System and method for testing breaking tenacity of material based on temperature-controllable electrochemical hydrogen charging environment
A fracture toughness and testing system technology, applied in the direction of applying stable tension/pressure to test the strength of materials, analyzing materials, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems that affect the experimental results, generate torque and bending moment, and cannot be simulated realistically and effectively. , to achieve the effect of improving safety, improving accuracy and reliability, and improving the overall experimental operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with drawings and embodiments.
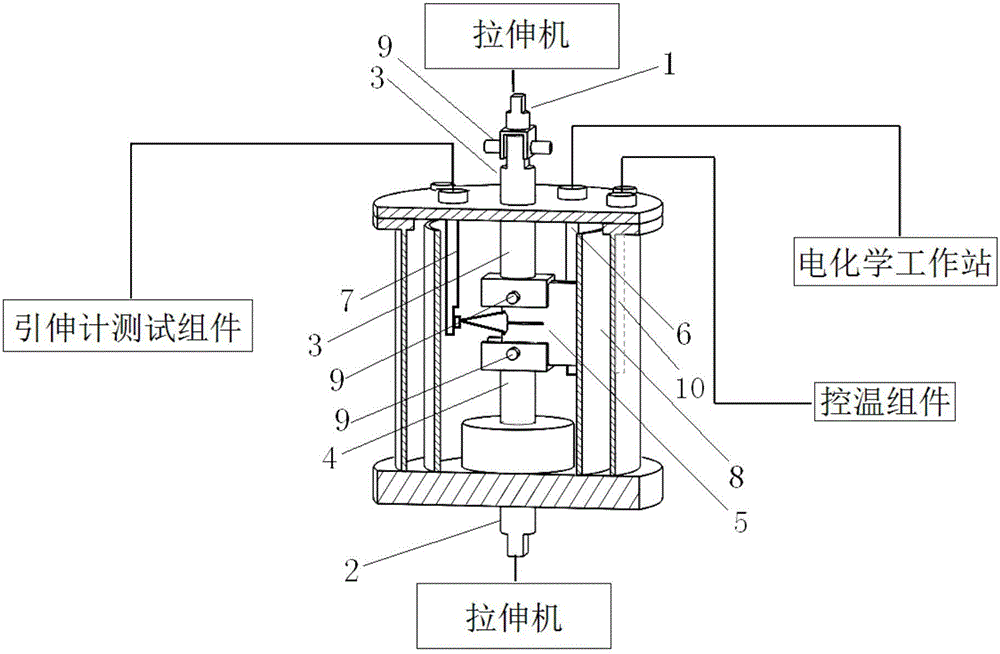
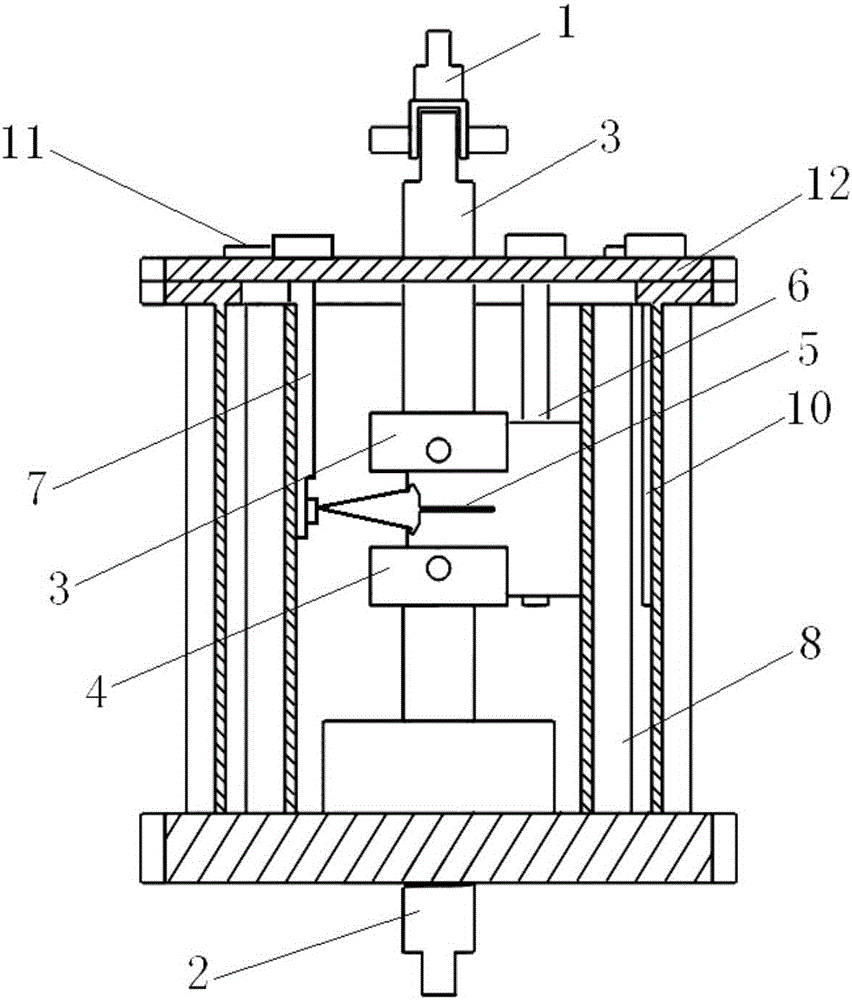
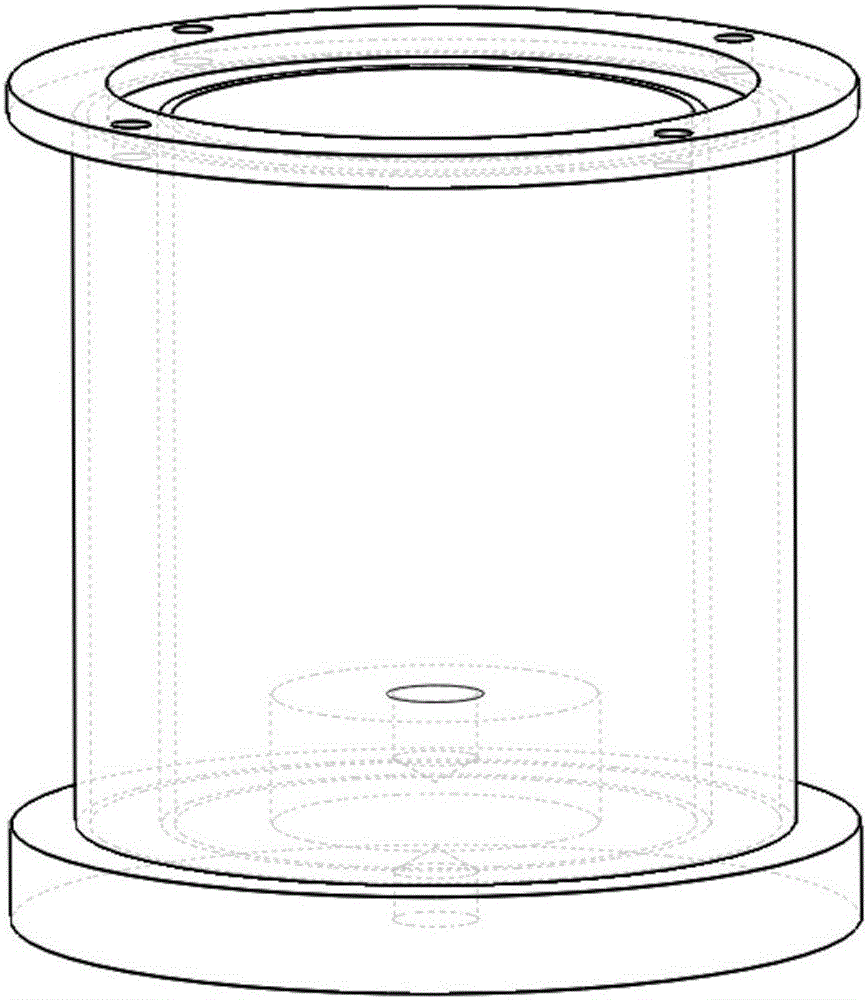
[0037] see Figure 1-Figure 11 , The material fracture toughness test system based on the temperature-controllable electrochemical hydrogen charging environment of the present invention includes a computer, an electrochemical workstation, a temperature control component, an extensometer test component, a corrosion-resistant plexiglass environment box, and several connectors. Wherein, the corrosion-resistant plexiglass environment box such as image 3 As shown, the main body of the environmental chamber adopts a double-layer plexiglass structure 8, the bottom of the double-layer plexiglass structure is fixedly connected to the heating base, the top is provided with a box cover 12, and the center of the heating base has a round platform protruding into the environmental box, and the outer ring of the round platform is set Ring-shaped heating element, the outer layer of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com