A method of improving catalyzed resolution properties of free lipase in an organic phase
A technology of free lipase and organic phase, applied in the field of non-aqueous phase lipase catalytic chiral separation, to achieve low cost, low catalytic performance and low catalytic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: a kind of method that improves free lipase catalytic resolution performance in organic phase, comprises the following steps:
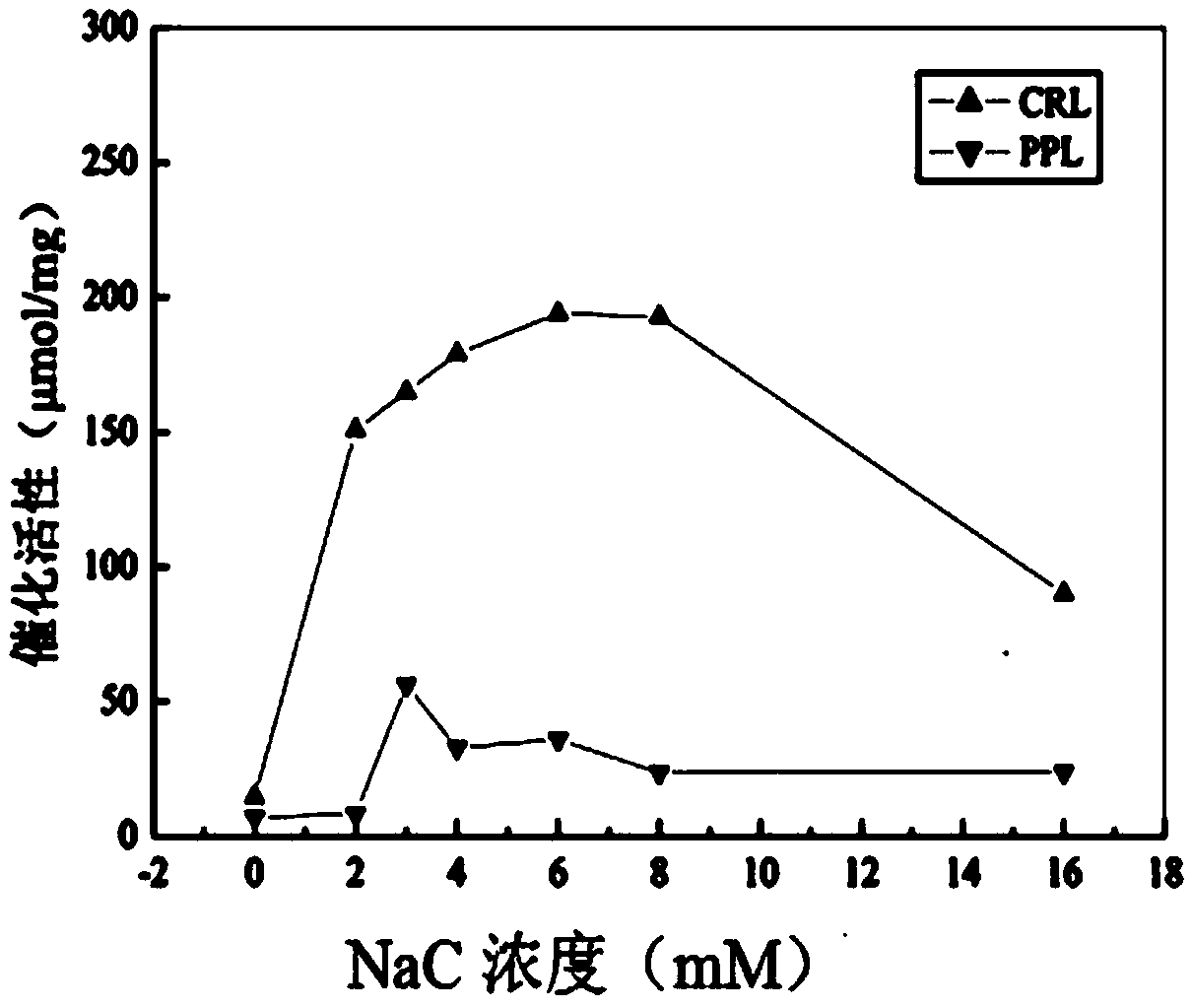
[0030] S1, take a certain mass of sodium cholate and dissolve it in a phosphate buffer solution with pH=7.5, prepare a sodium cholate concentration of 16mM, and dilute the sodium cholate buffer solution with a concentration of 16mM to a solubility of 2mM, 3mM, 4mM, 6mM, 8mM sodium cholate phosphate buffer solution;
[0031] Weigh 5 parts of 0.01g porcine pancreatic lipase (PPL) or Candida columnar lipase (CRL) coarse powder and place them in 5 sample bottles in turn, add 5 different concentrations of sodium cholate to the 5 samples respectively Phosphate buffer solution 2ml;
