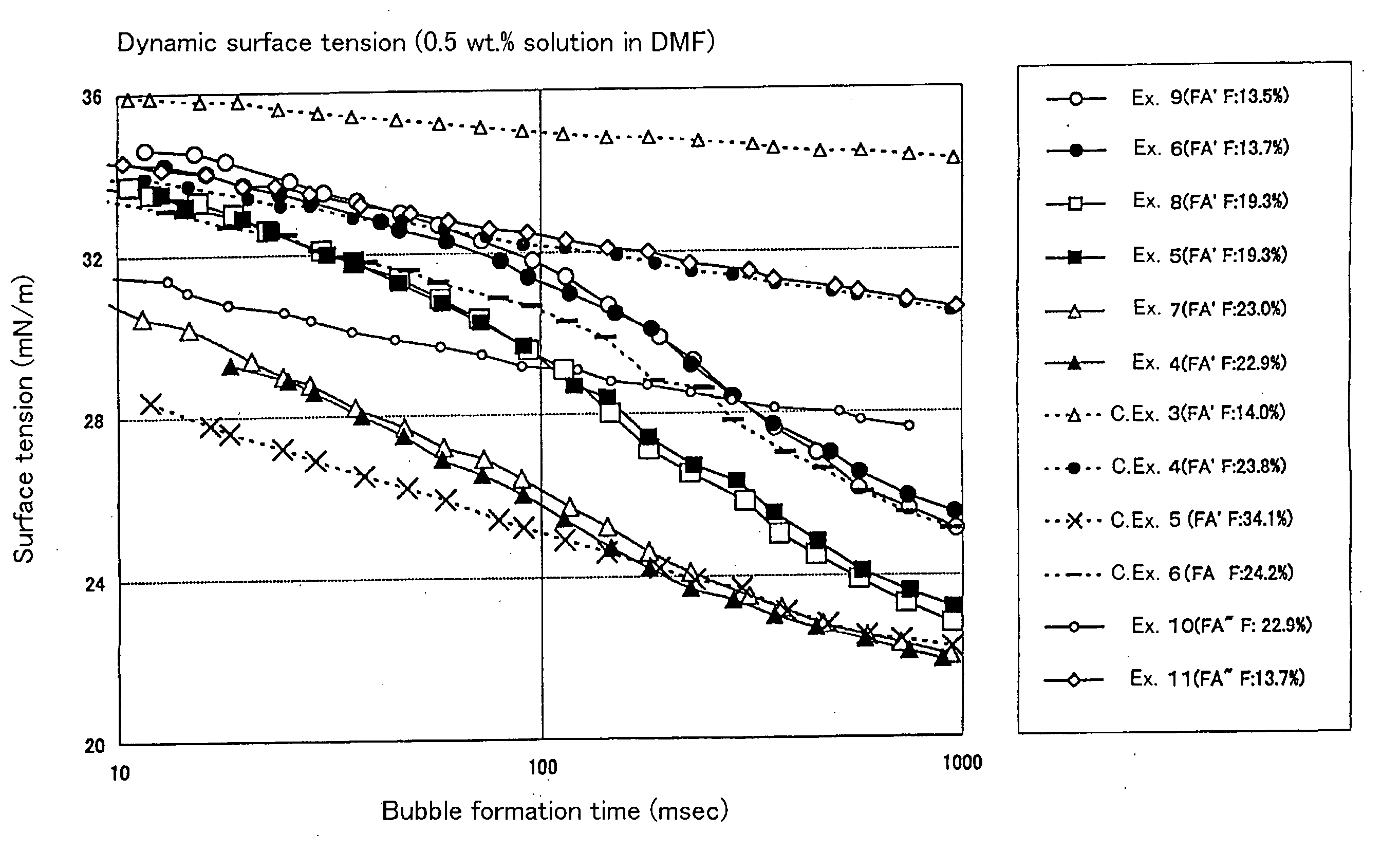
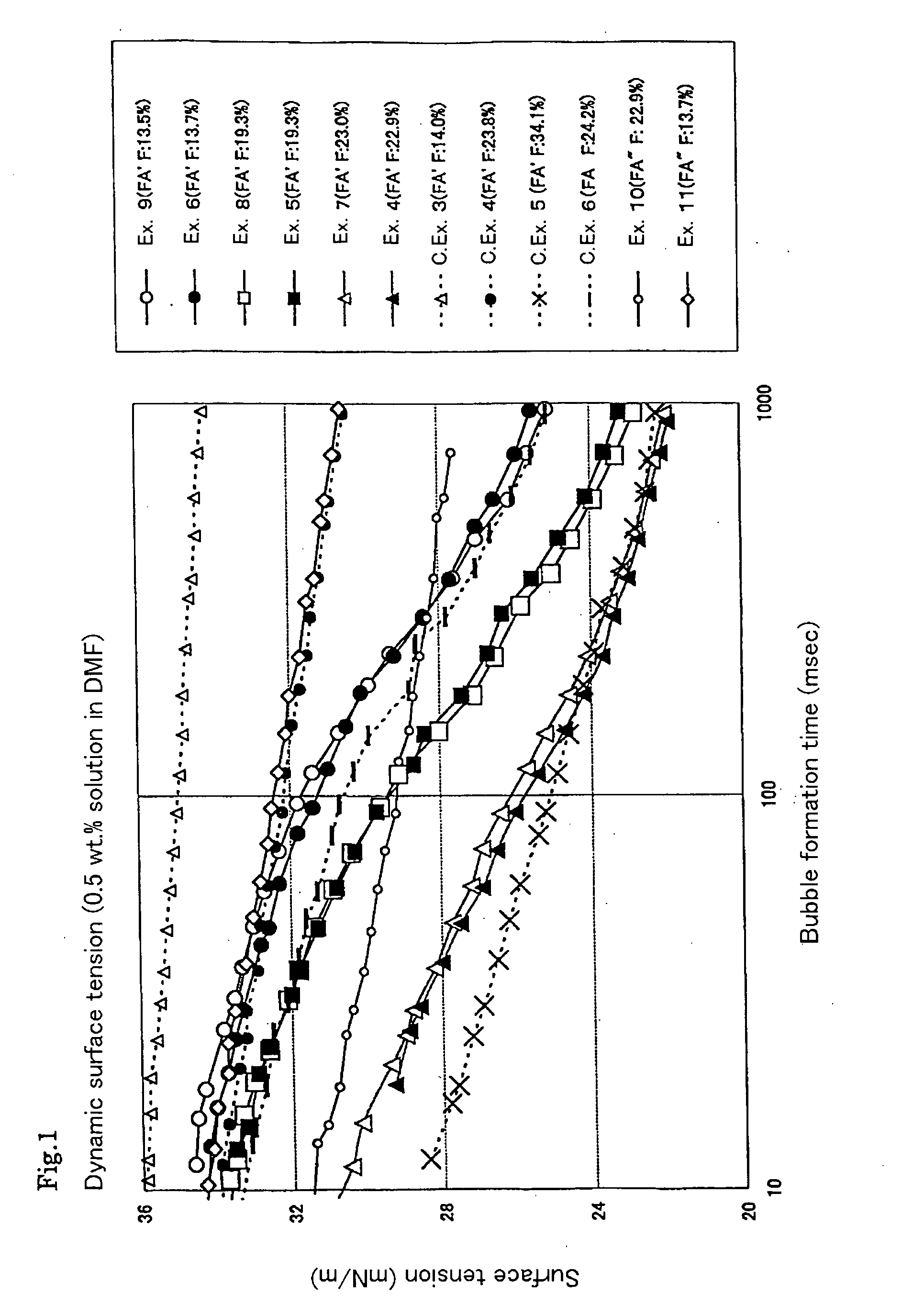
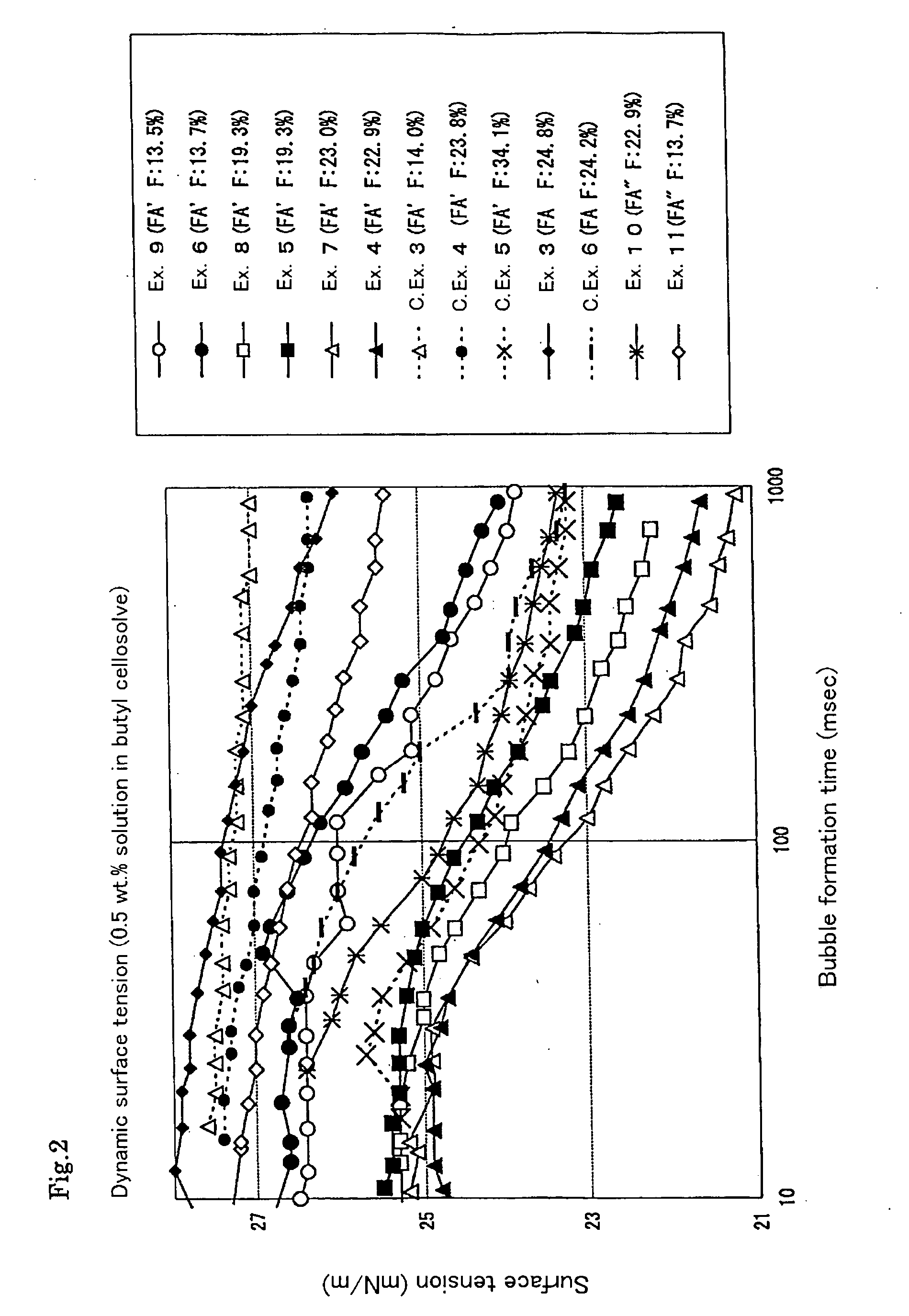
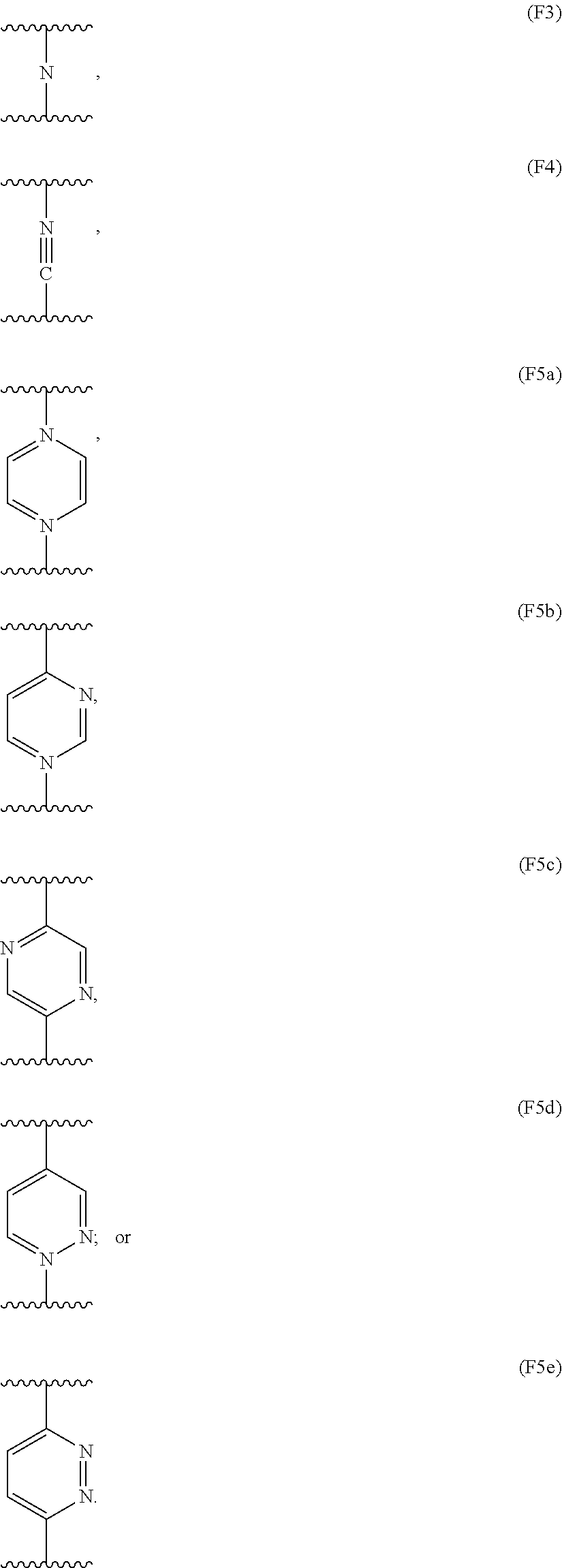
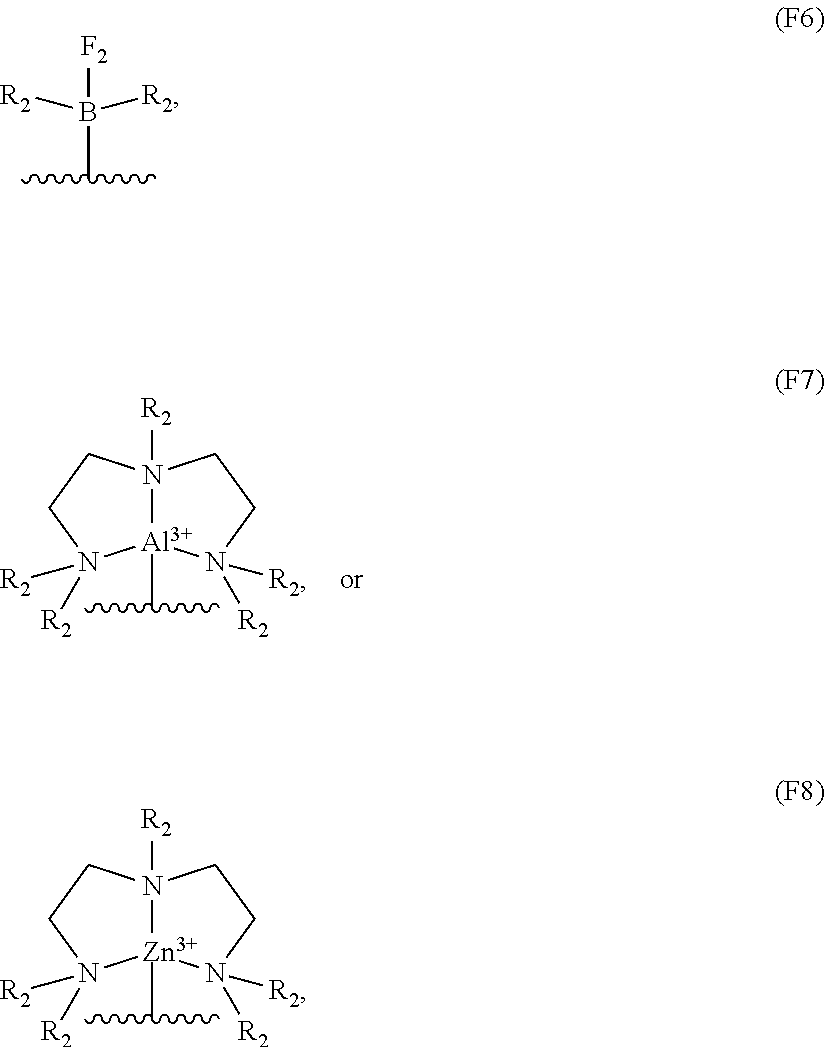
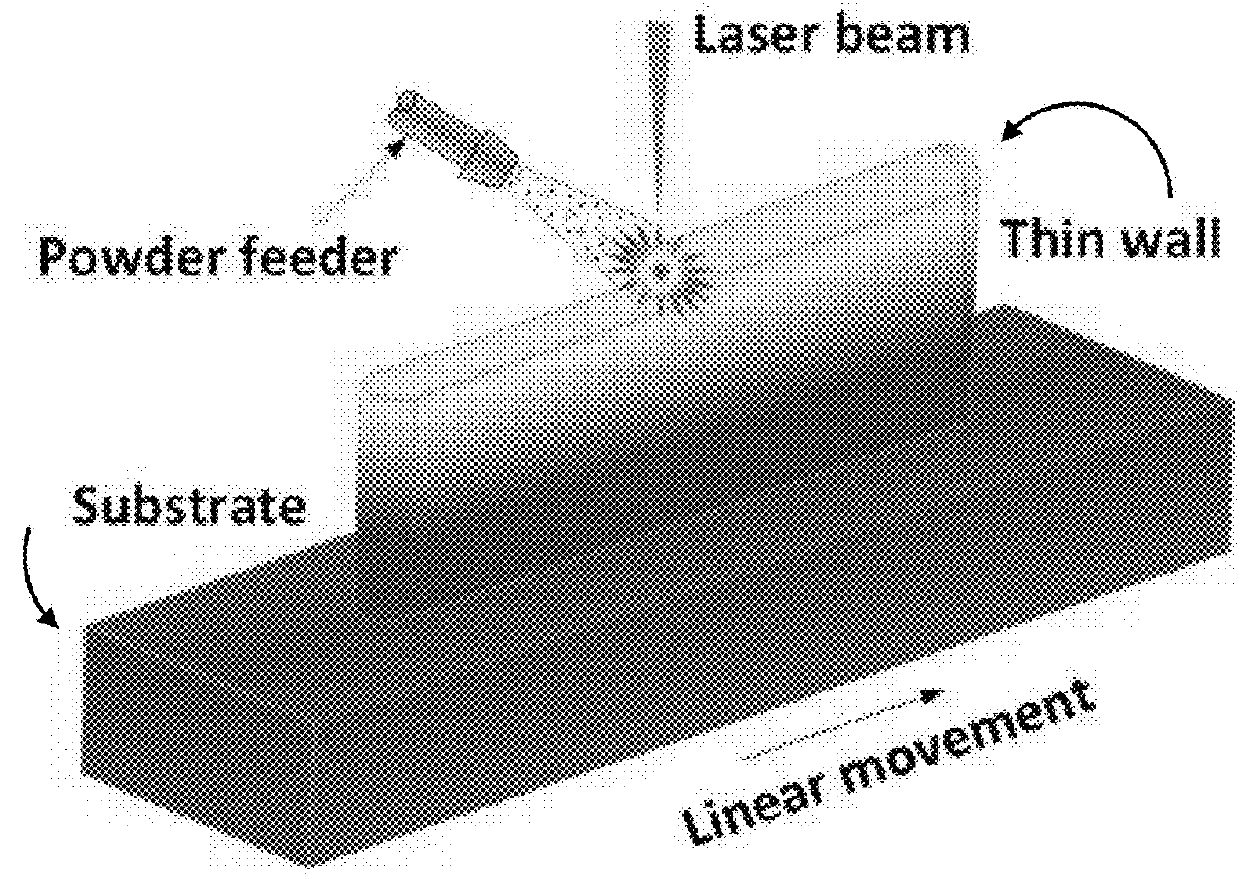
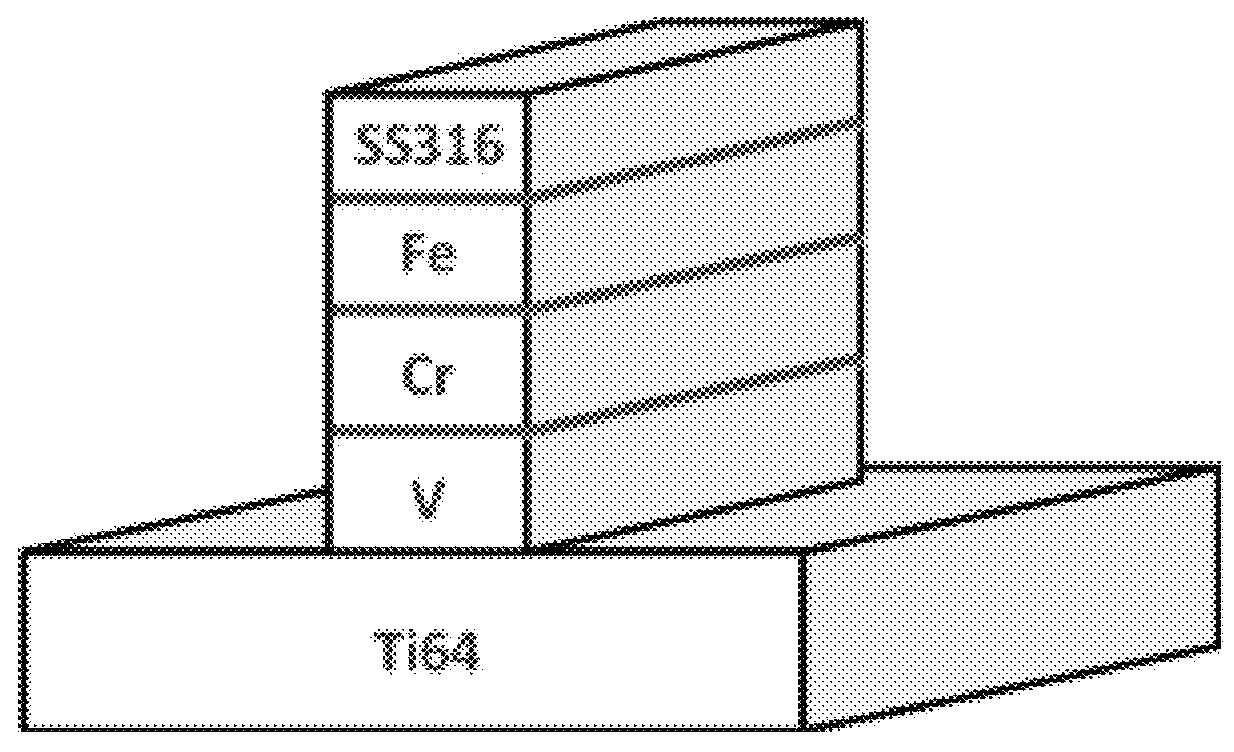
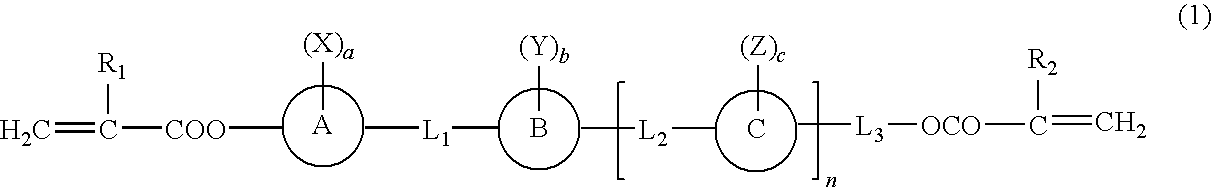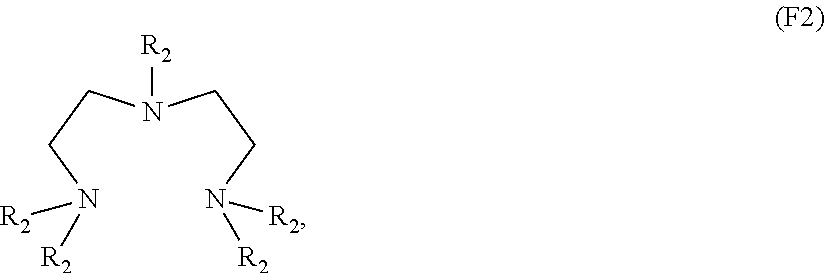Patents
Literature
43results about How to "High "solubility"" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
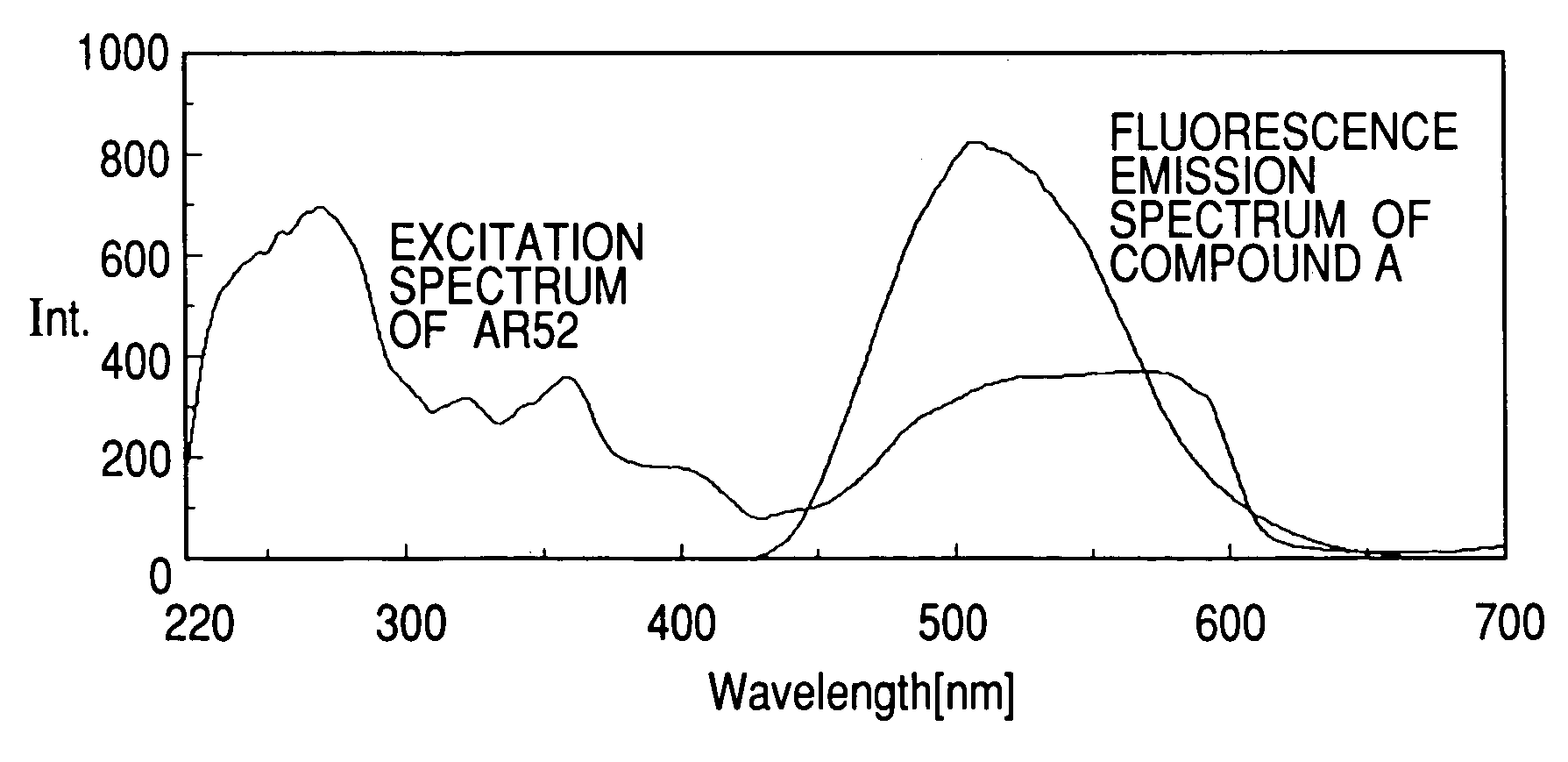
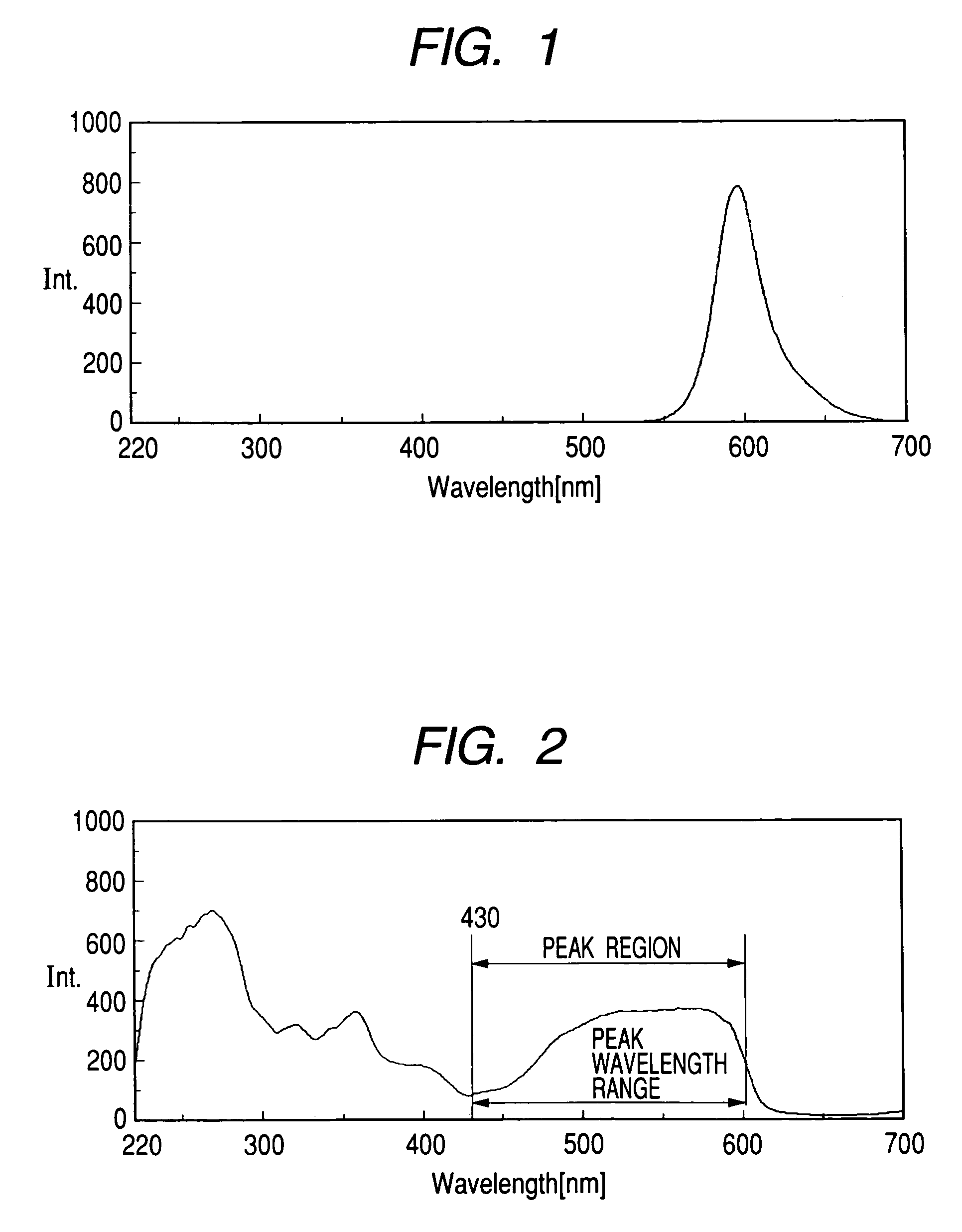
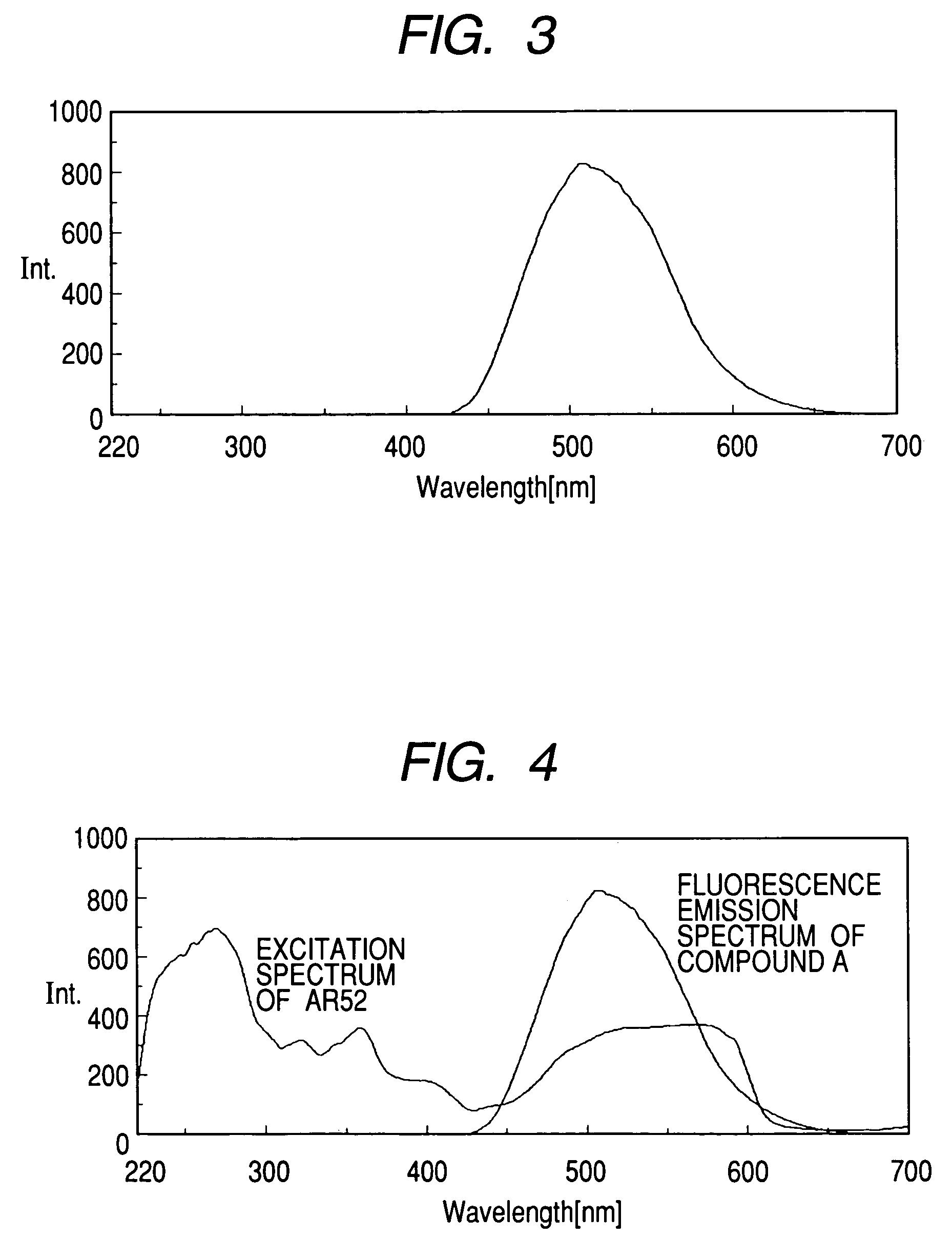
Print ink containing a plurality of fluorescent coloring materials and inkjet recording method
ActiveUS7144449B2High solubilityIncrease in fluorescence intensityDuplicating/marking methodsPattern printingExcitation wavelengthPrinting ink
The present invention provides a fluorescence ink having a high fluorescence intensity, and an ink jet recording method using the same. The ink contains a first fluorescent coloring material that emits fluorescence at a predetermined fluorescence wavelength to be used for measurement or determination with excitation at a predetermined excitation wavelength, a second fluorescent coloring material that emits fluorescence on excitation at the predetermined excitation wavelength, where the excitation spectrum of the first coloring material in the ink to obtain the fluorescence at the predetermined emission wavelength has a peak wavelength range next to the predetermined fluorescence wavelength, and the emission fluorescence spectrum of the second coloring material has an emission wavelength region substantially including at least the above peak wavelength range.
