Plant fiber/waste FPR composite material and preparation method thereof
A plant fiber and composite material technology, applied in fiber raw material processing, non-fibrous pulp addition, non-polymeric organic compound addition, etc., can solve the problem of no further processing of FRP, and achieve saving plant fiber raw materials, good performance, Versatile Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
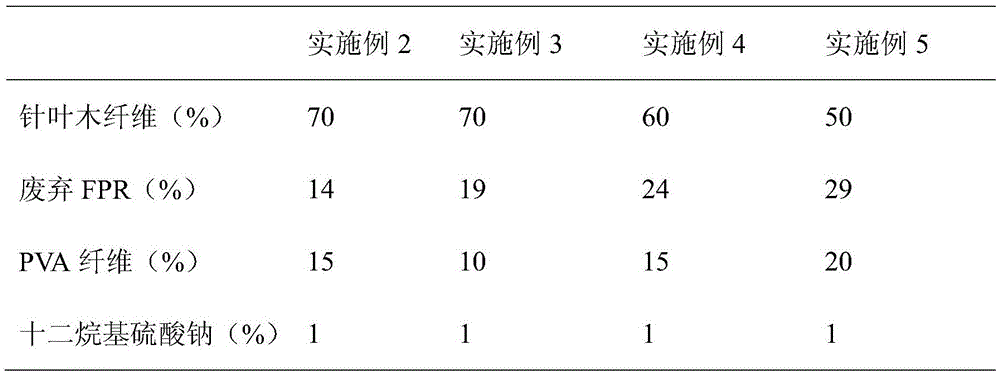
Embodiment 1
[0034] 1) Disperse softwood fibers with a beating degree of 46°SR and water-soluble PVA fibers at 90°C in water, and use a fiber disintegrator to continuously stir for 3 minutes to evenly disperse the fibers in the water. Then add waste FPR infiltrated with sodium lauryl sulfate, and continue to stir at a low speed for 30 seconds to obtain a slurry to be treated. Wherein the coniferous wood fiber accounts for 80% of the total mass, waste FPR accounts for 9% of the total mass, PVA fiber accounts for 10% of the total mass, and sodium lauryl sulfate accounts for 1% of the total mass.
[0035] 2) Using a paper scraper, the slurry obtained in step 1) is copied into a wet paper sheet.
[0036] 3) Pressing the wet paper, the pressing pressure is 5MPa, the pressing time is 60s, and finally the dryness of the paper is controlled at 30-40%.
[0037] 4) The wet paper sheet is dried, the temperature of the dryer is 105° C., and the drying time is 5 minutes. After the wet paper sheet is ...
Embodiment 6
[0044] 1) Disperse hardwood fibers with a beating degree of 43°SR and water-soluble PVA fibers at 90°C in water, and use a fiber disintegrator to continuously stir for 2 minutes to make the fibers evenly dispersed in water. Then add waste FPR soaked with polyethylene glycol p-isooctylphenyl ether, and continue to stir at a low speed for 20s to obtain a slurry to be treated. Wherein the hardwood fiber accounts for 65% of the total mass, the waste FPR accounts for 16% of the total mass, the PVA fiber accounts for 18% of the total mass, and the polyethylene glycol p-isooctyl phenyl ether accounts for 1% of the total mass.
[0045] 2) Using a paper scraper, the slurry obtained in step 1) is copied into a wet paper sheet.
[0046] 3) Pressing the wet paper, the pressing pressure is 4MPa, the pressing time is 40s, and finally the dryness of the paper is controlled at 30-40%.
[0047]4) The wet paper sheet is dried, the temperature of the dryer is 103° C., and the drying time is 4 m...
Embodiment 7
[0049] 1) Disperse cotton fibers with a beating degree of 44°SR and 90°C water-soluble PVA fibers in water, and use a fiber disintegrator to continuously stir for 2 minutes to make the fibers evenly dispersed in water. Then add waste FPR soaked with dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide, and continue to stir at a low speed for 25s to obtain a slurry to be treated. Wherein cotton fiber accounts for 75% of the total mass, waste FPR accounts for 19% of the total mass, PVA fiber accounts for 5% of the total mass, and dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide accounts for 1% of the total mass.
[0050] 2) Using a paper scraper, the slurry obtained in step 1) is copied into a wet paper sheet.
[0051] 3) Pressing the wet paper, the pressing pressure is 4.5MPa, the pressing time is 50s, and finally the dryness of the paper is controlled at 30-40%.
[0052] 4) The wet paper sheet is dried, the temperature of the dryer is 104° C., and the drying time is 4.5 minutes. After the wet paper sheet is co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com