Patents
Literature
313 results about "Stress free" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
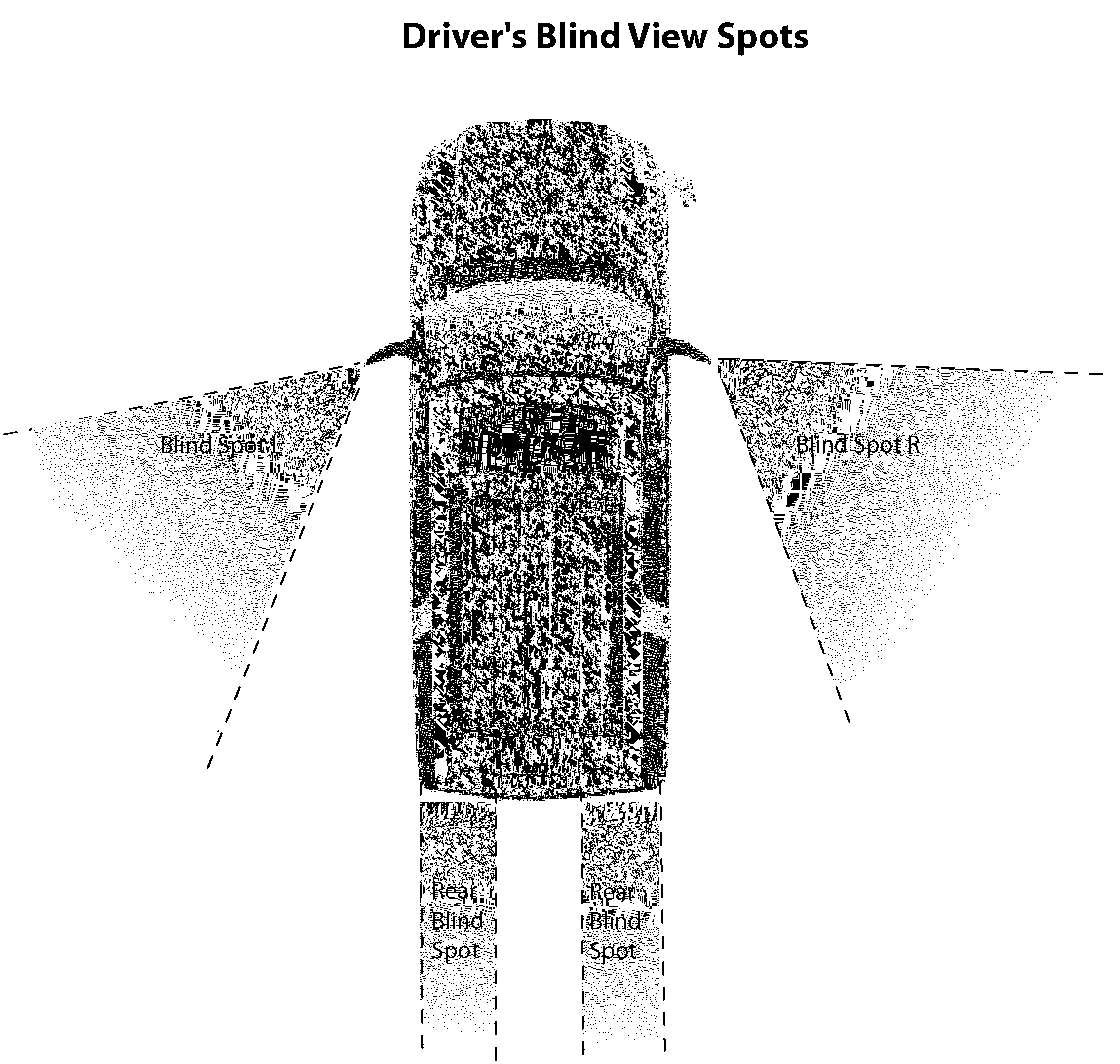
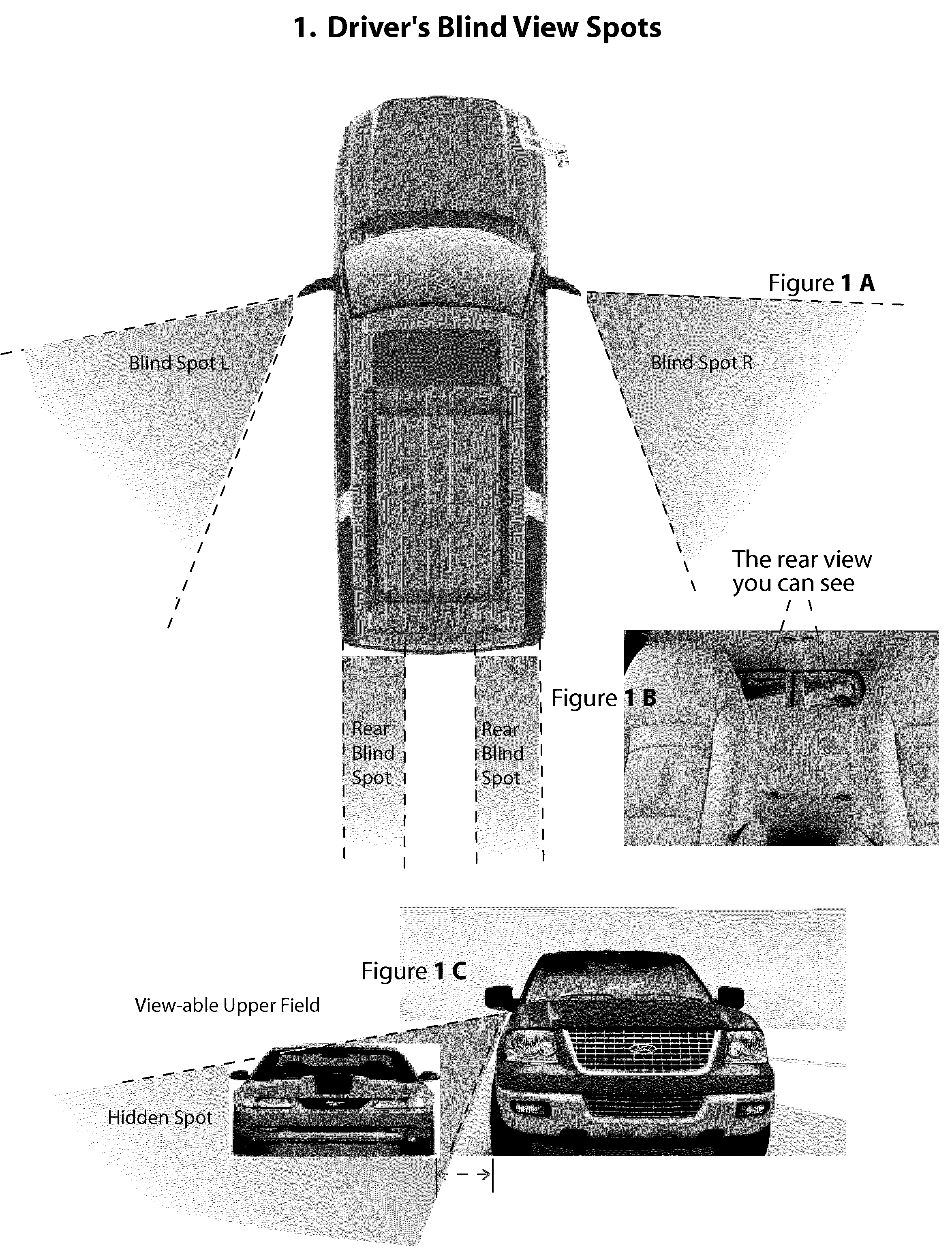
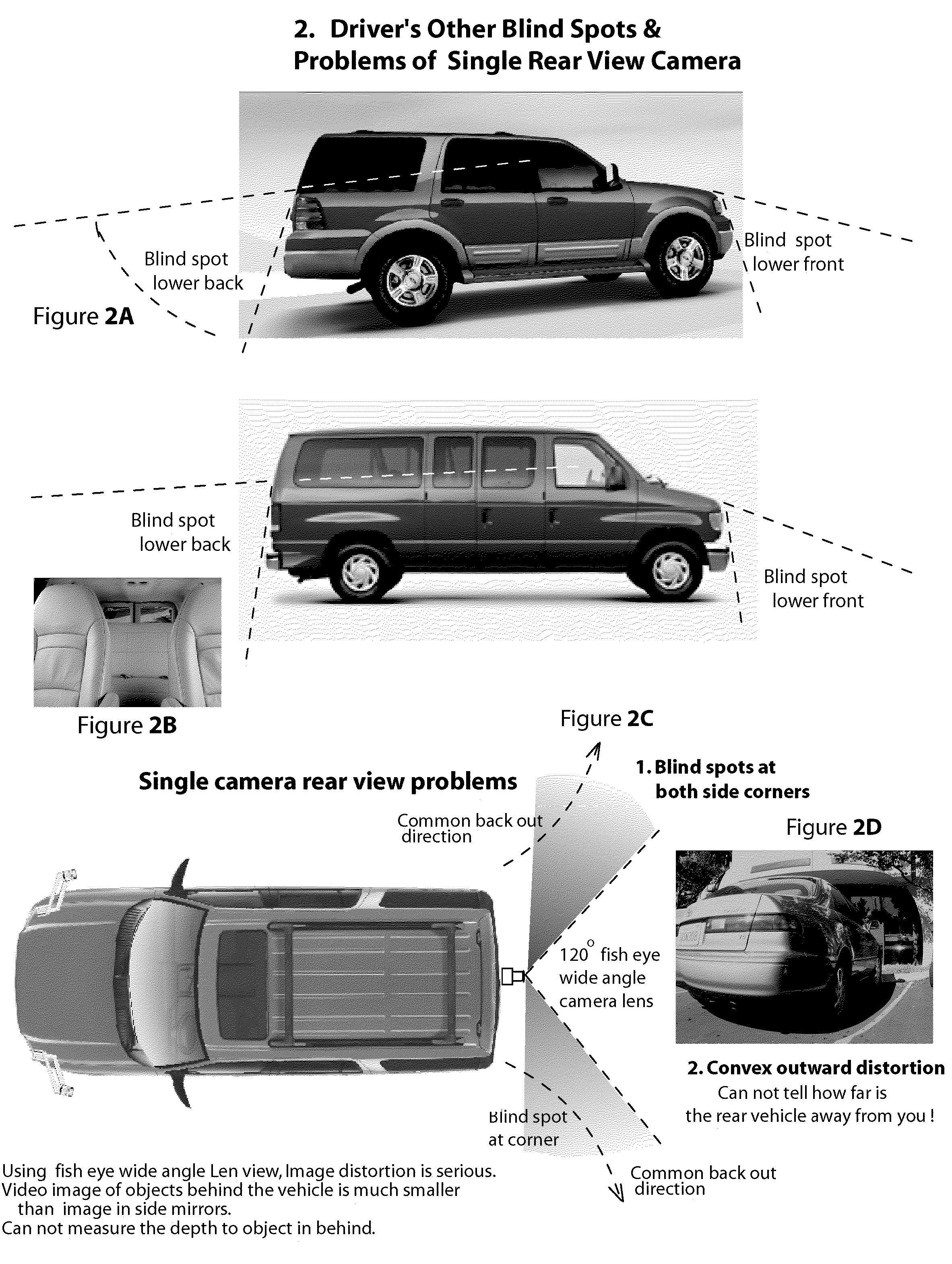
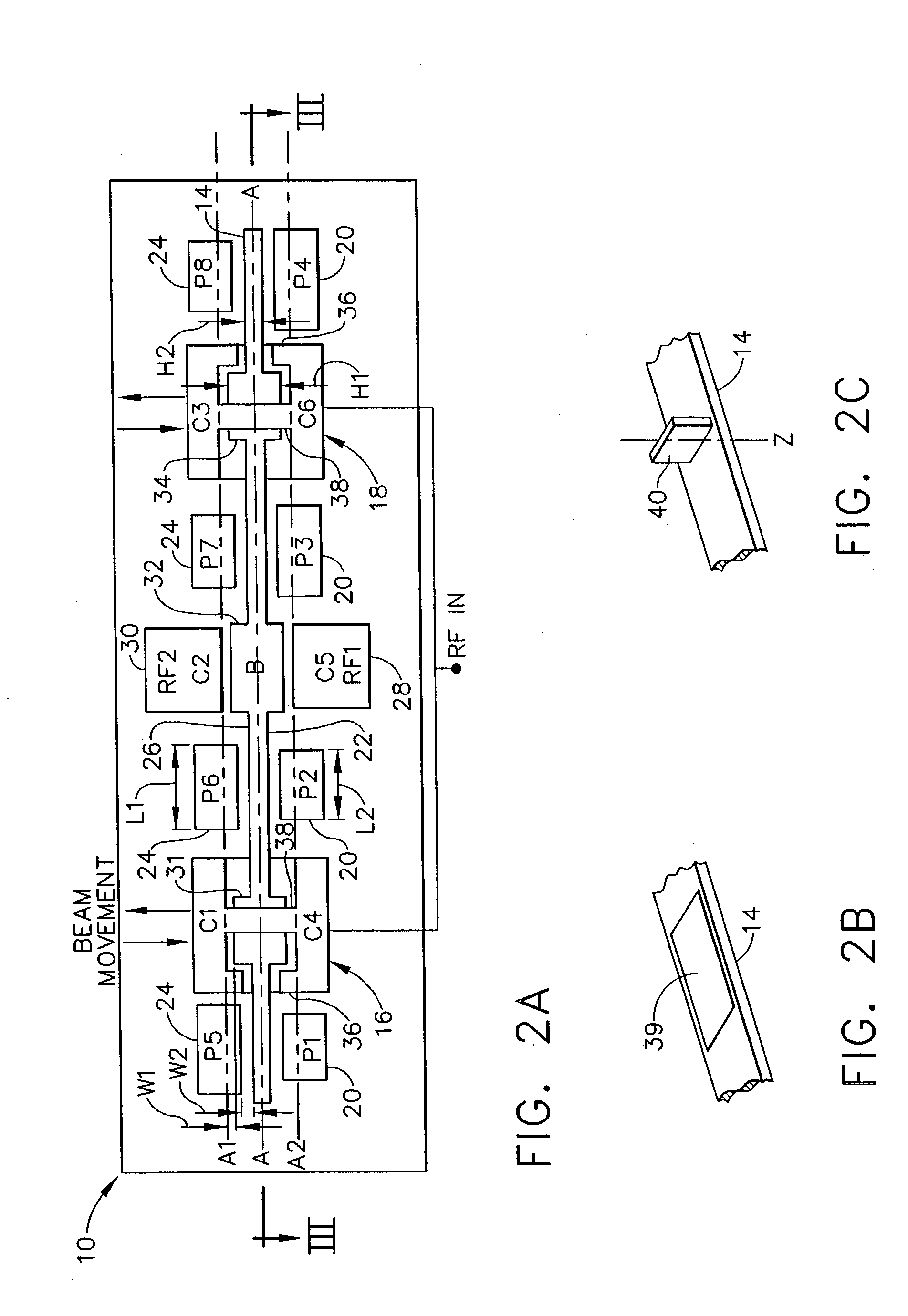
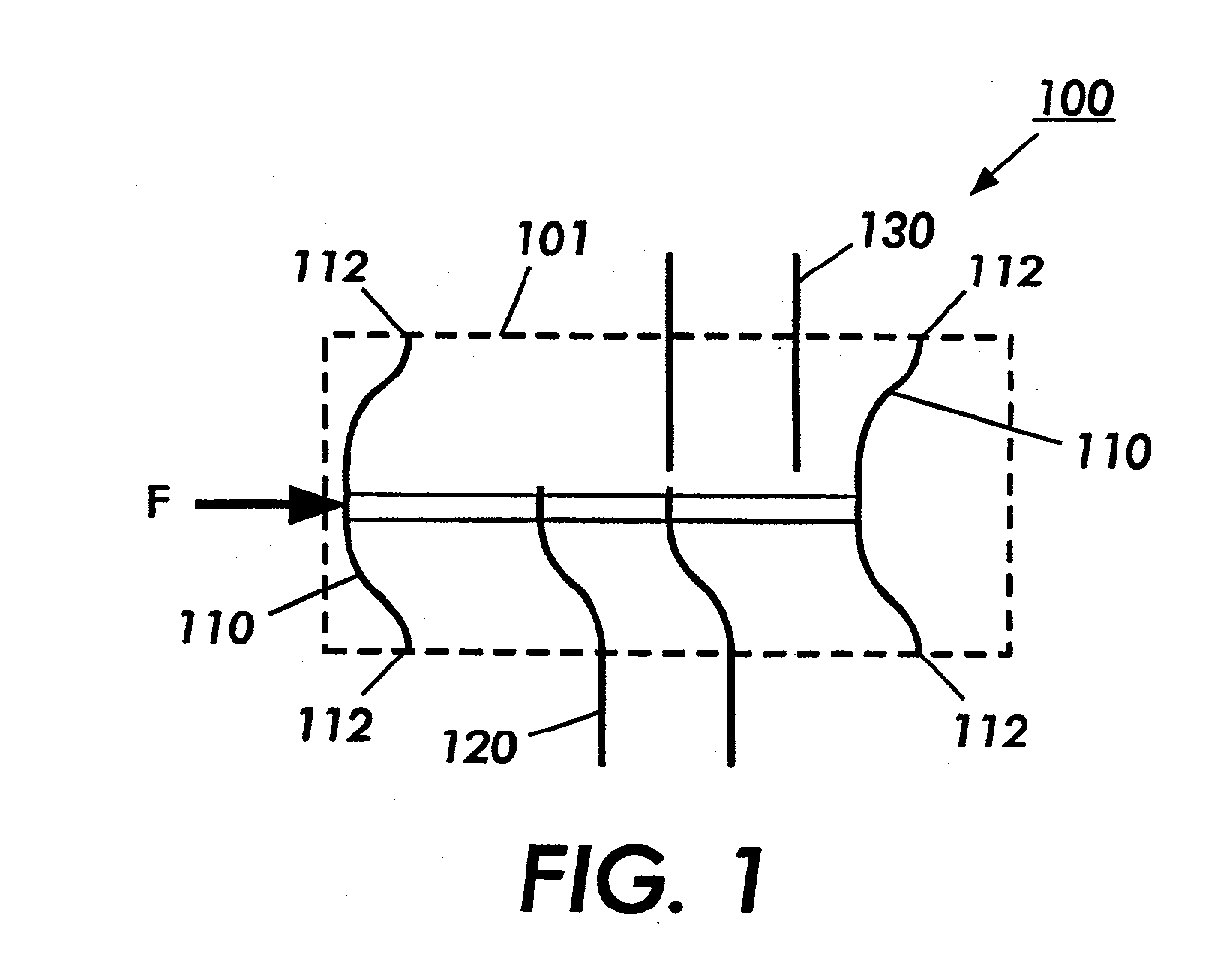
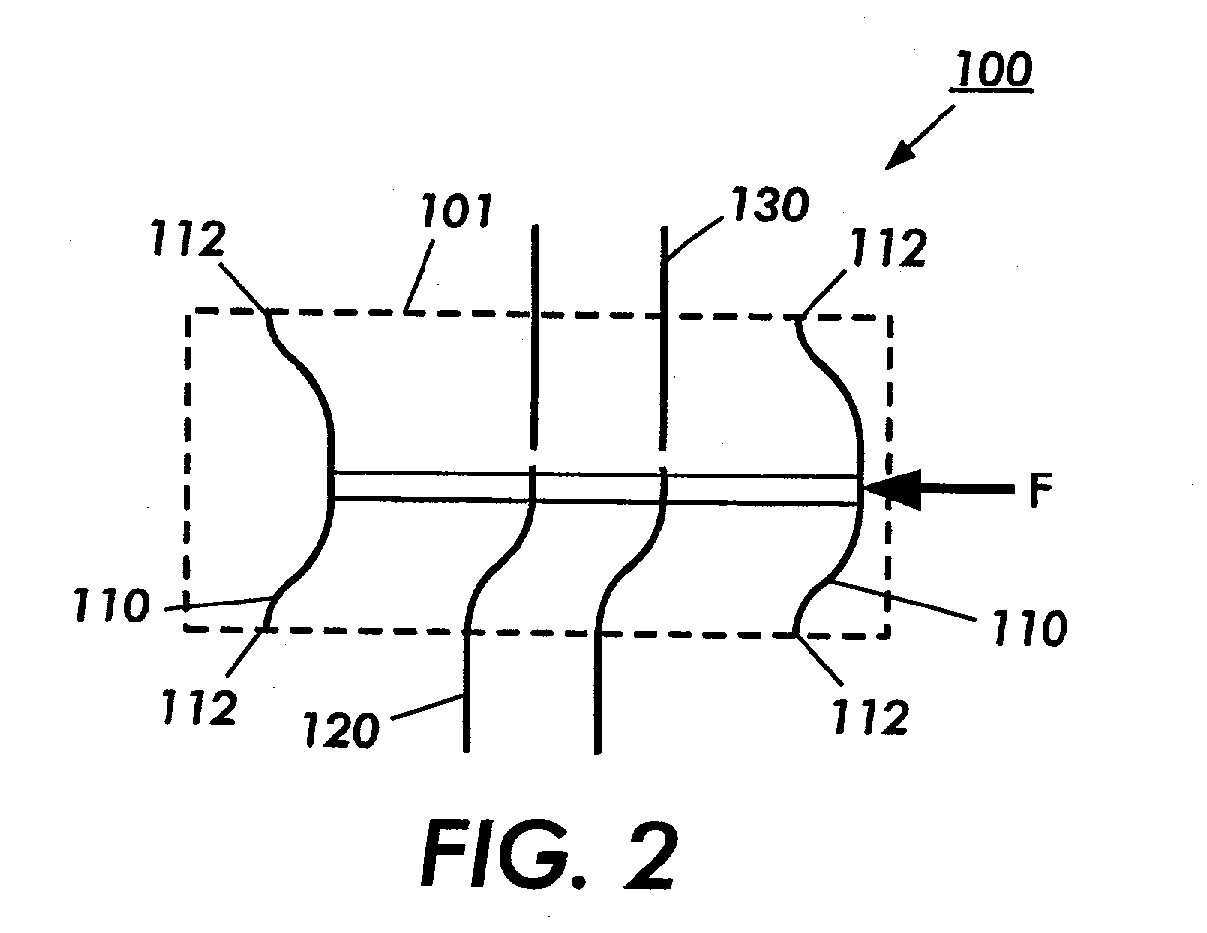
Object Approaching Detection Anti Blind e-Mirrors System
InactiveUS20050146607A1Improving driving safetyEasy to viewColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsDriver/operatorLow distortion
The e-Mirrors system promotes a new standard of driving safety views device, which upgrade regular glass mirrors from optical reflective to optoelectronic. The e-Mirrors system overcomes lots problems of conventional mirrors: blind spots, poor rear view, poor object approaching view etc. Variety new design vehicles made in the century 21 need higher standard safety view