Owner:CANON KK
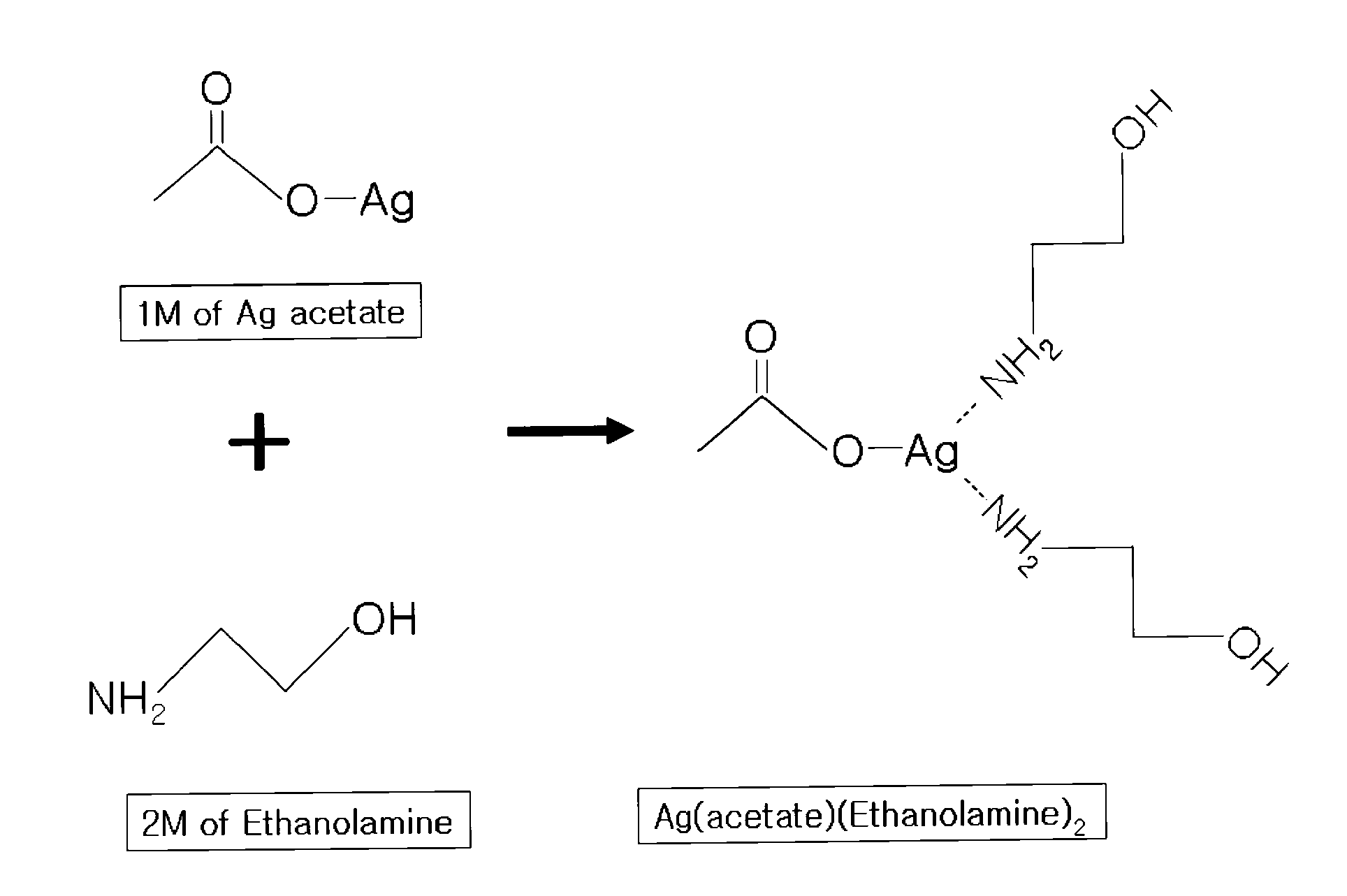
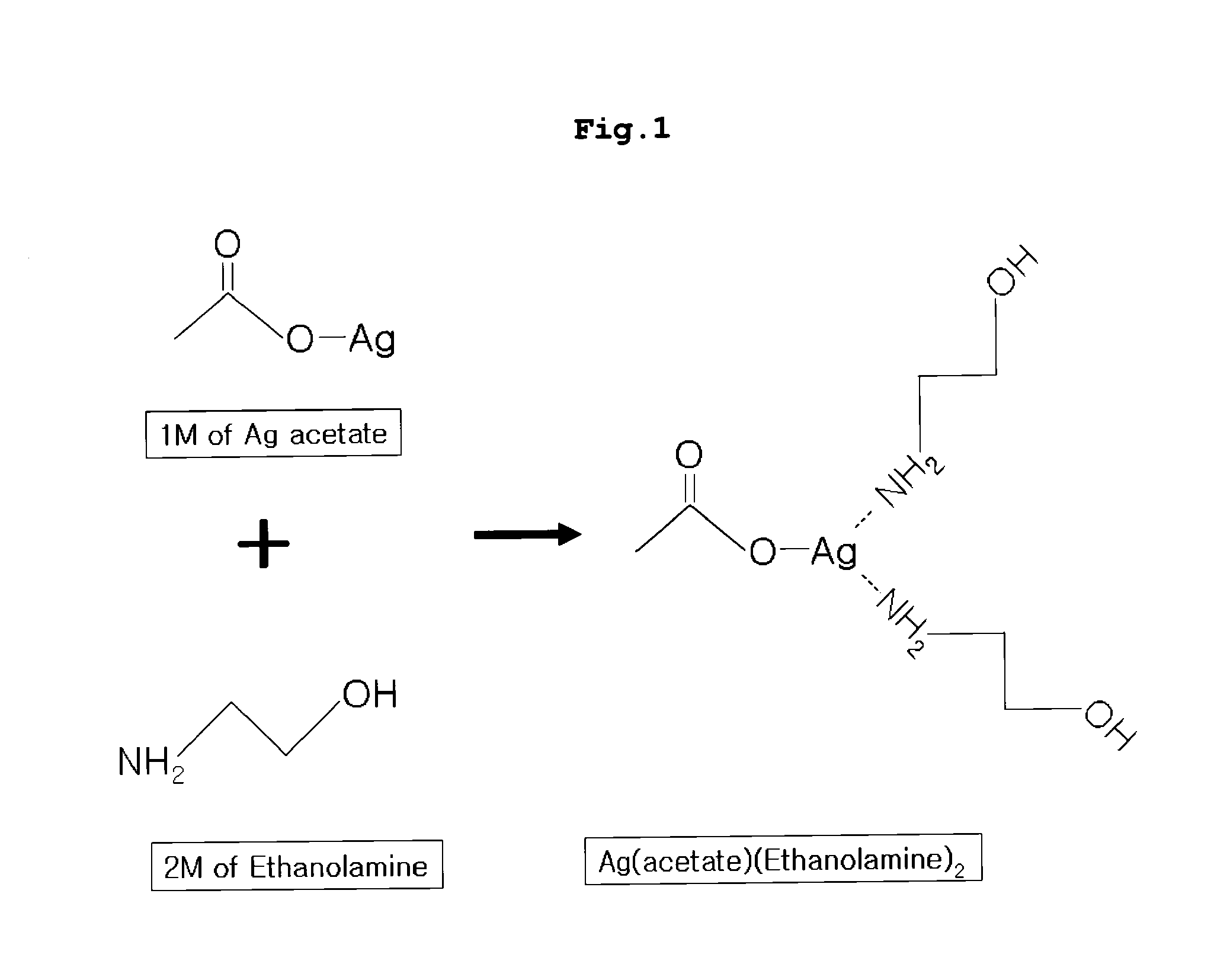
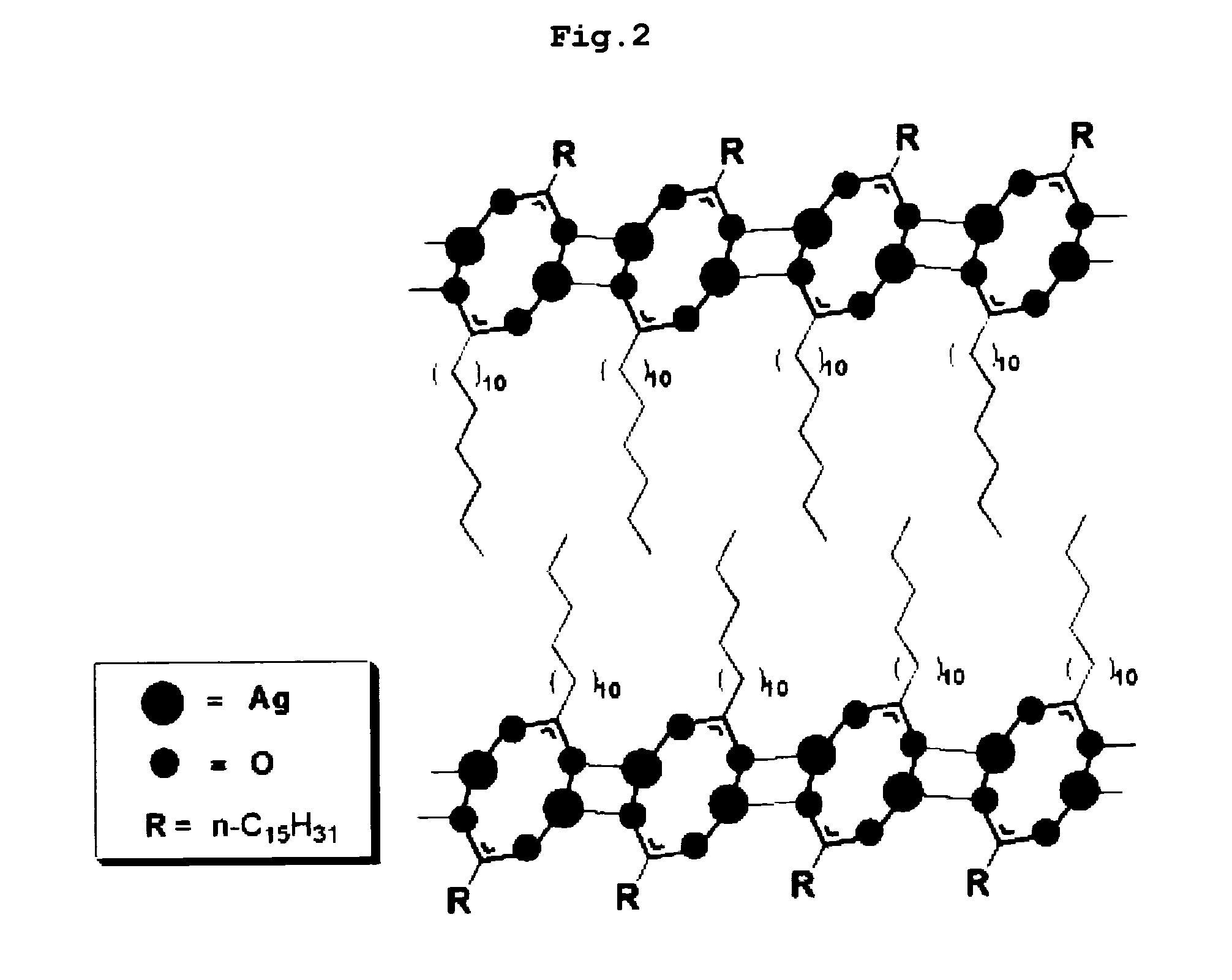
Organic silver complex compound used in paste for conductive pattern forming
InactiveUS20100021704A1High solubilityHigh viscosityFatty acid chemical modificationFatty acids production/refiningSolventChemistry
Disclosed is an organic silver complex compound in which an organic ligand, containing an amine group (—NH2) and a hydroxyl group (—OH), is bonded with aliphatic silver (Ag) carboxylate at an equivalent ratio of 2:1 to form a complex. Also disclosed is a conductive paste comprising: a silver source selected from the group consisting of silver oxide powder, silver powder and silver flake; and organic silver complex compound in which an organic ligand, containing an amine group and a hydroxyl group, is bonded with an organic silver compound to form a complex. The organic silver complex compound has high solubility in a solvent and is present in the liquid state at room temperature. Thus, an extra solvent is not used in a conductive pattern-forming paste containing the complex compound or is used in a small amount, such that the content of silver in the conductive pattern-forming paste can be increased. Also, the conductive pattern-forming paste containing the complex compound has high viscosity, and thus shows excellent stability without adding a dispersant and, at the same time, is easily industrially applied.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
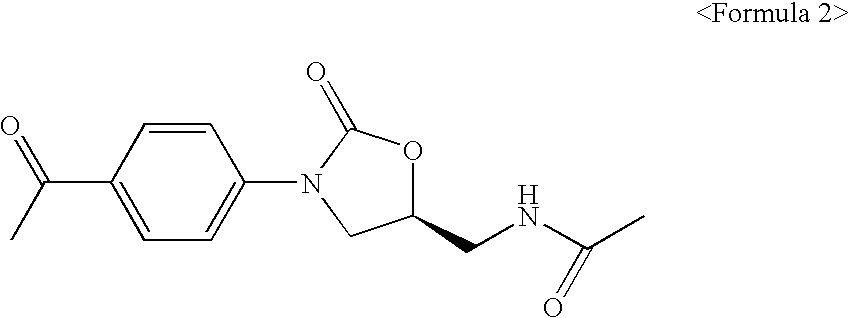
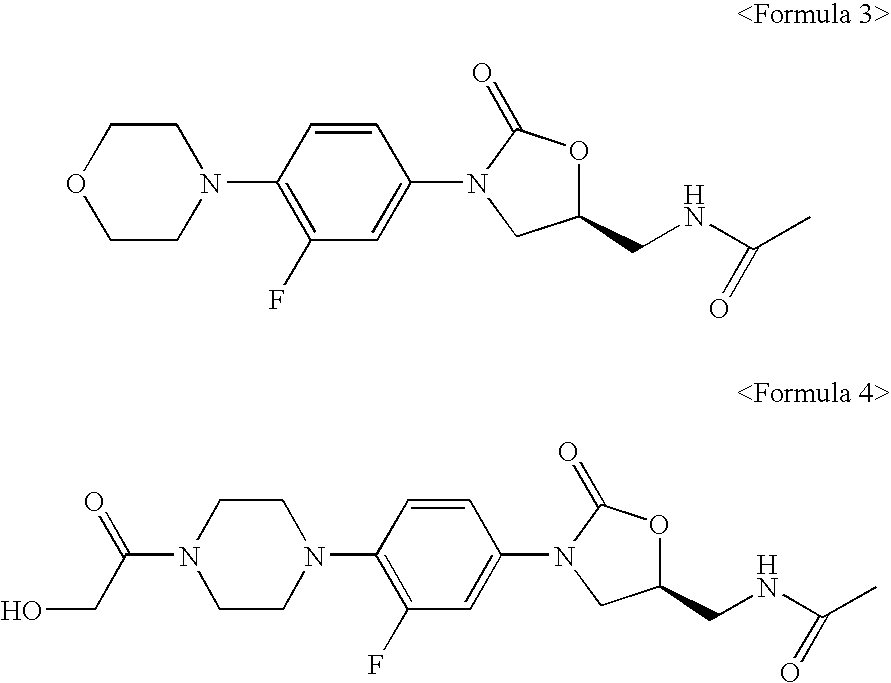
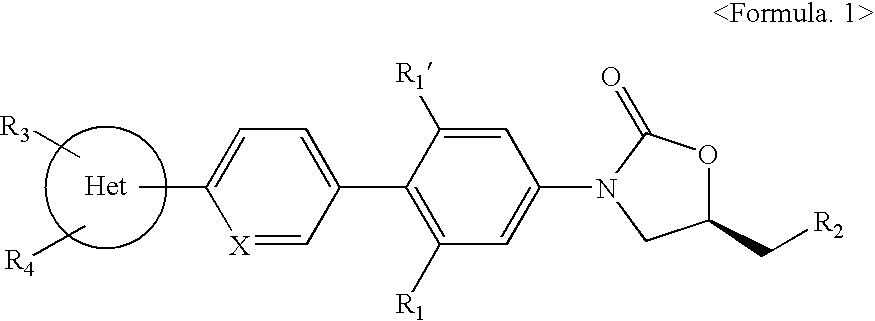
Novel oxazolidinone derivatives
The present invention relates to novel derivatives of oxazolidinone, a method thereof and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the derivatives for use in an antibiotic. The oxazolidinone derivatives of the present invention show inhibitory activity against a broad spectrum of bacteria and lower toxicity. The prodrugs, prepared by reacting the compound having hydroxyl group with amino acid or phosphate, have an excellent efficiency on solubility thereof against water. Further, the derivatives of the present invention may exert potent antibacterial activity versus various human and animal pathogens, including Gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococi, Enterococci and Streptococi, anaerobic microorganisms such as Bacteroides and Clostridia, and acid-resistant microorganisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium. Accordingly, the compositions comprising the oxazolidinone are used in an antibiotic. Data supplied from the esp@cenet database—Worldwide
Owner:DONG A PHARMA +1
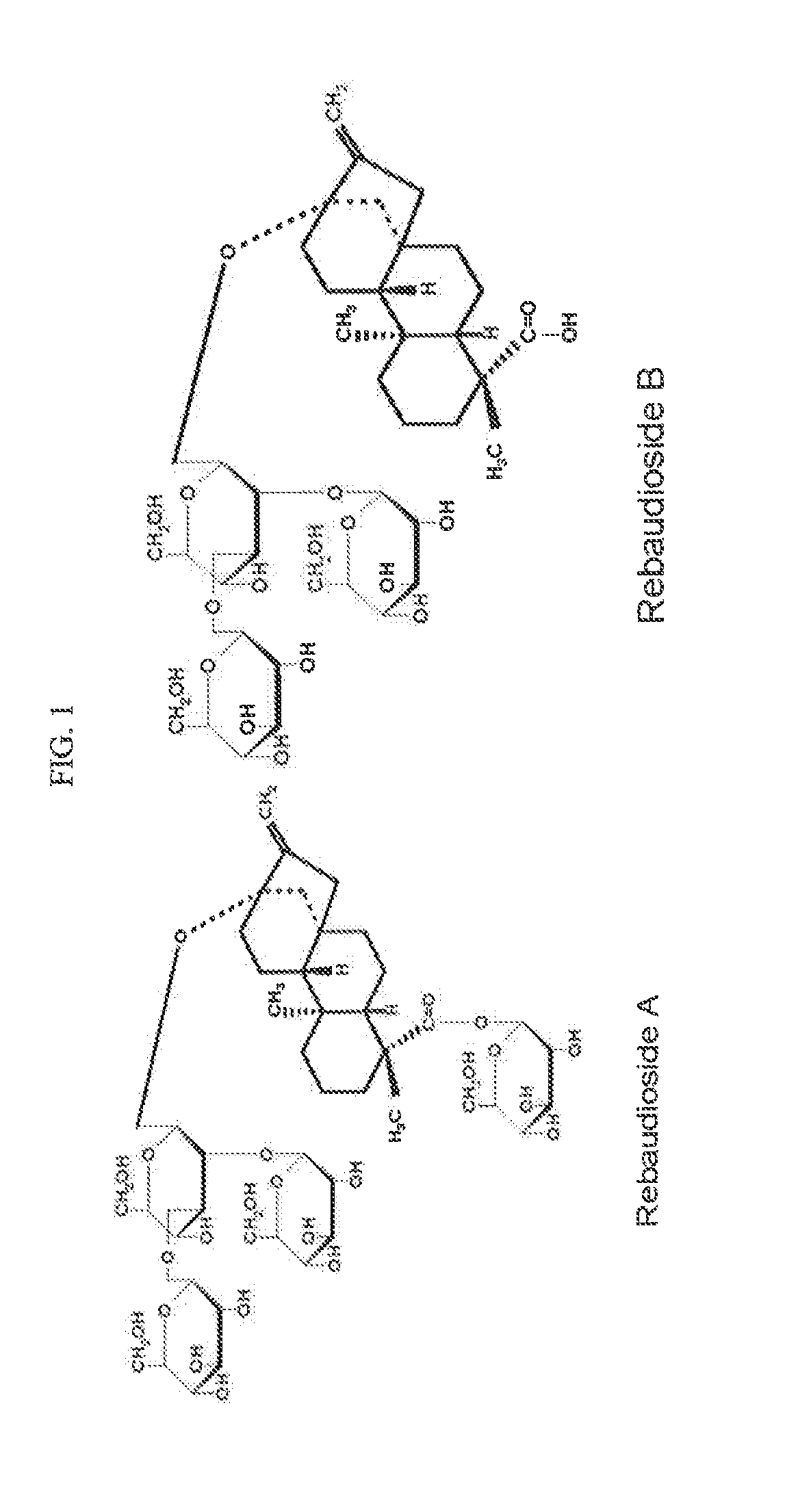
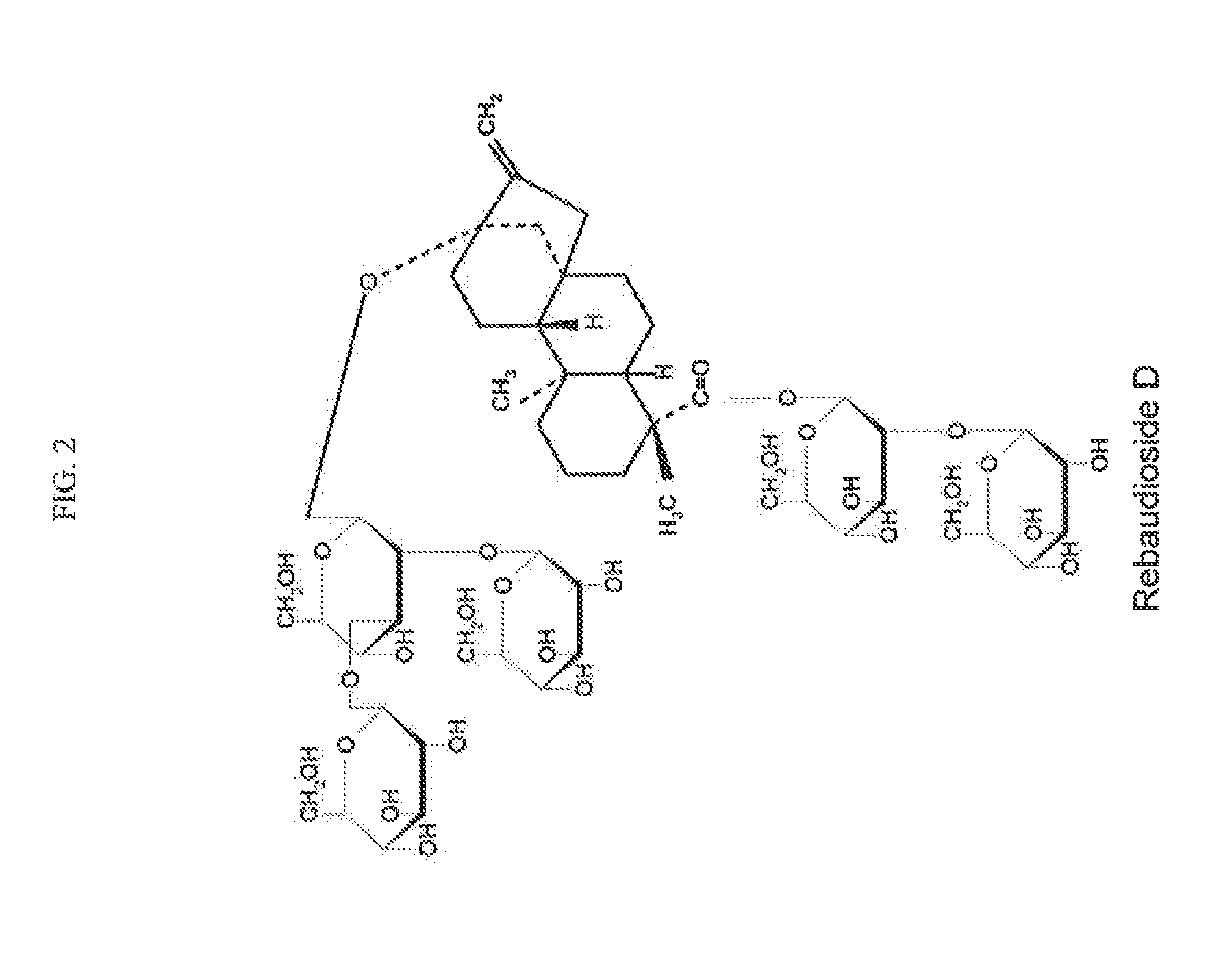
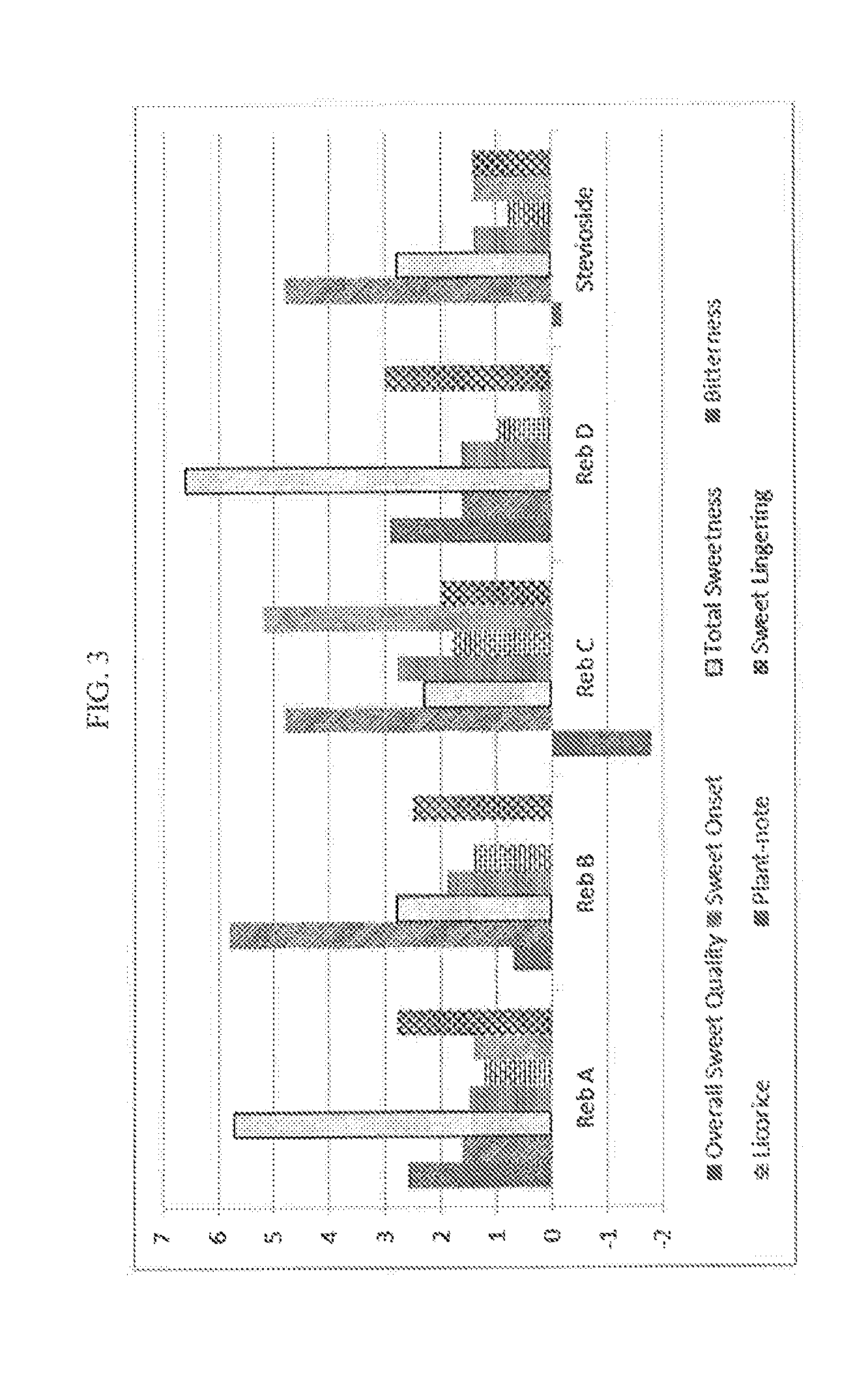
Stevia composition to improve sweetness and flavor profile
ActiveUS20130337138A1High solubilitySuperior taste and sweetness profileMilk preparationConfectioneryStevia connataSteviol glycoside
Stevia compositions are prepared from steviol glycosides of Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni. The compositions are able to provide a superior taste profile and can be used as sweetness enhancers, flavor enhancers and sweeteners in foods, beverages, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
Owner:PURECIRCLE SDN BHD
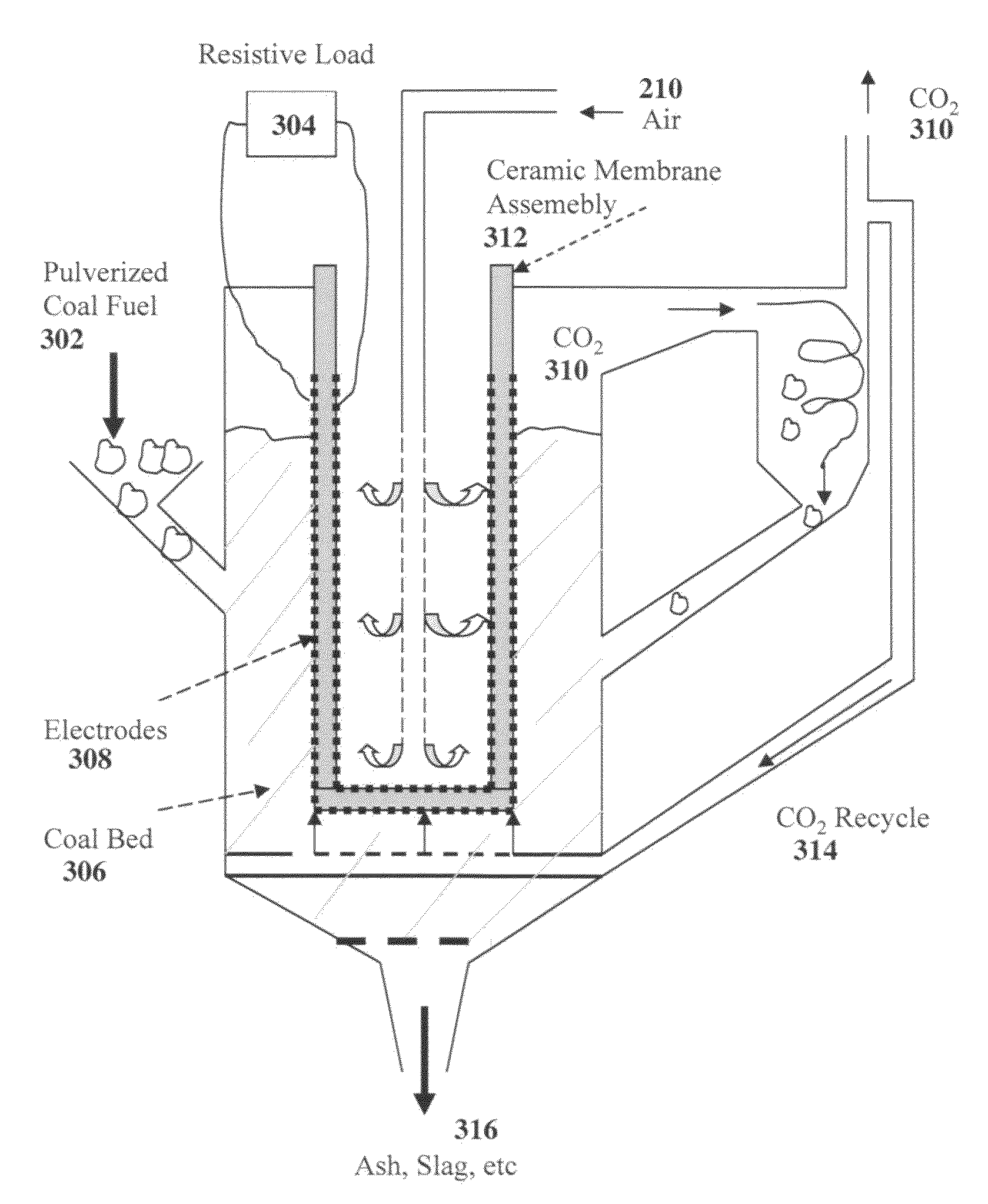
