Mechanical stress free multimode fiber beam speckle homogenization system
A multi-mode fiber, non-mechanical technology, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of complexity, limited improvement of spot uniformity, difficult to effectively promote, etc., and achieve the effect of uniform light intensity distribution of the spot.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
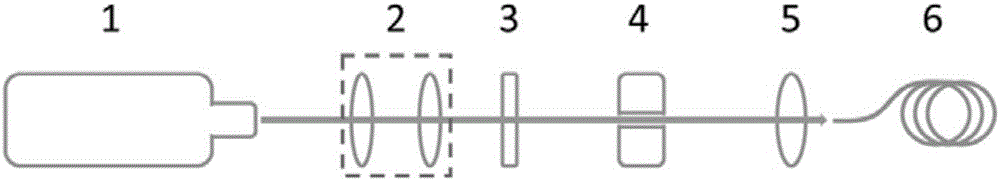
[0029] For a transmissive spatial light modulator, one can pass figure 1 The setup shown performs spot homogenization. The beam of the high-power semiconductor laser first generates a collimated beam of appropriate size through an optical beam expander or beam shrinker system, then adjusts the polarization direction through a half-wave plate, enters a transmission spatial light modulator for spatial mode modulation, and then passes through a fiber coupling system coupled to multimode fiber. figure 1 The optical beam expander or beam reducer system in is suitable for the case where the size of the laser beam spot does not match the size of the input surface of the spatial light modulator, and it is an optional part in practical applications. figure 1 The half-wave plate used to match the laser output polarization mode and the spatial light modulator uses the polarization mode, which is also an optional part.
Embodiment 2
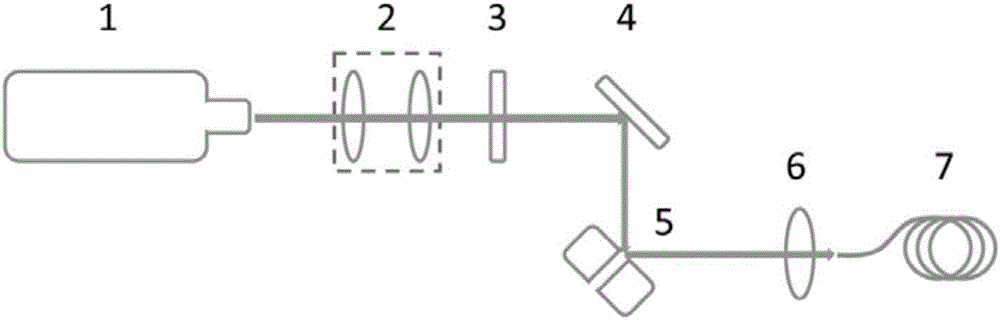
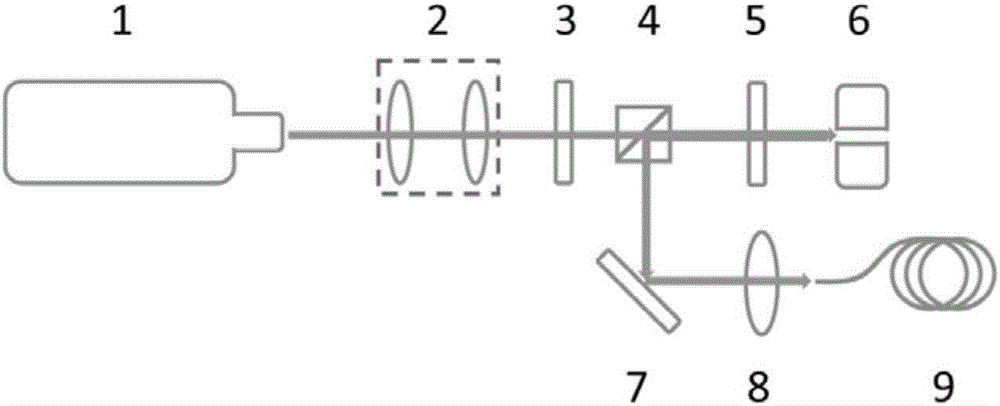
[0031] For reflective spatial light modulators, the figure 2 and image 3 The setup shown performs spot homogenization. figure 2 and image 3 The main difference is how reflective spatial light modulators are used. figure 2Using a non-perpendicular angle of incidence, image 3 Use a normal angle of incidence. figure 2 and image 3 The choice of depends on the requirements of the reflective spatial light modulator. Since spot homogenization does not require high modulation depth and modulation accuracy, try to use figure 2 The light path structure shown is more convenient to realize.
[0032] figure 2 The beam of the medium and high power semiconductor laser firstly generates a collimated beam of appropriate size through an optical beam expander or beam shrinker system, then adjusts the polarization direction through a half-wave plate, is reflected by a mirror to a reflective spatial light modulator for spatial mode modulation, and then passes through The fiber c...
Embodiment 3
[0036] For embedded spatial light modulators, the Figure 4 The setup shown performs spot homogenization. The collimated beam (with collimating lens system) generated by the high-power semiconductor laser tube is modulated by the integrated spatial light modulator system and then coupled into the multimode fiber by the modular fiber coupling system. Optical base housings are used to mechanically secure and protect the above optical components. Since the spatial light modulator is integrated into the laser system, the whole system can directly obtain the uniform beam output from the multimode fiber, which is more convenient to use.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com