Piglet small intestine epithelial cell classification and separation method
A technology for intestinal epithelial cells and epithelial cells is applied in the field of piglet intestinal epithelial cell fractionation, which can solve the problems of inability to realize high-throughput research on physiological processes and metabolic changes, and achieve the effects of low cost and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The method for fractionating piglet intestinal epithelial cells comprises the following steps:
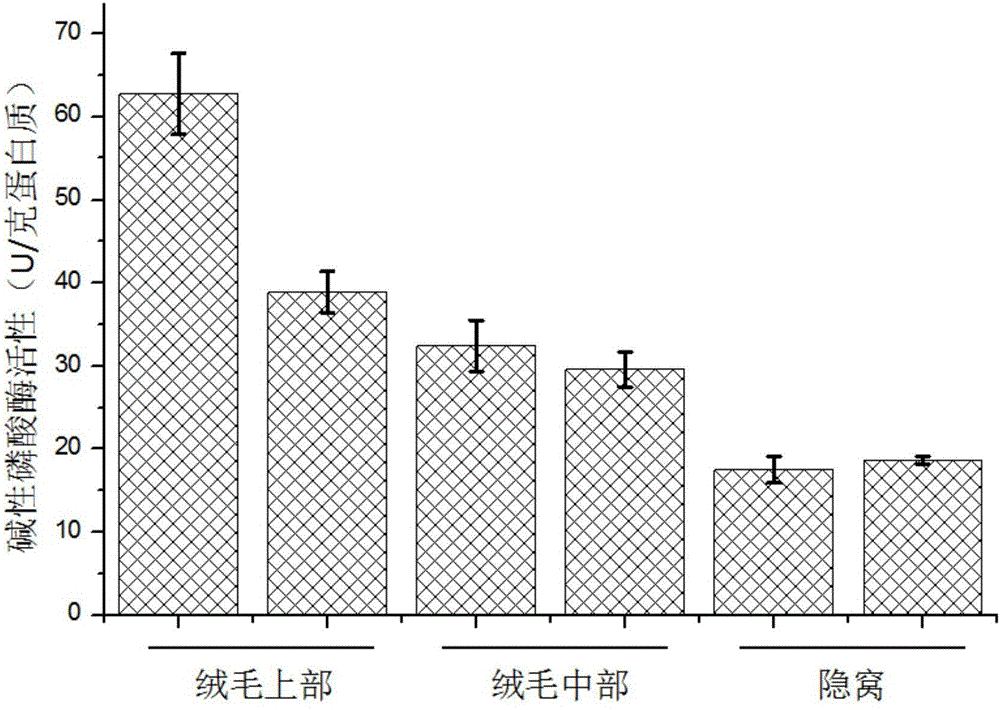
[0026] (1) Six 0-day-old suckling piglets were selected. After slaughtering, the small intestines of piglets with a length of 60 cm were cut, and 100 mL of preheated oxygenated phosphate buffer solution at 37 ° C was perfused into the intestinal cavity, and both ends were clamped with hemostatic forceps. Incubate in a water bath shaker at ℃ for 30 minutes at a shaking speed of 70 rpm;
[0027] Among them, the phosphate buffer solution is composed of: sodium chloride 150mM, sodium dihydrogen phosphate 4mM, disodium hydrogen phosphate 4mM, phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride 0.1mM, dithiothreitol 0.4mM, pH 7.4.
[0028] (2) Discard the phosphate buffer, perfuse 100mL of cell separation solution, and continue to incubate in a water bath shaker at 37°C for 2.5 hours at a shaking speed of 70 rpm. Minutes, 120 minutes and 150 minutes to collect cell separation fluid and perfuse new cel...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The method for fractionating piglet intestinal epithelial cells comprises the following steps:
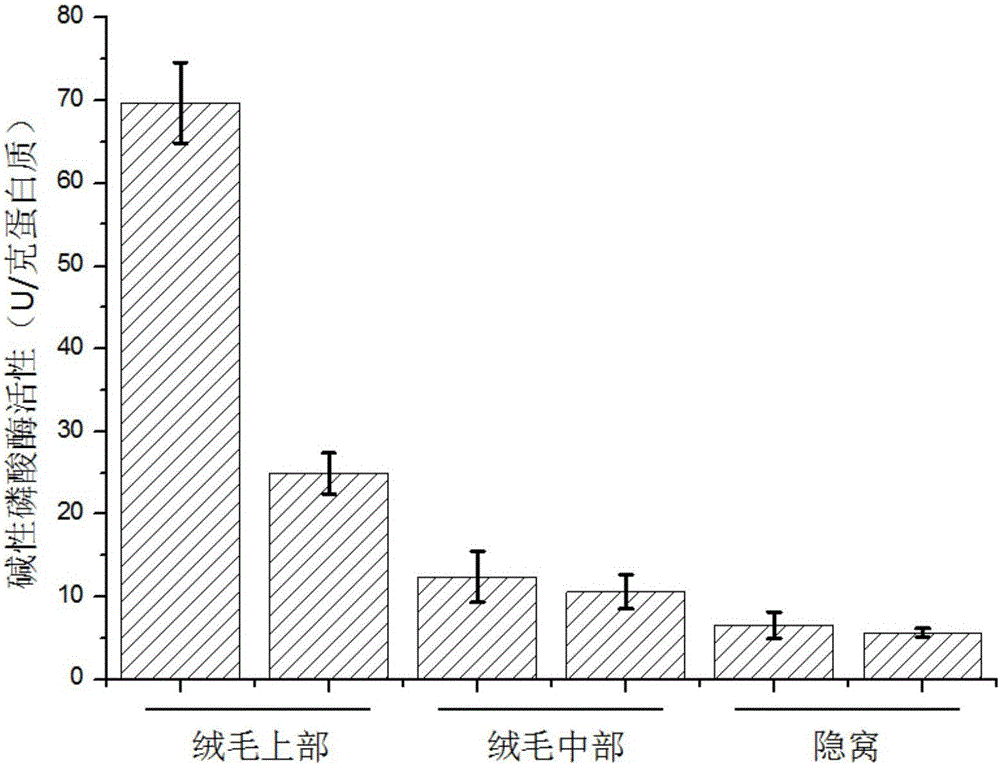
