Semiconductor device
A semiconductor and chip technology, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device components, output power conversion devices, etc., to solve problems such as noise, malfunction, and noise transmission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
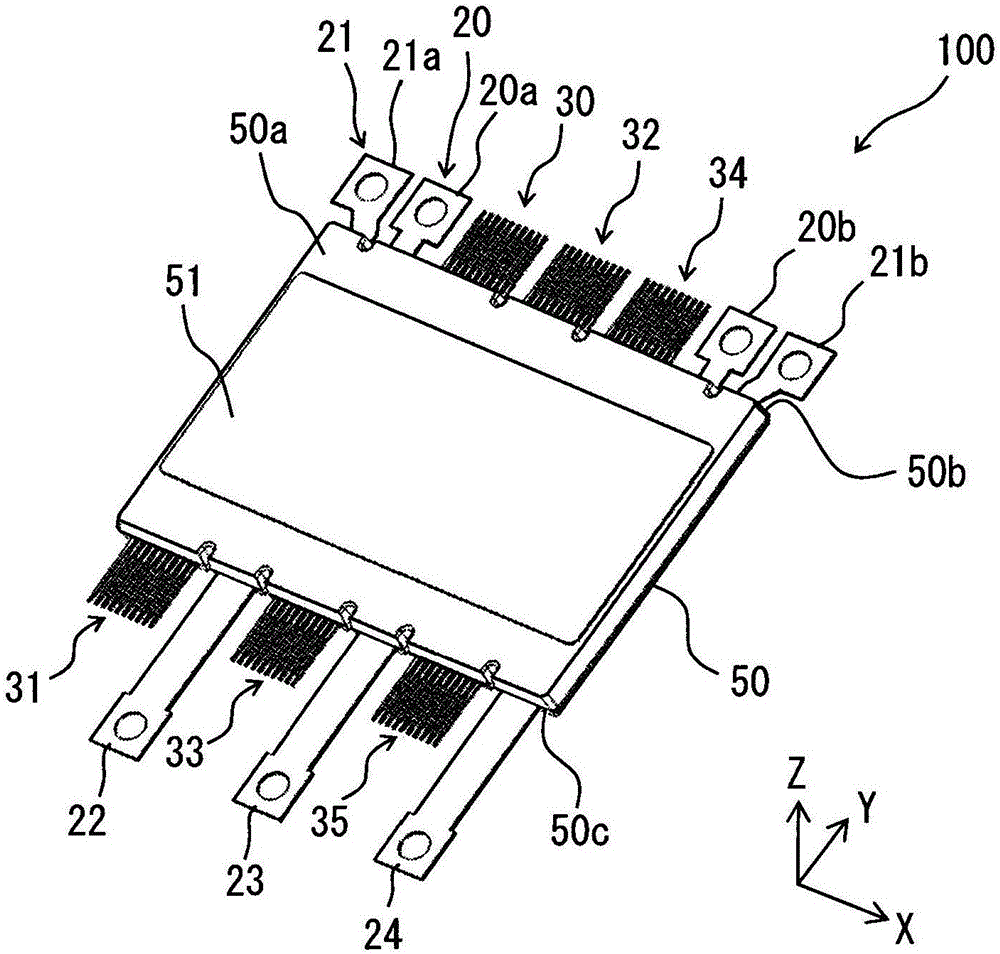
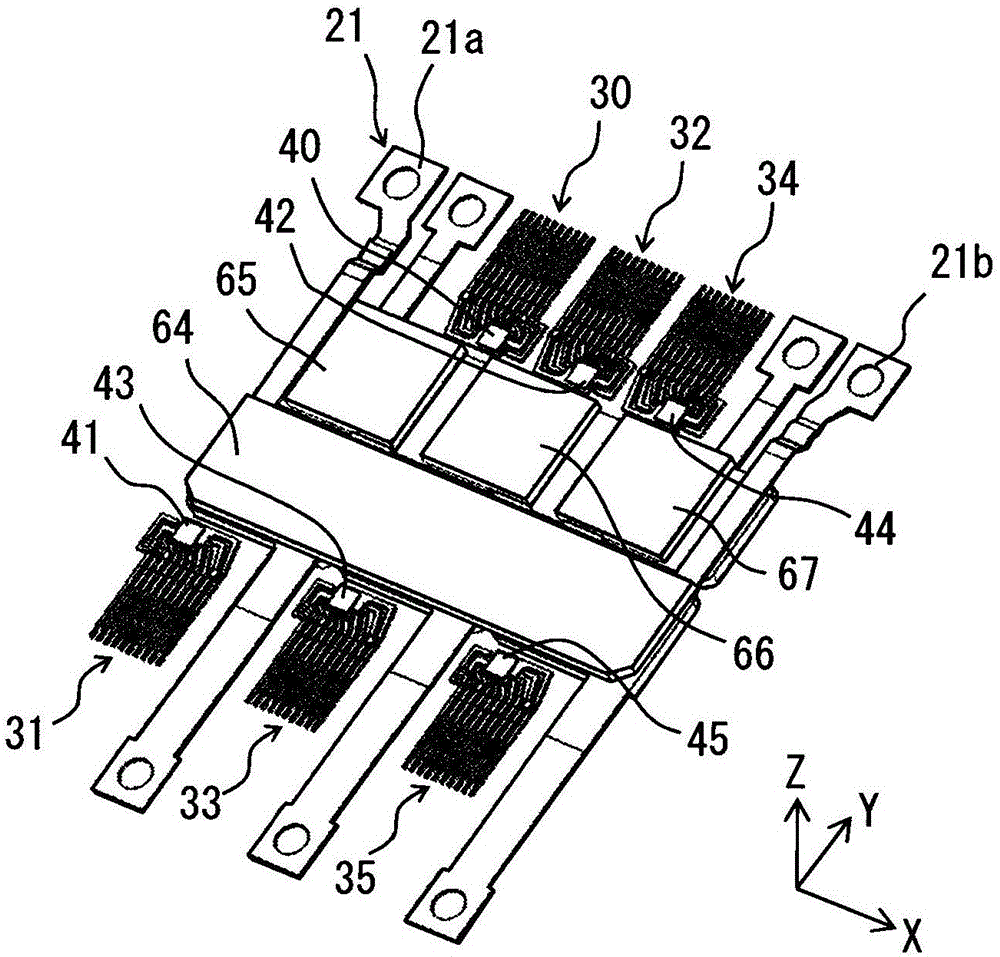
[0041] First, based on Figure 1 to Figure 6 The configuration of the semiconductor device 100 according to this embodiment will be described.
