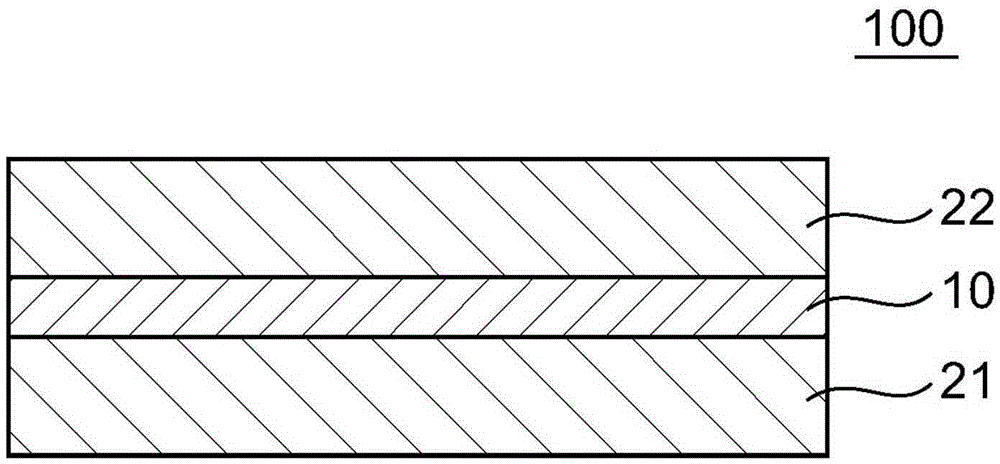
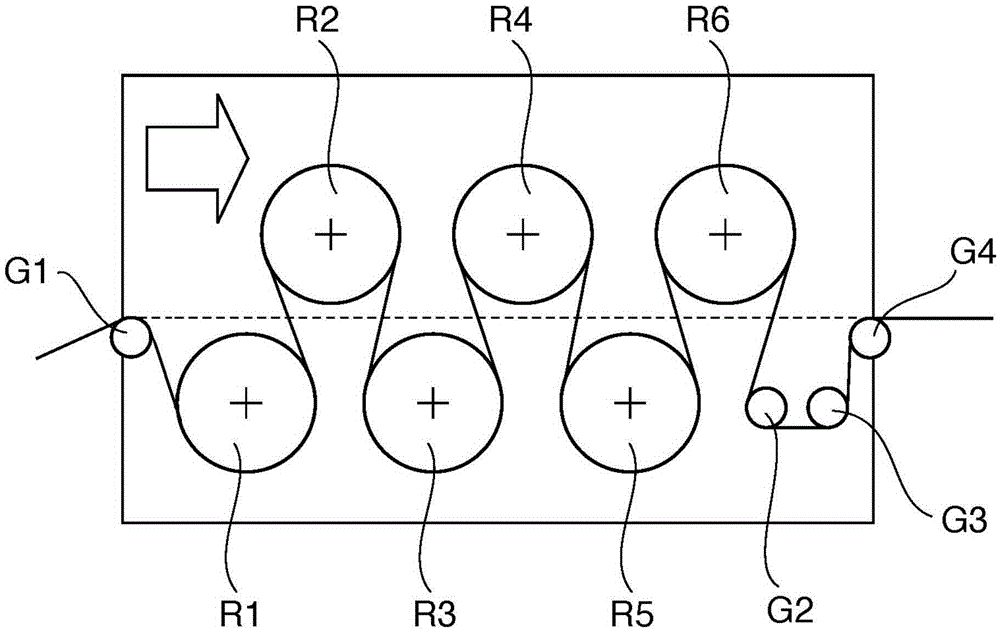
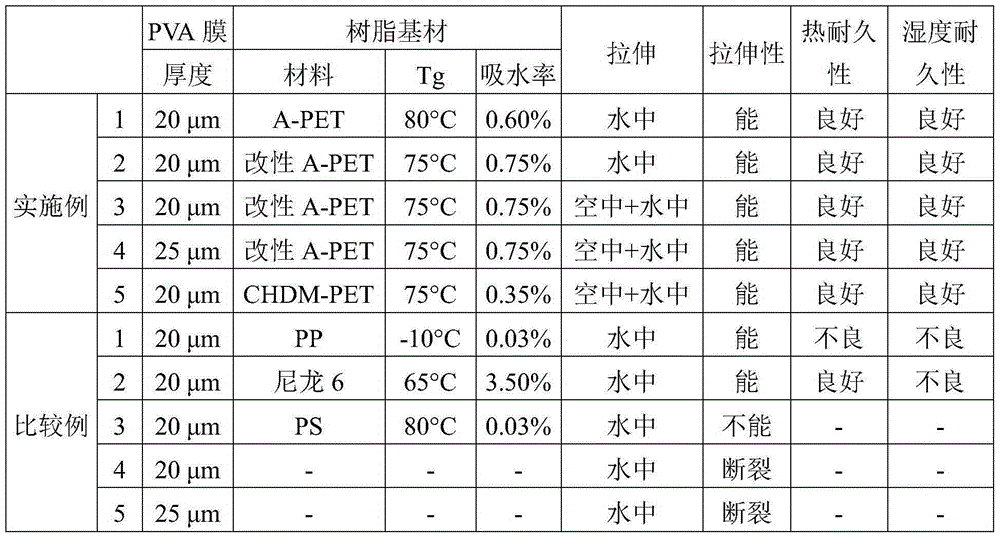
Polarizing plate
A polarizing plate and polarizing film technology, applied in the field of polarizing plates, can solve problems such as insufficiency, and achieve the effect of low cost and low manufacturing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] (manufacture of laminated body)
[0079] A polyvinyl alcohol film (polymerization degree: 2,400, saponification degree: 99.9 mol %) having a thickness of 20 μm and a resin substrate were used with a PVA-based resin aqueous solution (manufactured by The Nippon Synthetic Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., trade name: "GOHSEFIMER (trademark) Z -200", resin concentration: 3wt%) are laminated on each other as a binder to manufacture a laminated body. Amorphous polyethylene terephthalate (A-PET) film with a thickness of 100 μm and a corona-treated surface (manufactured by Mitsubishi Plastics, Inc., trade name: “NOVACLEAR”, Tg: 80° C., water absorption : 0.60%) was used as the resin substrate.
[0080] (manufacture of polarizing plate)
[0081] The obtained laminate was immersed in a swelling bath (pure water) at a liquid temperature of 30° C. (swelling treatment).