[0032] Weigh 0.01g of porcine pancreatic lipase (PPL) or Candida columnar lipase (CRL) coarse powder and place it in a sample bottle and add 2ml of phosphate buffered saline solution as blank control group 1;
[0033] Pipette 2ml of phosphate buffer solutio...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2: a method for improving the catalytic resolution performance of free lipase in the organic phase, comprising the following steps:
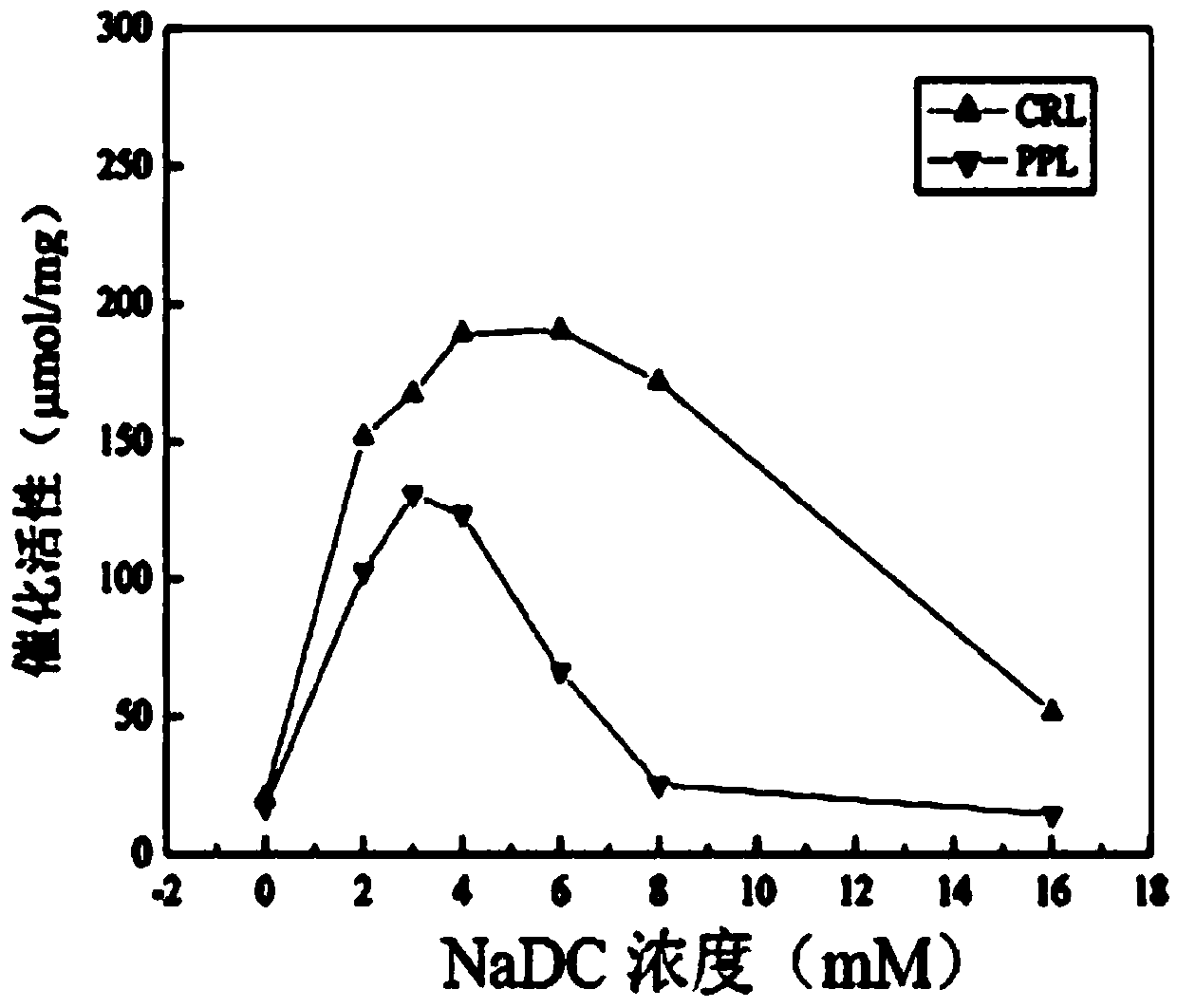
[0043] S1, weigh a certain amount of sodium deoxycholate and dissolve it in a phosphate buffer solution with a pH of 7.5, prepare a concentration of sodium deoxycholate of 16 mM, and dilute the sodium deoxycholate buffer solution with a concentration of 16 mM in sequence 2mM, 3mM, 4mM, 6mM, 8mM sodium deoxycholate phosphate buffer solution;
[0044] Weigh 5 parts of 0.01g porcine pancreatic lipase (PPL) or Candida columnar lipase (CRL) coarse powder and place them in 5 sample bottles in turn, add 5 different concentrations of deoxycholic acid to the 5 samples respectively Sodium phosphate buffer solution 2ml;
[0045] Weigh 0.01g of porcine pancreatic lipase (PPL) or Candida columnar lipase (CRL) coarse powder and place it in a sample bottle and add 2ml of phosphate buffered saline solution as blank control group 1;
