Method for delaying aging caused by in vitro culture of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
A bone marrow mesenchymal and in vitro culture technology, applied in the field of cell biology, can solve the problems of MSCs losing differentiation potential, no obvious benefits, difficult to control and achieve target conditions, and achieve the effect of improving in vitro expansion ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
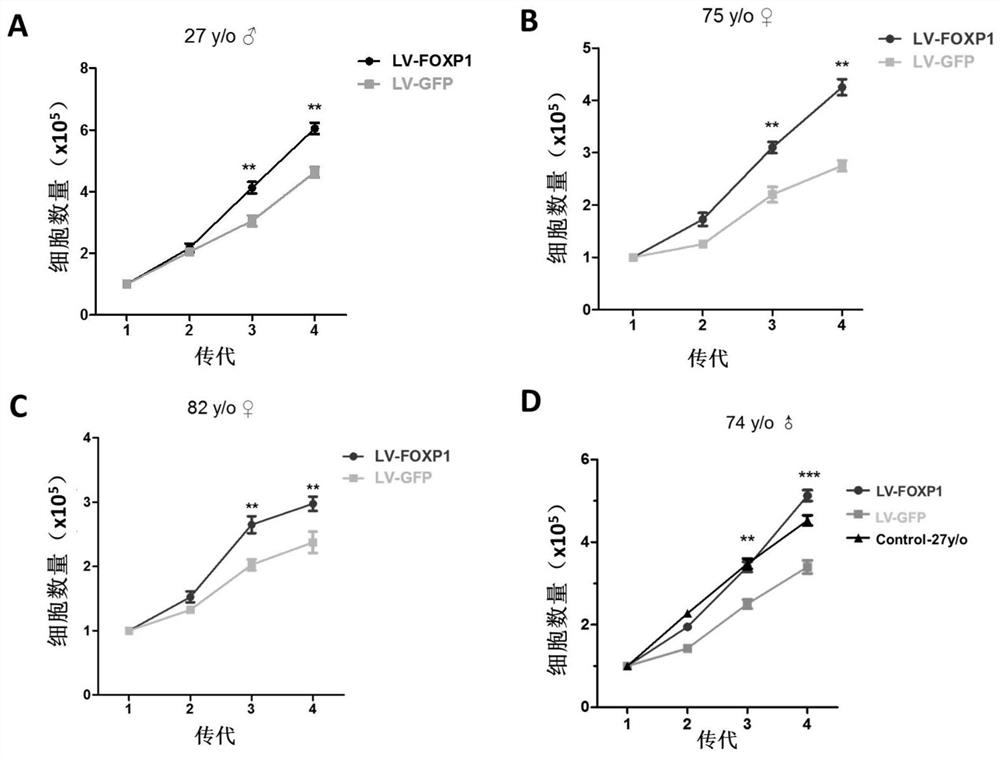
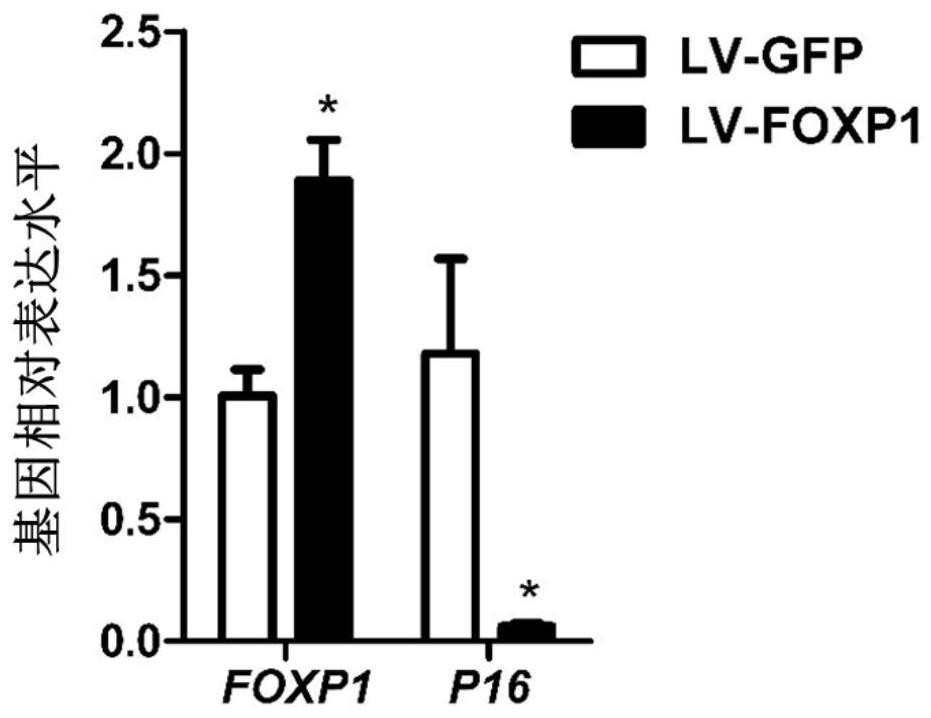
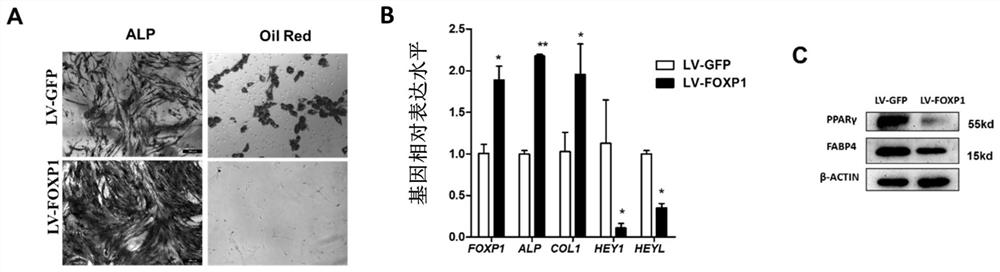
[0055] This embodiment relates to a method for delaying the senescence of human-derived bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) cultured in vitro; the method comprises the following steps:
[0056] 1) Isolation and culture of human bone marrow MSC
[0057] Aspirate 3 to 5 ml of bone marrow with a 10 ml sterile vacuum EDTA anticoagulant tube, mix gently, and store on ice. The sample can be used to isolate MSC within 6 hours after isolation. In this example, Shanghai Sangon's human bone marrow lymphocyte separation kit was used to separate mononuclear cells in bone marrow by density gradient centrifugation, and bone marrow MSCs were separated by an adherent culture method.
[0058] (1) Aspirate the bone marrow from the anticoagulant tube, resuspend it with 10 ml DMEM+10% FBS medium, filter it with a 100 micron filter, and collect it in a new centrifuge tube.
[0059] (2) The cells were collected by centrifugation at 500 g for 20 minutes, the supernatant was discarded, and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com