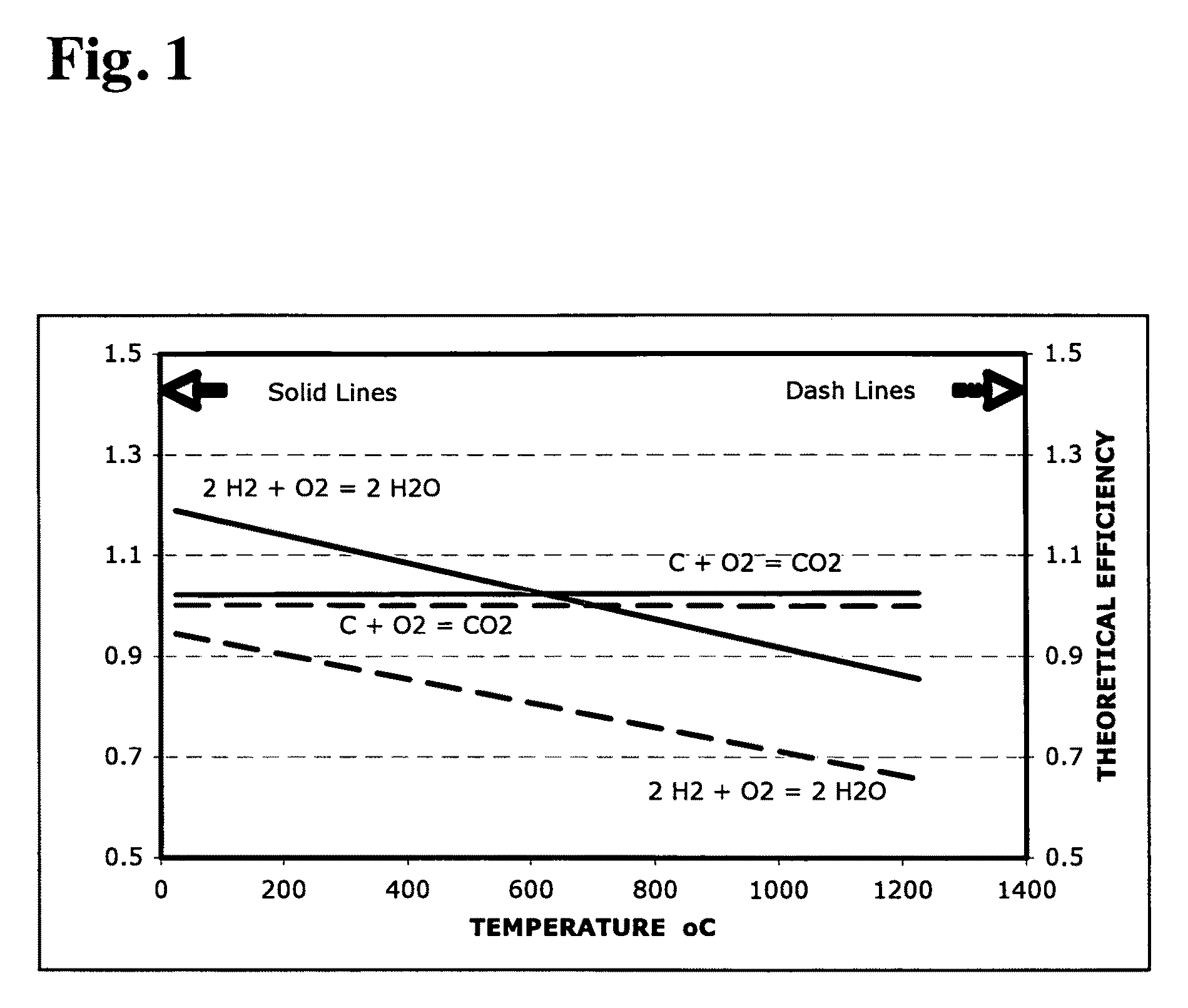
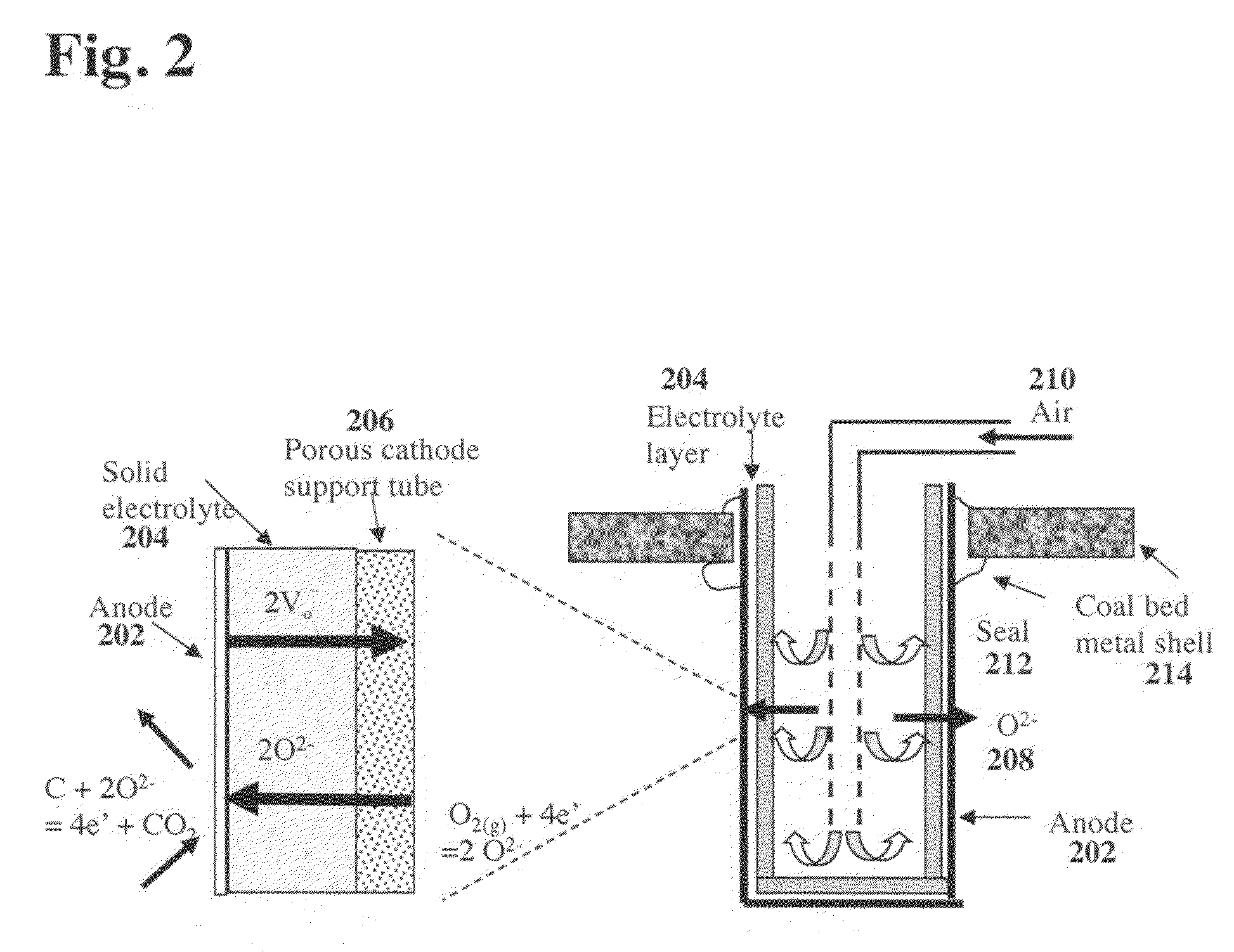
High temperature direct coal fuel cell
A fuel cell is provided that includes a chemically non-reactive and non-consumable molten anode that is chemically stable in composition and structure and is catalytically active, a cathode, where one surface of the cathode is in contact with air, where the air supplies oxygen to the cathode, a solid oxide electrolyte that selectively transports oxide ions from the cathode to the anode for an oxidation reaction, where the solid oxide electrolyte is disposed between the anode and the solid cathode, and a single temperature zone, where the anode is in direct physical contact with a carbon-containing fuel and electrical current is generated by the oxidation of the carbon-containing fuel by the oxygen.
Owner:GUR TURGUT M
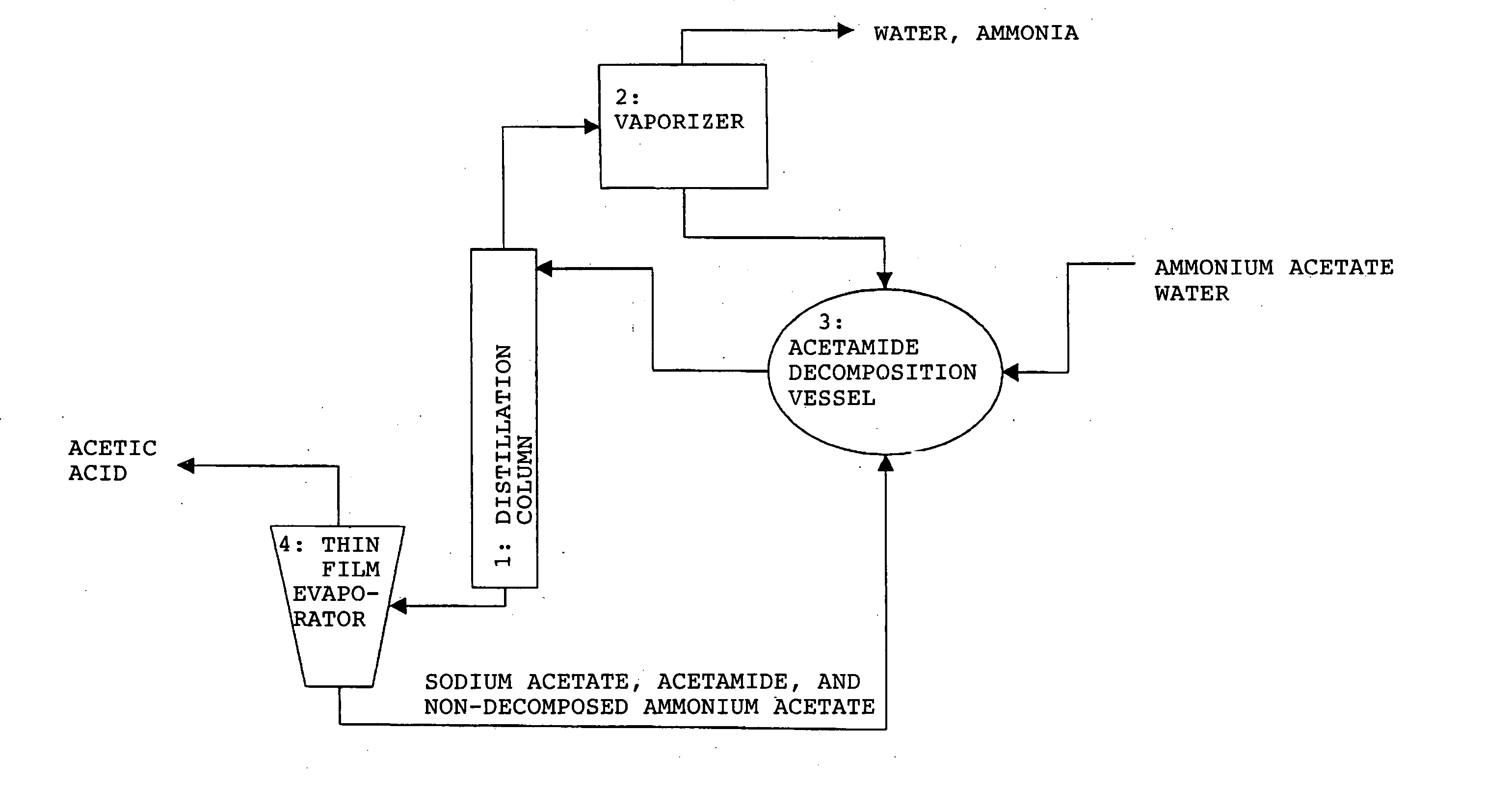
Method for producing organic acid
ActiveUS20050070738A1High temperature dependencyHigh solubilityPreparation from carboxylic acid saltsOrganic compound preparationIonizationOrganic acid
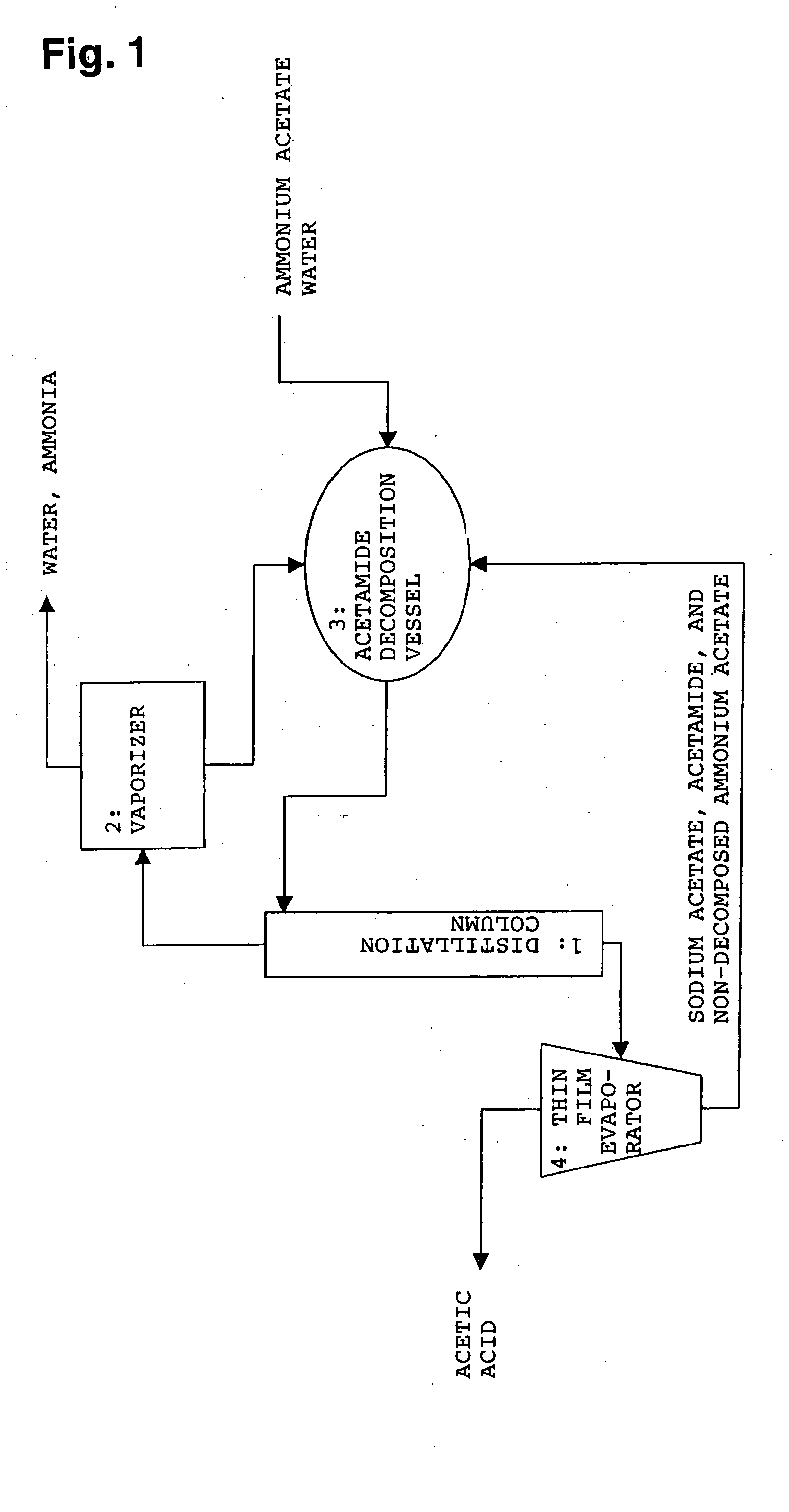
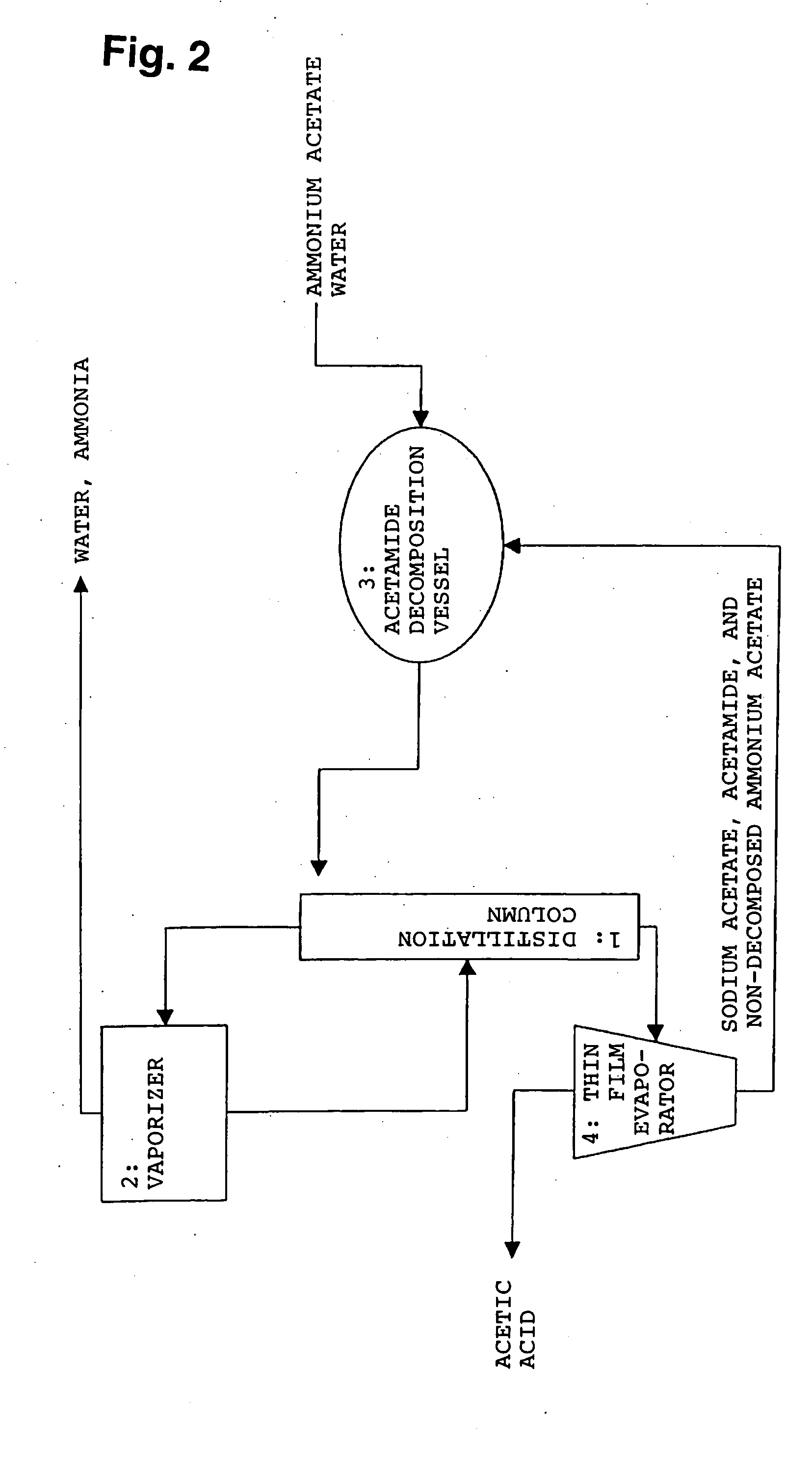
A novel method is provided whereby a free organic acid can be produced particularly from an ammonium salt of an organic acid having a high melting point obtainable by bioconversion of a carbon source in the presence of a neutralizing agent, efficiently at a low cost, and the used material for reaction and a byproduct can be recycled for reuse without being disposed. An ammonium salt of organic acid A such as a dicarboxylic acid, a tricarboxylic acid or an amino acid is subjected to reactive crystallization by means of acid B such as a monocarboxylic acid satisfying the following formula (1), to separate free organic acid A in solid form: pKa(A)≦pKa(B) (1) where pKa(A) and pKa(B) represent ionization indices of organic acid A and acid B, respectively, provided that when they have plural values, they represent the minimum pKa among them. The crystallization mother liquor after precipitating and separating organic acid A is, after separating acid B and then an ammonium salt of acid B, recycled for use in the reactive crystallization step. The ammonium salt of acid B is decomposed into acid B and ammonia, which are recycled for use in the reactive crystallization step and as a neutralizing agent in the bioconversion step, respectively.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Synthetic method and application of polydopamine-modified carbon nanotube composite material
InactiveCN103012806AHigh sensitivityGood reproducibilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansModified carbonBiocompatibility
The invention belongs to the field of nanotechnology, and particularly relates to a synthetic method and application of a polydopamine-modified carbon nanotube composite material. The synthetic method comprises the following steps in sequence: dispersing carbon nanotubes into dopamine-containing aqueous solution; quickly adding trismetyl aminomethane buffer solution into the dopamine-containing aqueous solution in which the carbon nanotubes are uniformly dispersed under magnetically stirring; mechanically stirring for 10 hours at room temperature; washing by water; and centrifugally separating to obtain the carbon nanotube composite material of which the surface is modified by polydopamine, wherein the carbon