Method for determining leaf nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium at almond fruit development stage
A technology of fruit development period and determination method, which is applied in the field of determination of nutrient elements in almond fruit development period, can solve the problems of insensitivity to identification of P and K elements, damage to plants and leaves, and slow detection speed, so as to reduce planting costs and improve The effect of almond yield and measurement data accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
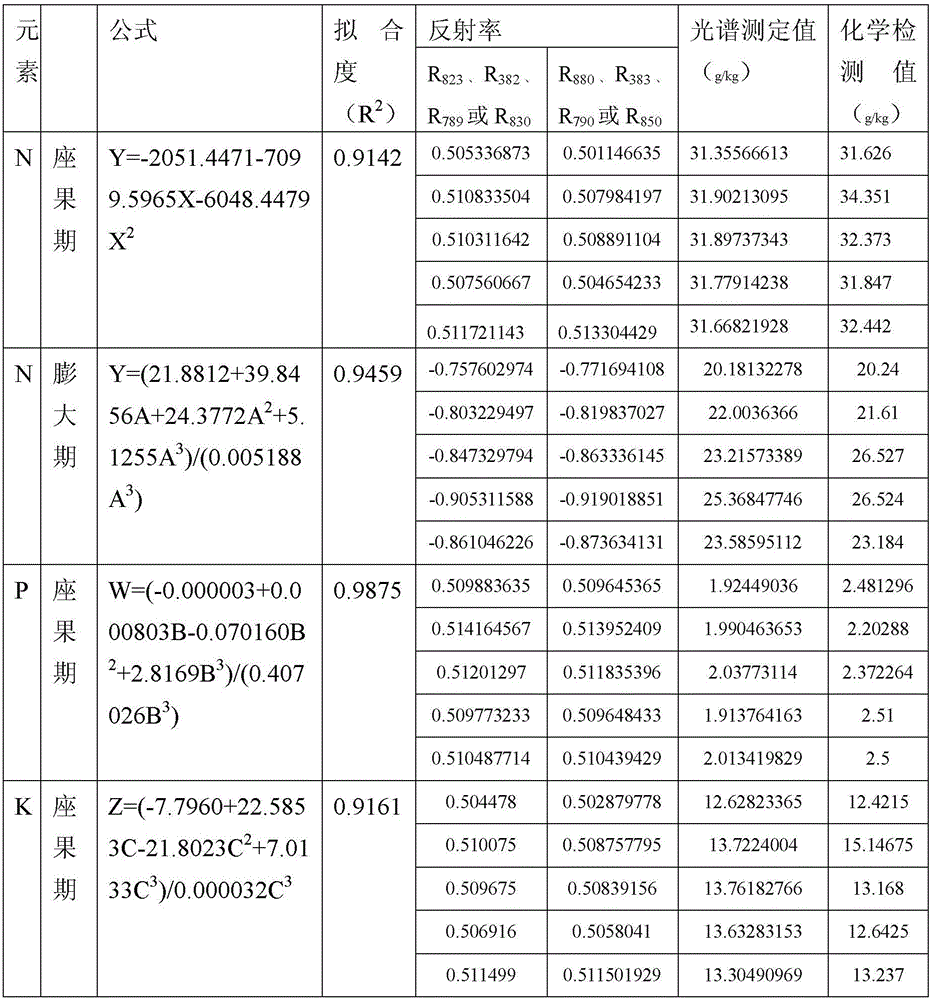
[0018] Specific embodiment one: the assay method of leaf nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium of present embodiment almond fruit growth stage carries out according to the following steps:
[0019] First measure the reflectance of almond leaves in the fruit development period; then calculate the content of N, P and K elements according to the calculation formula of N, P and K;
[0020] The calculation formula of N element in almond fruit setting stage leaves is Y=-2051.4471-7099.5965X-6048.4479X 2 ; where Y is the N element content of almond fruit-setting leaves, in g / kg, and X is LgR 823 +lgR 880 , R 823 is the reflectance of almond leaf surface to light with a wavelength of 825nm in the fruit setting stage, R 880 is the reflectance of the leaf surface of the almond fruit setting stage to the light with a wavelength of 880nm;
[0021] The formula for calculating the N element in leaves of almond fruit in the expansion stage is Y=(21.8812+39.8456A+24.3772A 2 +5.1255A 3 ) / (0...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0025] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: in the four directions of east, west, south and north of the central part of the almond tree crown to be tested, randomly select the growth health, and the new shoot bar 1 / 2~2 / 3 of the year Measure the reflectance of N pieces of healthy leaves with no pests and diseases and no mechanical damage between the lengths, where N≥3. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0026] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the spectrometer is calibrated before each data collection. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com