Novel low-cross-pollution full-automatic biochemical analyzer
A biochemical analyzer, cross-contamination technology, applied in the field of medical equipment, can solve the problems of affecting the detection results, cross-contamination instrument performance of automatic biochemical analyzers, detection errors, etc., to achieve simple instrument structure, eliminate cross-contamination, and reduce failure rates Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
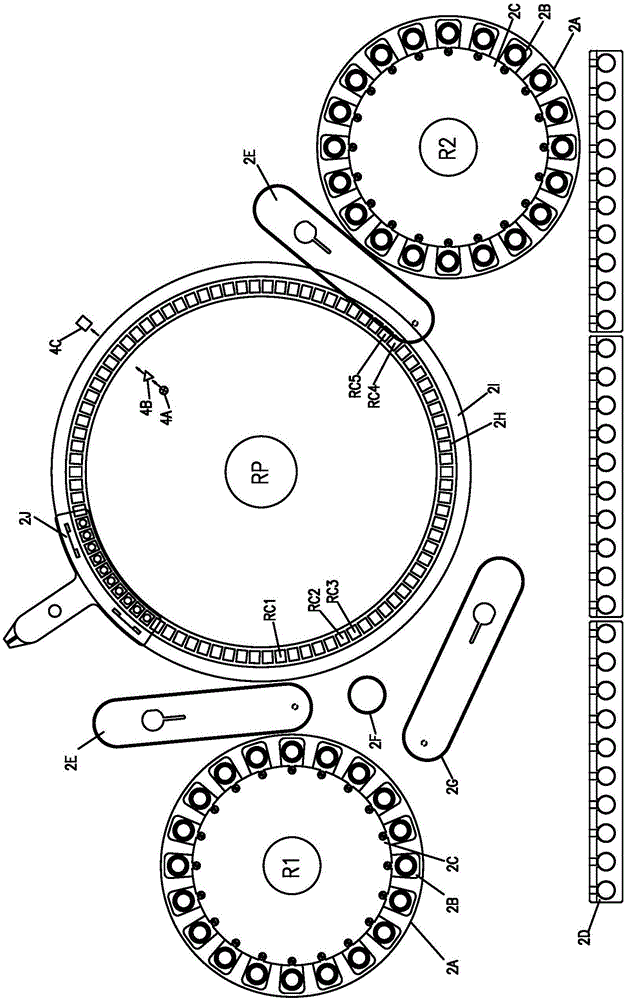
[0045] Such as Figure 1a , Figure 2a and Figure 3a Including: 2A: Reagent plate; 2B: Reagent bottle; 2C: Reagent needle holder; 2D; Sample; 2E: Moving arm of reagent needle moving device: 2F: Sample needle cleaning pool; 2G: Sample needle arm; R1: Reagent 1 plate ; R2: Reagent 2 trays; 2H: Detection cup and detection cup position; 2I: Reaction tray; 2J: Detection cup cleaning device. 3A: Reagent needle; 3D: Tubing between reagent aspiration syringe and reagent needle end connector; 3E: Reagent aspiration syringe; 3J: Pressure detector.
