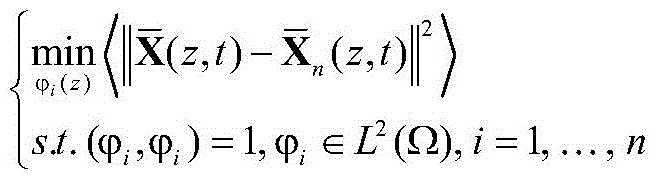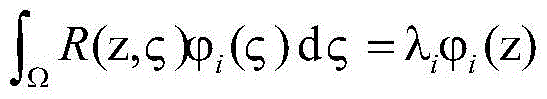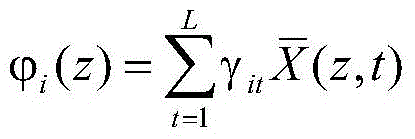Distributed principal component analysis neural network modeling method for chemical exothermic reaction
A neural network modeling and exothermic reaction technology, which is applied in the field of distributed principal element analysis neural network modeling of chemical exothermic reactions, and can solve problems such as the difficulty of modeling the catalytic rod object.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0070] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with embodiment.
[0071] Take the catalytic rod as the object of the actual process.
[0072] Step 1. Collect the real-time operation data of the catalytic rod process, and establish the distributed parameter model of the catalytic rod object.
[0073] 1.1 to The spatiotemporal data entered for the catalytic rod, The output data collected for the catalytic rod, and the corresponding catalytic rod state variables where t is the time series, L is the length of the time series, z i is the spatial position of the collected i-th group of catalytic rod output data, and N is the total number of collected output data.
[0074] 1.2 The space-time variable X(z,t) in the catalytic rod can be obtained by Fourier transform:
[0075]
[0076] According to the actual situation, it can be converted into a finite space:
[0077]
[0078] in is an approximation of n times, is the orthogonal basis fun...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com