nanotube composite material shows high dispersibility in water. The polydopamine-modified carbon nanotube composite material adopts the carbon nanotubes as the framework, and therefore, a large specific surface area is provided; the polydopamine-modified carbon nanotube composite material is excellent in environmental stability and biocompatibility and high in dispersibility in water; the synthetic method is simple and low in cost; and the polydopamine-modified carbon nanotube composite material can be used as the substrate for analyzing metabolite micromolecule under high-throughput MALDI-TOFMS (Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry).
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method of producing low-shrink polypropylene tape fibers
ActiveUS20030127768A1High solubilityLow shrinkage rateLayered productsHollow filament manufactureAspect ratioSodium benzoate
Improvements in preventing heat- and moisture-shrink problems in specific polypropylene tape fibers are provided. Such fibers are basically manufactured through the initial production of polypropylene films or tubes which are then slit into very thin, though flat (and having very high cross sectional aspect ratios) tape fibers thereafter. Such fibers (and thus the initial films and / or tubes) require the presence of certain compounds that quickly and effectively provide rigidity to the target polypropylene tape fiber after heat-setting. Generally, these compounds include any structure that nucleates polymer crystals within the target polypropylene after exposure to sufficient heat to melt the initial pelletized polymer and upon allowing such a melt to cool. The compounds must nucleate polymer crystals at a higher temperature than the target polypropylene without the nucleating agent during cooling. In such a manner, the "rigidifying" nucleator compounds provide nucleation sites for polypropylene crystal growth. Upon slitting of the initial film and / or tube, the fiber is then exposed to sufficient heat to grow the crystalline network, thus holding the fiber in a desired position. The preferred "rigidifying" compounds include dibenzylidene sorbitol based compounds, as well as less preferred compounds, such as sodium benzoate, certain sodium and lithium phosphate salts (such as sodium 2,2'-methylene-bis-(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl)phosphate, otherwise known as NA-11). Specific methods of manufacture of such inventive tape fibers, as well as fabric articles made therefrom, are also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Biodegradable Materials and Methods of Use
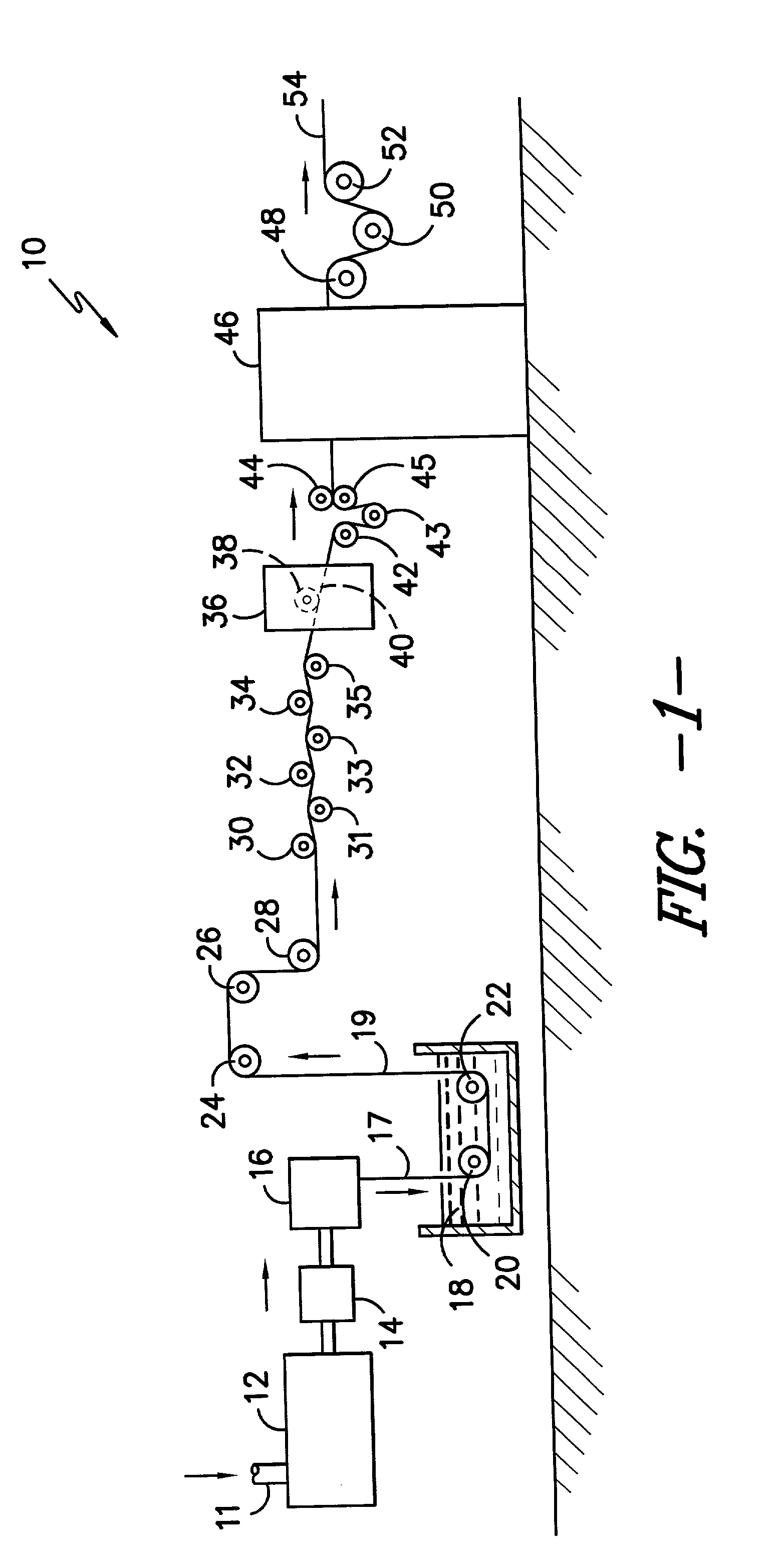
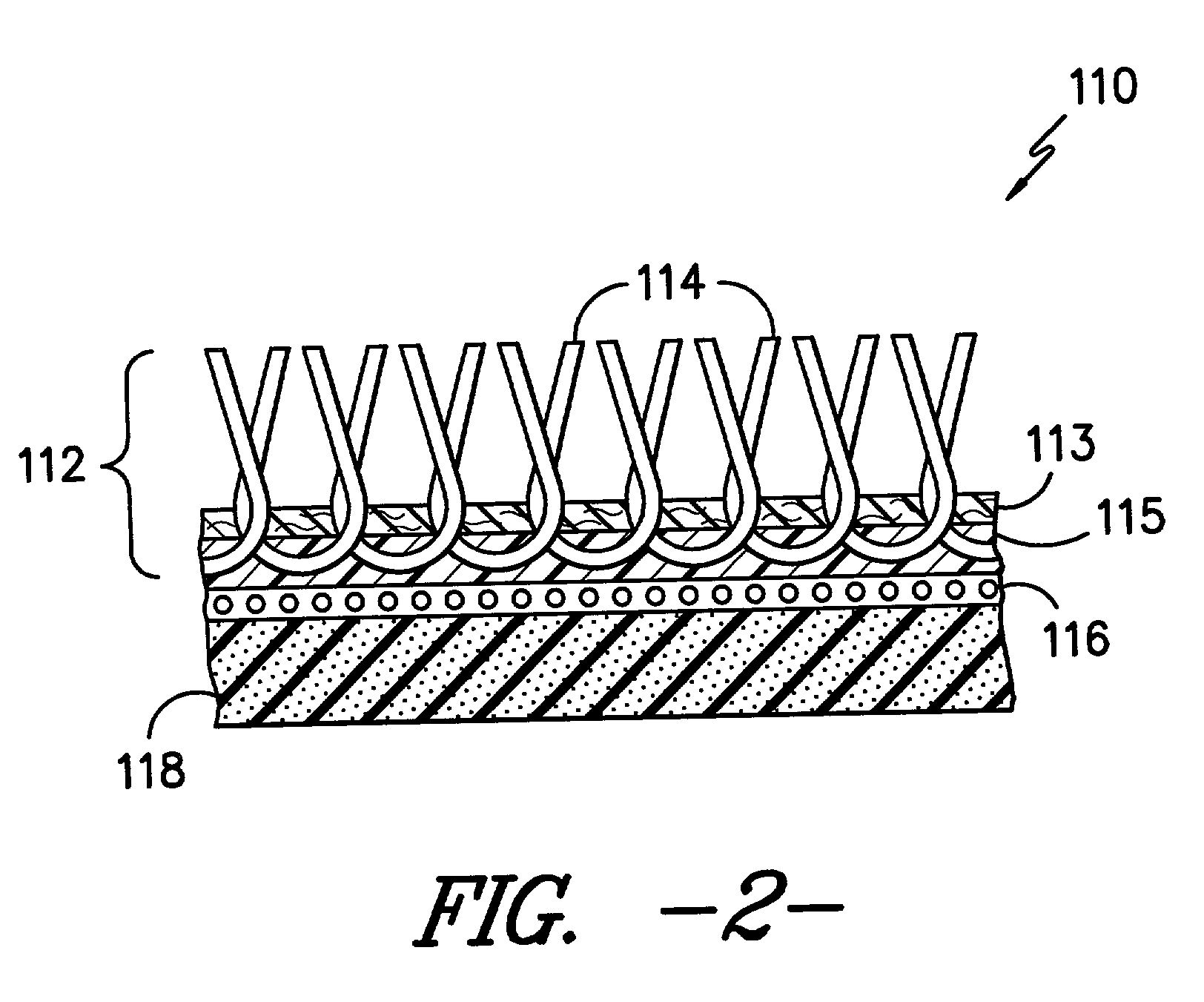
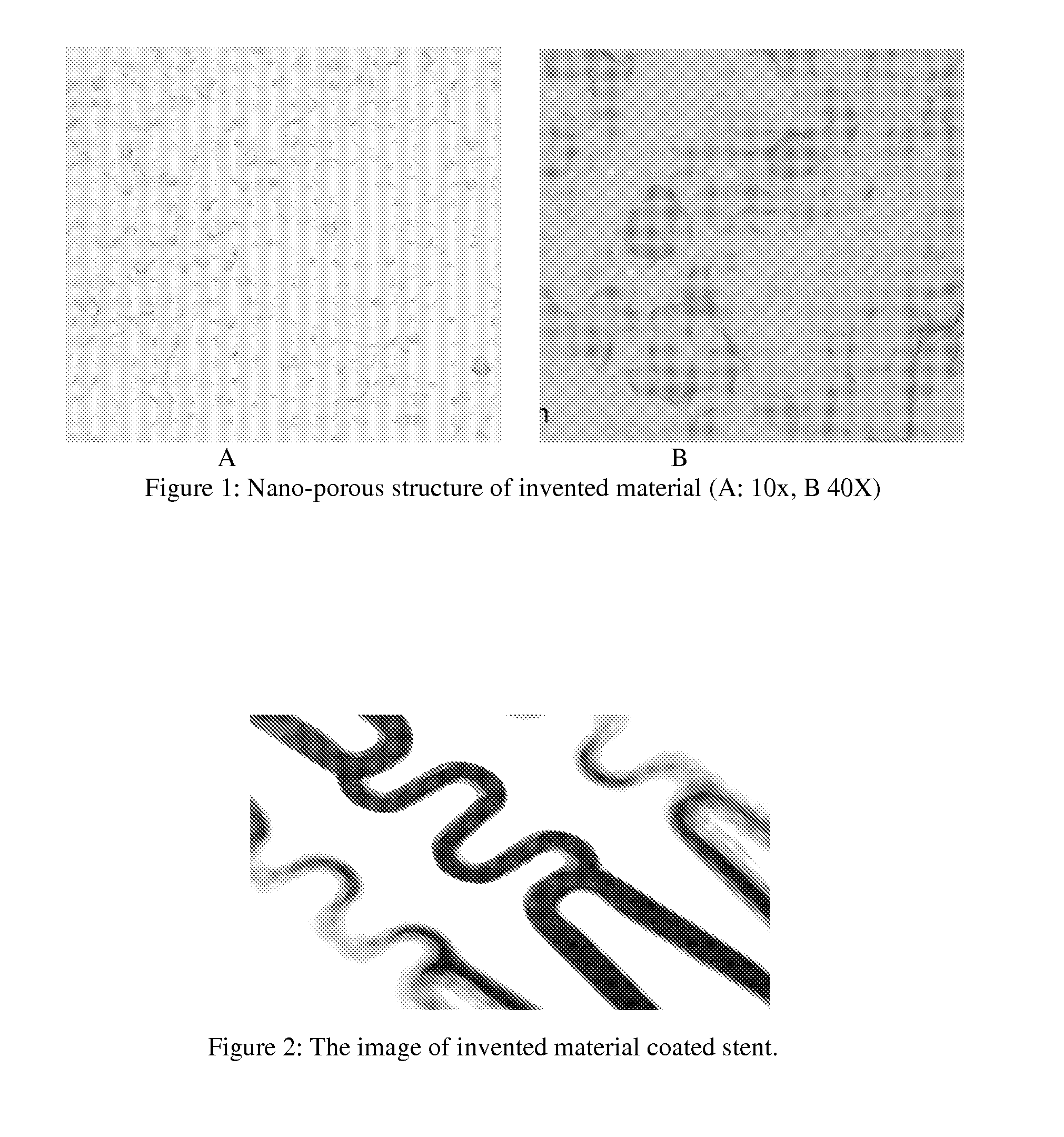
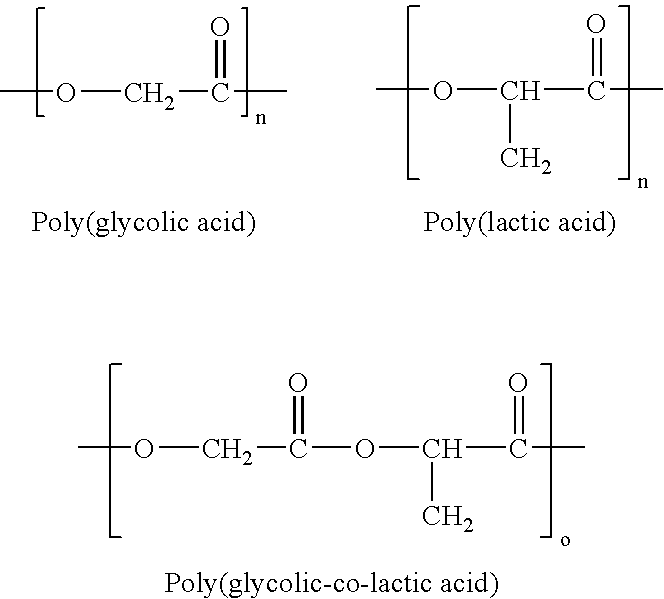
InactiveUS20080249633A1High solubilityImprove remineralizationSuture equipmentsBone implantAnti adhesiveBiocompatible material
The present invention provides novel and inventive biodegradable and biocompatible materials and methods of use in biomedical area. Inventive materials can be formed by blending PLGA with ACP or any one of their family members. Inventive materials can be used in making biodegradable products including but not limit to drug eluting stents, vascular graft, bone substitutes such as bone fixation screws, surgical sutures and anti-adhesive membranes, and / or drug-slow release control vehicle etc.
