Three-dimensional pored non-woven fabric
A non-woven and three-dimensional technology, applied in the field of open-pore three-dimensional non-woven fabrics, can solve the problems of easy falling off, shifting, and affecting the absorption effect, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing the bonding strength, increasing the contact area, and preventing back seepage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
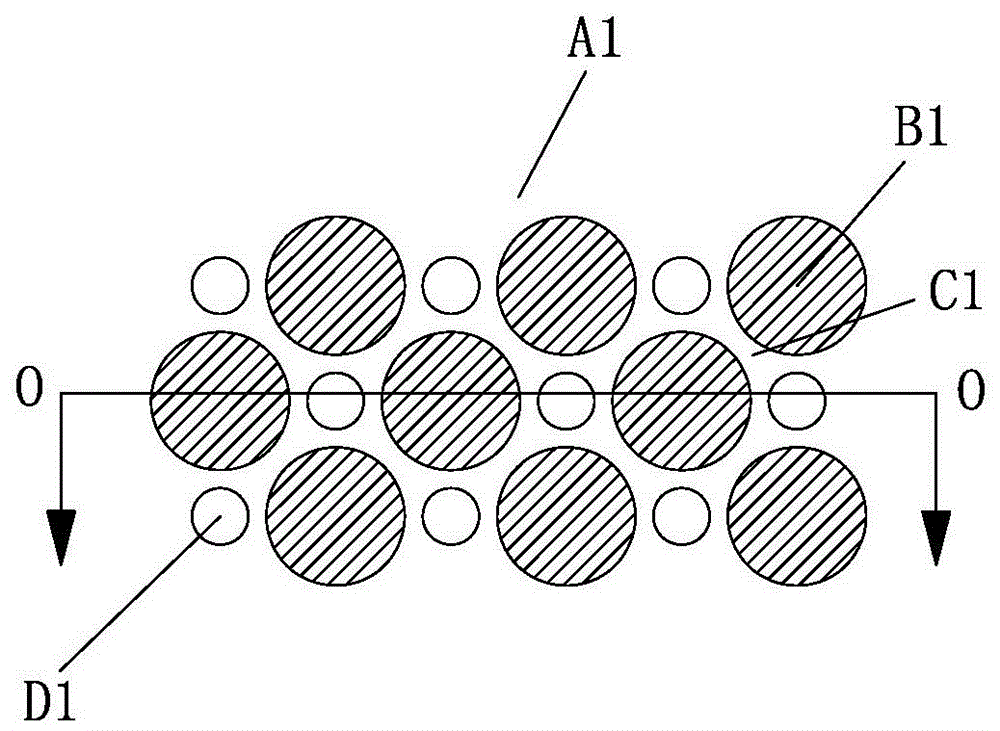
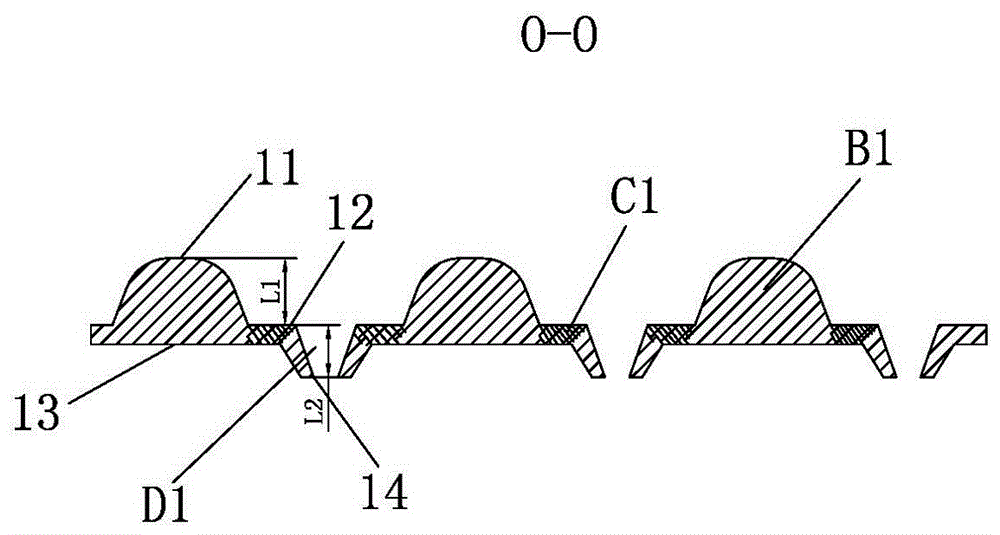
[0025] Take 1.5dtex*38mm PE / PP bicomponent fiber as raw material. During production, the fiber is unpacked and loosened by the bale opener and then sent to the carding machine, carded into a fiber web and entered into the oven. The temperature of the hot air is 145°C, and the frequency of the hot air blower is 38Hz for penetration heating. A number of bonding points are formed, and the consolidated fiber web is processed by a pair of heated meshing pin rolls and concave rolls to form a three-dimensional forming process such as figure 1 , Figure 1A Open-pore three-dimensional nonwoven fabric A1 shown.