[0046] ...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Embodiment 3: a method for improving the catalytic resolution performance of free lipase in the organic phase, comprising the following steps:
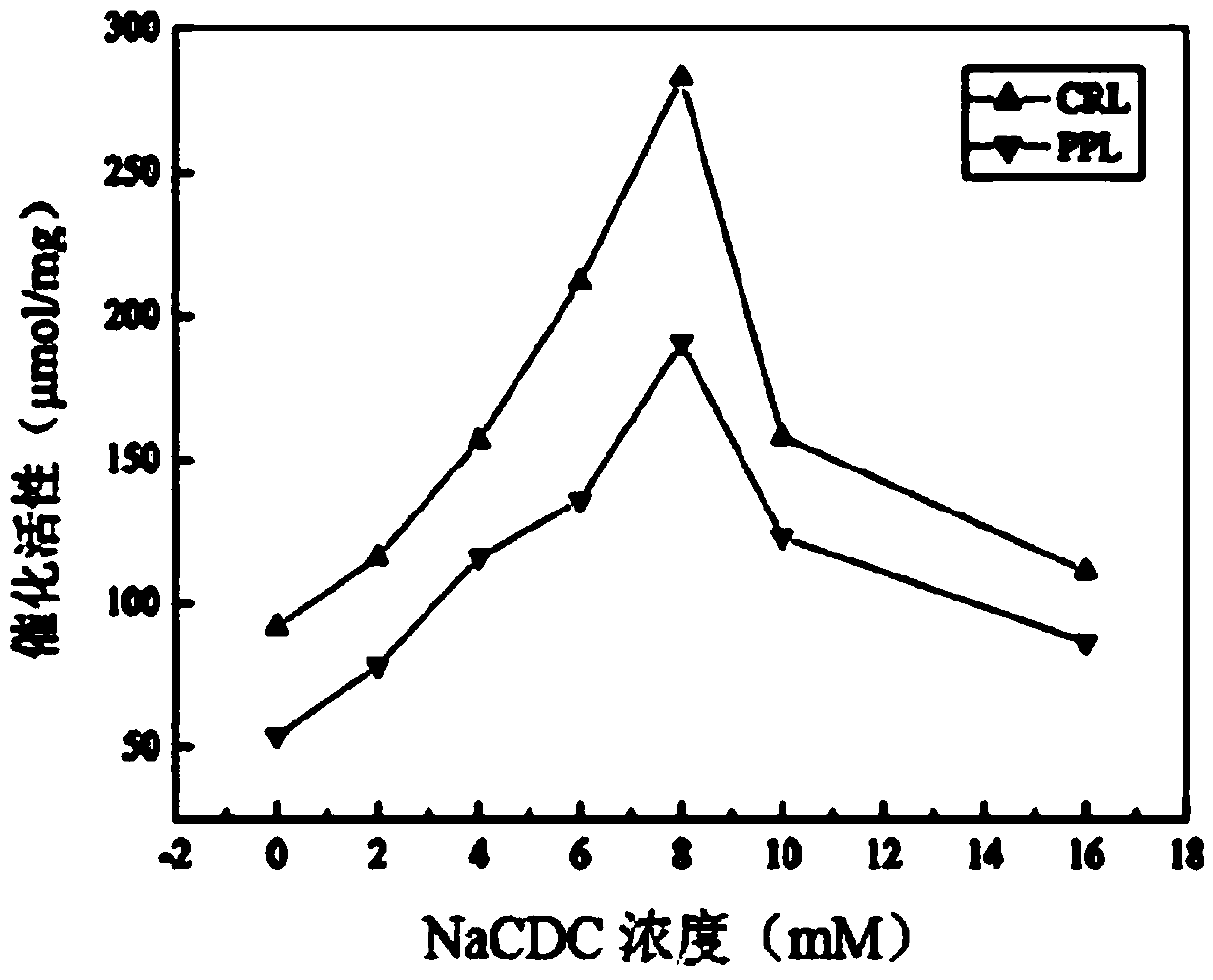
[0056] S1, weigh a certain amount of sodium chenodeoxycholate and dissolve it in a phosphate buffer solution with pH = 7.5, prepare a concentration of sodium chenodeoxycholate of 16 mM, and buffer The solution was successively diluted into sodium chenodeoxycholate phosphate buffer solution with a solubility of 2mM, 4mM, 6mM, 8mM and 10mM;
[0057] Weigh 5 parts of 0.01g porcine pancreatic lipase (PPL) or Candida columnar lipase (CRL) coarse powder and place them in 5 sample bottles in turn, add 5 different concentrations of goose deoxygenate to the 5 samples respectively Sodium cholate phosphate buffer solution 2ml;
[0058] Weigh 0.01g of porcine pancreatic lipase (PPL) or Candida columnar lipase (CRL) coarse powder and place it in a sample bottle and add 2ml of phosphate buffered saline solution as blank control group 1;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com