Owner:WU TIM
Liquid crystal composition and liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20130027654A1High solubilityHigh stabilityLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryChemistryDielectric anisotropy
To provide a liquid crystal composition satisfying at least one characteristic such as a high maximum temperature of a nematic phase, a low minimum temperature thereof, a small viscosity, a suitable optical anisotropy, a large negative dielectric anisotropy, a large specific resistance, a high stability to ultraviolet light and heat, or a liquid crystal composition having a suitable balance regarding at least two characteristics, and an AM device having a short response time, a large voltage holding ratio, a large contrast ratio and a long service life; a liquid crystal composition contains a specific compound having a polymerizable group as a first component, and may contain a specific compound having a large negative dielectric anisotropy and a low minimum temperature as a second component or a specific compound having a small viscosity or a large maximum temperature as a third component, and a liquid crystal display device contains the composition.
Owner:JNC CORP +1
Polymerizable liquid crystal compound having fused ring and homo- and copolymer of the polymerizable liquid crystal compound
InactiveUS20090137761A1High solubilityExcellent orientation propertyLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryKetoneSolubility
A polymerizable liquid crystal compound of formula (1). The compound has high optical (refractive index) anisotropy (Δn), exhibits a liquid crystal phase at room temperature (having a broad liquid crystal phase temperature range) without crystallization, has high solubility in cyclohexanone, methyl ethyl ketone or like organic solvents, exhibits excellent coating properties and orientation properties, and, after polymerization, has high transparency.wherein R1 and R2 each represent hydrogen, a methyl group or halogen; rings A to C each represent a benzene ring, a naphthalene ring, etc.; at least one of rings A to C is a fused ring; X, Y, and Z each represent a C1 to C6 alkyl group, etc.; L1L2, and L3 each represent —COO—, —OCO—, —O(CH2)j— (j=1 to 8), etc.; n is 0 or 1, and a to c are numbers such that the polymerizable liquid crystal compound may have at least one of X, Y, and Z.
Owner:ADEKA CORP +1
Biomass-derived epoxy compound and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20100155122A1High solubilitySatisfactory heat resistance propertyNon-fibrous pulp additionLayered productsBiomassEpoxide
There is disclosed a biomass-derived epoxy compound as an epoxidized product of a raw-material biomass-derived compound having a weight-average molecular weight of 300 to 10000. The biomass-derived epoxy compound has a weight-average molecular weight of 600 to 20000 and is soluble in an organic solvent for the preparation of a varnish. The epoxy compound is prepared by dissolving the raw-material biomass-derived compound in an aqueous alkali solution; adding epichlorohydrin to the solution and heating the mixture; and evaporating epichlorohydrin from the heated mixture and precipitating a biomass-derived epoxy compound, in which the aqueous alkali solution has a pH of 13.5 to 11.0. The biomass-derived epoxy compound has both high solubility in organic solvents and satisfactory heat resistance and can be manufactured in a high yield on the basis of the raw material through a less number of processes.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
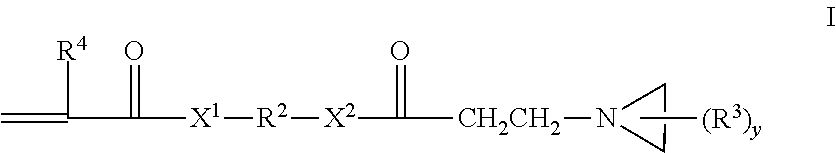
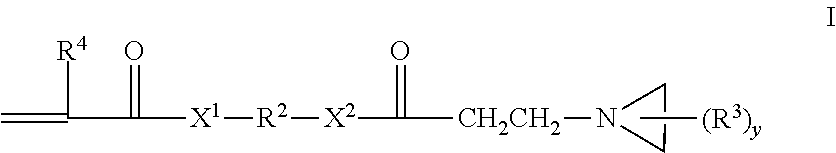
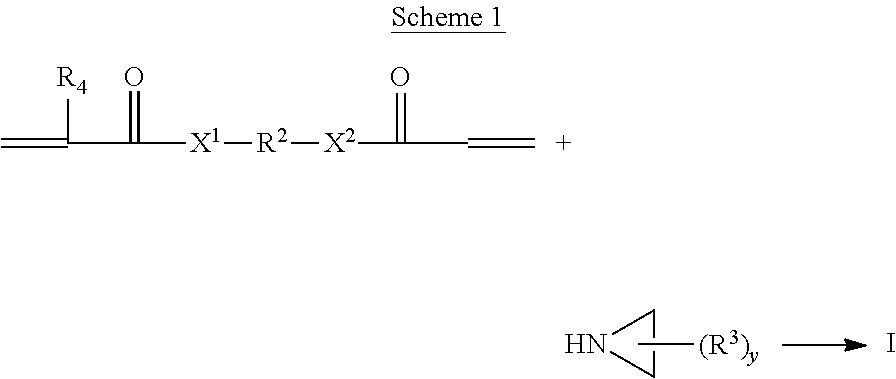
(METH)acryloyl-aziridine crosslinking agents and adhesive polymers
ActiveUS20110152445A1Reduce sensitivityHigh solubilityOrganic chemistrySynthetic resin layered productsPressure sensitiveChemistry
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
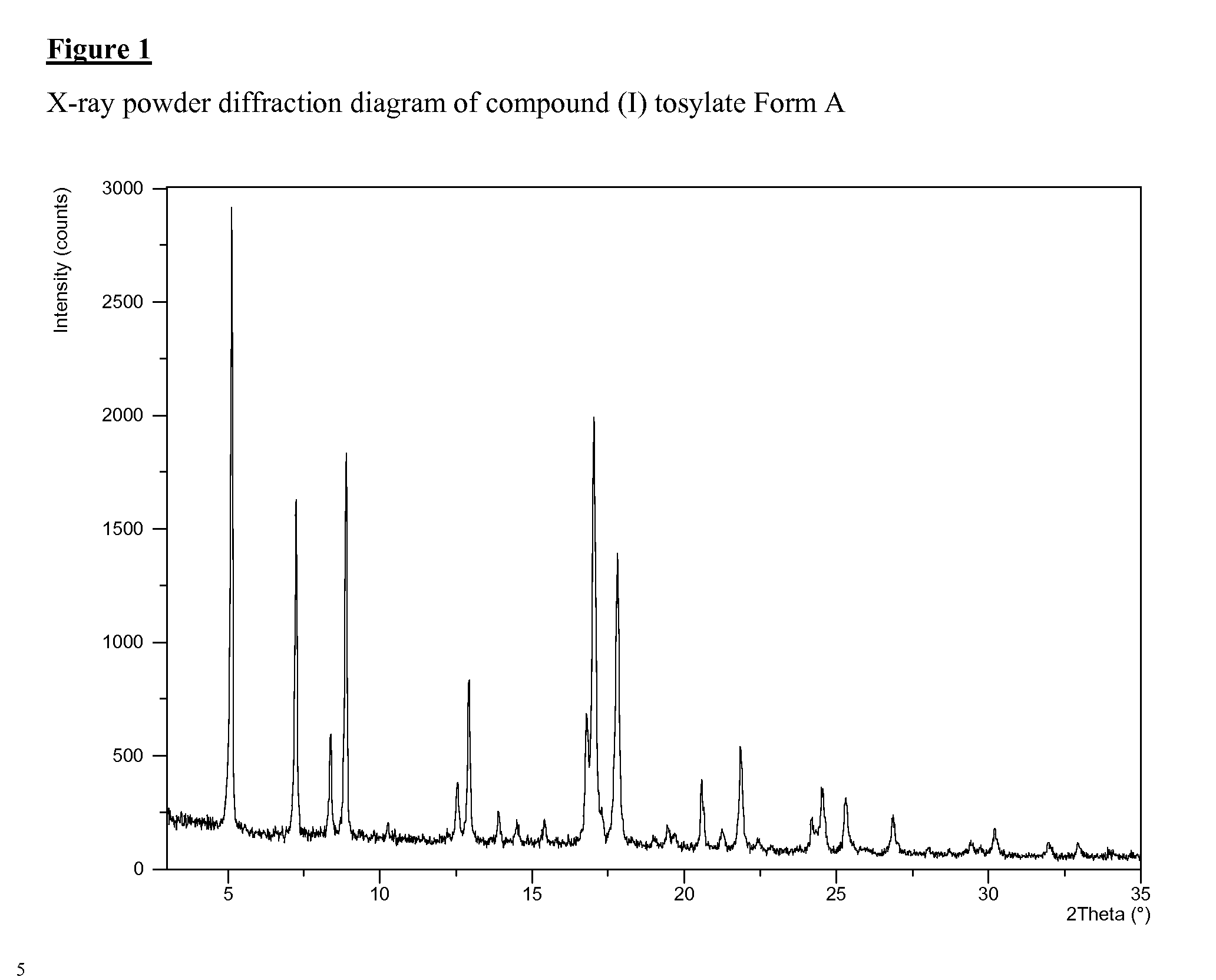
Novel salt 628
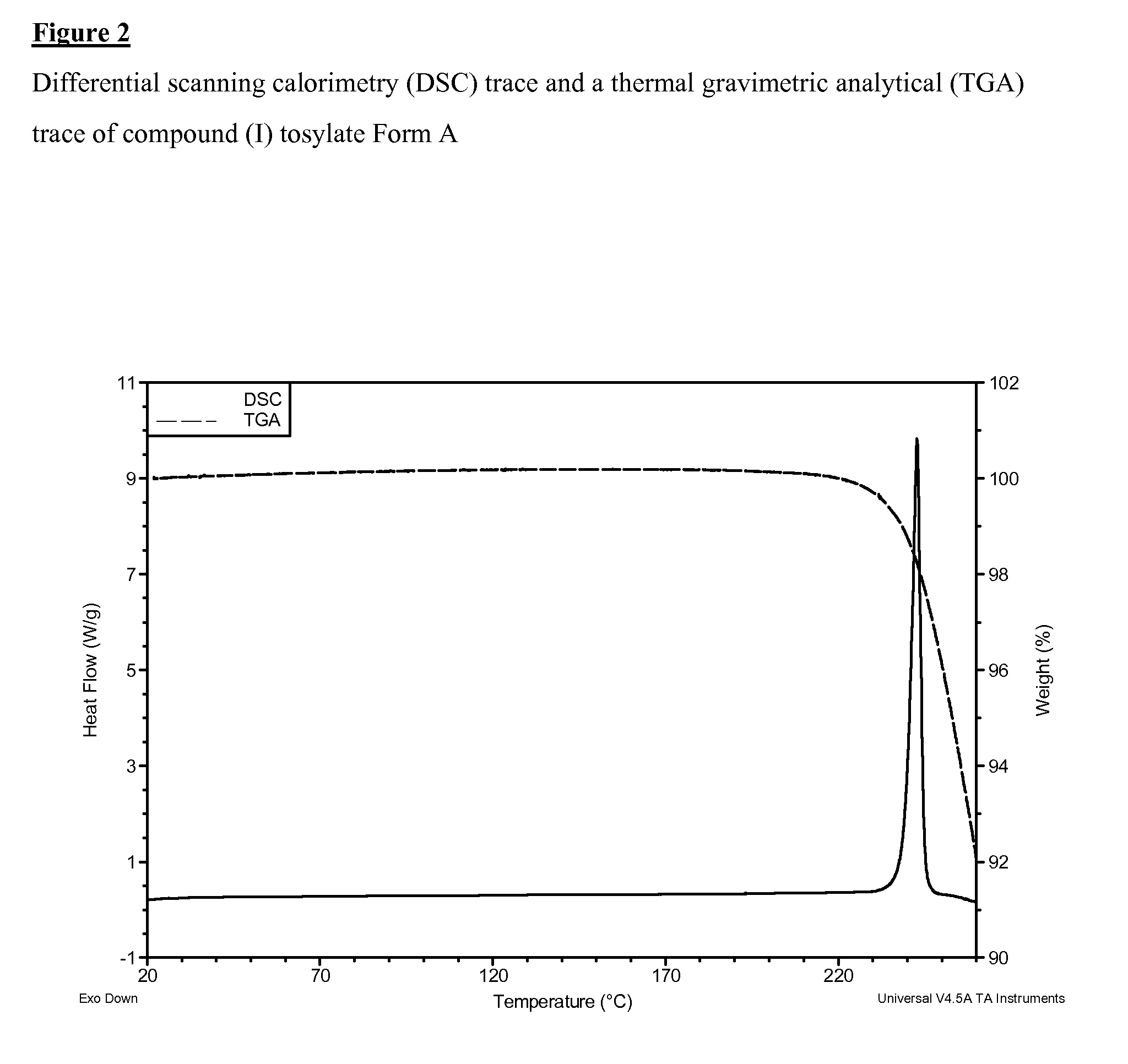
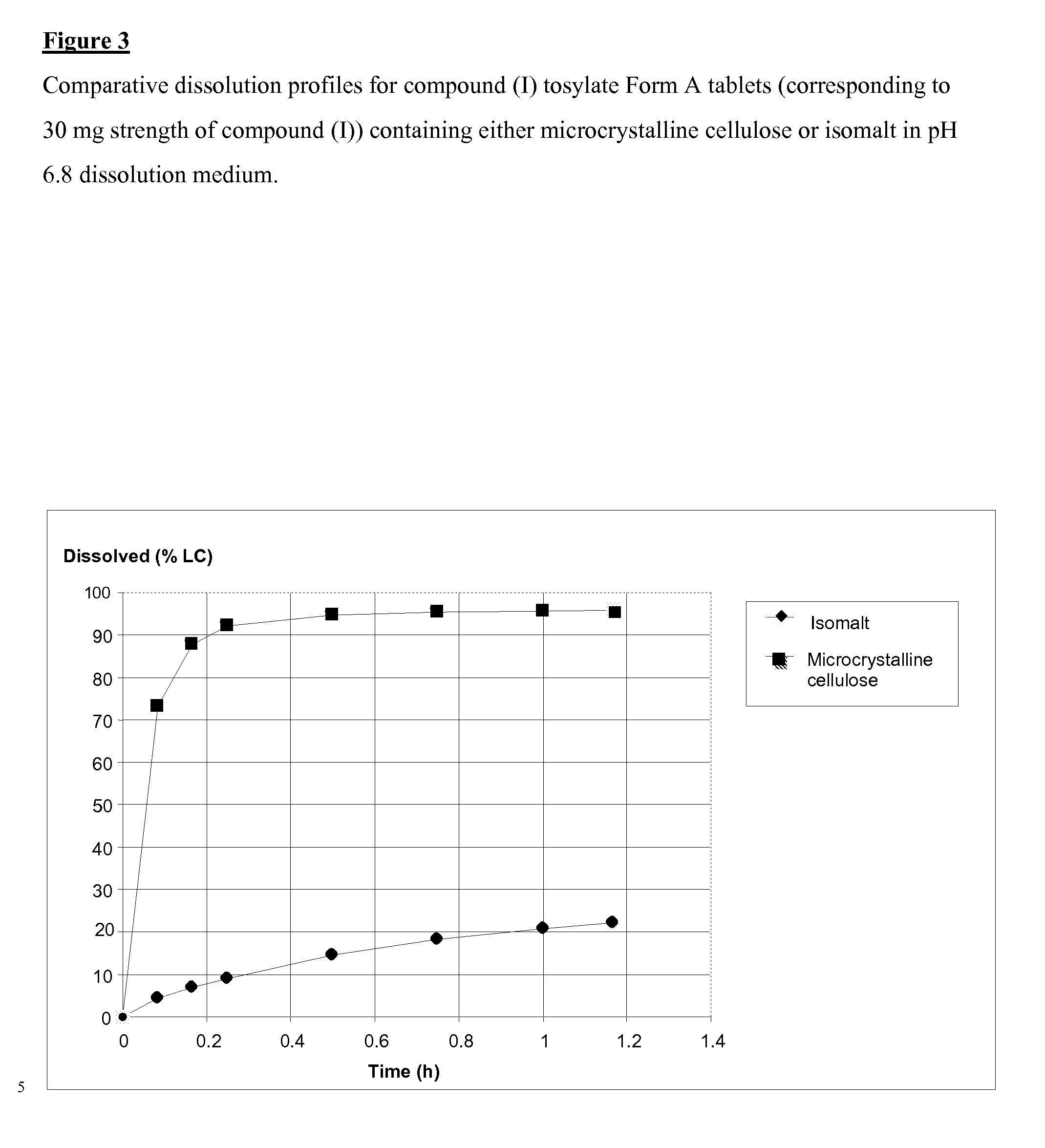
ActiveUS20100216843A1Improved physical propertyHigh solubilityBiocideOrganic chemistryPhenyl groupTrifluoromethyl
6-Methyl-5-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-N-{[5-(methylsulfonyl)pyridin-2-yl]methyl}-2-oxo-1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,2-dihydropyridine-3-carboxamide 4-methylbenzenesulfonate and a novel crystalline form thereof are disclosed together with processes for preparing such salt and form, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such a salt and form, and the methods of treatment using such a salt and form.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Curable composition for coating containing fluorine-containing highly branched polymer
ActiveUS20130302598A1High solubilityEasily moveSynthetic resin layered productsPhotomechanical apparatusDouble bondPerfluoropolyether
A curable composition for coating comprising: (a) a fluorine-containing highly branched polymer obtained by polymerization of a monomer A having two or more radical polymerizable double bonds in a molecule of the monomer A and a monomer B having a fluoroalkyl group and at least one radical polymerizable double bond in a molecule of the monomer B, in the presence of a polymerization initiator C at an amount of 5% by mole to 200% by mole per the number of moles of the monomer A, (b) at least one surface modifier selected from the group consisting of a perfluoropolyether compound and a silicone compound, (c) an active energy ray-curable polyfunctional monomer, and (d) a polymerization initiator that generates radicals by irradiation with an active energy ray; a cured film obtained from the composition; and a hard coating film obtained by use of the composition.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