[0026] The perforated three-dimensional nonwoven fabric A1 has four planes, the first plane 11 is formed by the top of the convex part B1, the second plane 12 is the plane where the concave part C1 is located, and the convex part B1 is Discontinuous, the concave part C1 is distributed around the convex part B1, the bottom of the convex part B1 and the bottom of the concave pa...
Embodiment 2
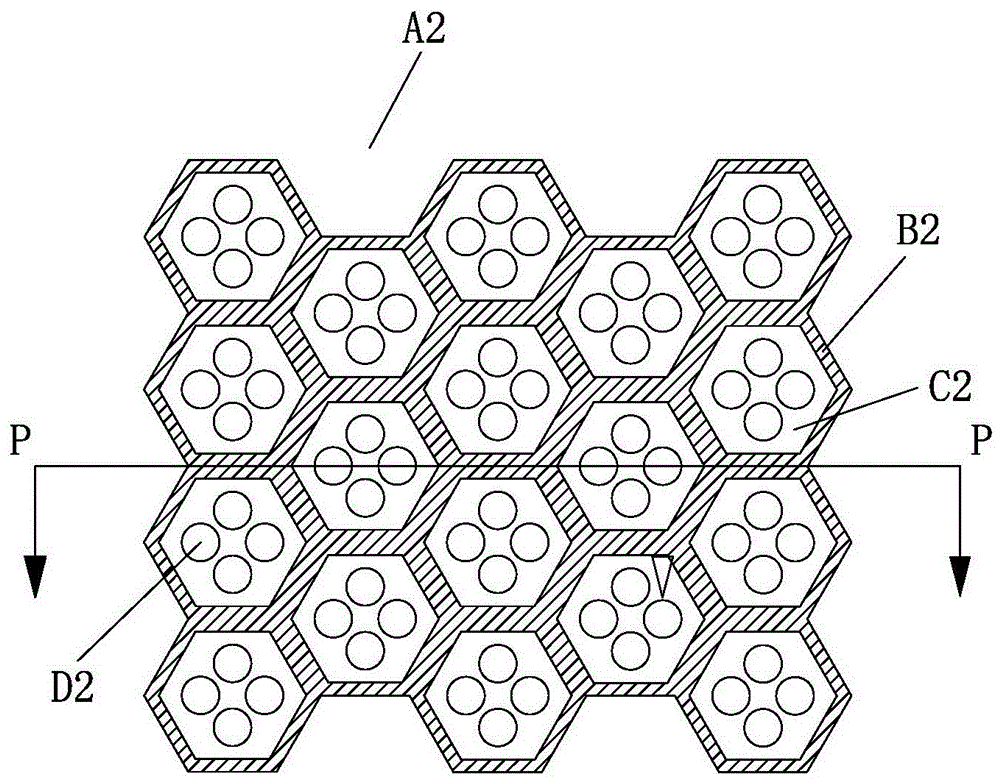
[0039] Take 2.0dtex*38mm PE / PET hydrophilic bicomponent fiber and 2.0dtex*38mmPE / PET hydrophobic bicomponent fiber as raw materials. During production, the two kinds of fibers are respectively unpacked and loosened by the unpacking machine and then sent to the carding machine. After being carded into a fiber web, it is laminated and then enters the oven. Through heating, a number of bonding points are formed between the fibers, and the consolidated fiber web is processed by a pair of heated meshing needle rollers and concave rollers for three-dimensional molding processing, such as figure 2 , Figure 2A The open-pored three-dimensional nonwoven fabric A2 is shown.
[0040]The perforated three-dimensional nonwoven fabric A2 has four planes, the first plane 21 is formed by the top of the convex part B2, the second plane 22 is the plane where the concave part C2 is located, and the convex part B2 is Continuously, the concave portion C2 is distributed around the convex portion ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Take 2.0dtex*38mm PE / PET hydrophilic bicomponent fiber as raw material. During production, the fibers are unpacked and loosened by the bale opener and then sent to the carding machine, carded into a fiber web and entered into the oven. The temperature of the hot air is 148°C, and the frequency of the hot air blower is 48 Hz for penetration heating. A number of bonding points are formed, and the consolidated fiber web is processed by a pair of heated meshing pin rolls and concave rolls to form a three-dimensional forming process such as image 3 , Figure 3A The open-pored three-dimensional nonwoven fabric A3 is shown.
[0044] The perforated three-dimensional nonwoven fabric A3 has four planes, the first plane 31 is formed by the top of the convex part B3, the second plane 32 is the plane where the concave part C3 is located, and the convex part B3 is It is made of protrusions of different sizes and shapes, and the concave portion C3 is distributed around the convex p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com