Primer group, probe and kit for kawasaki disease detection
A Kawasaki disease and probe sequence technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems affecting the specificity of detection results and achieve accurate results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Example 1 Reverse transcription primer, amplification primer and probe sequence for detecting Kawasaki disease
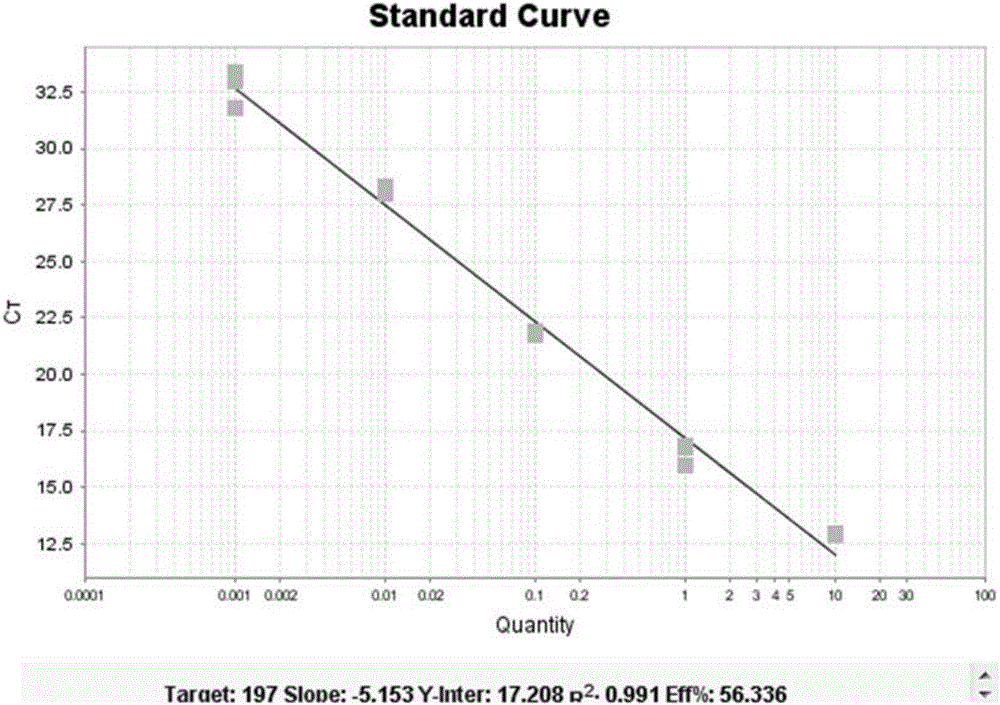
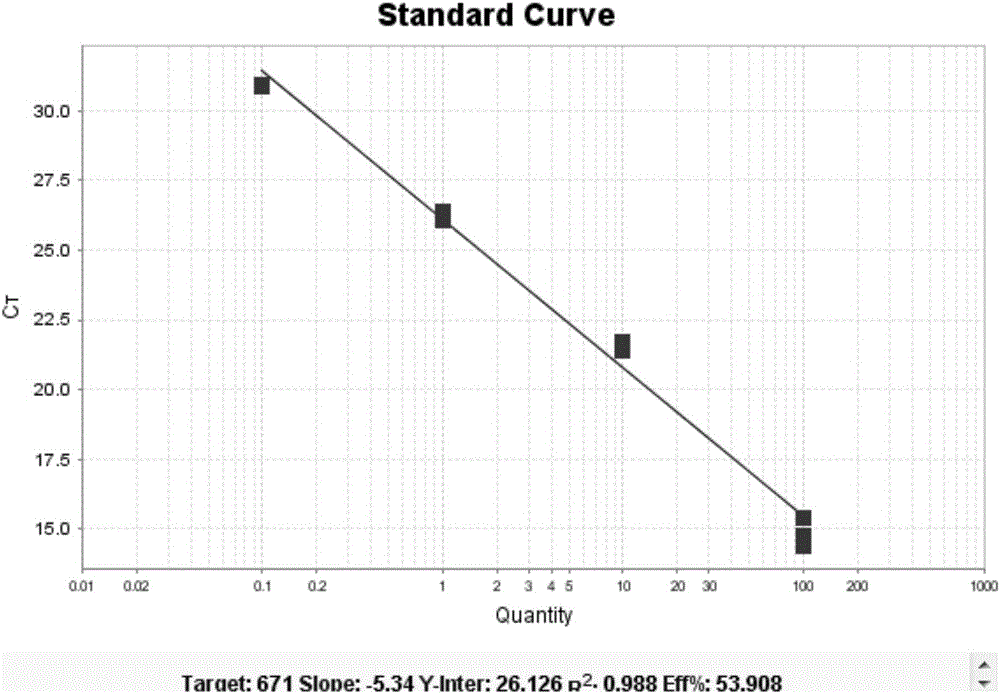
[0065] The detection markers for Kawasaki disease are: hsa-miR-197, hsa-miR-671, hsa-miR1246 and hsa-miR4436.
