Rapid molecular identification method for glycyrrhiza uralensis, glycyrrhiza glabra, glycyrrhiza inflate and hybrid variety thereof
A technology of Ural licorice and licorice flavonoids, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problem of lack of accurate and efficient molecular identification methods, and achieve the effect of accurate identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
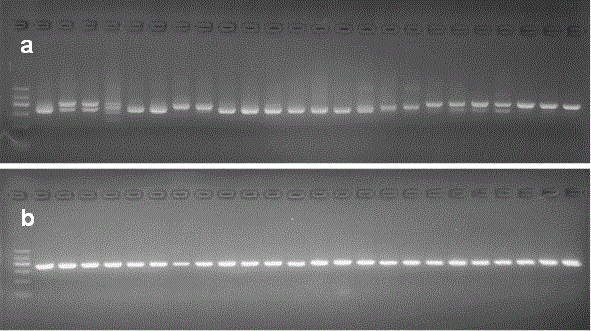
[0024] Embodiment 1, species identification of wild licorice samples.
[0025] 1) Collect 56 samples of wild licorice (all dry roots) from several main production areas of licorice in China. The specific information of the samples is shown in Table 1. The total DNA of the samples was extracted with a plant genomic DNA extraction kit (Tiangen Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing), and the specific steps were as follows:
[0026] ① Take 50mg of medicinal material powder in a 1.5mLEP tube, add liquid nitrogen and a small amount of quartz sand, and grind thoroughly with a grinding rod;
[0027] ② Add 700 μL of buffer solution GP1 (containing 0.5% mercaptoethanol) preheated at 65°C to the ground medicinal material powder, mix quickly, and bathe in water at 65°C for 40 minutes;
[0028] ③ Add 700 μL of chloroform, mix thoroughly, and centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 5 min;
[0029] ④ Transfer the aqueous phase to a new centrifuge tube, add 700 μL buffer GP2, and mix well;
[0030...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2, identification of the variety of Radix Glycyrrhiza decoction pieces.
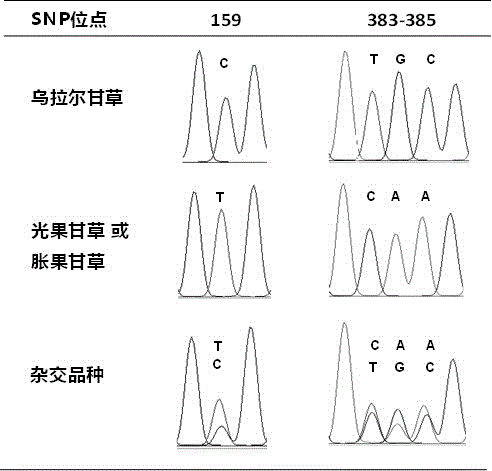
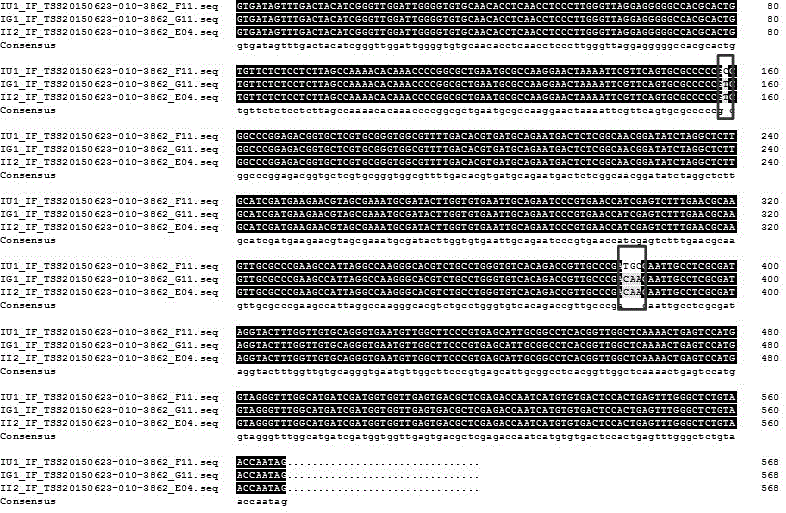
[0047] The experimental method was basically the same as in Example 1, except that the samples were changed from wild licorice samples to commercially available licorice pieces, including 31 batches of raw licorice pieces and 2 batches of processed products (honey roasted). Glycyrrhizae decoction pieces were ground under liquid nitrogen to extract DNA, and PCR amplification and sequence analysis were performed. Table 3 shows the information and identification results of licorice decoction pieces. The results showed that the method could distinguish and identify the source varieties of licorice commercial decoction pieces. The above four SNP sites can be detected in the amplified ITS sequence, and one SNP site can be detected in the ndhC-trnV transcription spacer. Based on this, the identification results of each batch of samples are obtained. According to the determination results, t...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3, the variety identification of Radix Glycyrrhizae seed and seedling.
[0051] The experimental method is basically the same as in Example 1, except that the sample is changed from dried roots of licorice to licorice seeds and germinated licorice seedlings. The results showed that the method can be used for species identification of licorice seeds and seedlings.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com