Method for controlling crack formation in heat affected zones in nickel-based alloy multi-layer laser filler wire welding
A heat-affected zone and laser wire filling technology, applied in laser welding equipment, manufacturing tools, welding equipment, etc., can solve the problem of changing the stress distribution of joints, reducing the formation rate of liquefaction cracks in the heat-affected zone, and reducing the high temperature residence time in the heat-affected zone, etc. problem to avoid stress concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
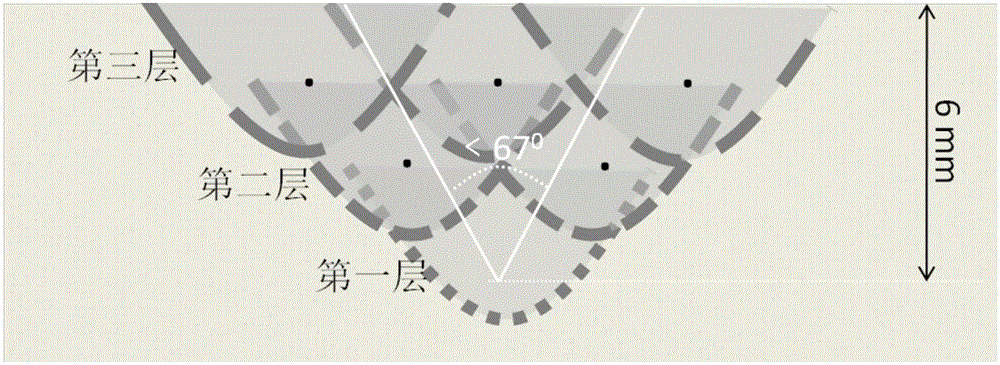
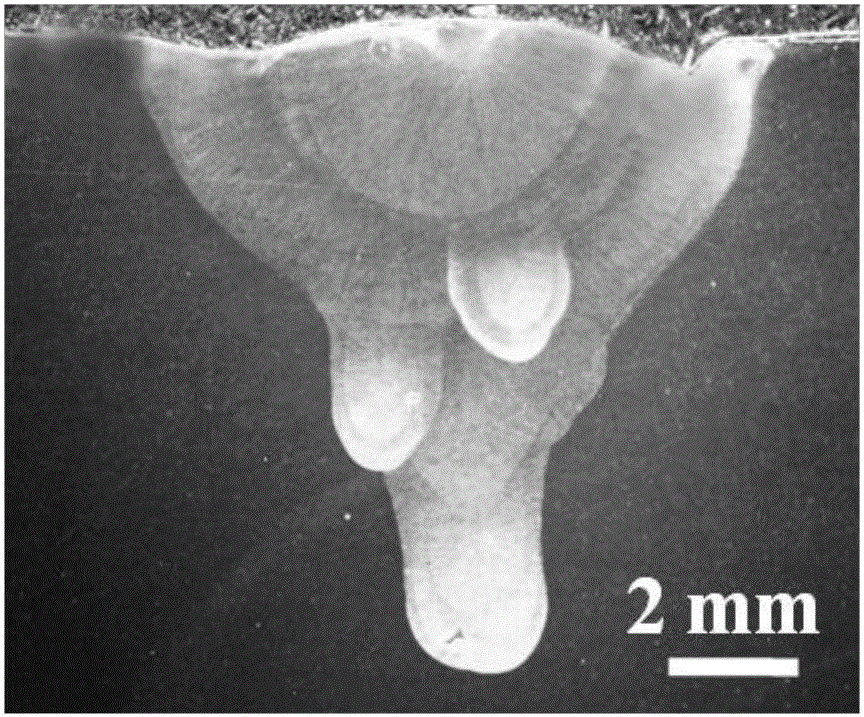
[0032] A method for controlling the formation of liquefaction cracks in the heat-affected zone of nickel-based alloy multilayer laser wire-filled welding, please refer to figure 1 As shown, the cross-sectional morphology of the sample after welding is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0033] This implementation case is butt welding, in which the plate to be welded is 718 nickel-based alloy, and the thickness of the welded plate is 10mm. Using CO 2 Laser wire filling welding method, the filler material is consistent with the composition of 718 alloy, the shielding gas is pure He, the gas flow rate is 30L / min, the laser output power is 6kW, the welding speed is 1.5m / min, and the wire feeding speed is 3m / min. The focal weight is +20mm, and the heat input is 4J / mm.
[0034] The welding process includes the following steps:
[0035] The first step is to process into figure 1 For the groove sample shown, the angle of the processed V-shaped groove is less than 67°, and the depth of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Upper surface width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Plate thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com