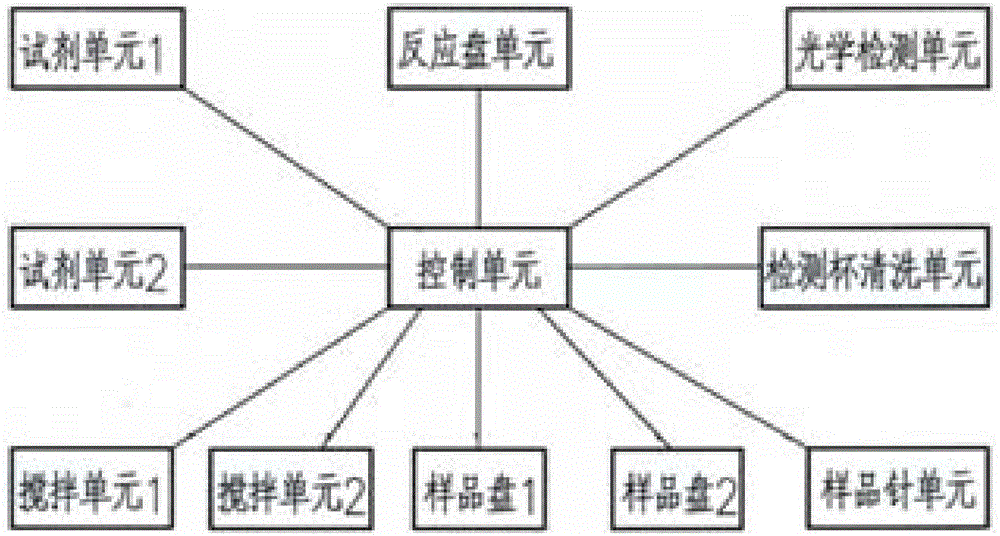
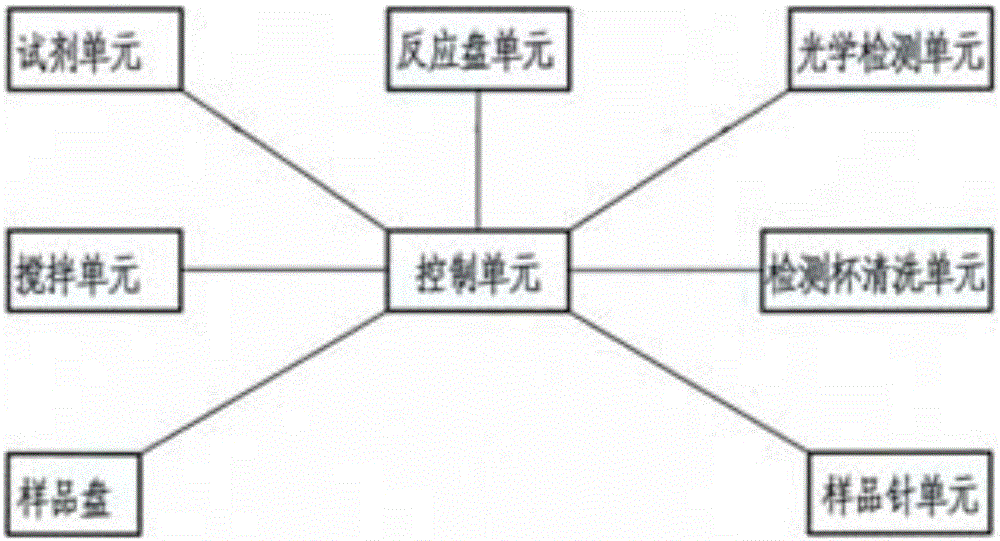
[0046] The main structure of the instrument includes an instrument control unit, a reaction plate unit (including a reaction plate 2I and multiple detection cups 2H on the reaction plate), an optical detection unit (including: a light source 4A, a monochromator 4B, and an optical signal detector 4C), a detection Cup cleaning unit 2J, non-intersecting reagent unit (comprising reagent disc 2A, a plurality of reagent bottles 2B loaded on the...
Embodiment 2
[0070] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is that this embodiment does not adopt the non-intersecting reagent unit designed by the present invention, but uses the existing common reagent plate and reagent needle structure, and adopts the non-contact type reagent unit designed by the present invention in addition. The uneven air pressure stirring unit is used to stir the reactants in the detection cup. An air pressure stirring needle 7M is respectively provided at positions RC3 and RC5 of the instrument reaction discs for stirring the reactants in the detection cup. The way it is stirred is as Figure 7a and 7b and 7c and 7d are shown. Figure 7a The medium air pressure stirring needle pressurizes and injects gas to one side of the liquid in the detection cup, causing the pressurized liquid in the detection cup to move downward and to the other side; Figure 7b It shows that when the air pressure stirring needle stops spraying and pressurizing into the dete...
Embodiment 3
[0076] The embodiment of a new type of fully automatic biochemical analyzer with low cross-contamination designed in this embodiment: the instrument has a non-cross-type reagent unit (comprising a plurality of reagent bottles loaded on the reagent tray, the reagent tray, and each reagent bottle respectively) at the same time. Equipped with independent reagent needle brackets and reusable reagent needles equipped on each bracket, a common reagent suction syringe and a common reagent needle connector connected by pipelines, reagent needle moving devices, etc.) and non-contact Type uneven air pressure stirring unit (its composition includes: air pump, pipeline, air pressure stirring needle, etc., and the unit can also include one of flow adjustment / switching device, air flow constant pressure device, gas heating and constant temperature device, etc. composed of several or all components). When the instrument is running, the non-crossing reagent unit is used to distribute the reag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com