[0082] Next, the laminate was immersed in a dyeing bath at a liquid temperature of 30° C. while adjusting the iodi...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Except that an amorphous isophthalic acid-copolymerized polyethylene terephthalate (IPA-copolymerized PET) film (Tg: 75°C, water absorption: 0.75%) with a thickness of 100 μm was used as the A polarizing plate was manufactured in the same manner as in Example 1 except for the resin base material under manufacture.
Embodiment 3
[0091] (manufacture of laminated body)
[0092] A polyvinyl alcohol film (polymerization degree: 4,300, saponification degree: 99.3 mol %) having a thickness of 20 μm and a resin substrate were used with a PVA-based resin aqueous solution (manufactured by The Nippon Synthetic Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., trade name: "GOHSEFIMER (trademark) Z -200", resin concentration: 3wt%) are laminated on each other as a binder to manufacture a laminated body. An amorphous isophthalic acid-copolymerized polyethylene terephthalate (IPA-copolymerized PET) film (Tg: 75° C., water absorption: 0.75%) having a thickness of 100 μm and having a corona-treated surface was used as Resin base.
[0093] (manufacture of polarizing plate)
[0094] The obtained laminate was subjected to free-end uniaxial stretching (in-air stretching) at 2.0 times in the longitudinal direction (longitudinal direction) between rolls at different peripheral speeds in an oven at 120°C.
[0095] Next, the obtained laminate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com