devices to drive in more & more crowded traffic system since population is growing rapidly. Time to change! Trend to go optoelectronic safety view. The e-Mirrors system integrates ultra night vision multi micro CCD cameras, high definition low distortion Lens, multiple mini LCD panels, New concept design camera mounts, video processor (or switch) all in 1. Each component apply unique design, each view setting has its technique. Using e-Mirrors to fill the absence of central rear mirror in trucks and buses large vehicles, drivers will be stress free. Driving everyday becomes easy, safely and fun! After tested in many vehicles, this e-Mirrors system proofs the most creative and the state of the art safety device since the invention of airbag. Its application will significantly reduce the traffic accidents causing by driver's “did not see it” error every year. Airbags now are legal mandatory devices for motor vehicles. However, airbags deploy to reduce lost of lives only after the collision, not able to reduce traffic accidents. Wish this handy e-mirrors system, cost less than airbags, be the second mandatory device for all vehicles soon!
Owner:LINN ROMEO S
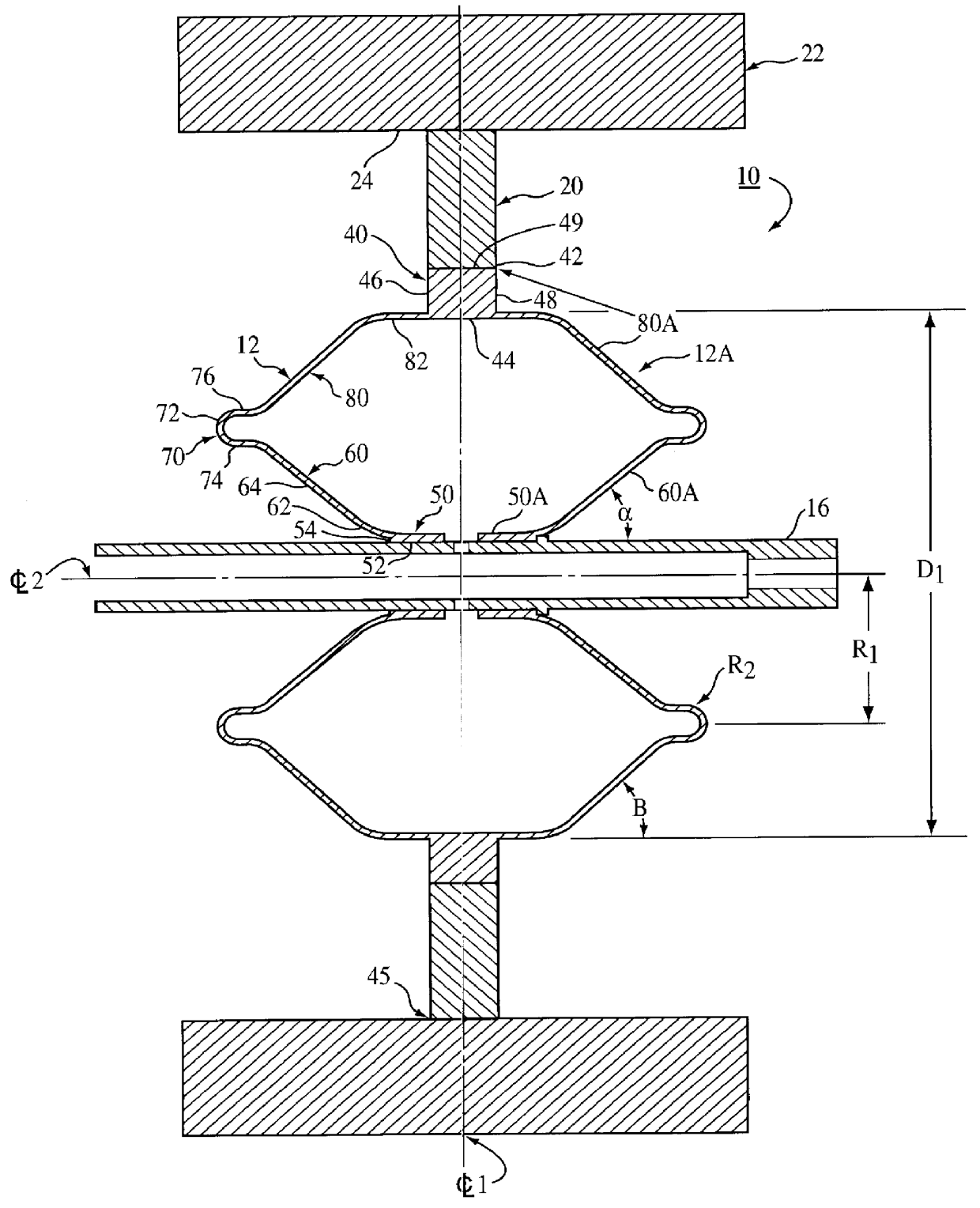
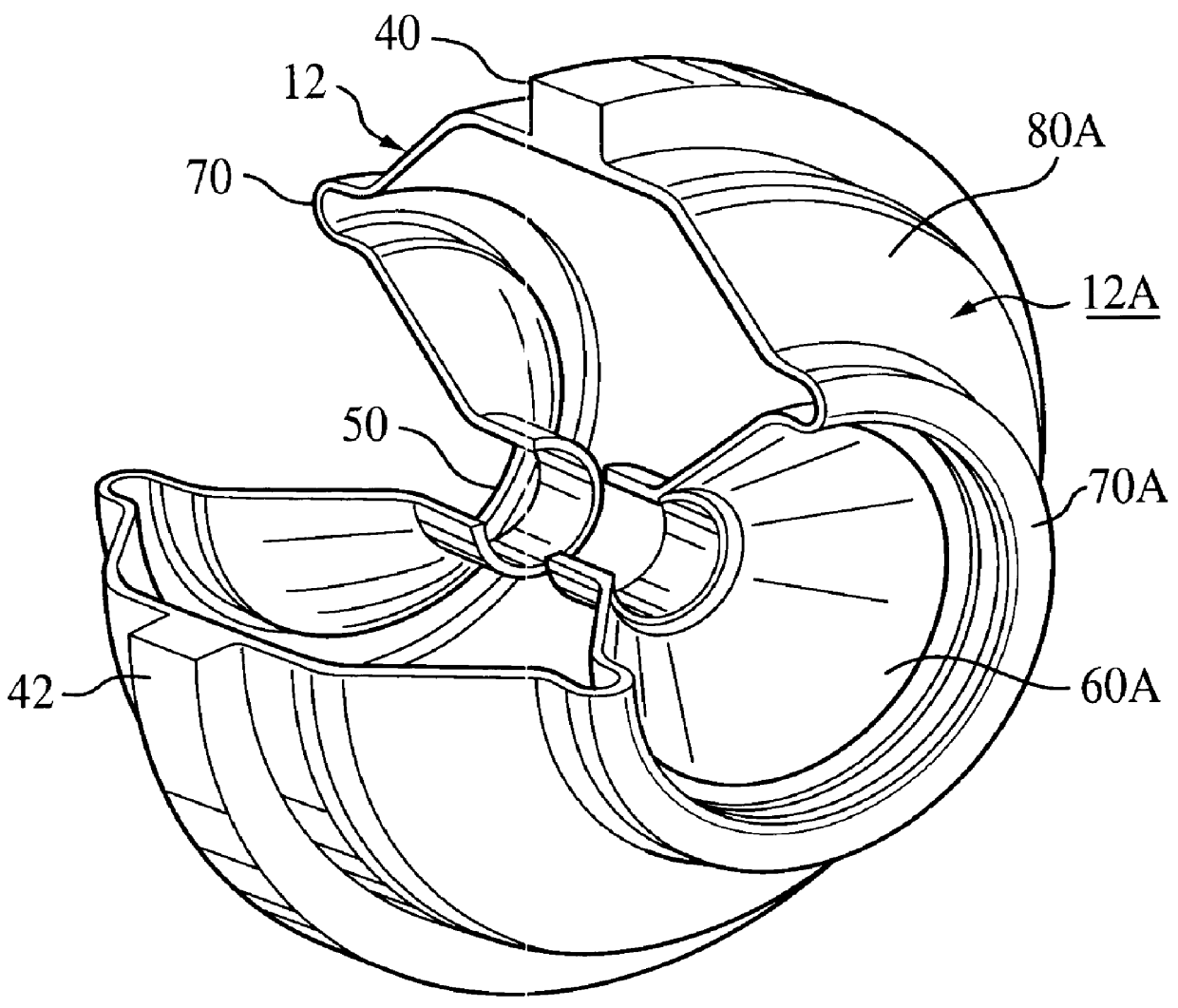
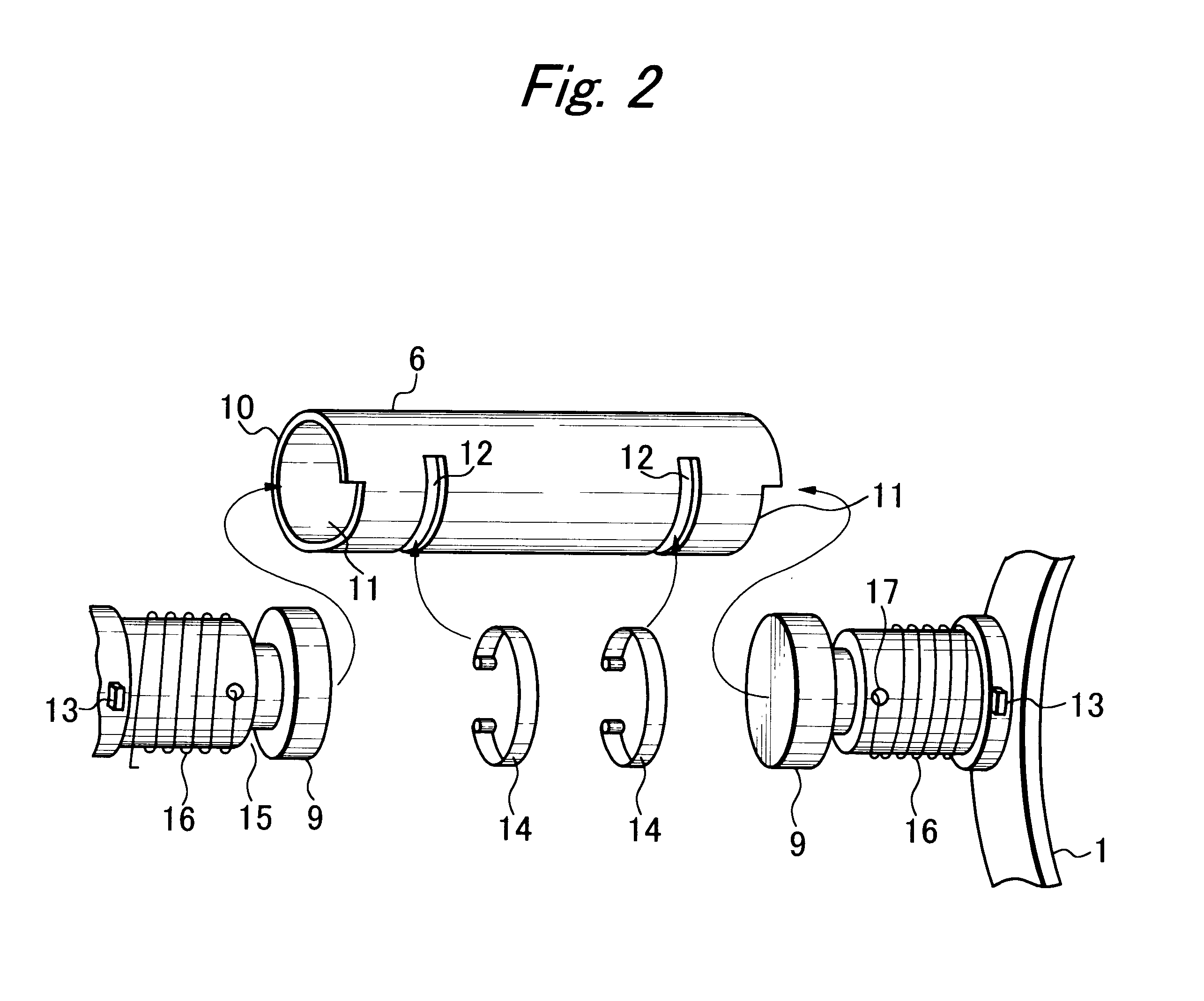
Flexible Intravascular Implant
InactiveUS20080195190A1High risk of damageHigh riskStentsBlood vesselsInsertion stentSacroiliac joint
The stent matrix of a stent incorporates joints that permit stress-free relative movement of first and second structural portions (10, 12) of the matrix as the facing surfaces of the joint between the structural portions slide relative to one another. The joints are formed in the thickness of an annular wall of the stent, and are created by a computer-controlled laser beam cutting procedure.
Owner:ANGIOMED GMBH & CO MEDIZINTECHNIK KG
