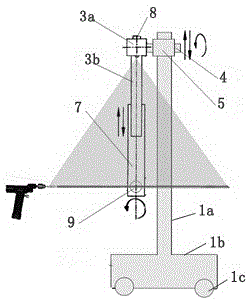
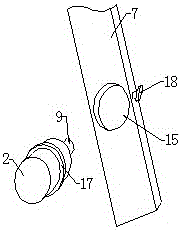
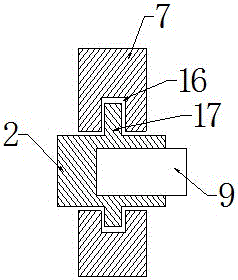
In-vitro laser alignment guidance system for minimally invasive intracranial hematoma cleaning operation and positioning method
A technology of laser collimation and intracranial hematoma, applied in the direction of stereotaxic surgical instruments, etc., can solve the problems of complicated operation steps, rough methods, puncture errors, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing the surgical field, wide clinical application, and avoiding steric hindrance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Patient Chen Moumou, female, 64 years old, was admitted to the hospital due to "sudden left limb weakness for three days". Previous history of hypertension. Physical examination: drowsiness, shallow left nasolabial fold, left tongue deviation, left limb muscle strength level 0, shallow hypoesthesia, and positive left Pap sign. Head CT in the outer hospital showed cerebral hemorrhage in the right basal ganglia. Diagnosis: hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage. After admission, minimally invasive puncture evacuation of intracranial hematoma was planned.
[0059] Preoperative cranial CT positioning shows a large amount of bleeding, and the midline structure is slightly shifted, such as Figure 8 shown.
[0060] Intracranial hematoma was minimally invasively evacuated, and the extracorporeal laser alignment and guidance system was reexamined immediately after puncture, and the positioning was accurate. The puncture needle reached the center of the hematoma, that is, the punc...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Patient Zhang Moumou, female, 77 years old, was admitted to the hospital due to "sudden right limb weakness for one day". Previous history of hypertension. Head CT showed: cerebral hemorrhage in the left frontotemporal lobe. Diagnosis: spontaneous cerebral hemorrhage. After admission, minimally invasive puncture evacuation of intracranial hematoma was performed.
[0067] Simple CT image positioning, no extracorporeal laser alignment and guidance system for minimally invasive removal of intracranial hematoma.
[0068] CT images can be reviewed after surgery Figure 12 As shown, the CT scan after 6 days is as follows Figure 13 As shown, it indicates that the puncture point is offset, the puncture site does not reach the target point, the drainage of the hematoma is not smooth, and the treatment effect is not good.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com