Rotor of permanent magnet synchronous motor and motor
A technology for permanent magnet synchronous motors and rotors, which is applied in the direction of synchronous machine parts, magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuits, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing eddy current loss, reducing electromagnetic noise, and high sine of air gap flux density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
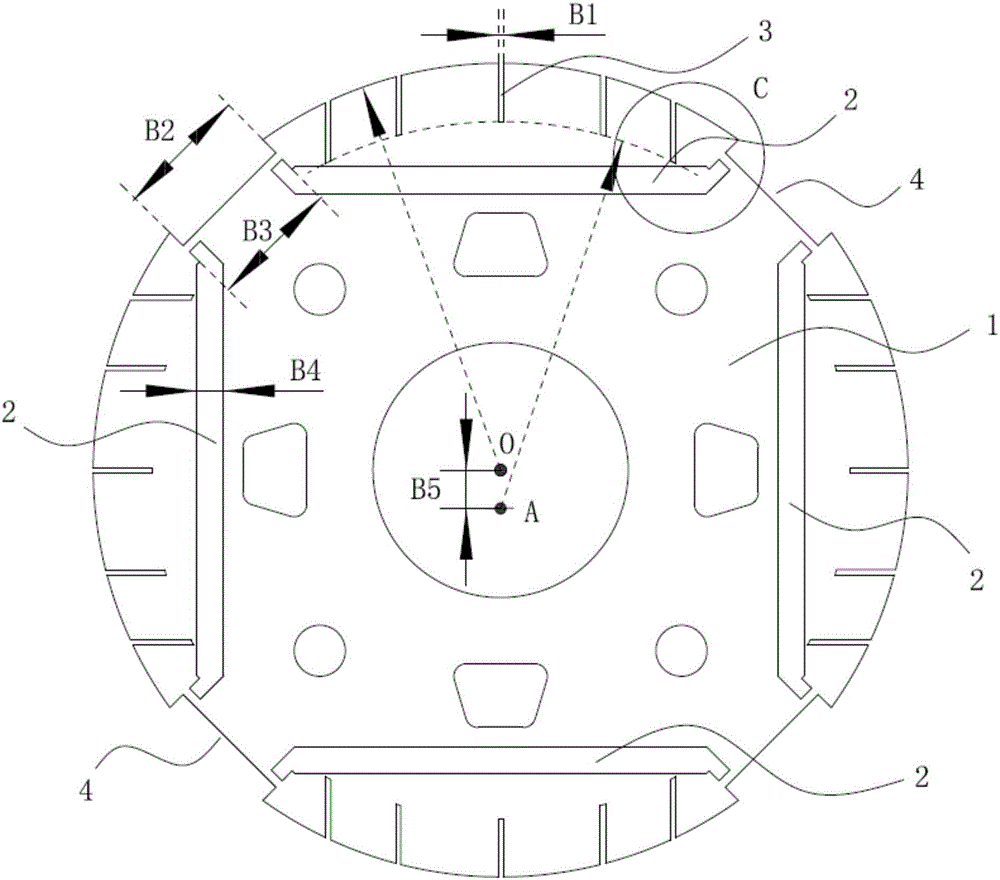
[0028] The preferred embodiment discloses a rotor of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. Such as figure 1 with figure 2 As shown, a plurality of magnetic steel slots 2 are evenly distributed along the circumferential direction on the rotor body 1, and permanent magnets (not shown in the figure) are inserted in the magnetic steel slots 2, and the polarities of adjacent permanent magnets are opposite; A plurality of slits 3 are arranged on the outer edge of the magnetic steel slot 2 corresponding to the position, the slits 3 are connected to the air gap between the stator and the rotor, and the inner ends of the slits 3 are located on the same arc line.
[0029] Preferably, the width of all slits 3 is the same; the slits 3 corresponding to the same magnetic steel groove 2 are the same group, and all the slits 3 in each group of slits 3 are arranged symmetrically about the center line of the permanent magnet; each group of slits The slits 3 include five slits 3, and the roto...
