Semiconductor device forming method
A semiconductor and device technology, applied in the field of semiconductor device formation, can solve problems such as reducing the yield of semiconductor devices and affecting the performance of semiconductor devices, and achieve the effects of improving electrical performance, increasing low-frequency line width roughness, and improving morphology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
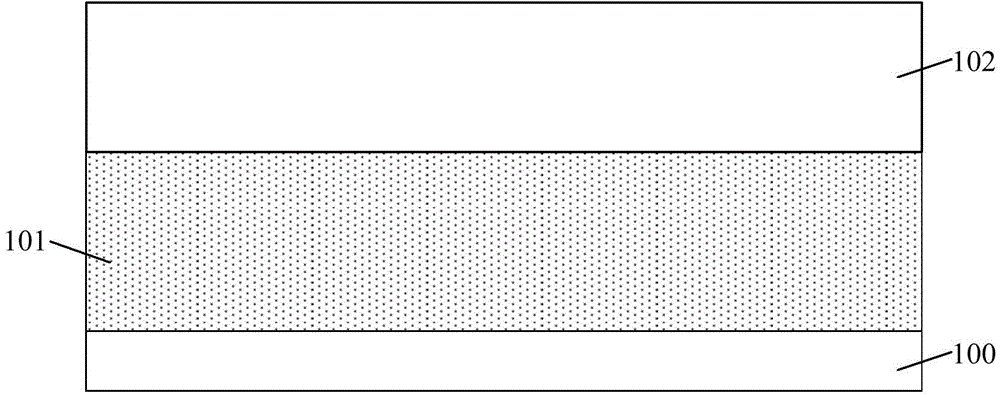
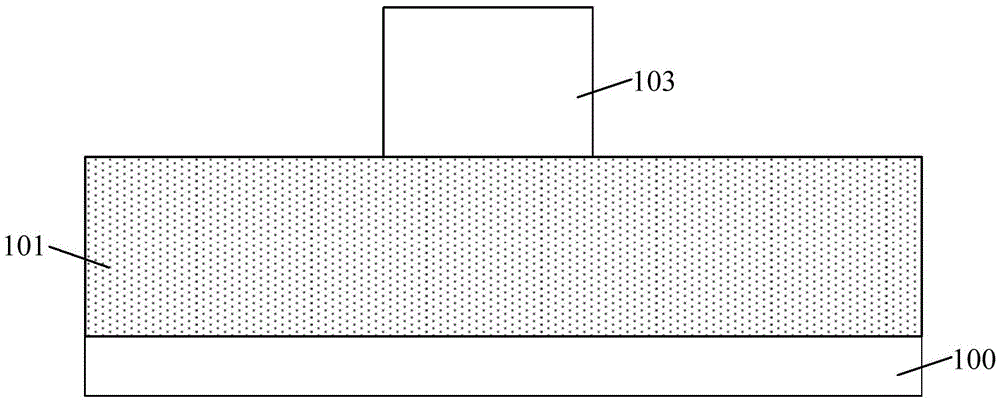
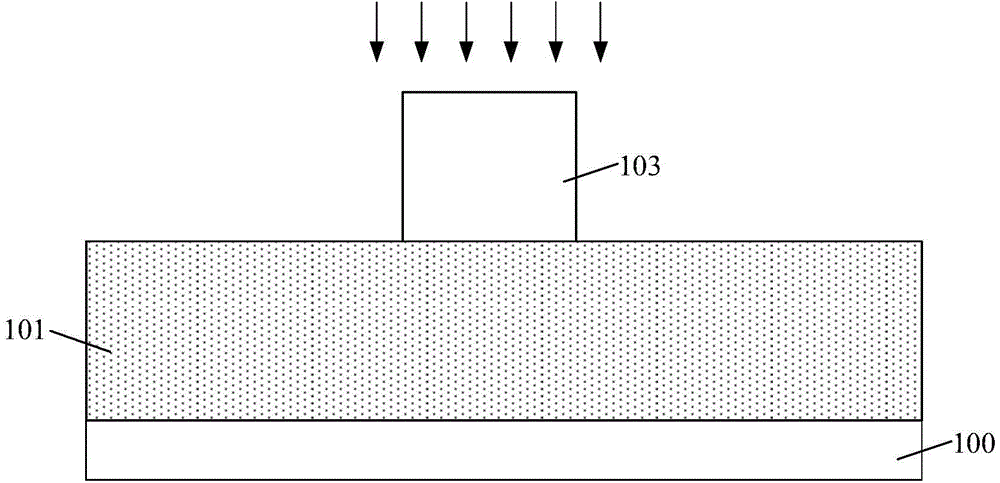
[0031] It can be seen from the background art that in the process of forming a semiconductor device, the line width roughness of the photoresist layer is one of the important factors affecting the performance and yield of the semiconductor device.
[0032] After research, it is found that in addition to the line width roughness of the photoresist layer, the "roughness profile" of the photoresist layer can also include line edge roughness, and short, medium, and long distance line width roughness changes, and its parameters correspond to It exhibits different length scales in the direction along which the line width changes. In addition to the absolute value of line width roughness or line edge roughness, the length scale at which this variation occurs is also one of the keys to semiconductor device fabrication.
[0033] The long-distance line width roughness change of the photoresist layer corresponds to the low frequency (Low Frequency) line width roughness; the middle distan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com