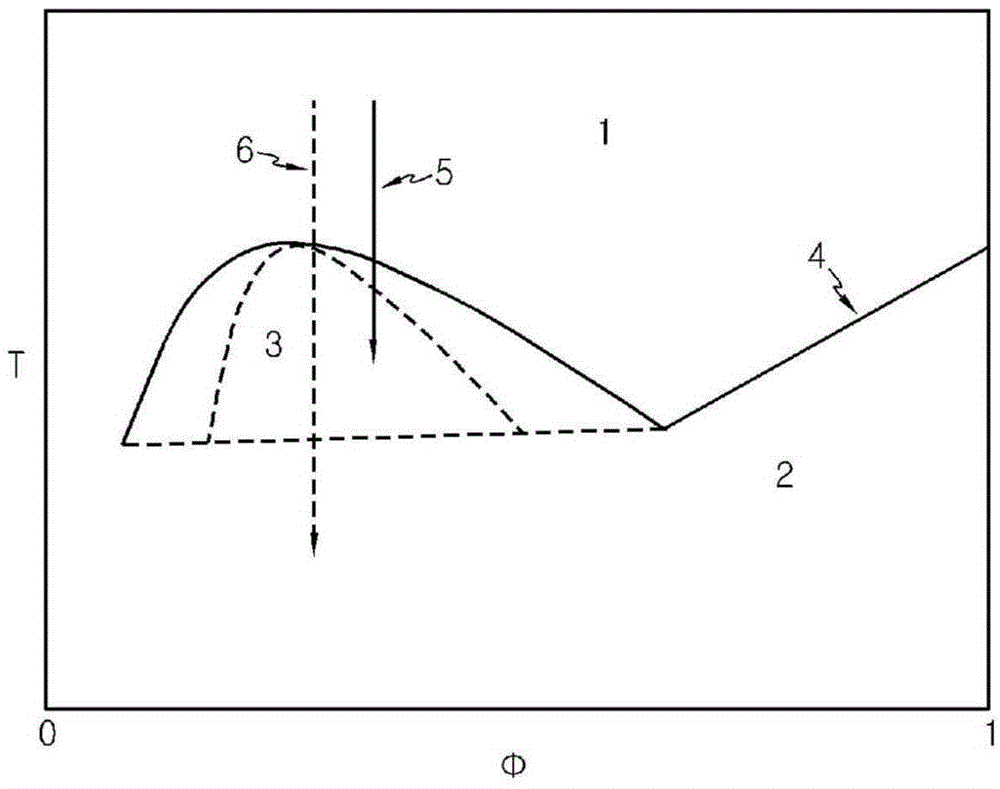
Method for manufacturing asymmetric polyvinlylidenefluoride hollow fiber membrane and hollow fiber membrane manufactured therefrom
A fiber membrane, asymmetric technology, used in fiber processing, rayon manufacturing, hollow filament manufacturing, etc., can solve problems such as low compatibility, achieve high porosity, high water permeability, and easy to prepare parameters.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0085] Manufacturing of PVDF hollow fiber membrane
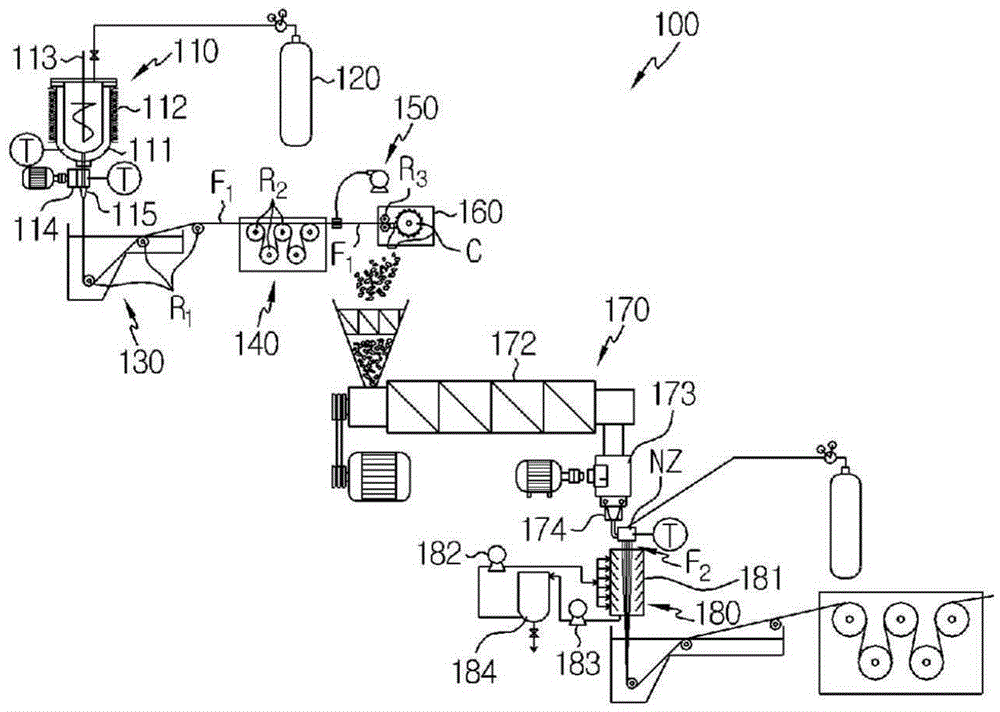
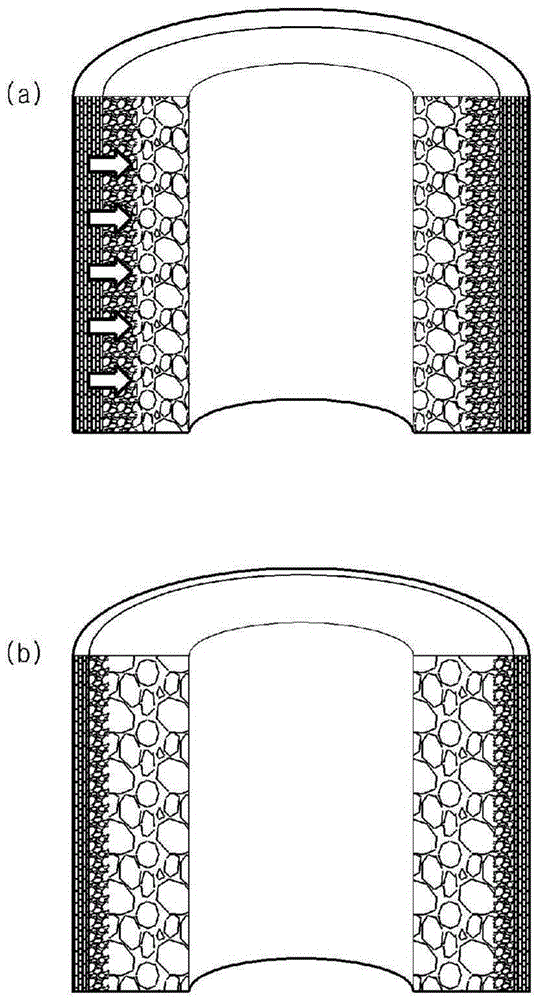
[0086] use for figure 2 The device shown in to prepare PVDF hollow fiber membrane precursors. The prepared PVDF hollow fiber membrane precursor is wound around a rectangular parallelepiped bobbin. Then, the wound PVDF hollow fiber membrane precursor is cut at the edge portion of the rectangular parallelepiped bobbin, and then the diluent is extracted from the cut PVDF hollow fiber membrane precursor by a solvent extraction method using ethanol as an extractant. After drying at 50°C for 2 hours, the PVDF hollow fiber membrane precursor passes through Figure 5 (a) The intermittent clamp drafting method shown draws 125%. Therefore, if necessary, the obtained PVDF hollow fiber membrane is heat-treated under tension. The details of the relevant equipment, operating conditions and composition of the raw materials are described in Table 1 and Table 2.
[0087] Table 1
[0088] Device
Operating conditions
Mix at...
Embodiment 2
[0101] Evaluation Example 2: Surface evaluation of PVDF hollow fiber membrane