Embodiment 2
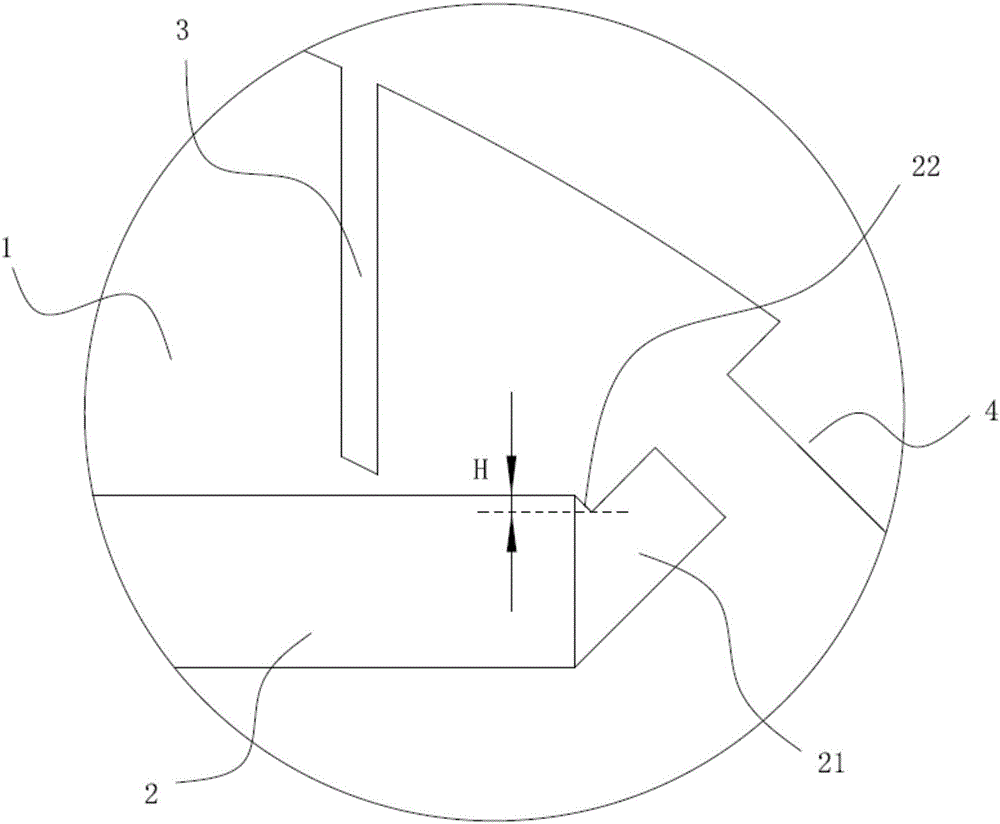
[0039] This preferred embodiment discloses a rotor of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, the structure of which is basically the same as that of the first preferred embodiment. The difference is that if image 3 with Figure 4 As shown, a plurality of slits 3 are provided on the outer edge of the rotor body 1 corresponding to the magnetic steel groove 2, the slits 3 communicate with the magnetic steel groove 2, and the outer ends of the slits 3 are located on the same arc line superior. The center of the arc line where the outer end of the slit 3 is located coincides with the center of the rotor body 1 .
[0040] The magnetic circuit of the rotor is improved, the air gap magnetic field distribution is more sinusoidal, the influence of high harmonics on the stator, rotor and permanent magnet is weakened, the electromagnetic noise is further suppressed, and the core loss is reduced.
Embodiment 3
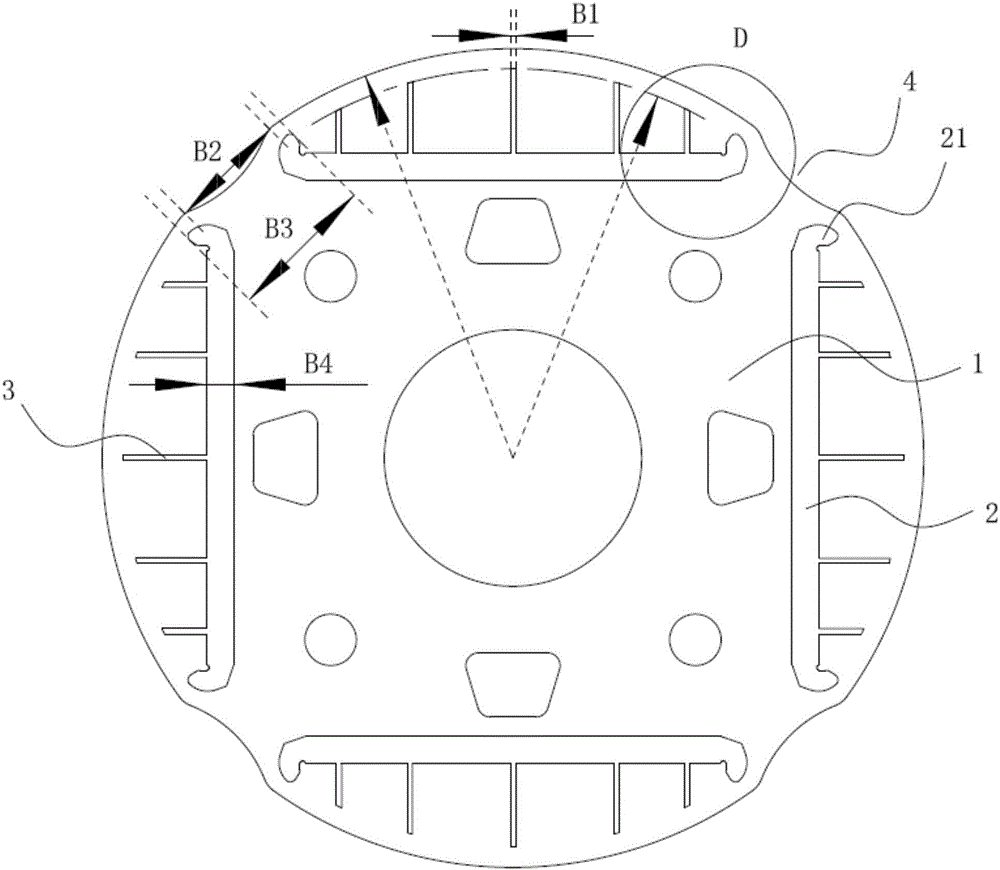
[0042] This preferred embodiment discloses a rotor of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, the structure of which is basically the same as that of the second preferred embodiment. The difference is that if Figure 5 As shown, in a group of slits 3 corresponding to the same magnetic steel slot 2, all the slits 3 are inclined to the left and right sides with the center line of the magnetic steel slot 2 as the reference, and at the center line of the corresponding magnetic steel slot 2 A through hole 5 is provided, and the through hole 5 communicates with the magnetic steel slot 2 .
[0043] In order to improve the air gap flux density and rotor flux, and increase the anti-demagnetization ability of the permanent magnet, the angle θ between the slit 3 and the outer surface of the magnetic steel slot 2 is preferably greater than or equal to 30° and less than or equal to 60°.
[0044] In order to ensure that the permanent magnet is not easy to break when it is stressed, suppress ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com