Continuous baby weighing method of baby incubator
An incubator and infant technology, applied in the field of infant incubators, can solve problems such as high price, inability to adapt to big data collection, inability to distinguish zero-point drift, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0083] The embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. This embodiment is implemented on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation methods and specific operating procedures are provided, but the scope of protection of the present invention is not limited to the following Described embodiment.
[0084] The infant incubator infant continuous weighing method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0085] Step 1. Building a Baby Scale
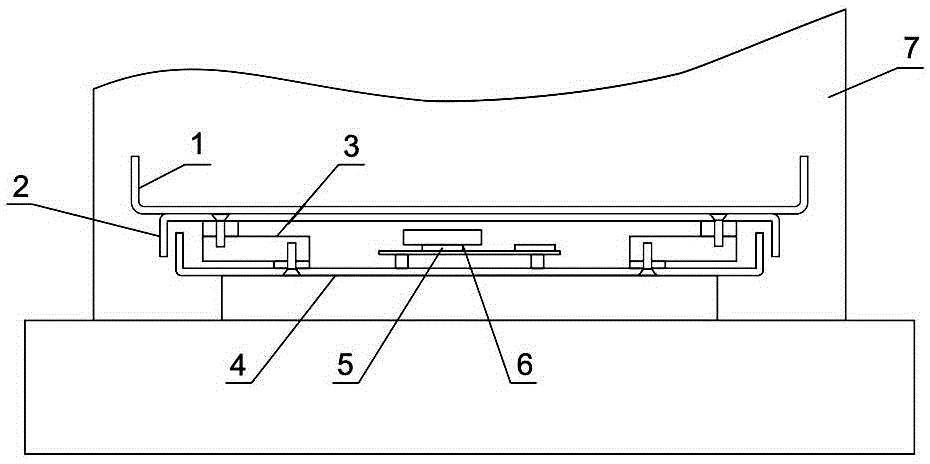
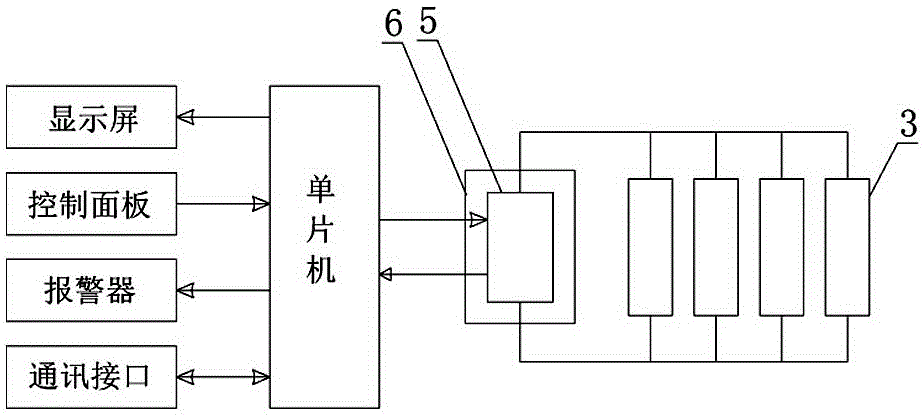
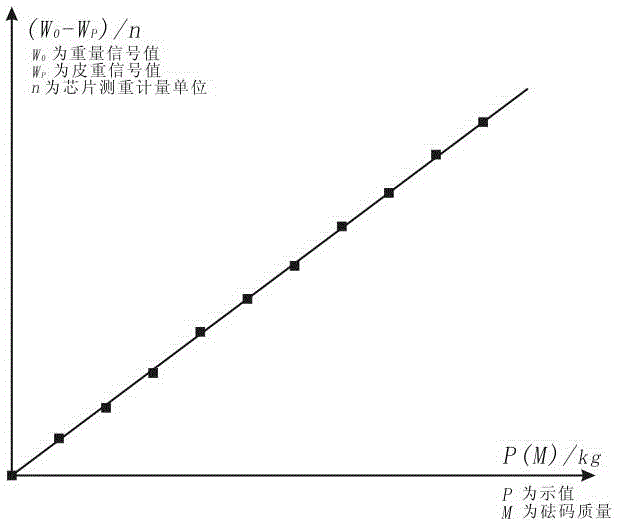
[0086] Such as figure 1 , 2 As shown, first a load cell 3 is connected to the four corners of the scale top cover 2 fixed with the crib tray 1, and the scale top cover 2 is supported and fixed on the scale base 4 by the load cell 3, and the four weighing After the sensors 3 are connected in parallel with each other, they are connected to the signal input terminal of the weighing chip 5, then the weighing c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com