A biological cell ultrasonic atomic force microscopy detection system and method
A technology of atomic force microscopy and biological cells, applied in the direction of using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic waves, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve damage, fail to fully reflect the acoustic characteristics of living cells, lack research methods, ultra-micro internal structure analysis methods, etc. problem, to avoid damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
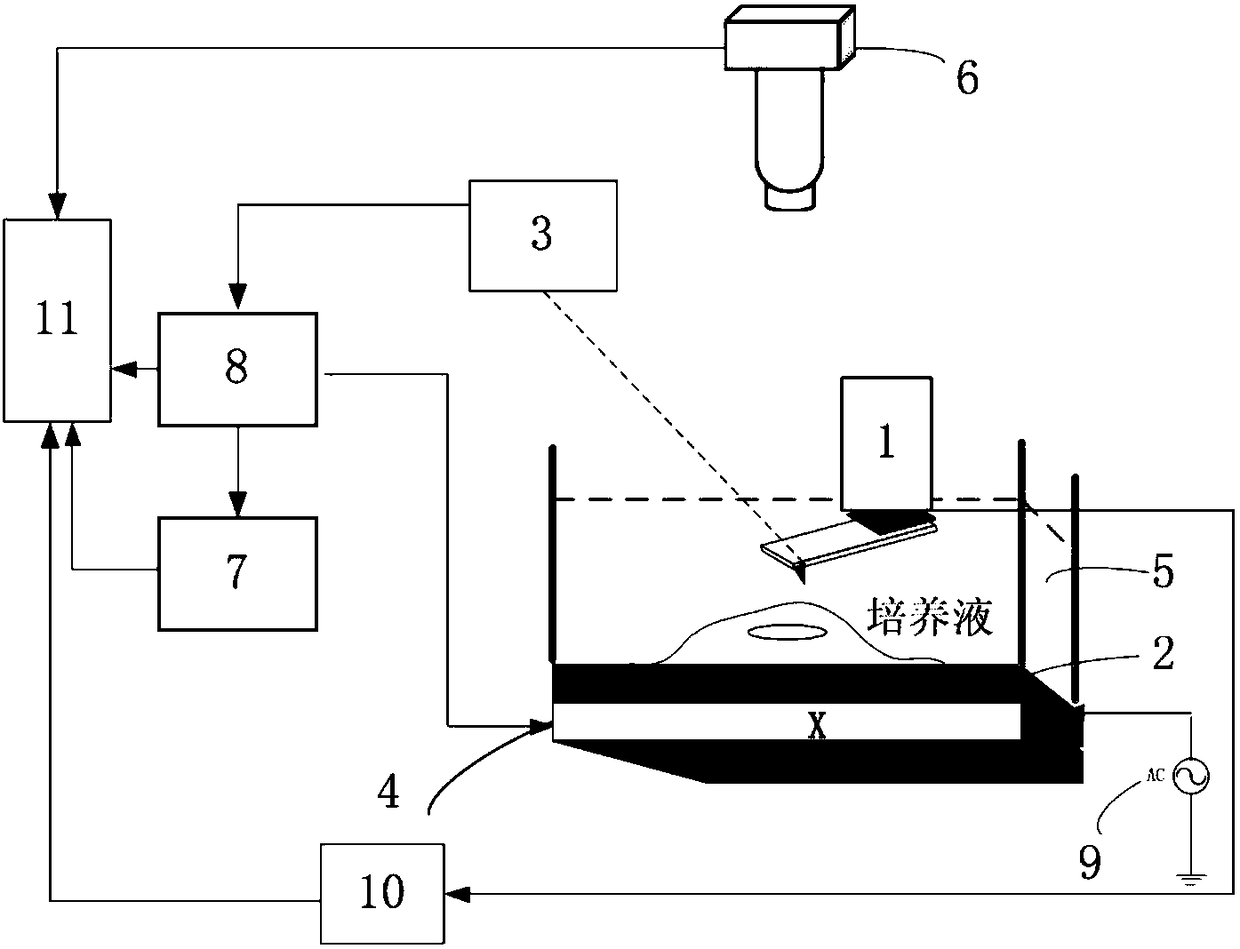
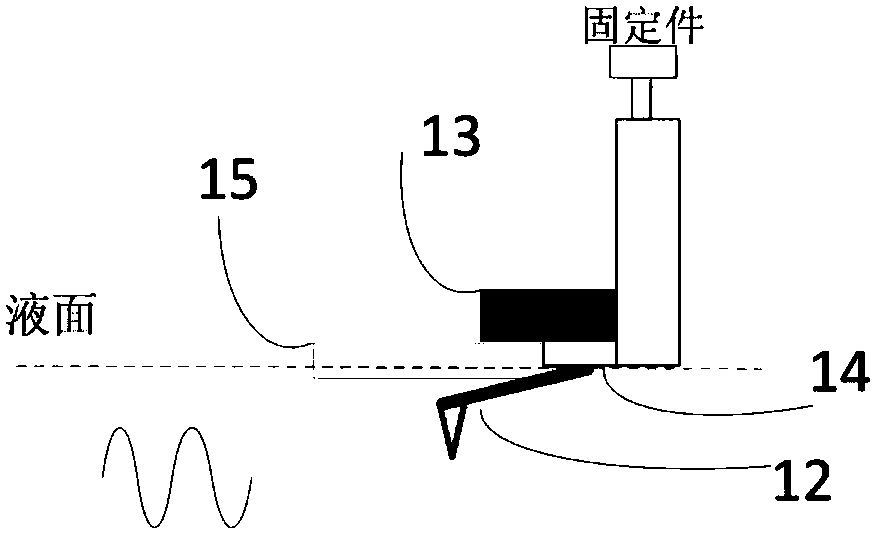
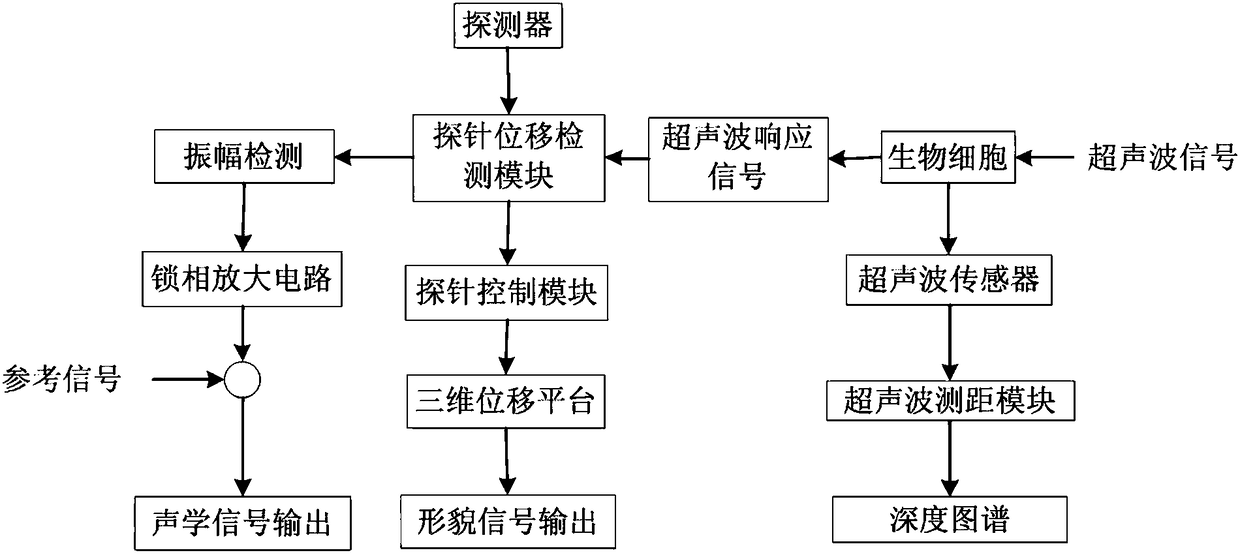
[0029] Such as figure 1 As shown, the biological cell ultrasonic atomic force microscopic detection system of the present invention includes a detector 1, a piezoelectric transducer 2, a probe displacement detection module 3, a three-dimensional displacement platform 4, a liquid pool 5, an optical microscope 6, and a lock-in amplifier circuit 7 , a probe control module 8, a signal generator 9, an ultrasonic ranging module 10 and a display module 11; the biological cells to be measured are placed in a liquid pool 5 filled with culture fluid, and the liquid pool 5 is placed on the piezoelectric transducer 2 , the piezoelectric transducer 2 is connected with the signal generator 9 for transmitting ultrasonic signals, a three-dimensional displacement platform 4 is installed under the piezoelectric transducer 2, and the three-dimensional displacement platform 4 can move in the XYZ direction for controlling the probe 12 Scanning direction, the detector 1 is placed above the biologic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com