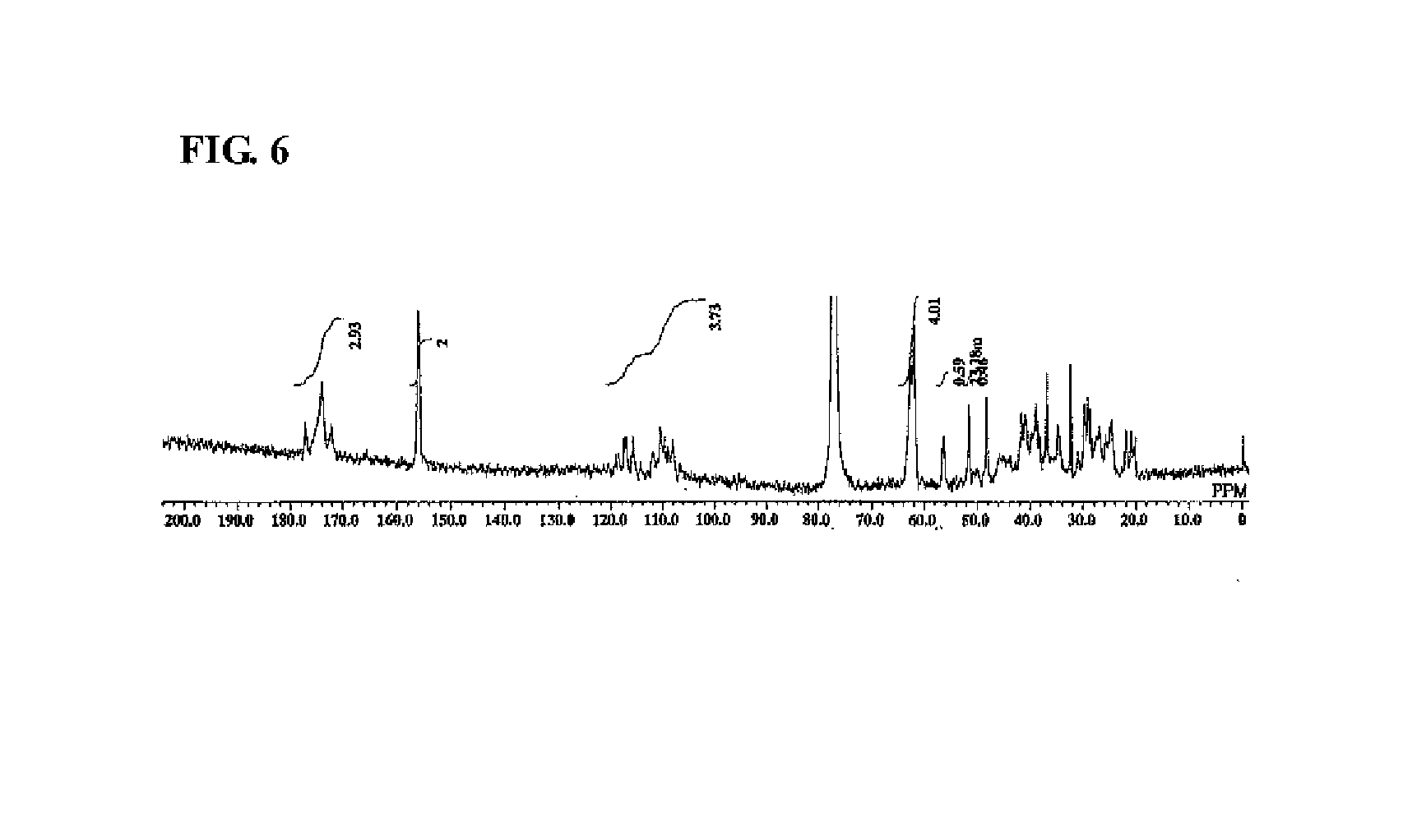
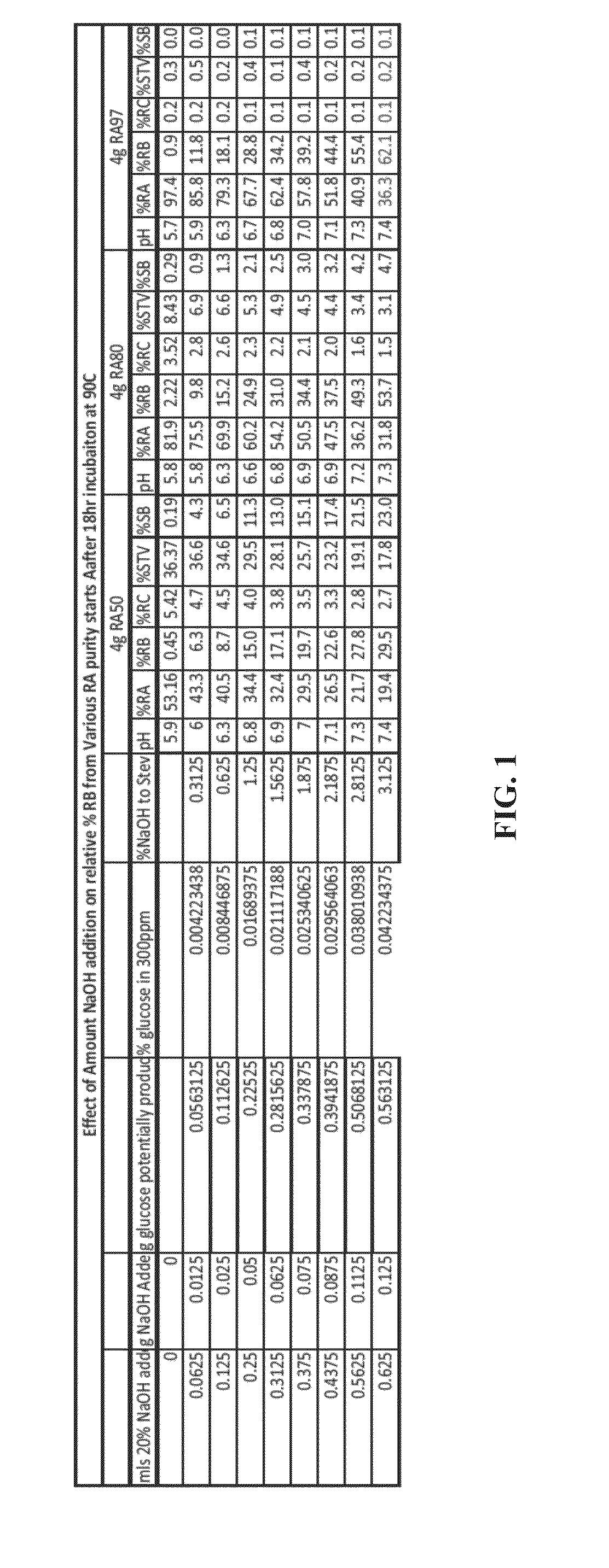
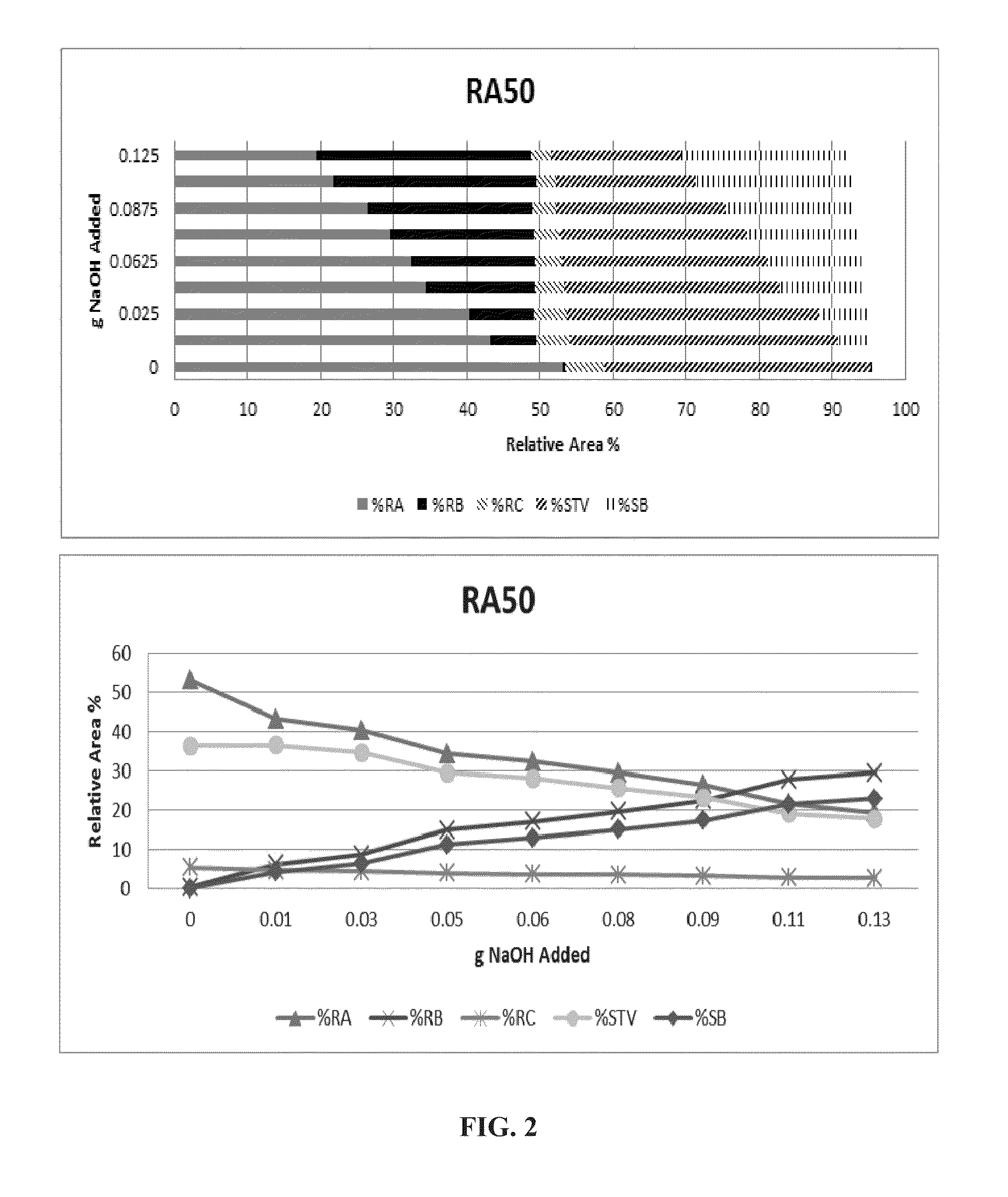
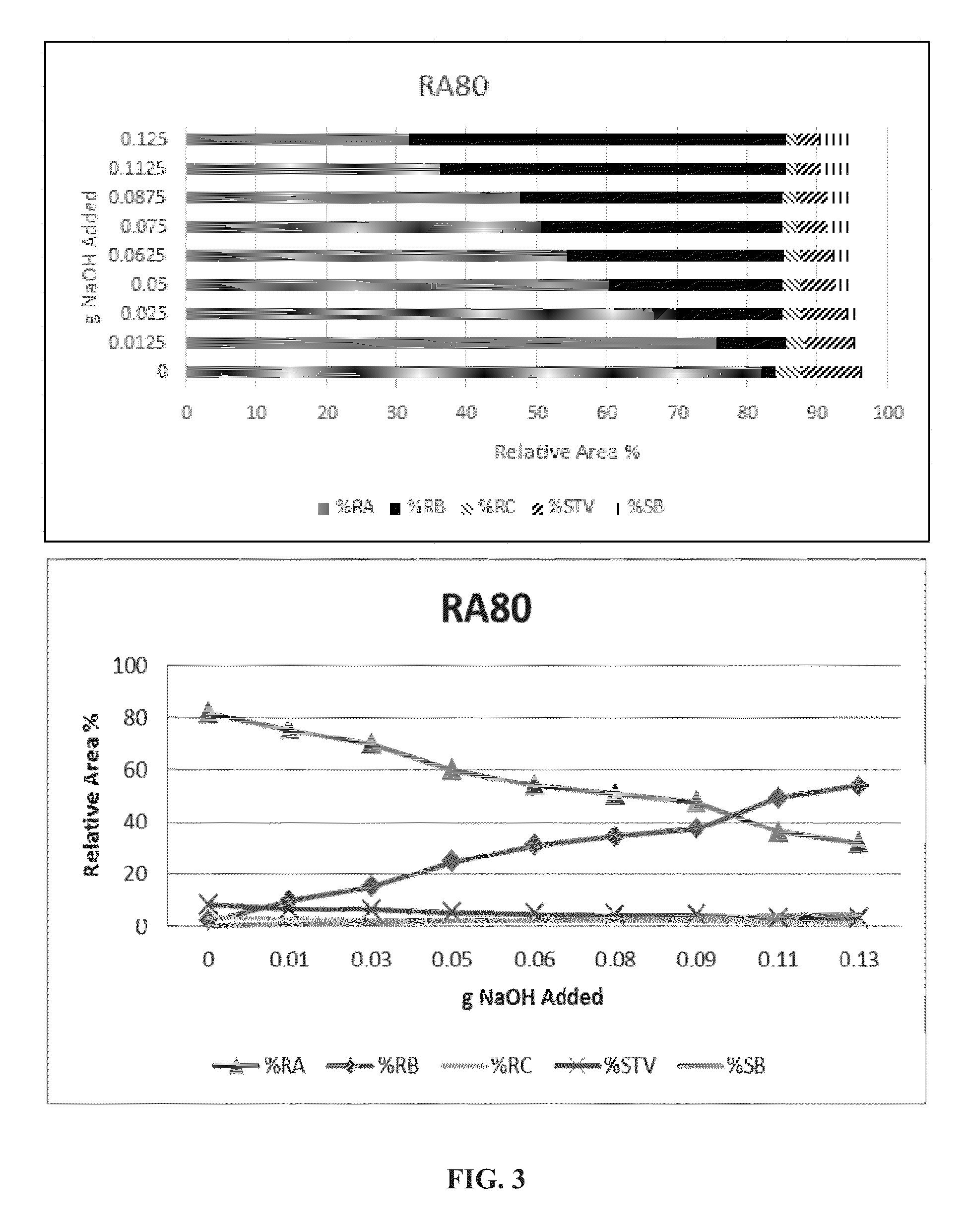
Rebaudioside a and stevioside with improved solubilities
ActiveUS20150359251A1High solubilityImproved sensory profileMilk preparationSugar food ingredientsSensory profileSteviol glycoside
The invention describes sweetening compositions and methods to prepare sweetening compositions containing steviol glycosides, salts, and other natural or synthetic sweeteners with improved solubilities and sensory profiles.
Owner:SWEET GREEN FIELDS USA
Base generator, base-reactive composition containing said base generator, and base generation method
ActiveUS20160122292A1High solubilityLow nucleophilicityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationSubject specificSolubility
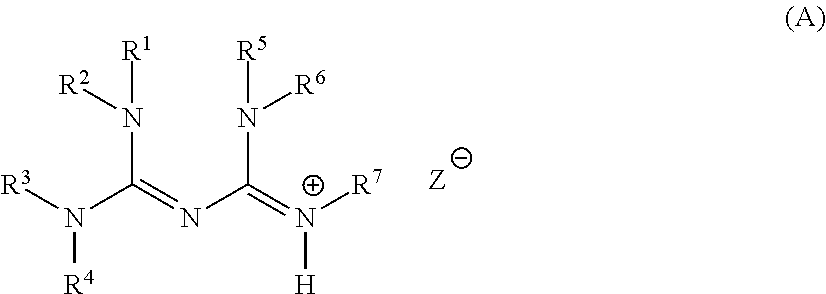
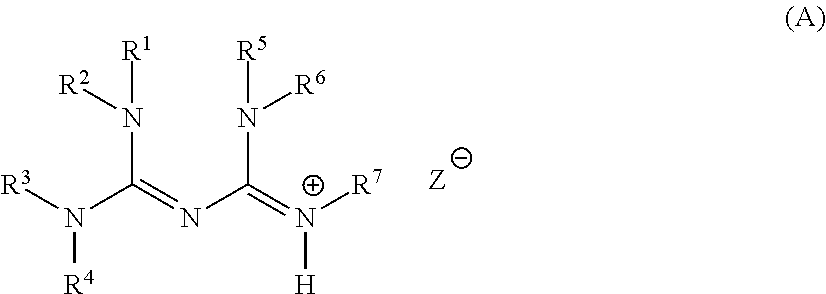
It is a subject of the present invention to provide a base generator which has high solubility to general-purpose organic solvents, can dissolve directly into a base-reactive compound, such as an epoxy-based compound, further is provided with both performance of high heat resistance and low nucleophilicity, and generates a strong base, a base-reactive composition comprising the base generator and a base-reactive compound, as well as a method for generating a base, etc.The present invention relates to a compound represented by the general formula (A), a base generator comprising the compound, a base-reactive composition which comprises the base generator and a base-reactive compound, as well as a method for generating a base, etc.(wherein R1 to R5 each independently represent a hydrogen atom; an alkyl group; an aryl group which may have a substituent; or an arylalkyl group which may have a substituent, R6 represents a hydrogen atom; an alkyl group which may have a substituent; an alkenyl group; an alkynyl group; an aryl group which may have a substituent; or an arylalkyl group which may have a substituent, R7 represents a hydrogen atom; an alkyl group which may have an amino group; an aryl group which may have a substituent; or an arylalkyl group which may have a substituent, and Z− represents an anion derived from a carboxylic acid having a specific structure.)
Owner:TOKYO UNIV OF SCI EDUCATIONAL FOUND ADMINISTRATIVE ORG +1
Aromatic ring compound
InactiveUS20150018422A1Superior GPR40 agonist activityHigh solubilityBiocideOrganic chemistryDiabetes mellitusMedicinal chemistry
Provided is an aromatic ring compound having a GPR40 agonist activity. A compound represented by the formula (I):wherein each symbol is as described in the DESCRIPTION, or a salt thereof has a GPR40 agonist activity, and is useful as an agent for the prophylaxis or treatment of diabetes and the like.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMACEUTICA CO LTD
Curable composition
Provided is a curable composition in which the solubility in a solvent (in particular, water) is high and in which properties of a cured film obtained using the curable composition stored for a predetermined time are superior. The curable composition includes: a compound A represented by Formula (A) and at least one compound X selected from the group consisting of compounds represented by Formulae (X1) to (X4), in which a content of the compound X is 0.01 to 2.0 mass % with respect to a total mass of the compound A and the compound X; or a compound B represented by Formula (B) and a compound Y represented by Formula (Y), in which a content of the compound Y is 0.01 to 2.0 mass % with respect to a total mass of the compound B and the compound Y.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Solid dispersion preparation
ActiveUS20070248681A1Good solubilityHigh solubilityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryDrugWater soluble polymers
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Method for separating insect proteins, oil and chitin in one step by natural deep-eutectic solvents, and application thereof
PendingCN110183510AEasy to prepareHigh solubilityPeptide preparation methodsFatty-oils/fats productionSolventChitin formation
The present invention belongs to the field of processing and utilization of agricultural products, and discloses a method for separating insect proteins, oil and chitin in one step by natural deep-eutectic solvents, and an application thereof. The method uses insect powder as a raw material, the insect powder is added to natural deep-eutectic solvents, a heat reaction is conducted until a tissue structure of the insect powder is fully dissociated, an upper layer oil component is collected by centrifugation, a lower part is filtered and washed to collect chitin, a solvent part is subjected to acold treatment to precipitate insect proteins, the solvent is recovered, and finally drying is conducted to obtain an initial extract of the insect chitin and proteins. The natural deep-eutectic solvents are used as a multifunctional medium, and the one-step method can realize the separation of the insect proteins, oil and chitin, and can increase added value of insect resources. The method can completely replace traditional multi-step separation processes, and is simple in processes and mild in conditions, the products are liable to separate, the solvent can be recycled, cost and energy consumption are reduced, and the processes have better economy and environmental protection, so that deep utilization of the insect resources is feasible.
