Method for in-situ test of high-energy electron irradiation effect of electronic component under temperature changing condition based on argon environment
An electronic component and temperature-changing technology, applied in the field of electronics, can solve the problems of inaccurate in-situ testing of electrical properties and low evaluation efficiency, and achieve the effects of optimizing anti-radiation performance, easy operation, and reducing time and cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
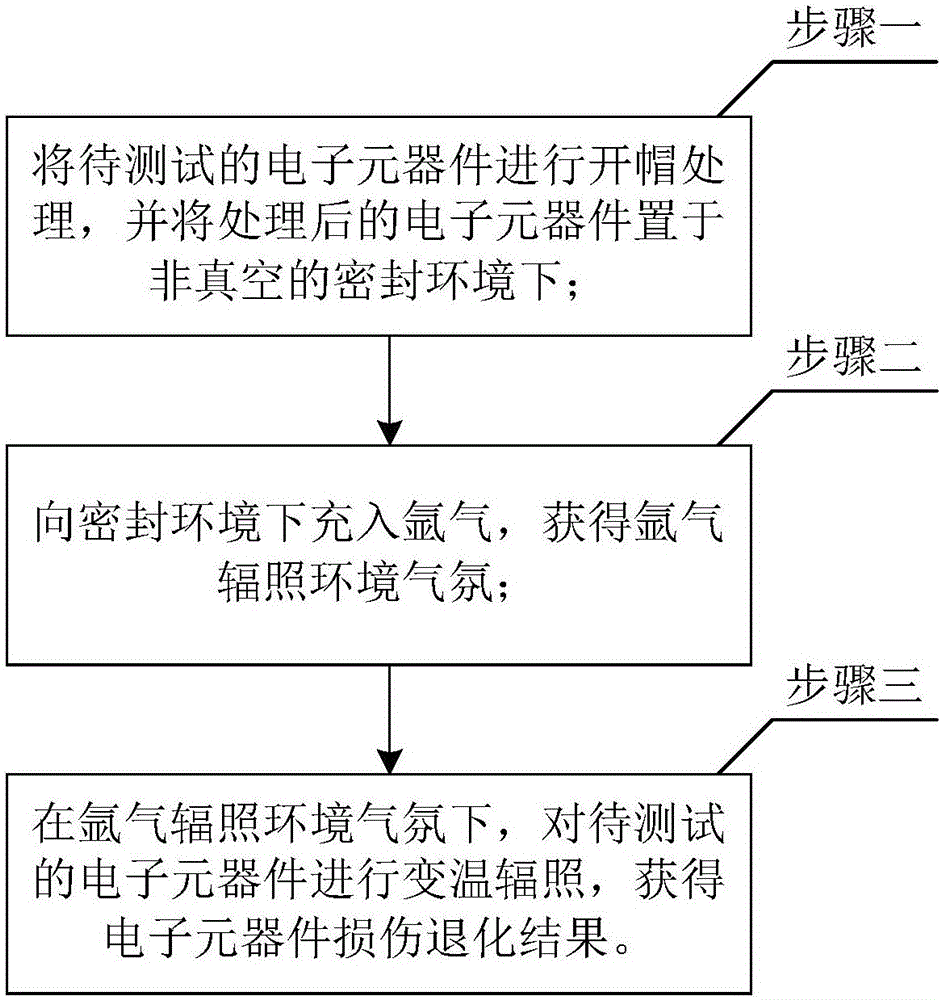
[0030] Specific embodiment 1. The in-situ test method for the high-energy electron irradiation effect of electronic components and parts under the condition of changing temperature based on the argon environment, comprising the following steps:
[0031] Step 1: First place the temperature control device in the sealed chamber, and connect the lead wire of the temperature control device with the vacuum plug of the sealed chamber, and then adjust the temperature range to the required range, namely: 20°C to 500°C;
[0032] Step 2: Uncap the electronic components to be irradiated (that is, the test sample), test the initial parameters once, and then fix the sample on a special fixture and fix it on the temperature control device;
[0033] Step 3: Connect the lead wire of the electrical performance test of the sample to the semiconductor electrical performance tester through the vacuum plug, perform the second initial parameter, and compare it with the result of the previous initial ...
specific Embodiment 2
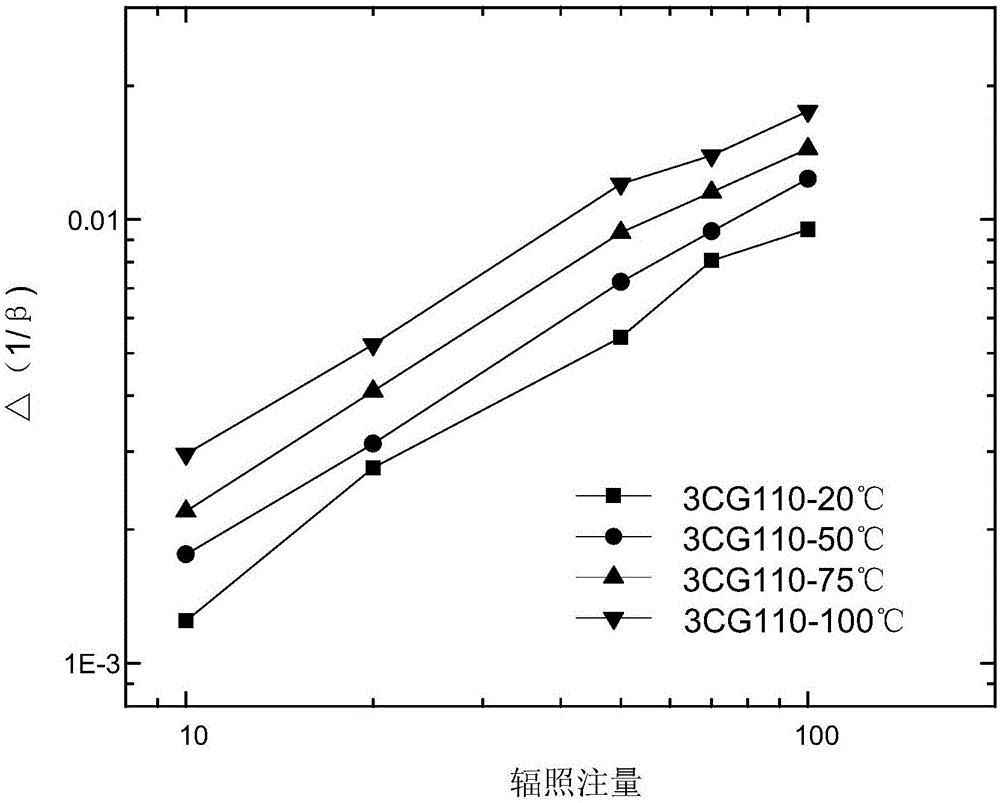
[0036] Specific embodiment two, the in-situ test method of the transistor 3CG110 high-energy electron irradiation effect under the condition of changing the temperature based on the argon environment described in this embodiment, the specific steps of the method are:
[0037] Step 1: First, test the raw data of the bipolar transistor 3CG110, select samples that meet the performance indicators for future use, and record the initial value;
[0038] Step 2: Fix the sealed chamber at the corresponding position of the high-energy electron radiation source, and place a temperature control device in the irradiation area of the sealed chamber, and adjust the temperature of the heating stage until the horizontal plane is perpendicular to the incident direction of electrons;
[0039] Step 3: Uncap the transistor 3CG110 of the sample to be irradiated, test the parameters of 3CG110 with a semiconductor electrical performance tester, and then fix the sample on a special fixture and fix it...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com