A personalized design method for diabetic foot insoles
A technology of diabetic foot and design method, applied in the direction of design optimization/simulation, calculation, instrument, etc., can solve the problems of long response period, insufficient personalized design, lack of efficient, fast and mechanically based design process, etc. The effect of reducing the cost of individualization, shortening the design cycle, and correcting the maximum stress peak and distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0034] This embodiment carries out the whole process from the collection of patient data to the output of the diabetic foot insole model, which is only used to illustrate and explain the present invention, and is not intended to limit the present invention.
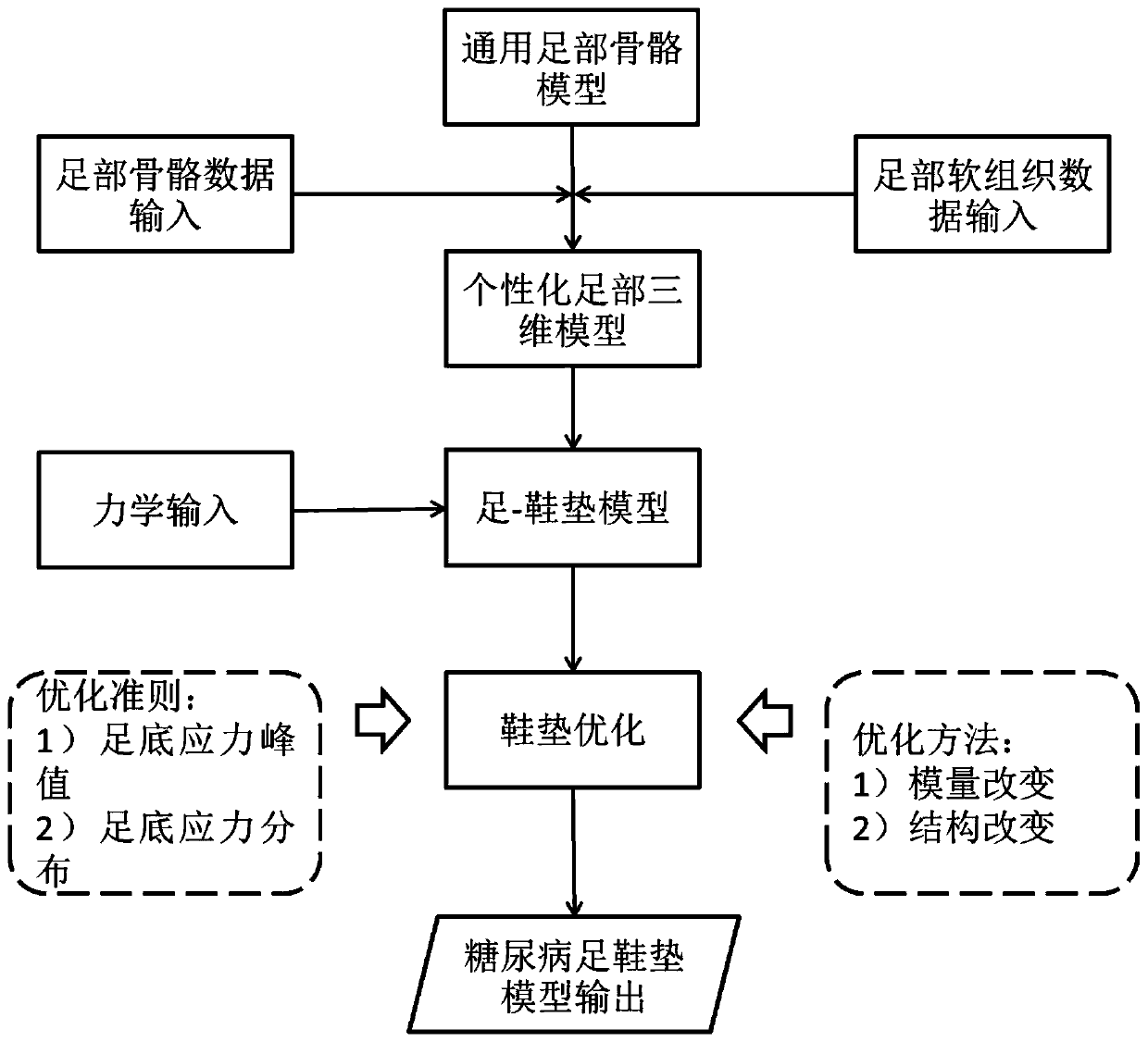
[0035] refer to figure 1 , a personalized design method for diabetic foot insoles, comprising the following steps:
[0036] Step 1: Collect a large number of CT and MRI data of the patient's foot, and use Mimics (Version 16.0, Materialize, Belgium) to construct a parametric model of the patient's internal bones, ligaments, muscles, etc., to form a set of geometric features of the foot bones, bone- Muscle assembly features, ligament-skeleton assembly features, and cartilage features are a patient foot parametric model library, and a general foot bone model is established;
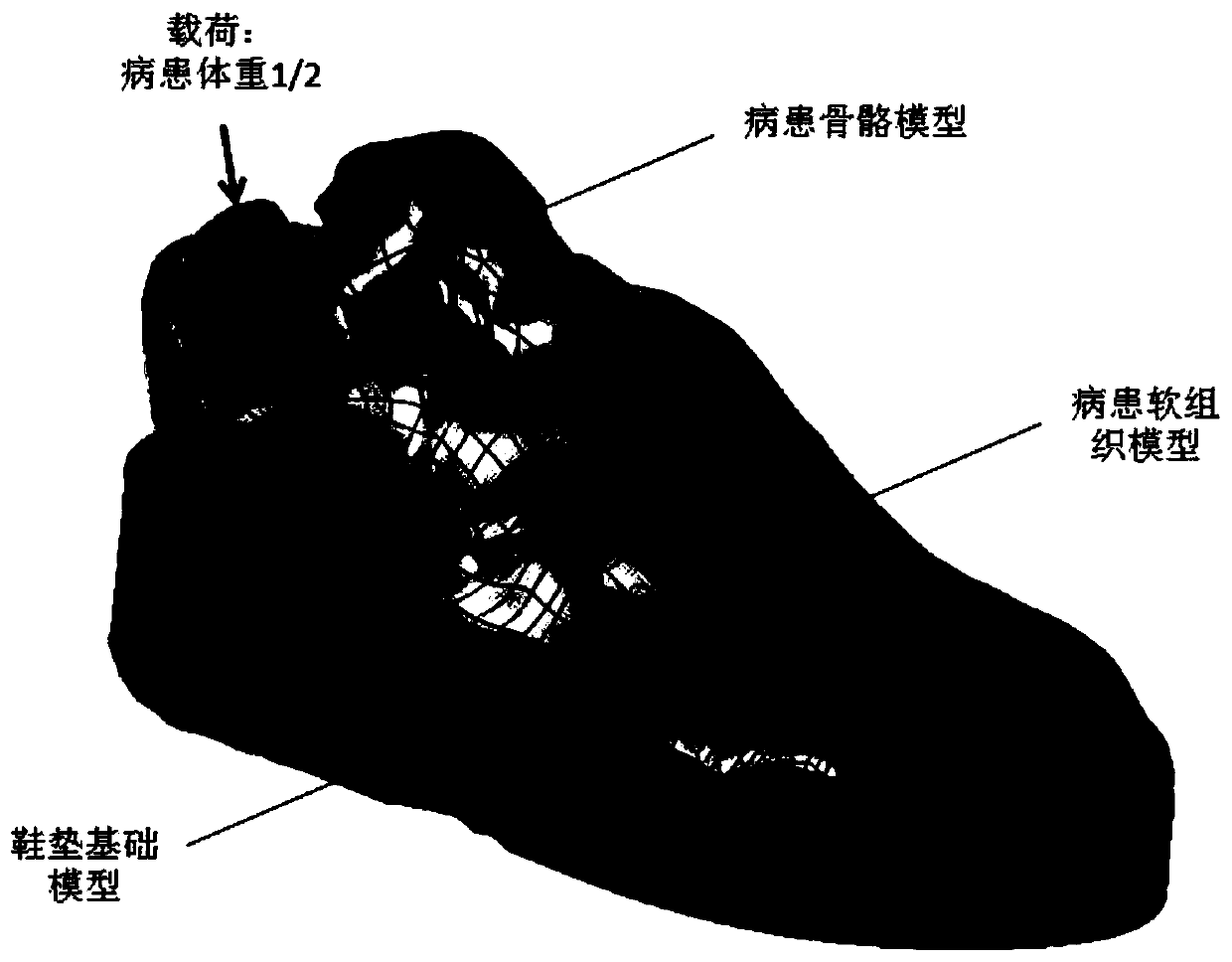
[0037] Step 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com