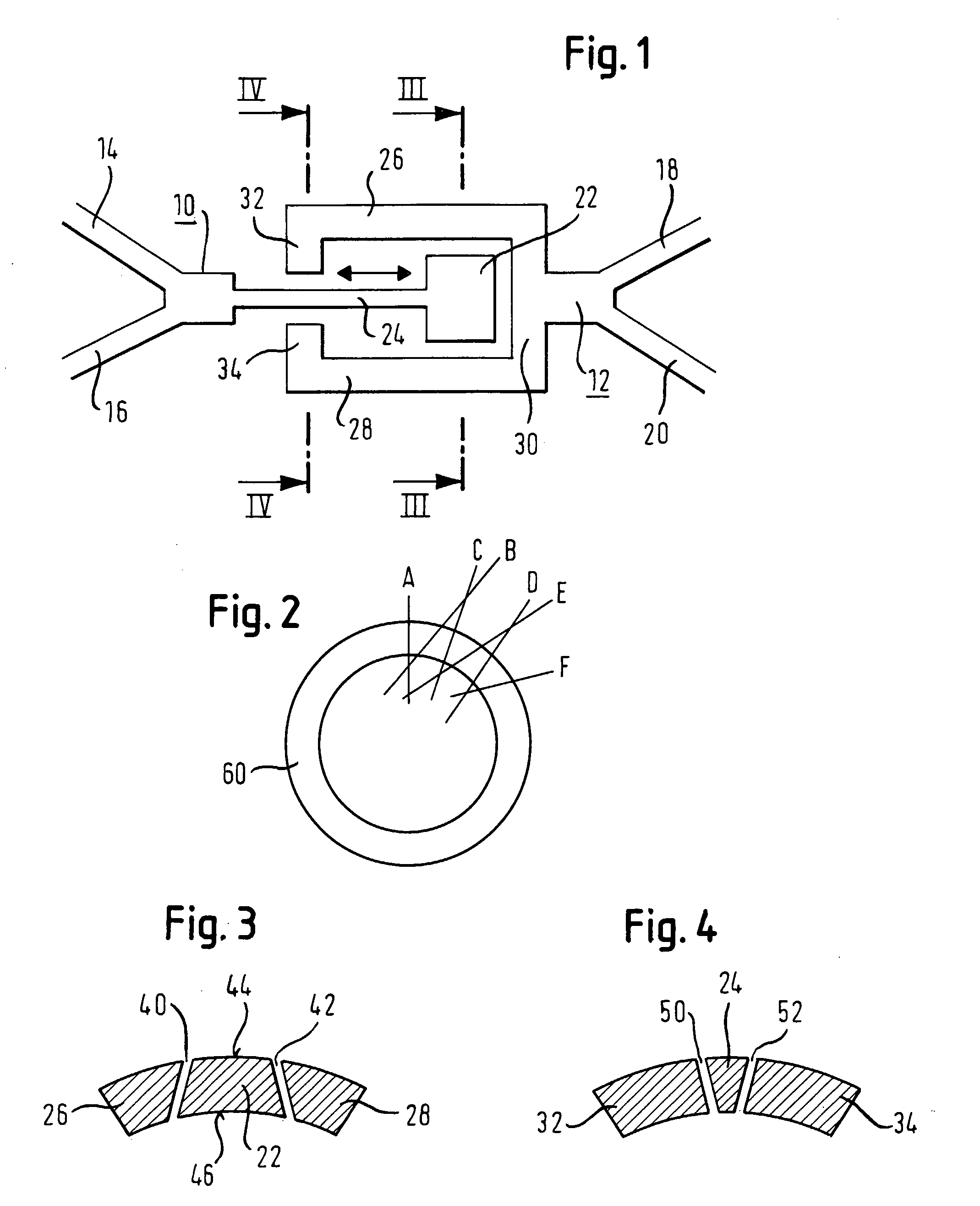
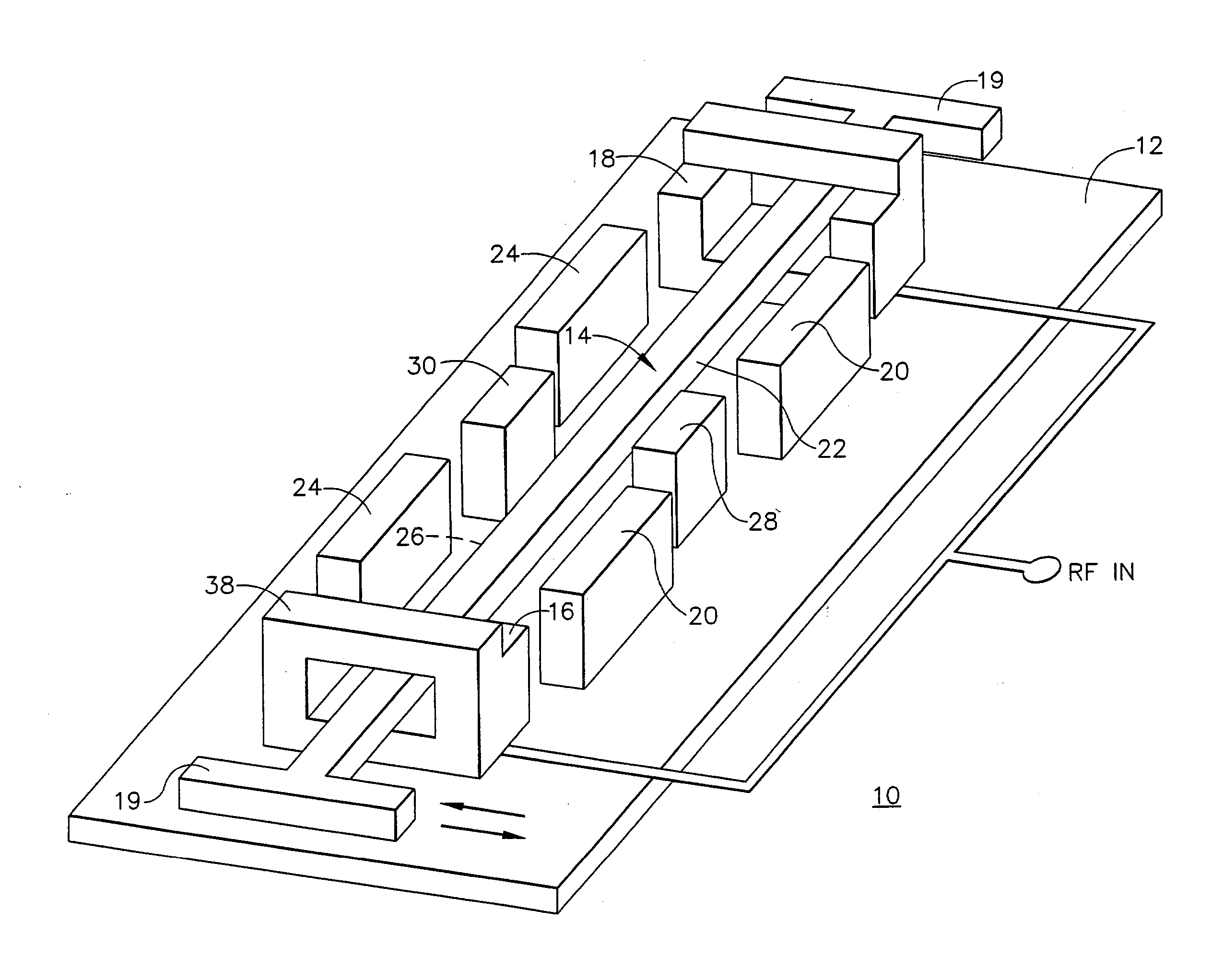
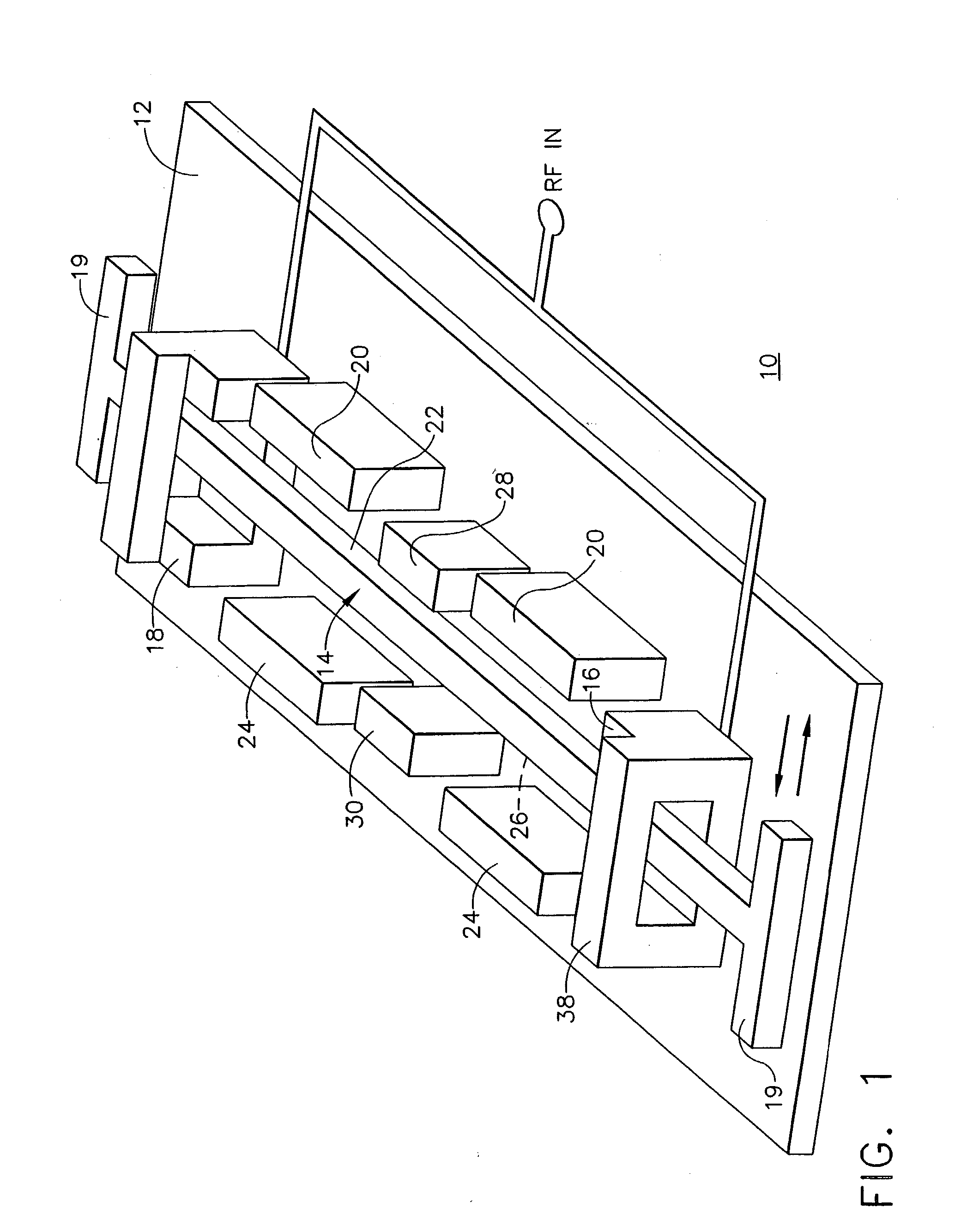
Anchorless electrostatically activated micro electromechanical system switch
InactiveUS20050068128A1Control displacementPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysEngineeringStress free
A micro electromechanical system (MEMS) switch (10) includes a substrate (12) and a stress free beam (14) disposed above the substrate (12). The stress free beam (14) is provided within first and second platforms (16, 18) to limit displacement of the stress free beam (14) in directions that are not substantially parallel to the substrate (12). A set of one or more control pads (20) is disposed in a vicinity of a first lengthwise side (22) of the stress free beam (14) for creating a potential on the first lengthwise side (22) of the stress free beam (14). The stress free beam (14) is displaceable in directions substantially parallel to the substrate (12) in accordance with the potential for providing a signal path.