[0102] Scanning electron micrographs (SAERON, AIS2100) of the outer surface and inner surface of the PVDF hollow fiber membrane prepared from the PVDF hollow fiber membrane precursor prepared in Example 1 through diluent extraction and drafting Picture 12 Means in. in Picture 12 In the middle, the SEM image on the left is an image of the outer surface and the SEM image on the right is an image of the inner surface. From Picture 12 It can be seen that the outer surface of the PVDF hollow fiber membrane manufactured in Example 1 has a porous structure with small pores and low porosity, while the inner surface has a porous structure with large pores and high porosity. Therefore, it was confirmed that the PVDF hollow fiber membrane manufactured in Example 1 had an asymmetric structure.
Embodiment 3
[0103] Evaluation Example 3: Evaluation of physical properties of PVDF hollow fiber membranes
[0104] The tensile strength, average pore size, porosity, and water permeability of PVDF hollow fiber membranes manufactured in Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 were measured as described below. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0105] (Measurement of tensile strength)
[0106] The tensile strength is measured according to ASTM D2256.
[0107] (Measurement of average pore size and porosity)
[0108] The average pore size and porosity are measured as follows. After using a scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM, CarlZeissSupra55) to obtain an SEM image of the surface of the PVDF hollow fiber membrane, use an image analyzer (Image-ProPlus) to measure the average length of the long axis and the short axis of the hole from the SEM image to determine Average pore size. In addition, the porosity was determined by measuring the ratio of the apparent area of the surface of the PVDF hollow fi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com