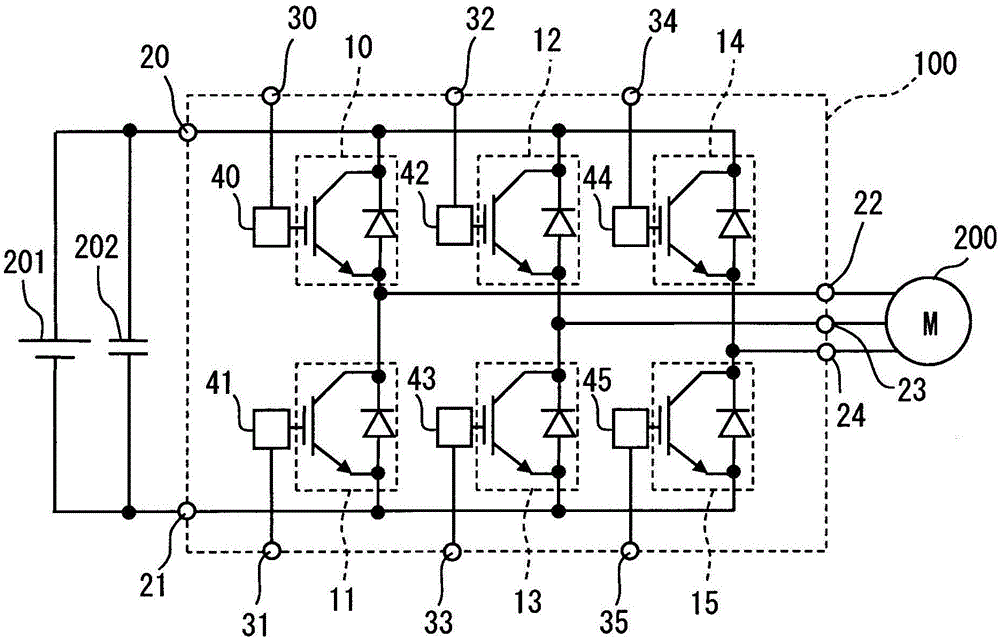
[0042] Such as figure 1 As shown, the semiconductor device 100 has three-phase upper and lower arms connected between the positive pole (high potential side) and the negative pole (low potential side) of the DC power supply 201 in order to drive the motor 200 as a load. In this way, the semiconductor device 100 is configured as a three-phase converter, which converts DC power into a three-phase AC and outputs it to the motor 200 . Such a semiconductor device 100 is mounted in, for example, an electric vehicle or a hybrid vehicle. in addition, figure 1 Reference numeral 202 is shown as a capacitor for smoothing.
[0043]A semiconductor chip constituting each arm has a power switching element such as an IGBT or a MOSFET, and a FWD element connected in antiparallel to the switching element. In addition, the power switching element...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0090] In this embodiment, descriptions of parts common to the semiconductor device 100 described in the first embodiment are omitted.
[0091] The technical concept of making the combined inductances of the five signal paths substantially equal to make the noise voltages generated in the respective signal paths substantially equal when the large current 75 flows instantaneously is the same as that of the first embodiment.
[0092] In this embodiment, if Figure 15 and Figure 16 As shown, output terminals 22 to 24 are provided in pairs, respectively. The U-phase output terminal 22 is branched and has two output terminals 22a and 22b. Furthermore, in the X direction, they are arranged on both sides of the signal path of the U-phase lower arm so as to sandwich the U-phase control terminal 31 , that is, the signal path including the control terminal 31 . Similarly, the V-phase output terminal 23 is branched to have two output terminals 23a and 23b. Then, in the X direction, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com