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
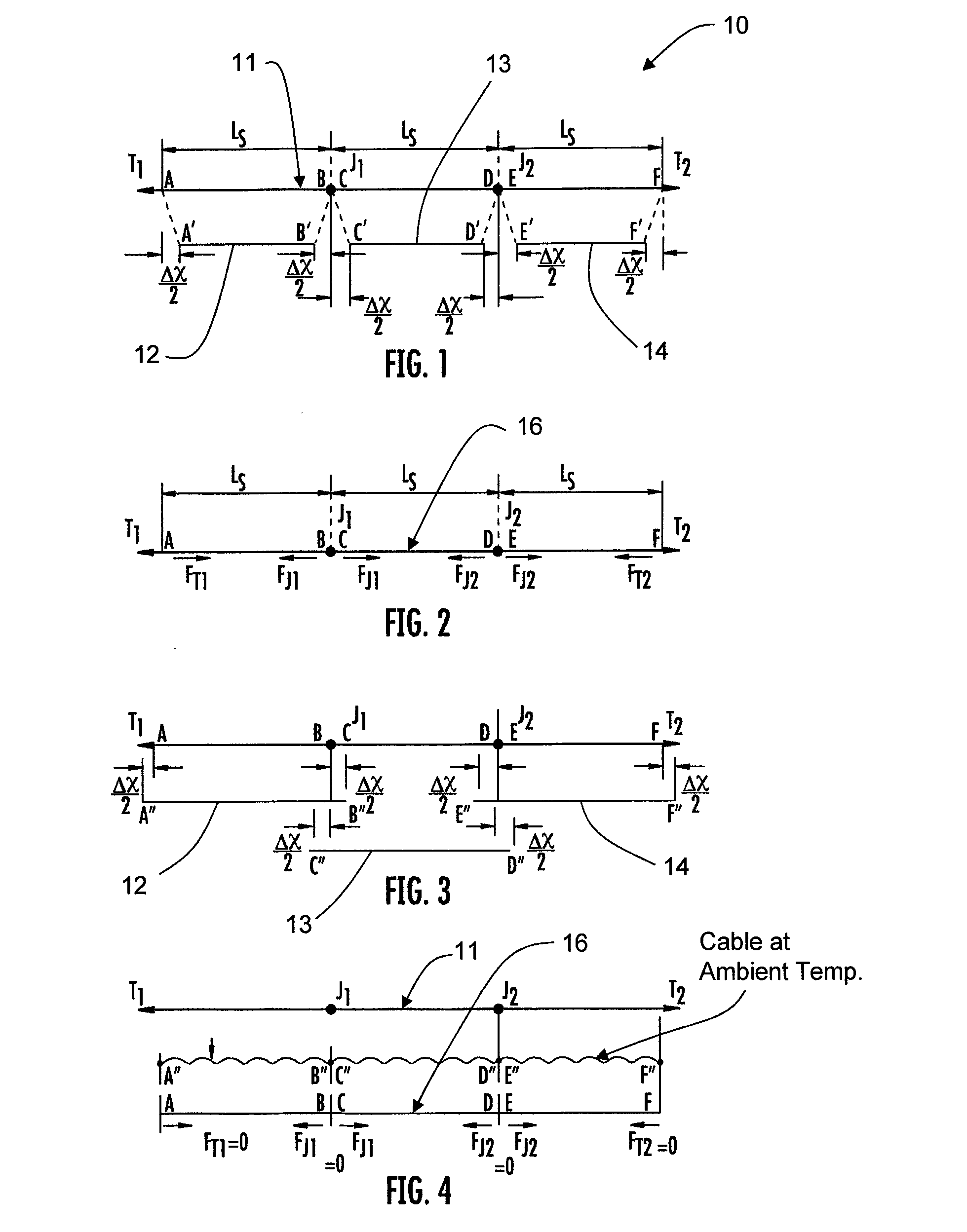
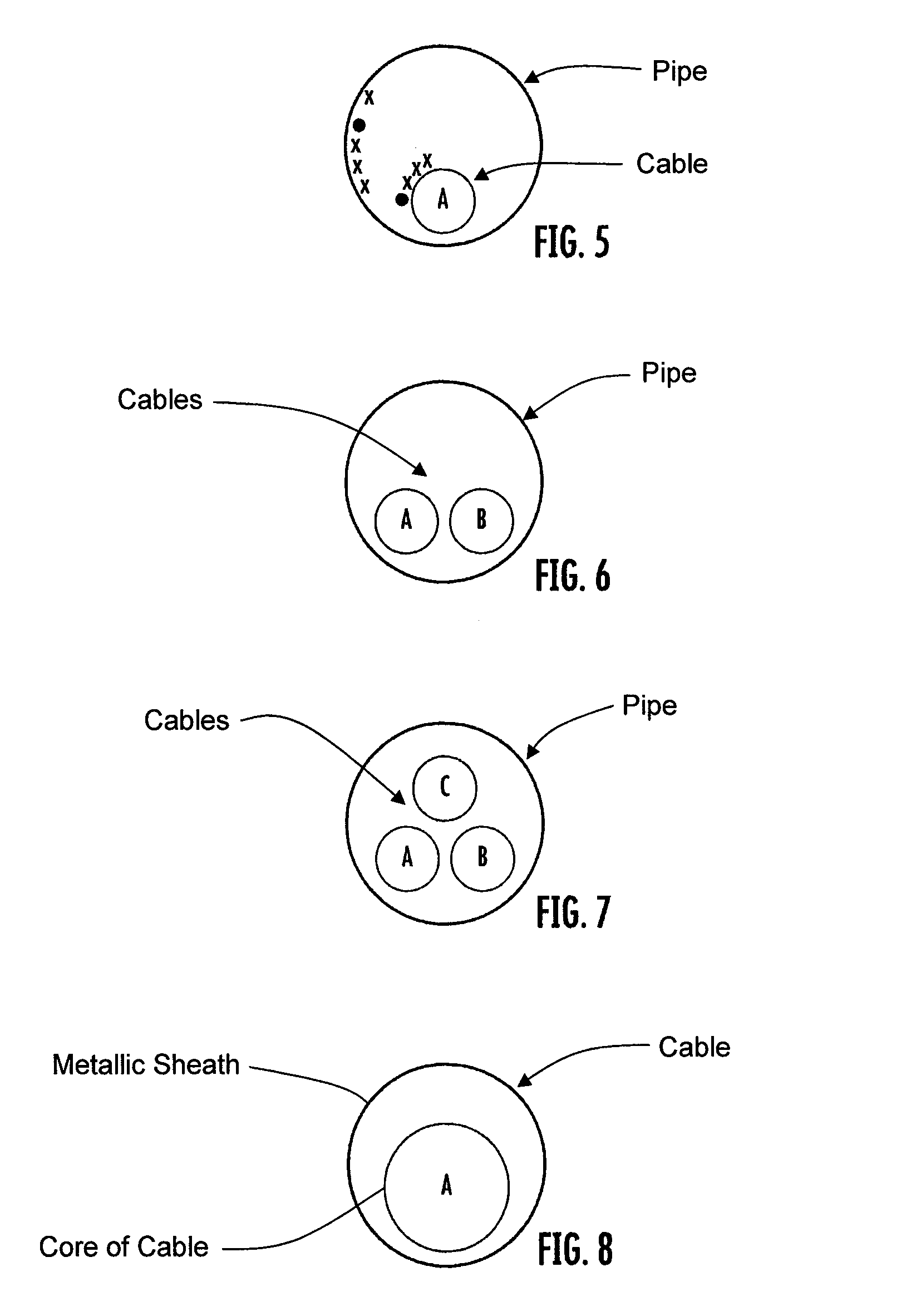
Thermal contraction compensation for superconducting and cryo-resistive cables
InactiveUS20100285968A1Eliminate and reduce magnitude of thermomechanicalSuperconductors/hyperconductorsApparatus for feeding conductors/cablesEngineeringThermal contraction
A method of compensating for thermal contraction of superconducting and cryo-resistive cables. The method includes the steps of determining a compensation length for a cable such that when the cable is subjected to an operating temperature, the cable is in or near a stress-free state, and installing the cable into a pipe such that portions of the cable extend outwardly past ends of the pipe. The method further