Method for enabling female aedes albopictus affected by Wolbach bacteria to be infertile
A technology of Wolbachia albopictus and Aedes albopictus, which is applied in animal husbandry and other fields, can solve the problems of great impact on host fitness, low efficiency, and prolonging the breeding time, so as to eliminate the threat of population replacement and improve production efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] 1. Rapid identification of female and male pupae of Aedes albopictus includes the following steps:
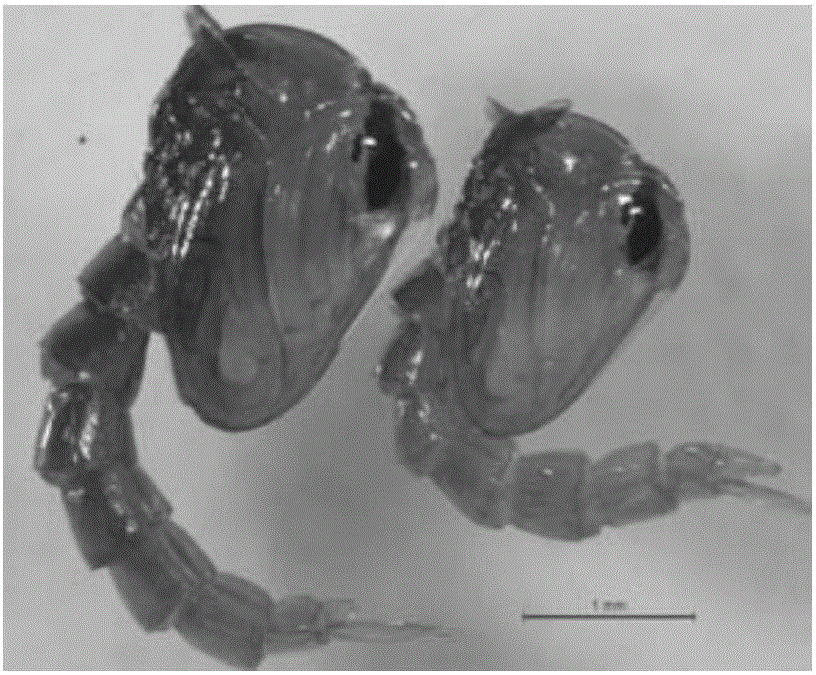
[0021] (1) After the larvae of Aedes albopictus infected with Wolbachia have developed to the pupal stage, use a Pasteur pipette to pick out the pupae and place them on a petri dish, absorb the water around the pupae, and then observe the pupae under a dissecting microscope of the tail. Such as figure 1 , the short tail apparatus is the female pupa (left in the picture), and the long one is the male pupa (right in the picture).
[0022] 2. Sterility evaluation of female mosquitoes after radiation:
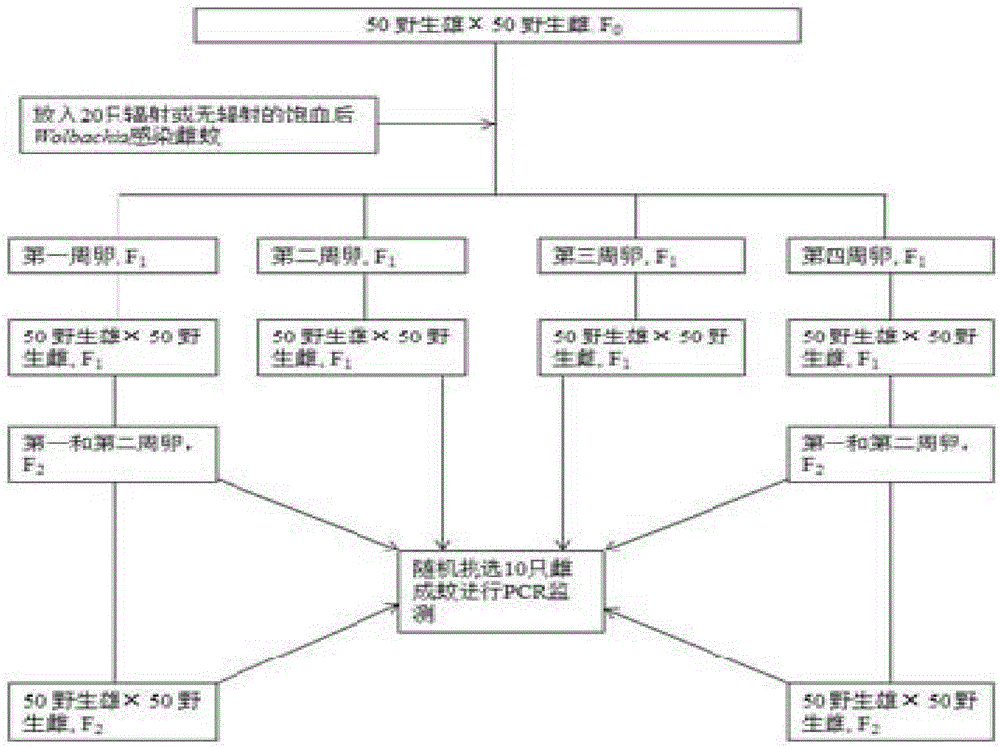
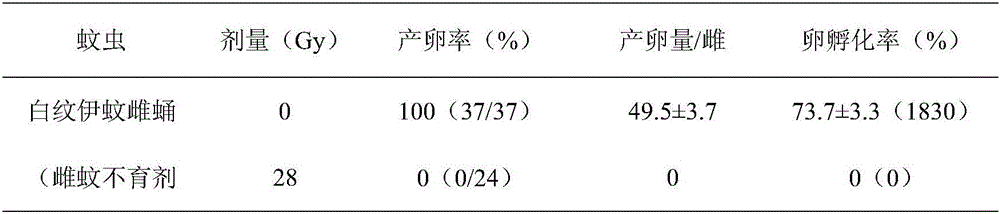
[0023] (1) After separating the female pupae under the microscope (the pupal age is 4-24 hours), place the female pupae in the middle of the radiation disk, and then use an X-ray radiation instrument (RS 2400) to irradiate (0, 23, 26, 28 , 32, 40Gy), about 50 female pupae were irradiated each time. After irradiation, the irradiated female pupae and the non-irradiated male...
Embodiment 2
[0040]1. Sterility evaluation of female mosquitoes after radiation:
[0041] (1) Large-scale rearing of Aedes albopictus larvae infected with Wolbachia to the pupal stage (4-40 hours), and then using a Fay-Morlan separator to preliminarily separate the female and male pupae. Take about 60,000-70,000 male pupae, mix them with 5,000 female pupae, then concentrate the pupae in a radiation cup, and use an X-ray radiation apparatus (Wolbaki ray apparatus) to irradiate (0, 40, 50 and 60Gy). After the irradiation, the male and female pupae were separated again using the separator, and the irradiated female pupae and the non-irradiated male pupae were placed in a clean cage at a ratio of about 1000:400.
[0042] (2) After all the pupae have emerged, provide 10% glucose solution to the adult mosquitoes. After 4 to 5 days, the female mosquitoes were given a blood meal. 48 hours after the blood meal, put it into the oviposition cup and collect the mosquito eggs for 48 hours. Then give...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com