3D printing composite material with high rebound resilience and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of 3D printing and composite materials, which is applied in the field of 3D printing composite materials with high resilience and its preparation, to achieve the effect of improving bonding strength, superior mechanical properties, and easy processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] In terms of mass fraction, the contents of each component of the 3D printing composite material in this embodiment are respectively:
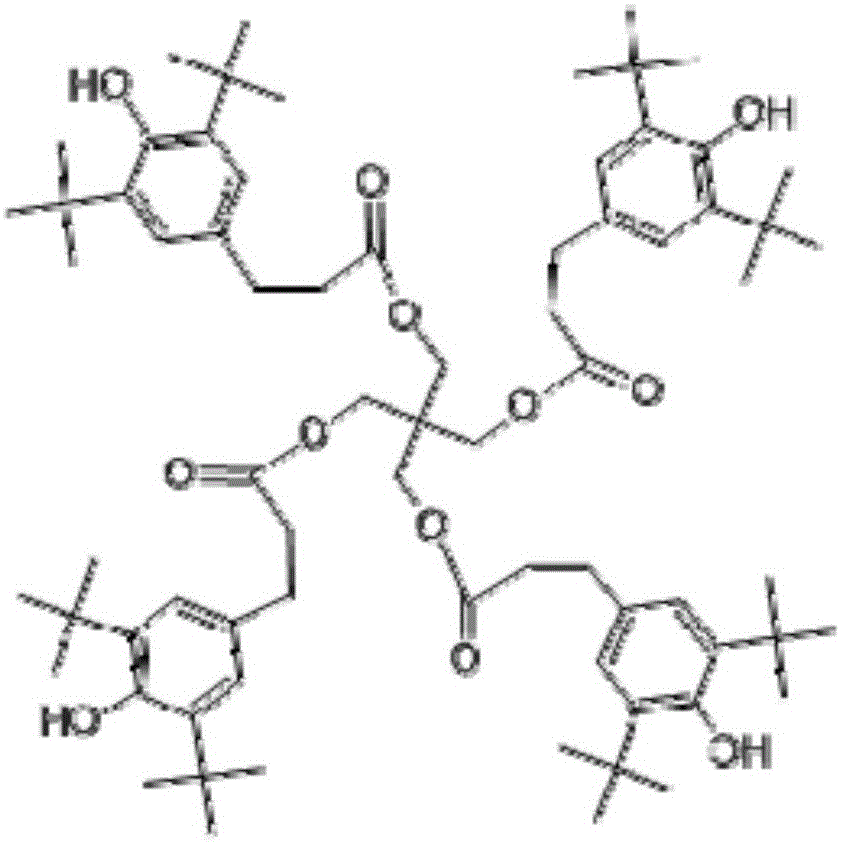
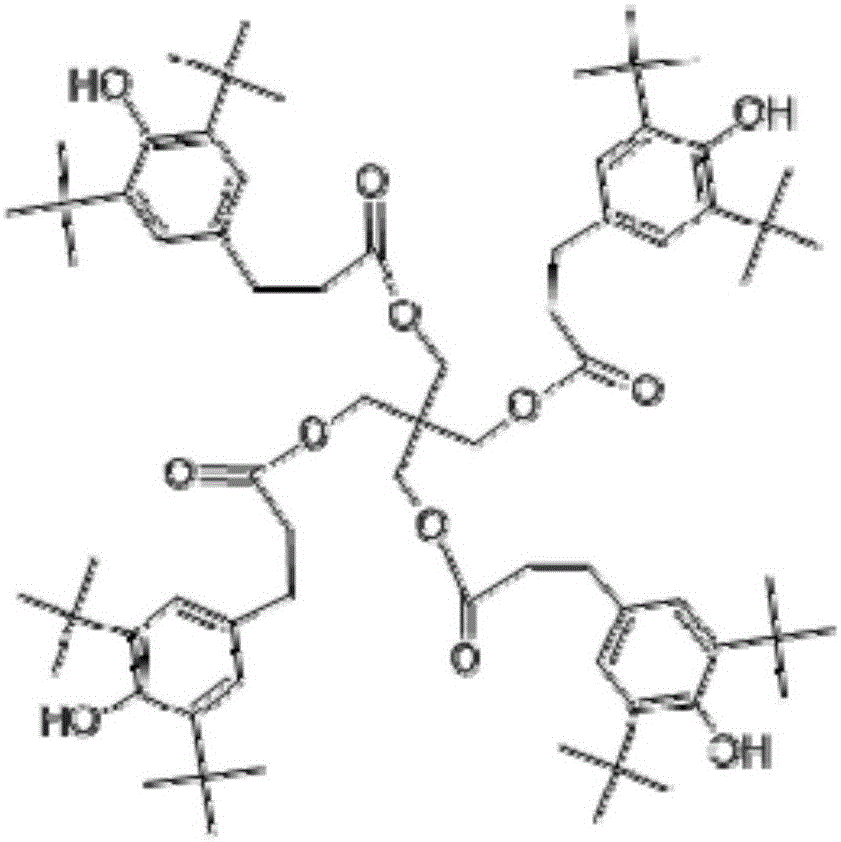
[0038] TPU content 70.2%, polyethylene (PE 5000S) content 28%, PP-g-MAH content 1%, 1010 (tetra[β-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) propionic acid] pentaerythritol ester) content 0.1%, polyethylene wax content 0.2%, ethylene bis stearamide content 0.5%
Embodiment 2
[0040] In terms of mass fraction, the contents of each component of the 3D printing composite material in this embodiment are respectively:
[0041] TPU content 65.3%, polyethylene (PE 5000S) content 32.9%, PP-g-MAH content 1%, 1010 (tetra[β-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid] pentaerythritol ester) content 0.2%, polyethylene wax content 0.2%, ethylene bis stearamide content 0.4%,
Embodiment 3
[0043] In terms of mass fraction, the contents of each component of the 3D printing composite material in this embodiment are respectively:
[0044] TPU content 60.3%, polyethylene (PE 5000S) content 40%, EVA-g-MAH content 1%, 1010 (tetra[β-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid] pentaerythritol ester) content 0.1%, polyethylene wax content 0.2%, ethylene bis stearamide content 0.4%,
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com