includes the steps of marking each end of the cable such that the determined compensation length is visibly shown, forcing the cable into the pipe at an ambient installation temperature such that a cable pattern is formed therein, and maintaining the cable in the pipe to prevent the cable from being pushed out of the pipe.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST INC
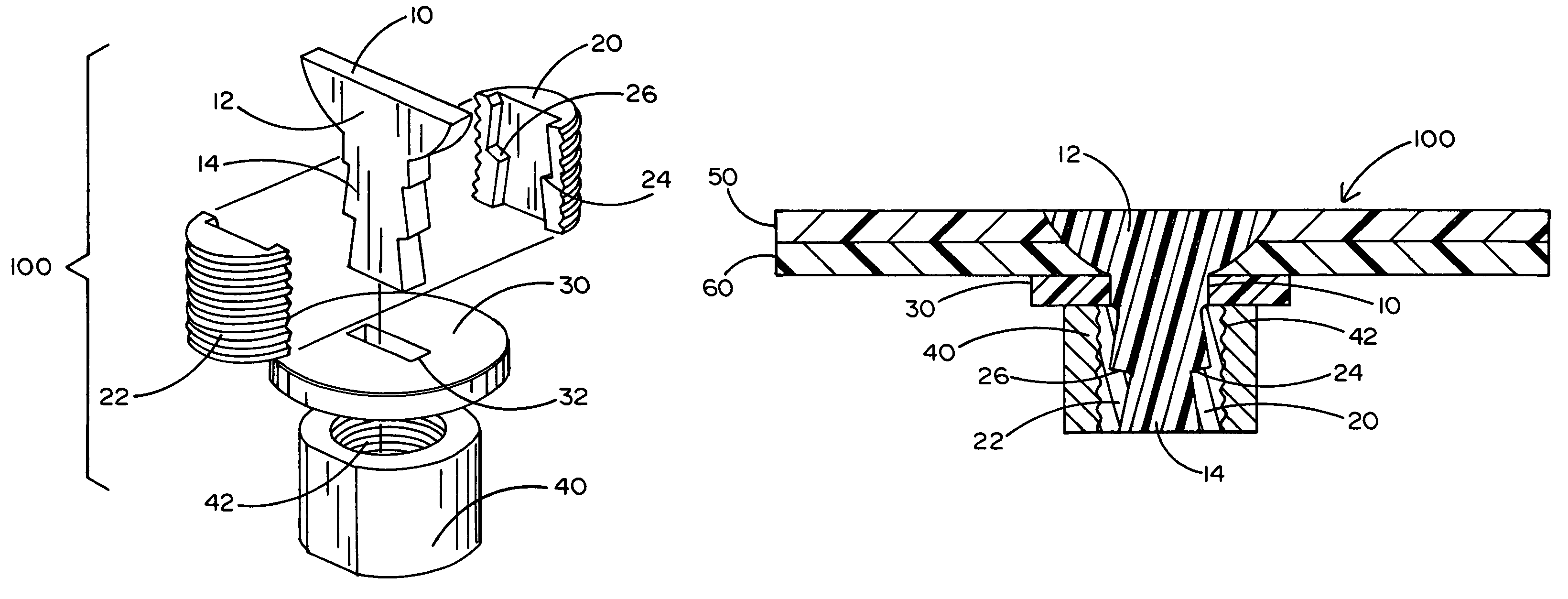
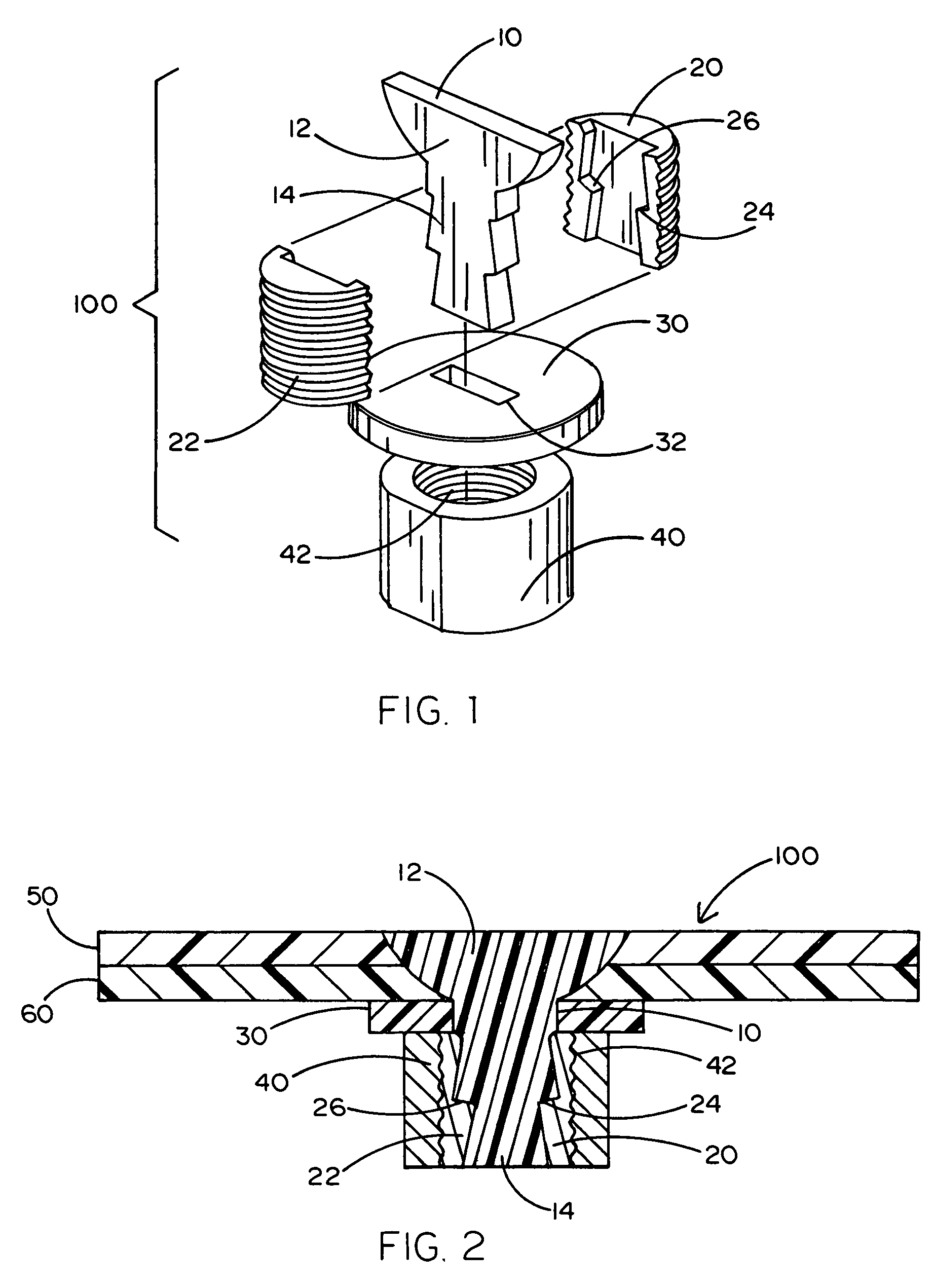
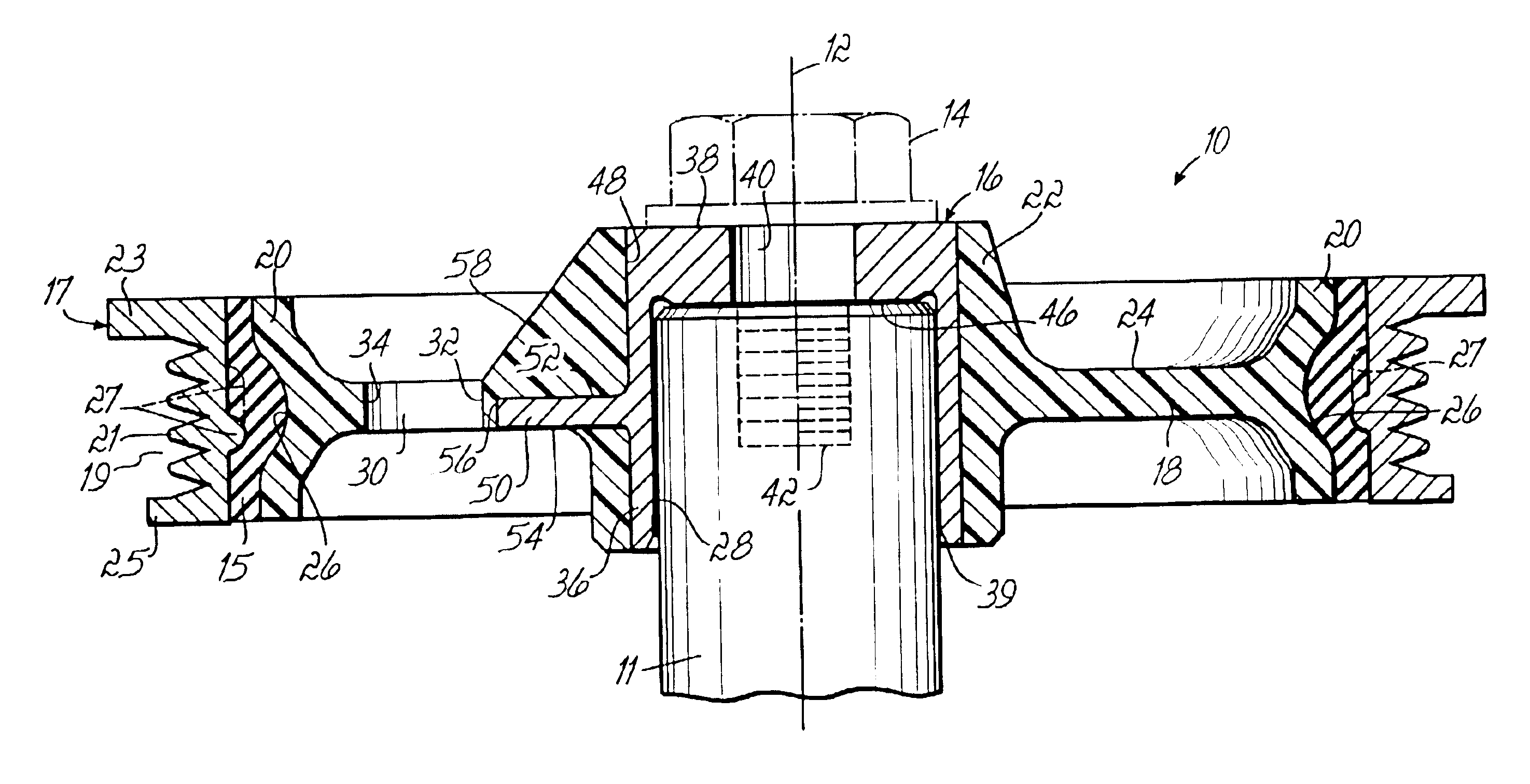
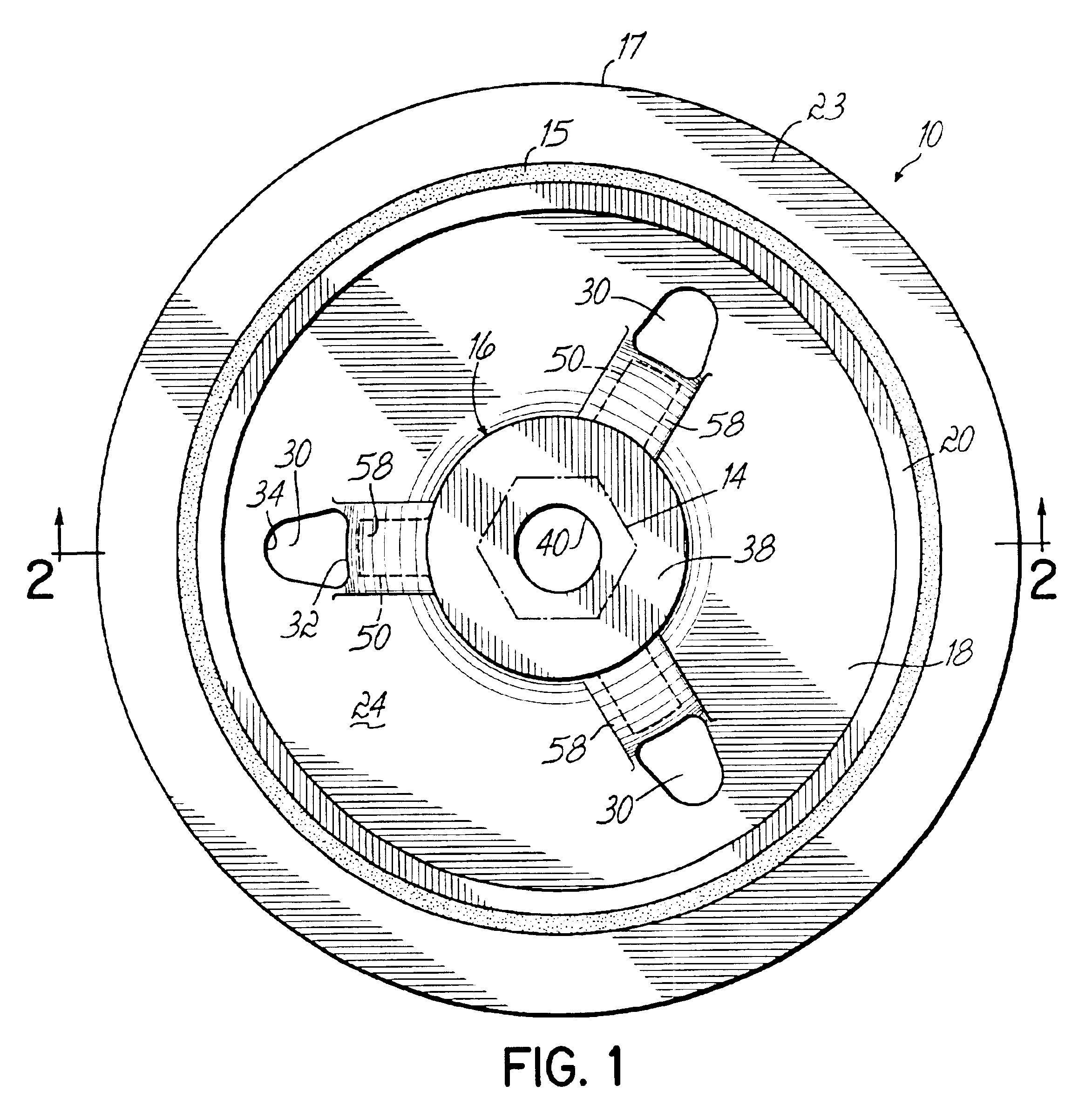
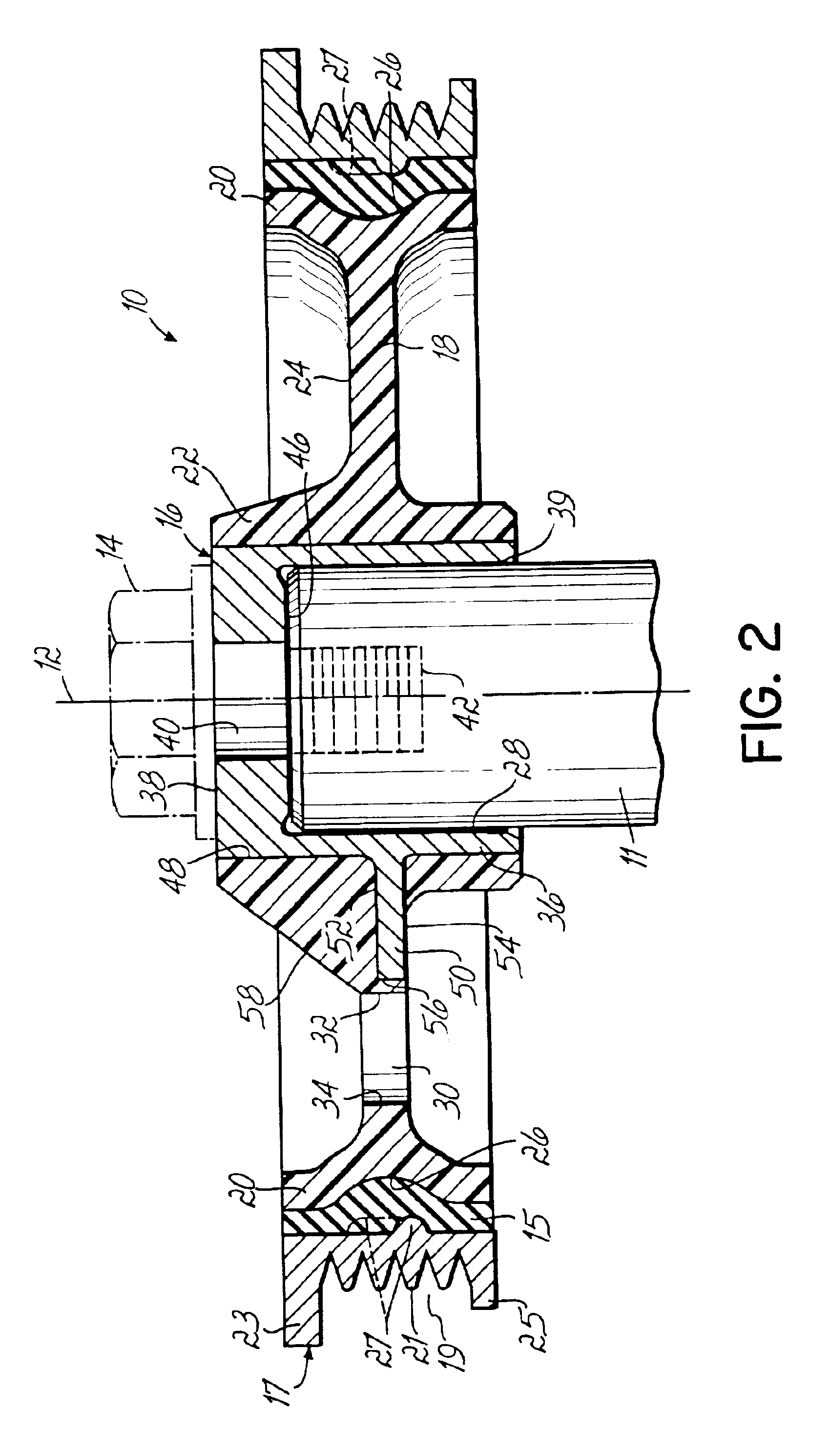
Mechanical fastener system for high-temperature structural assemblies
ActiveUS7988395B2Prevent removalAvoid separationNutsKey type connectionsMatched pairCeramic composite
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE HIGH TEMPERATURE COMPOSITES INC
Torsional vibration damper
InactiveUS6875113B2Without inflicting significant mechanical damageReliable mechanical interconnectionRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingRotational axisSnubber
A torsional vibration damper mountable to a rotatable shaft. The torsional vibration damper is a composite structure including a body formed of a polymer, such as a glass-reinforced polyamide, that surrounds an insert formed of a structurally-rigid material, such as a metal. The insert includes one or more support flanges that extend radially outward into the polymer body. When the torsional vibration damper is removed from the rotatable shaft, axial forces applied to the damper are transferred by the support flanges to the insert such that the polymer body remains substantially stress-free. In addition to, or instead of, the support flanges, the insert may include torque-locking structure that locks the polymer annular body with the insert to prevent relative rotation therebetween.