[0066] The reverse transcription primer sequence is:
[0067] RT-miR197:
[0068] G TCGTATCCAGTGCAGGG T CCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATA CGACGCTGGG;
[0069] RT-miR671:
[0070] G TCGTATCCAGTGCAGGG T CCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATA CGACTTTTTTTTTTTCTCCAGCC;
[0071] RT-miR1246:
[0072] G TCGTATCCAGTGCAGGG T CCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATA CGACCCTGCT;
[0073] RT-miR4436:
[0074] G TCGTATCCAGTGCAGGG T CCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATA CGACGGCAGGGC;
[0075] The amplification primer sequence is:
[0076] Universal reverse primer R-KD: TCGTATCCAGTGCAGGG ;
[0077] F-miR197: TTCACCACCTTCTCCACC;
[0078] F-miR671: GAGAGGAAGCCCTGGAG;
[0079] F-miR1246: GCCGAATGGATTTTTGGAG;
[0080] F-miR4436: TCCTGTCCACTTCTGCCT;
[0081] The probe sequence is: CCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGAT .
[0082] In the above primer sequence, the...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Example 2 Detection method of Kawasaki disease
[0084] (1) Extraction of serum exosomal miRNA
[0085] The operation of extracting serum exosomal miRNA includes the following steps:
[0086] 1) Place 250μl of serum on ice to dissolve naturally, then add 60μl of exosome extraction reagent, gently pipette to mix, then let stand on ice for 30min; centrifuge at 1500g at 4℃ for 10min; remove as much as possible with a pipette All the supernatant and the precipitation part are exosome;
[0087] 2) Add 1ml Trizol to the exosome extracted above to fully lyse (ultrasound and mix well), and let it stand for 5 minutes;
[0088] 3) Add 200μl of chloroform, shake and mix well for about 30s, make the water phase and organic phase fully contact, and let it stand at room temperature for about 10min;
[0089] 4) Centrifuge at 14000g for 15min at 4℃, and transfer RNA in the upper water phase to another new Rnase-free EP tube;
[0090] 5) Add an equal volume of isopropanol, mix gently and thoroughl...
Embodiment 3
[0124] Example 3 Specificity evaluation experiment
[0125] There are 8 Kawasaki disease-specific miRNAs: miR-4739, miR-16, miR-483, miR-21, miR-19, miR-22, miR-1260, miR-134 in serum exosome of Kawasaki disease patients and healthy people There is a significant difference between the medium and the average, which may affect the detection specificity of the primers and probes of the present invention.
[0126] Respectively use miR-4739, miR-16, miR-483, miR-21, miR-19, miR-22, miR-1260, miR-13410nM standard cDNA after reverse transcription as a template, using the above example 1 and The primers, probes and methods described in 2 were tested and verified 8 miRNAs specific to Kawasaki disease: miR-4739, miR-16, miR-483, miR-21, miR-19, miR-22, miR-1260, Whether miR-134 can be amplified.
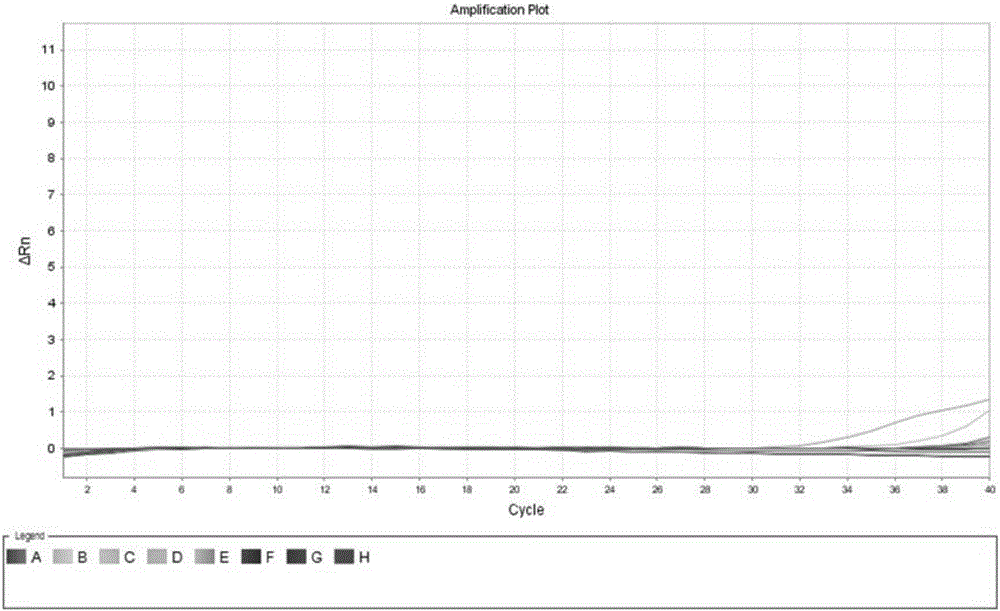
[0127] The experimental results are as figure 1 Shown. figure 1 Among them, curves A~H are respectively miR-4739, miR-16, miR-483, miR-21, miR-19, miR-22, miR-1260, miR-134 10nM standard cDNA Q- P...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com