Owner:SERICULTURE & AGRI FOOD RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
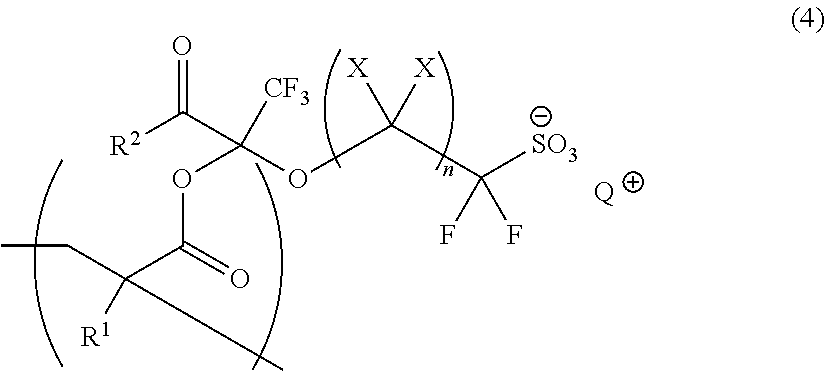
Polymerizable Fluorine-Containing Sulfonate, Fluorine-Containing Sulfonate Resin, Resist Composition And Pattern-Forming Method Using Same
ActiveUS20130209937A1High solubilityHigh resolutionOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationComposite materialSide chain
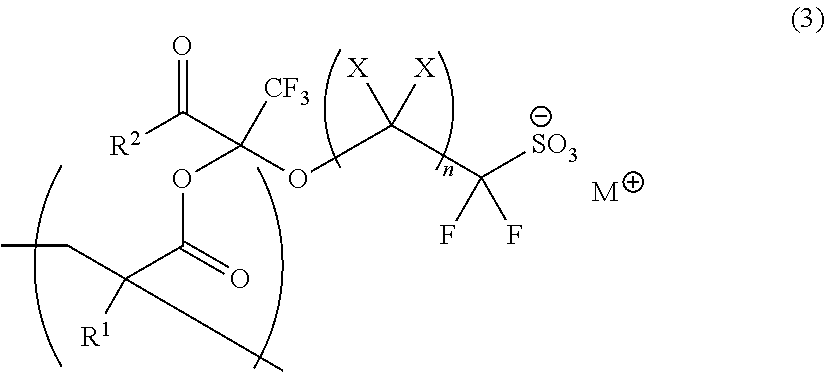
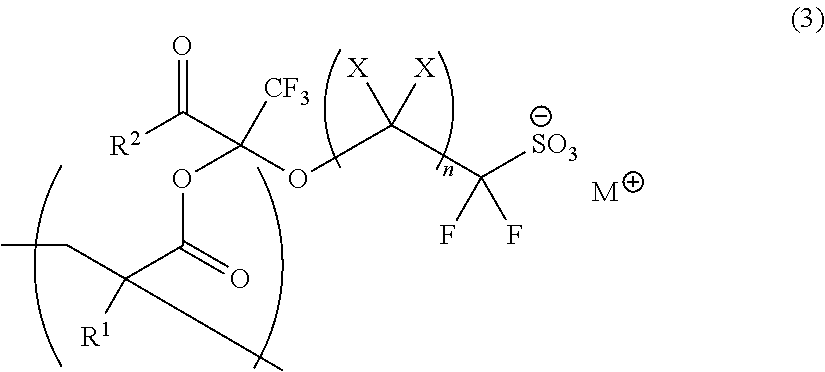
According to the present invention, there is provided a sulfonate resin having a repeating unit of the following general formula (3):where X each independently represents a hydrogen atom or a fluorine atom; n represents an integer of 1 to 10; R1 represents a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, a C1-C3 alkyl group or a C1-C3 fluorine-containing alkyl group; R2 represents either RAO or RBRCN; and M+ represents a monovalent cation.The sulfonate resin has an onium sulfonate incorporated in a side chain thereof with an anion moiety of the sulfonate salt fixed to the resin and can suitably be used as a resist resin having a high solubility in propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
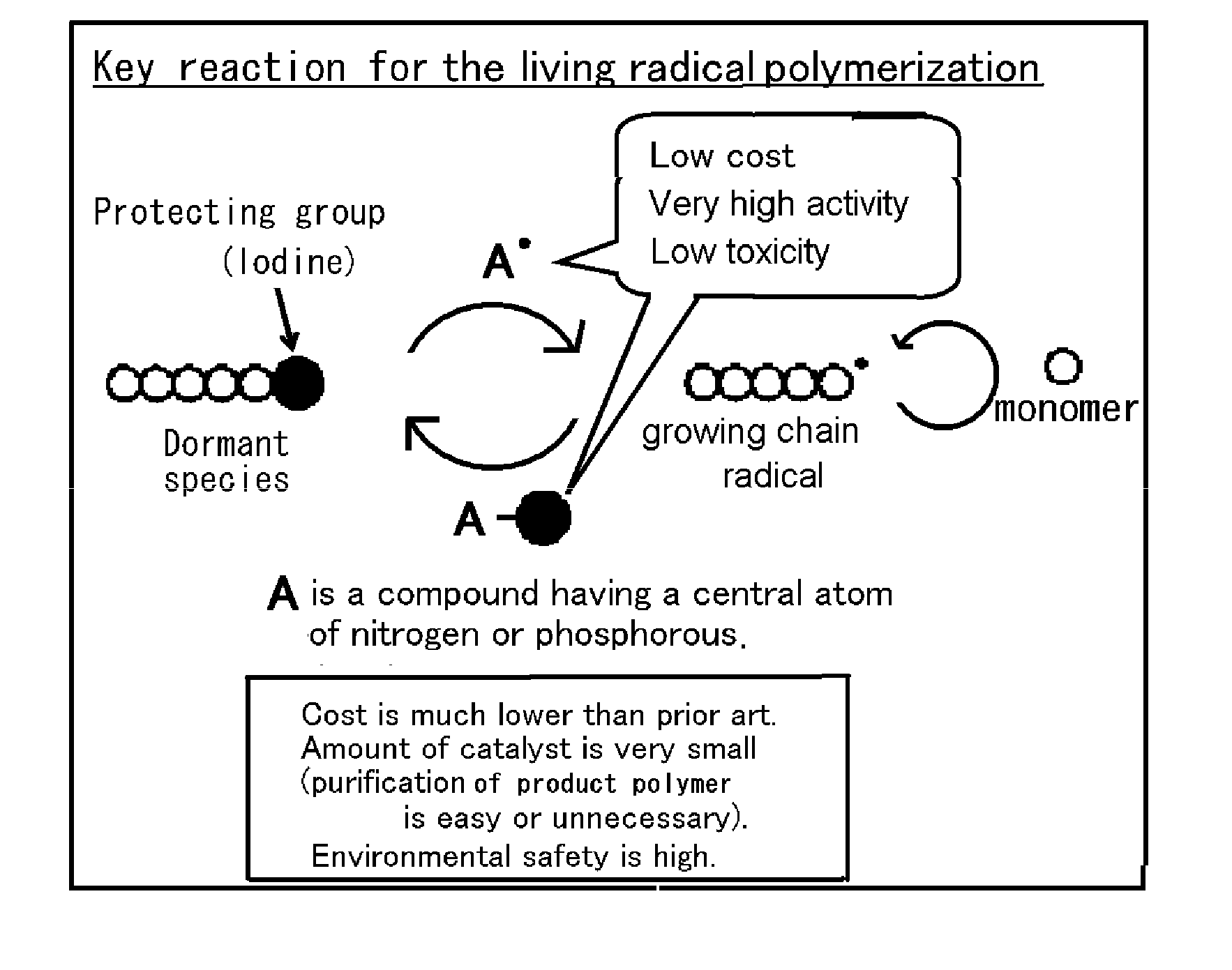
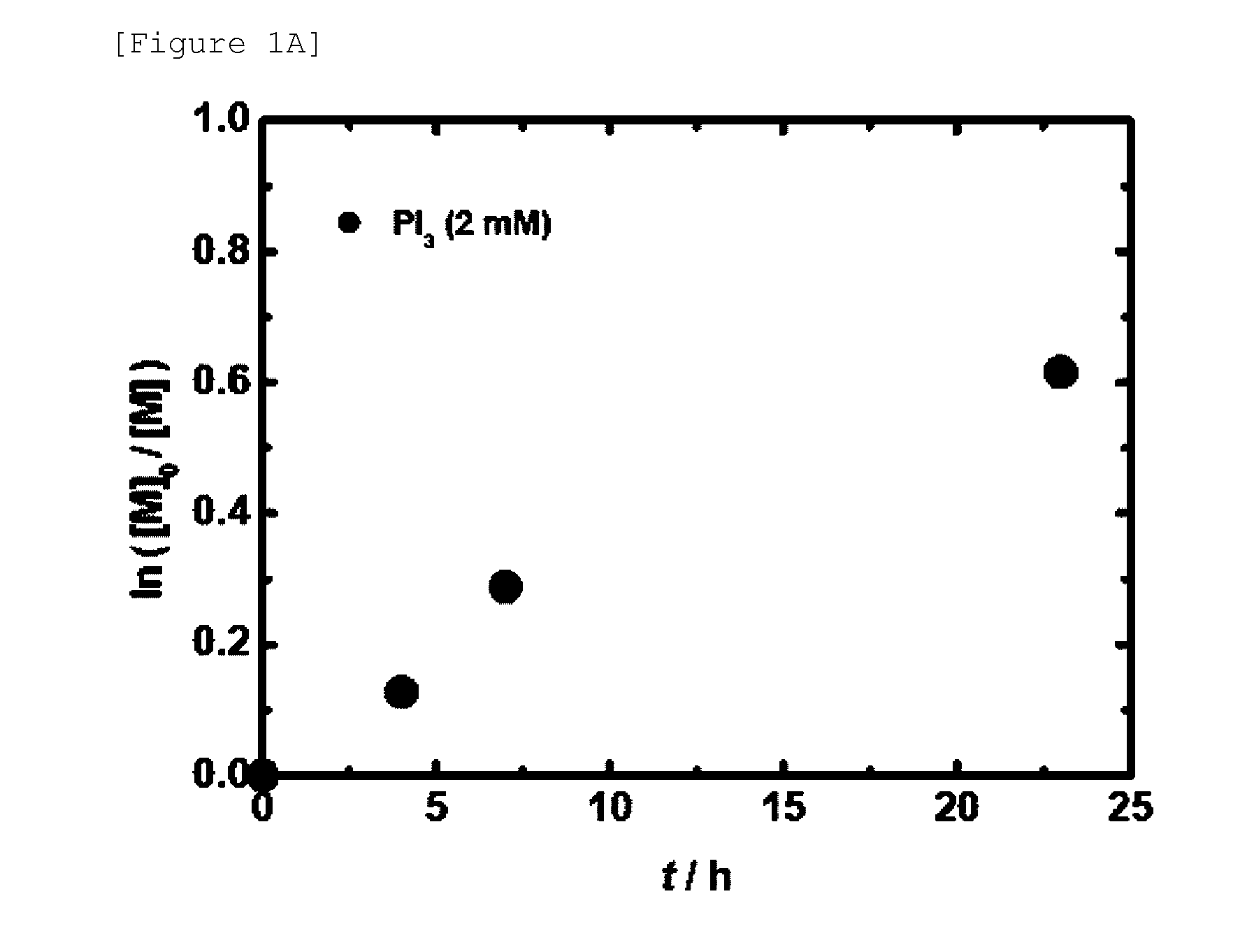
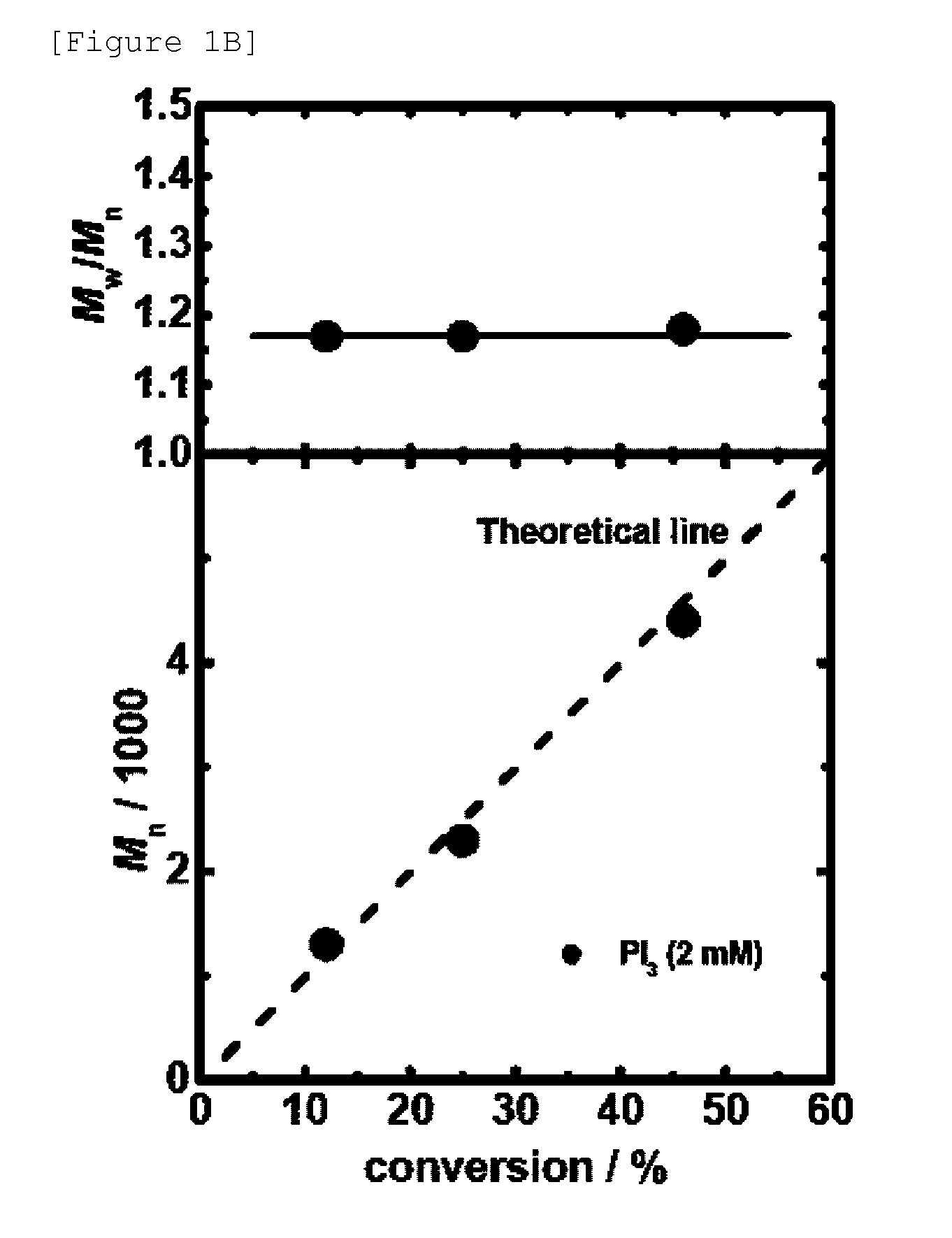
Novel living radical polymerization method using a phosphorus compound or nitrogen compound as a catalyst
ActiveUS20100298499A1Low toxicityHigh solubilityOrganic chemistryPhosphorus halides/oxyhalidesSolubilityCompound (substance)
A highly active and environment-friendly catalyst for use in a living radical polymerization is provided. A catalyst for use in a living radical polymerization method is provided. The catalyst comprises a central element, which is selected from nitrogen and phosphorus, and at least one halogen atom, which is bound to the central element. A monomer having a radical reactive unsaturated bond is subjected to a radical polymerization reaction in the presence of the catalyst, thereby it is possible to obtain a polymer having narrow molecular weight distribution. The present invention has the merits such as low toxicity of the catalyst, a small amount of the catalyst being required, high solubility of the catalyst in the polymerization media, mild reaction conditions, no coloration, no odor (unnecessary post-treatment of molded products). The method of the present invention is more environment-friendly and economical than other living radical polymerization methods.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Method for drying a protein composition, a dried protein composition and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the dried protein
InactiveUS20100179090A1High solubilityLow aggregaton potentialPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDrugProtein formation
The present invention relates to a method for spray-drying of protein solutions and the spray-dried protein product. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions containing such spray-dried protein, to methods of treating diabetes and hyperglycaemia using the spray-dried protein of the invention and to the use of such spray-dried protein in the treatment of diabetes and hyperglycaemia.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Active ester resin, epoxy resin composition, cured product thereof, prepreg, circuit board, and build-up film
ActiveUS20150344617A1High solubilityLow dielectric constantPretreated surfacesThin material handlingSolventChemistry
There is provided a novel active ester resin which has a high solubility in a variety of solvents. The active ester resin includes a structural moiety in which a structural unit (I) in which a plurality of arylene groups (a) are bonded to each other via an alicyclic hydrocarbon group is bonded to another structural unit (I) or an aryl group (d) via an arylene dicarbonyloxy group (c), wherein at least one of the arylene groups (a) in the molecule has a structural part (b) represented by Structural Formula (i) and positioned on its aromatic nucleus (in the formula, each R1 independently represents a methyl group or a hydrogen atom; Ar1 represents a phenylene group, a naphthylene group, or a phenylene group or naphthylene group which has one to three alkyl groups each having 1 to 4 carbon atoms on its aromatic nucleus; and n is 1 or 2).
Owner:DAINIPPON INK & CHEM INC
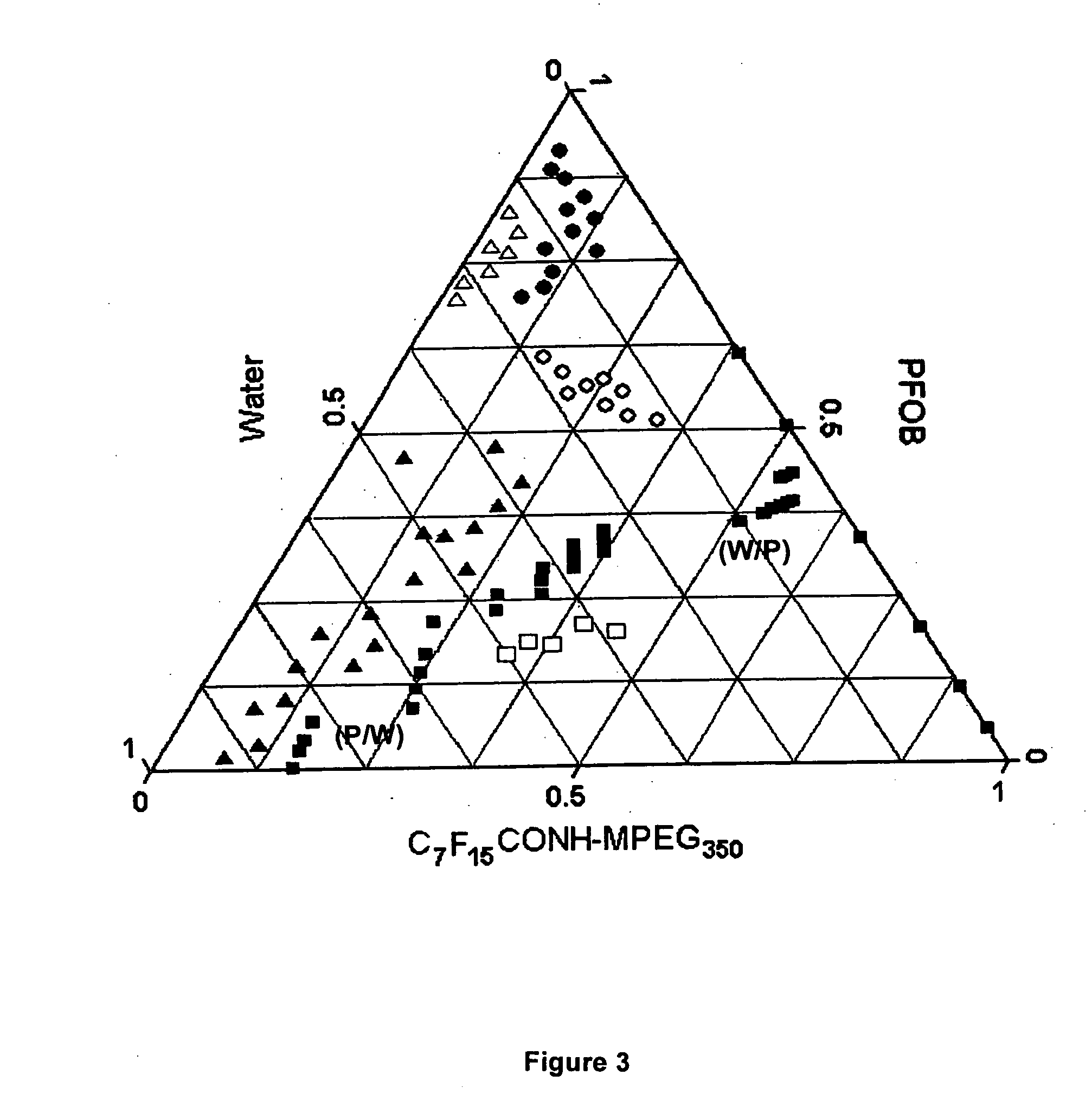
Perfluorocarbon-soluble compounds
InactiveUS20060002881A1High yieldHigh solubilityCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsInorganic fluorine compoundsAqueous solution
The invention describes syntheses and purifications of several perfluorocarbon-soluble compounds having a general formula RF-L-X or RF-L-X-L-RF, wherein RF is a perfluorocarbon group, X is a hydrophilic moiety, and L is an amide linkage of general structure —CO—NH—. The invention also provides microemulsions comprising a PFC forming an oil phase, water or aqueous solution forming a water phase, and a PEG-based fluorosurfactant with an HFB (hydrophilic groups to fluorophilic groups balance) value from about 7 to about 13. The invention also provides a method of amidification of a fluorocompound. The method involves mixing perfluoroacid chloride of a general formula CnF2n+1COCl with a compound containing an amine group with a general structure R—NH2 under reaction conditions sufficient to obtain a product having a general formula CnF2n+1—CONH—R.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Low-shrink polypropylene tape fibers
InactiveUS20030134118A1High solubilityLow shrinkage rateSynthetic resin layered productsFloor coveringsSodium benzoateAspect ratio
Improvements in preventing heat- and moisture-shrink problems in specific polypropylene tape fibers are provided. Such fibers are basically manufactured through the initial production of polypropylene films or tubes which are then slit into very thin, though flat (and having very high cross sectional aspect ratios) tape fibers thereafter. Such fibers (and thus the initial films and / or tubes) require the presence of certain compounds that quickly and effectively provide rigidity to the target polypropylene tape fiber after heat-setting. Generally, these compounds include any structure that nucleates polymer crystals within the target polypropylene after exposure to sufficient heat to melt the initial pelletized polymer and upon allowing such a melt to cool. The compounds must nucleate polymer crystals at a higher temperature than the target polypropylene without the nucleating agent during cooling. In such a manner, the "rigidifying" nucleator compounds provide nucleation sites for polypropylene crystal growth. Upon slitting of the initial film and / or tube, the fiber is then exposed to sufficient heat to grow the crystalline network, thus holding the fiber in a desired position. The preferred "rigidifying" compounds include dibenzylidene sorbitol based compounds, as well as less preferred compounds, such as sodium benzoate, certain sodium and lithium phosphate salts (such as sodium 2,2'-methylene-bis-(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl)phosphate, otherwise known as NA-11). Specific methods of manufacture of such inventive tape fibers, as well as fabric articles made therefrom, are also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Surfactant and dispersion aid each comprising graft fluoropolymer
InactiveUS20050202997A1High solubilityExcellent actionSurface-active detergent compositionsTransportation and packagingSolubilityHigh concentration
A surfactant comprising a graft polymer having a branch polymer and a trunk polymer, at least one of which contains a fluoroalkyl group, has high solubility in a liquid medium and shows a superior surface tension-lowering action, in spite of containing fluoroalkyl groups at a high concentration. The surfactant also has high solubility in a liquid medium, in spite of containing a short-chain perfluoroalkyl group which is poor in surface tension-lowering action, and further shows a superior action to decrease the surface tension of a solution. The use of this surfactant can provide a liquid dispersion well dispersed in a liquid medium having a small environmental load.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
High performance inorganic complexes for next-generation redox flow batteries
ActiveUS20180254478A1High solubilityWider rangeCell electrodesRegenerative fuel cellsSolventCoordination sphere
In an aspect, a redox flow battery comprises a catholyte and an anolyte; wherein at least one of said catholyte and said anolyte is a metal-coordination complex, said metal-coordination complex comprising: (i) a metal; (ii) one or more first ligands coordinated with said metal atom, wherein each of said first ligands is independently a Lewis basic ligand; and one or more second ligands associated with said one or more first ligands, wherein each of said second ligands is independently a Lewis acid ligand; and a nonaqueous solvent, wherein said catholyte, said anolyte or both are dissolved in said nonaqueous solvent. One or more first ligands may be provided in a primary coordination sphere of said metal-coordination complex and one or more second ligands may be provided in a secondary coordination sphere of said metal-coordination complex. The one or more first ligands independently may comprise a Lewis basic functional group and each of said one or more second ligands independently may comprise a Lewis acidic functional group.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Joining metallurgically incompatible metals
InactiveUS20180161931A1High solubilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusSoldering apparatusIntermetallicMetal
A method for joining a second alloy material to a first alloy material where the two alloy materials are incompatible, comprising forming three successive interface layers over a substrate comprising the first alloy material, followed by forming a structure of the second alloy material over the interface layers, wherein the composition and deposition method for each of the layers is selected so that brittle intermetallics are not formed between elements of the adjacent layer compositions.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com