place it in an oil bath at 120° C. for mechanical stirring for 2 hours, transport it to a screw press for extrusion and swelling, and obtain a sample for later use;
[0036]Take 4.30 g of the sample containing glycerol in the impregnating solution (glycerol content is 92.00%), add it to 30 g of N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide monohydrate solution, place it in a water bath at 85° C. and stir it mechanically for 2 hours at a speed of 400r / min, a lignocellulose solution with a concentration of 1% can be obtained. In the obtained lignocellulose solution, the lignocellulose content is 1%, the glycerol content is 11.53%, the N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide content is 75.83%, and the rest is water.
[0037] Take 10 g of the sample containing the impregnating solution and use centrifugal washing method to wash away the glycerol contained in the sample, and dry it for later use.
[0038] Take 0.30 g...
Embodiment 3
[0040] 20g of dry poplar pulp with a lignin content of 6.89% was added to 160g of glycerol, placed in a 120°C oil bath for mechanical stirring for 2 hours, and then transported to a screw press for extrusion and swelling, and the obtained sample was set aside;
[0041] Take 3.25g of the sample containing glycerol in the impregnating liquid (glycerol content is 89.78%), add it to 30g of N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide monohydrate solution, place it in a water bath at 85°C and stir it mechanically for 3 hours at a speed of 400r / min, a lignocellulose solution with a concentration of 1% can be obtained. In the obtained lignocellulose solution, the lignocellulose content is 1%, the glycerol content is 8.78%, the N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide content is 78.23%, and the rest is water.
[0042] Take 1 g of the sample containing the impregnation solution and use centrifugal washing to wash away the glycerol contained in the sample, and dry it for later use.
[0043] Take 0.30g of an absolute ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com