[0034] (1) Six 25-day-old weaned piglets were selected. After slaughtering, the piglets’ small intestines with a length of 80 cm were cut, and 110 mL of preheated oxygenated phosphate buffer solution at 37 ° C was perfused into the intestinal cavity, and both ends were clamped with hemostatic forceps. Incubate in a water bath shaker at ℃ for 30 minutes at a shaking speed of 70 rpm;
[0035] Among them, the phosphate buffer solution is composed of: sodium chloride 142mM, sodium dihydrogen phosphate 5mM, disodium hydrogen phosphate 5mM, phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride 0.2mM, dithiothreitol 0.5mM, pH 7.4.
[0036] (2) Discard the phosphate buffer, perfuse 110mL of cell separation solution, and continue to incubate in a water bath shaker at 37°C for 2.5 hours at a shaking speed of 70 rpm. Minutes, 115 minutes and 150 minutes to collect cell separation fluid and perfuse new cell s...
Embodiment 3
[0041] The method for fractionating piglet intestinal epithelial cells comprises the following steps:
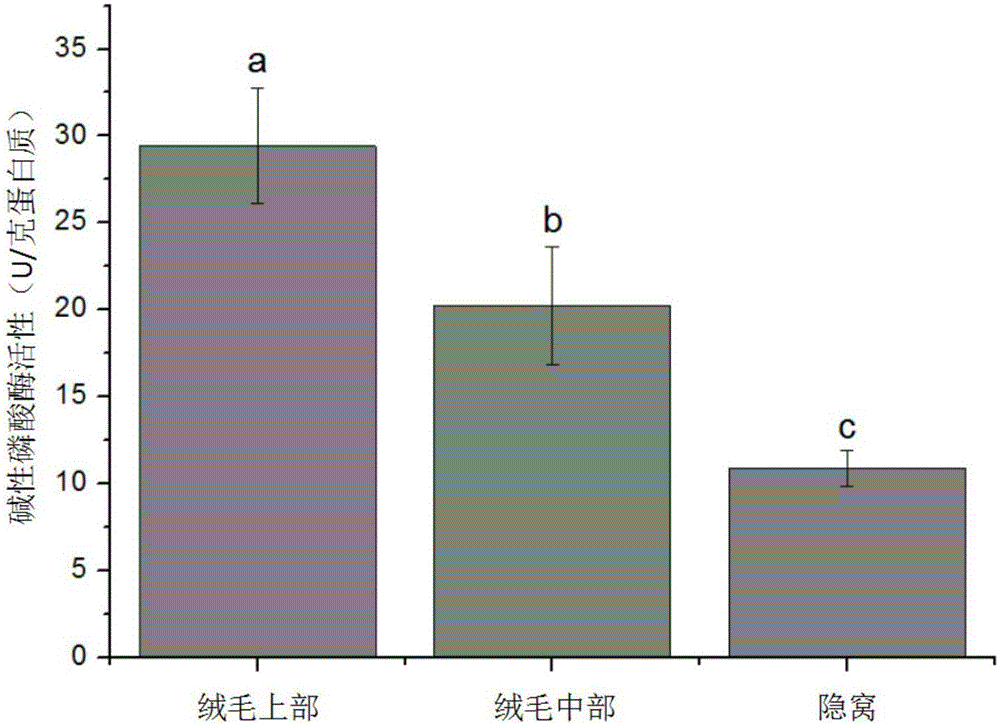
[0042] (1) Select 6 70-day-old piglets, cut the small intestine section with a length of 90cm after slaughtering, perfuse 150mL of preheated oxygenated phosphate buffer solution at 37°C in the intestinal cavity, clamp both ends with hemostatic forceps, and incubate at 37°C Incubate in a water bath shaker for 30 minutes at a shaking speed of 70 rpm;
[0043] Among them, the phosphate buffer solution is composed of: sodium chloride 135mM, sodium dihydrogen phosphate 6mM, disodium hydrogen phosphate 6mM, phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride 0.3mM, dithiothreitol 0.6mM.
[0044] (2) Discard the phosphate buffer, perfuse 150mL of the cell separation solution, and continue to incubate in a water bath shaker at 37°C for 2.5 hours at a shaking speed of 70 rpm, and collect the cells at 40 minutes, 90 minutes and 150 minutes after incubation. Separation fluid and perfuse new cell separation f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com