Scanning photon counting non-visual-field three-dimensional imaging device and method
A technology of photon counting and three-dimensional imaging, which is applied in the field of non-line-of-sight three-dimensional imaging technology, can solve problems such as inability to image non-line-of-sight scenes, and achieve the effect of improving flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
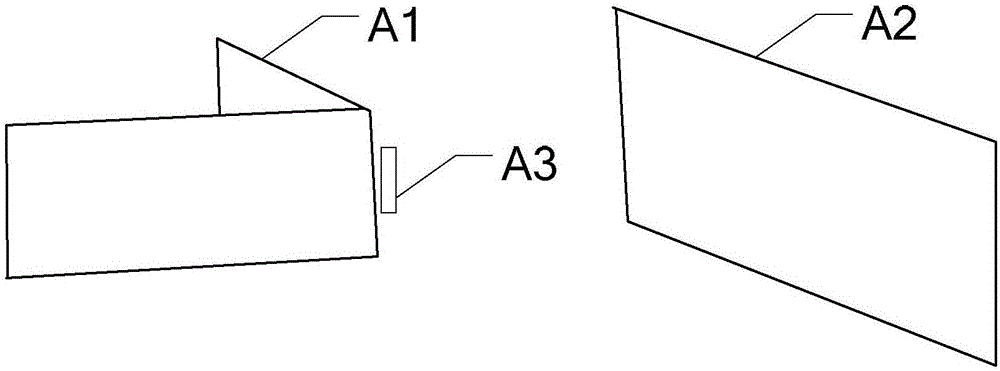
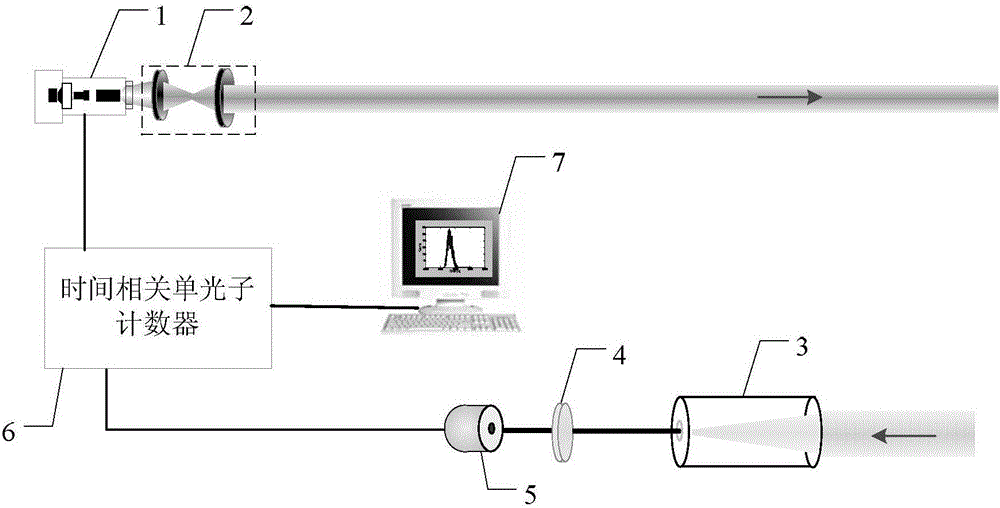
[0042] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 2 and image 3 Describe this embodiment in detail. A scanning photon counting non-view-field three-dimensional imaging device described in this embodiment includes a pulsed laser 1, a beam shaping system 2, a receiving optical system 3, a single-photon detector 5, and a time-correlated single-photon Counter 6, computer 7;
[0043] The pulsed laser 1 emits laser light and sends a time signal to the time-correlated single photon counter 6. The laser emitted by the pulsed laser 1 is shaped by the beam shaping system 2 and then incident on the wall. The laser scattered by the wall is reflected by the target and then incident on the wall again. The receiving optical system 3 receives the laser light returned by the wall, the laser is incident on the single photon detector 5, the output end of the single photon detector 5 is connected to the input end of the time-correlated single photon counter 6, and the output end of the t...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0046] Embodiment 2: Based on the imaging method of a non-scanning photon counting non-sight three-dimensional imaging device described in Embodiment 1, the method includes the following steps:
[0047] The pulse laser 1 emits laser light and gives a time signal to the time-correlated single photon counter 6;
[0048] Using a beam shaping system 2 to shape the laser light emitted by the pulse laser 1;
[0049] The shaped laser is incident on the wall, and the laser scattered by the wall is reflected by the target and then incident on the wall again;
[0050] The receiving optical system 3 receives the laser light returned by the wall, and makes the image square field of view of the receiving optical system 3 the same as the field of view of the single photon detector 5;
[0051] The time-correlated single photon counter 6 calculates the photon flight time of the photon incident to the single photon detector 5 from the pulse laser 1 to the photon flight time returning to the s...
specific Embodiment approach 3
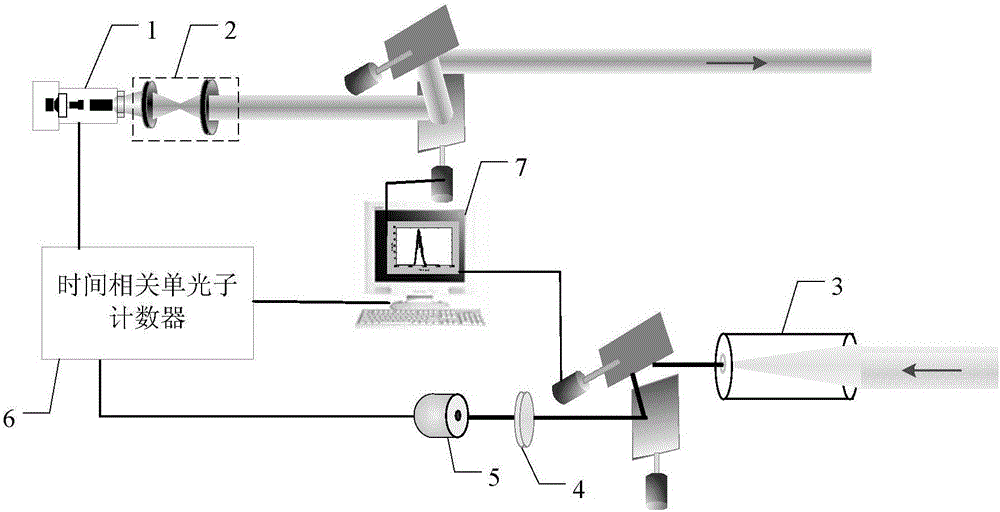
[0055] Specific implementation mode three: combination Figure 4Describe this embodiment in detail. This embodiment is a further description of the scanning photon counting non-view-field three-dimensional imaging method described in the second embodiment. In this embodiment,
[0056] The computer 7 reconstructs the three-dimensional image of the target according to multiple time photon counting images to obtain the three-dimensional image, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0057] Back projection:
[0058] To establish a model, pulse laser 1 is located at point L, single photon detector 5 is located at point D, and the point where the laser emitted by pulse laser 1 is incident on the wall is the source point, S j The jth source point, the single photon detector 5 corresponds to a point on the wall, which is the image point, I i is the i-th image point;
[0059] Back-project each time photon map into three-dimensional space, and the value of each moment in t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com