Method for removing residual hose cell DNA in recombinant Hansenula polymorpha hepatitis B surface antigen
A technology of HBsAg and Hansenula, applied in peptide preparation methods, retroviral DNA viruses, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve difficult problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0035] 1.3 Preparation of upper column material liquid
[0036] Through the ultrafiltration device 100KD Vivaflow 50 purchased from Sartorius, Germany, the buffer solution in the sample containing HBsAg feed solution was replaced with a PB solution containing a specific concentration of NaCl, and the replacement flow rate was 50ml / min, thereby preparing the upper column feed solution (sample solution).
[0037] 1.4 Chromatography process
[0038] 1.4.1 Monolith-QA medium balance:
[0039] Equilibrate the CIM-MonolithsQA medium with the same PB solution containing NaCl at a specific concentration as the buffer in the sample solution, and set the flow rate according to the Monolith-QA column specifications (1ml Monolith-QA is 4ml / min; 8ml Monolith-QA is 10ml / min; 80ml Monolith-QA, 80ml / min), the total buffer volume is greater than 10 column bed volumes, and the baseline is a straight line, then the material (sample) can be loaded.
[0040] 1.4.2 Loading (sample):
[0041] Pu...
Embodiment 1
[0066] Using a 100KD Vivaflow 50 ultrafiltration device, 20121010 batches of HBsAg feed liquid samples purified by Butyl-4B hydrophobic chromatography were dissolved in 20mM PB (pH7.2) containing 300, 400, 500 and 600mM NaCl respectively by liquid replacement In, as the sample solution;
[0067] For 1ml monolith-QA columns, use 20mMPB containing 300, 400, 500 and 600mM NaCl as the loading buffer, and 20mM PB (pH7.2) containing 2M NaCl as the elution buffer. for 5ml. The breakthrough peak and elution peak samples were collected respectively, and the DNA level and HBsAg level in the breakthrough peak and elution peak were detected.
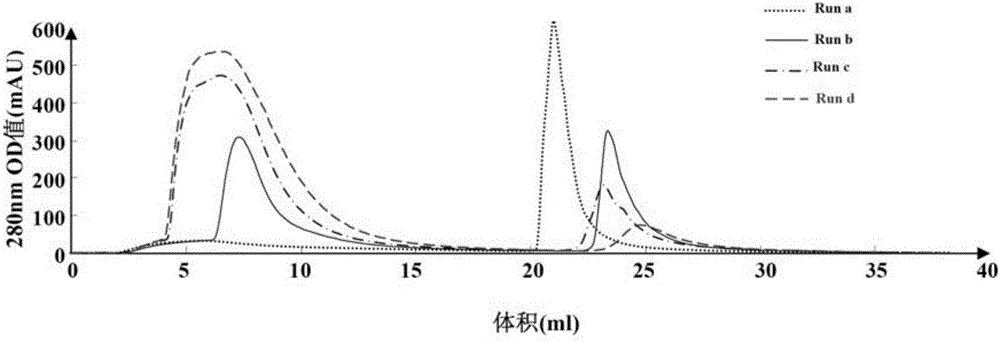
[0068] Chromatograms of HBsAg samples loaded under different NaCl concentrations (1ml Monolith-QA column) see figure 1 .
[0069] See Table 1 for the experimental results of chromatography (1ml Monolith-QA column) of HBsAg samples loaded under different NaCl concentration conditions.
[0070] Table 1. Chromatographic experimental results of load...
Embodiment 2
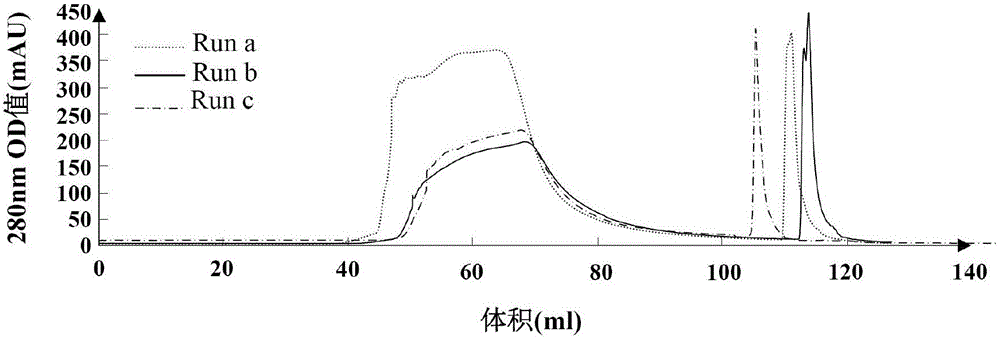
[0076] Take 20100908, 20101009, 20101010 and 20120605 batches of HBsAg feed liquid samples refined and purified by Butyl-4B hydrophobic chromatography, and use a 100KD Vivaflow 50 ultrafiltration device to dissolve the samples in 20mM PB containing 500mM NaCl (pH7.2 ) as the loading solution, and used 8ml Monolith-QA to carry out different loading tests, the loading volumes were 16ml, 24ml and 120ml respectively, the elution buffer was 20mM PB (pH7.2) containing 2MNaCl, and the breakthrough Peak solution and measure its volume, detect breakthrough peak HBsAg concentration and DNA concentration. The DNA level in the breakthrough peak and the HBsAg yield and DNA removal rate were evaluated.
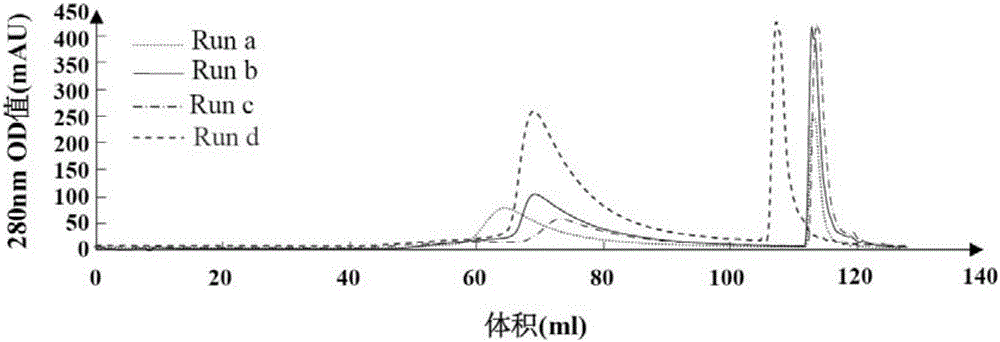
[0077] (1) 16ml sample volume
[0078] For the experimental results of 16ml sample volume, see figure 2 and Table 2.
[0079] Table 2, 8ml Monolith-QA column 16ml HBsAg sample loading chromatography results
[0080]
[0081] from figure 2 And table 2 result can find out, when usin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com