Vitamin C individualized quantitative compensating detecting method based on genetic typing
A detection method and genotyping technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problem that the demand for vitamin C varies from person to person.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Example 1 Sample collection and DNA template preparation:
[0060] Proceed as follows:
[0061] 1) Use oral swabs to collect the oral epithelial cells of the person to be tested. The method is to insert the swab into the oral cavity so that the head of the swab fully contacts the mucous membranes on the inside of the cheek and the upper and lower gums, and rubs up and down with the force of brushing teeth, while rotating the swab. Let the swab head fully touch the oral mucosa, and repeat this action for 1 minute.
[0062] 2) Using the standard buccal swab DNA extraction kit and corresponding steps, place the swab stained with buccal cells in 800 μL of normal saline, rinse for 20 seconds to make the cells fall off completely, stick to the wall of the centrifuge tube and squeeze dry the swab. For liquid, centrifuge at 12,000rpm for 5min.
[0063] 3) Discard 700 μL of supernatant, and the remaining 100 μL of supernatant, fully shake and mix for 15 seconds, add 200 μL of ...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Embodiment 2 primer design:
[0070] For the SLC23A1 gene and the NQO1 gene, specific amplification primers for common sites and rare sites were designed (the two primers differ only in terminal bases, denoted by F1 and F2, respectively), and corresponding reverse primers ( R indicates), 3 primers are combined to form a primer premix. The 5' ends of the two forward primers are respectively connected with different detection sequences for fluorescence detection. Specific amplification primers for common sites and rare sites are underlined, and detection primer sequences are indicated in lowercase fonts, where the part connected to F1 corresponds to blue fluorescence, and the part connected to F2 corresponds to red fluorescence. For GSTM1 gene and GSTT1 gene, the two primers in the master mix are F and R respectively, the specific sequence is underlined at the 3' end, and the detection sequence is indicated in lowercase font, corresponding to the above blue or red fluore...
Embodiment 3
[0085] The establishment of embodiment 3PCR detection system:
[0086] The PCR amplification system includes commercially purchased 2x Mix (including Taq enzyme, 4 kinds of dNTPs, and two probes corresponding to the detection primer sequence of the forward primer). The PCR system is as follows:
[0087] PCR amplification system (10μL):
[0088]
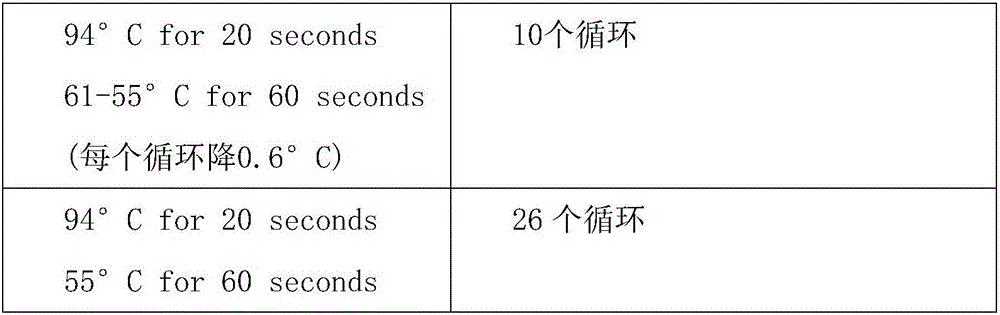
[0089] The PCR amplification procedure is as follows:
[0090]
[0091] Fluorescence reading:
[0092] In an environment below 40°C, read the fluorescence value.
[0093] Interpretation of results:
[0094] For the SLC23A1 gene, if the individual only contains G at the rs33972313 site, only the F1 primer can amplify, and the corresponding fluorescent signal is blue, and the site is recorded as GG; if the site only contains A, only the F2 primer can amplify Amplification, the corresponding fluorescent signal is red, and the site is recorded as AA; if the individual contains both G and A, both F1 and F2 primers can be amplifi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com