Owner:DAYCO IP HLDG
Stress-free socketed optical display package with die non-rigidly attached to containment structure
A liquid crystal display package including a liquid crystal cell having a die with a pixel array, and a transparent plate attached to the die. A liquid crystal material is disposed in a gap region between the die and the transparent plate. The display assembly further includes a containment structure adapted to couple to and at least partially receive liquid crystal cell therein, and an electrical connector portion integrated with the containment structure. A plurality of conductive contacts are positioned in the containment structure for secured support thereof, and in substantially stress-free electrical connection with the pixel array. The conductive contacts further are configured to releasably couple to mating conductive contacts of an opposed electrical connector.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Bistable microelectromechanical system based structures, systems and methods
InactiveUS20030210115A1Increase flexibilityReduce complexityElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysCoupling light guidesStable stateThermal impact
A bistable microelectromechanical system (MEMS) based system comprises a micromachined beam having a first stable state, in which the beam is substantially stress-free and has a specified non-linear shape, and a second stable state. The curved shape may comprises a simple curve or a compound curve. In embodiments, the boundary conditions for the beam are fixed boundary conditions, bearing boundary conditions, spring boundary conditions, or a combination thereof. The system may further comprise an actuator arranged to move the beam between the first and second stable states and a movable element that is moved between a first position and a second position in accordance with the movement of the beam between the first and second stable states. The actuator may comprise one of a thermal actuator, an electrostatic actuator, a piezoelectric actuator and a magnetic actuator. The actuator may further comprise a thermal impact actuator or a zippering electrostatic actuator.
Owner:XEROX CORP
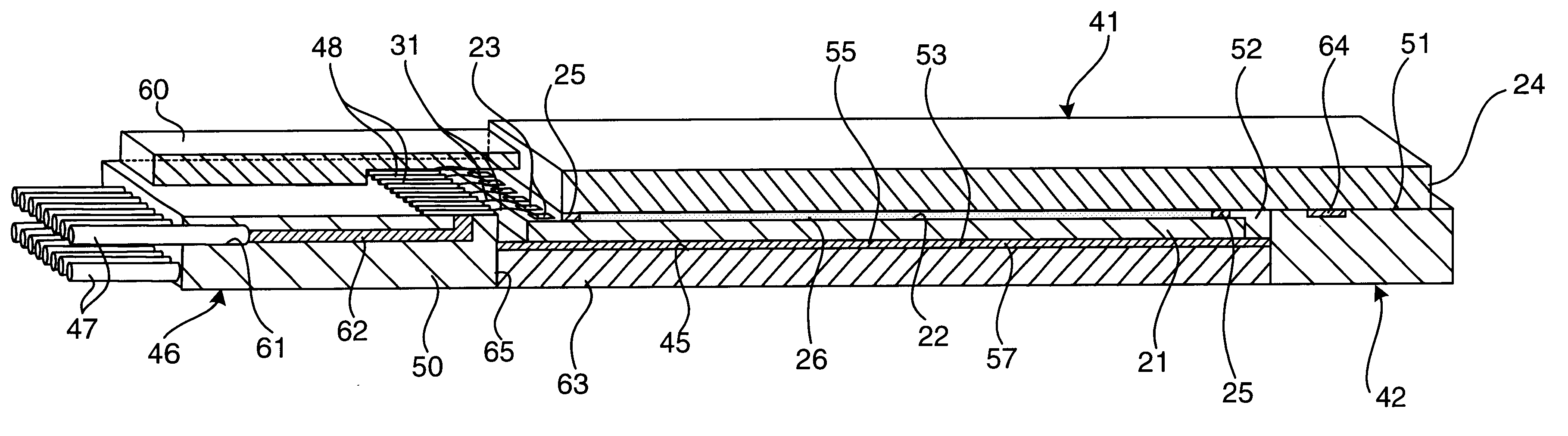
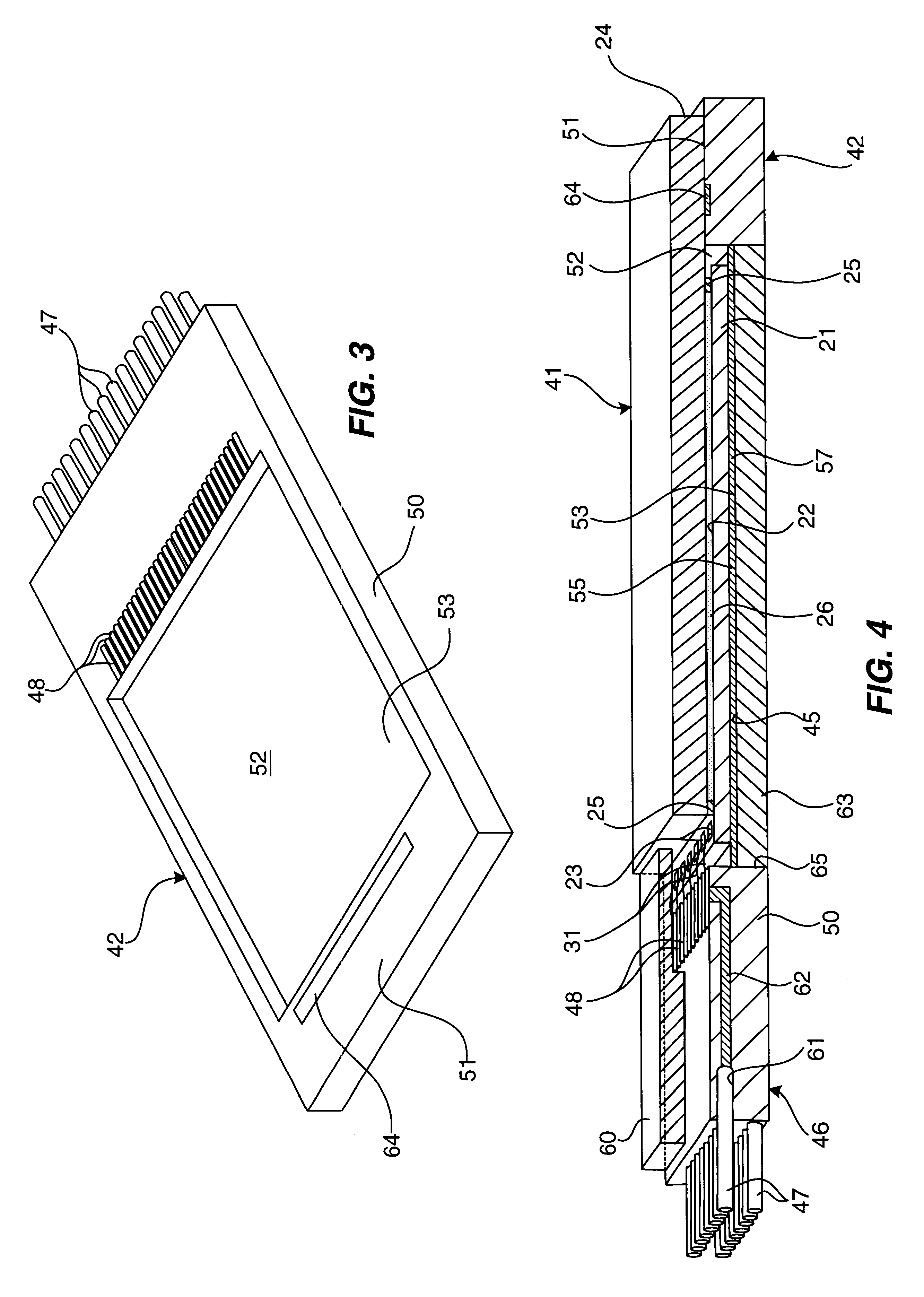
Stress free package and laminate-based isolator package
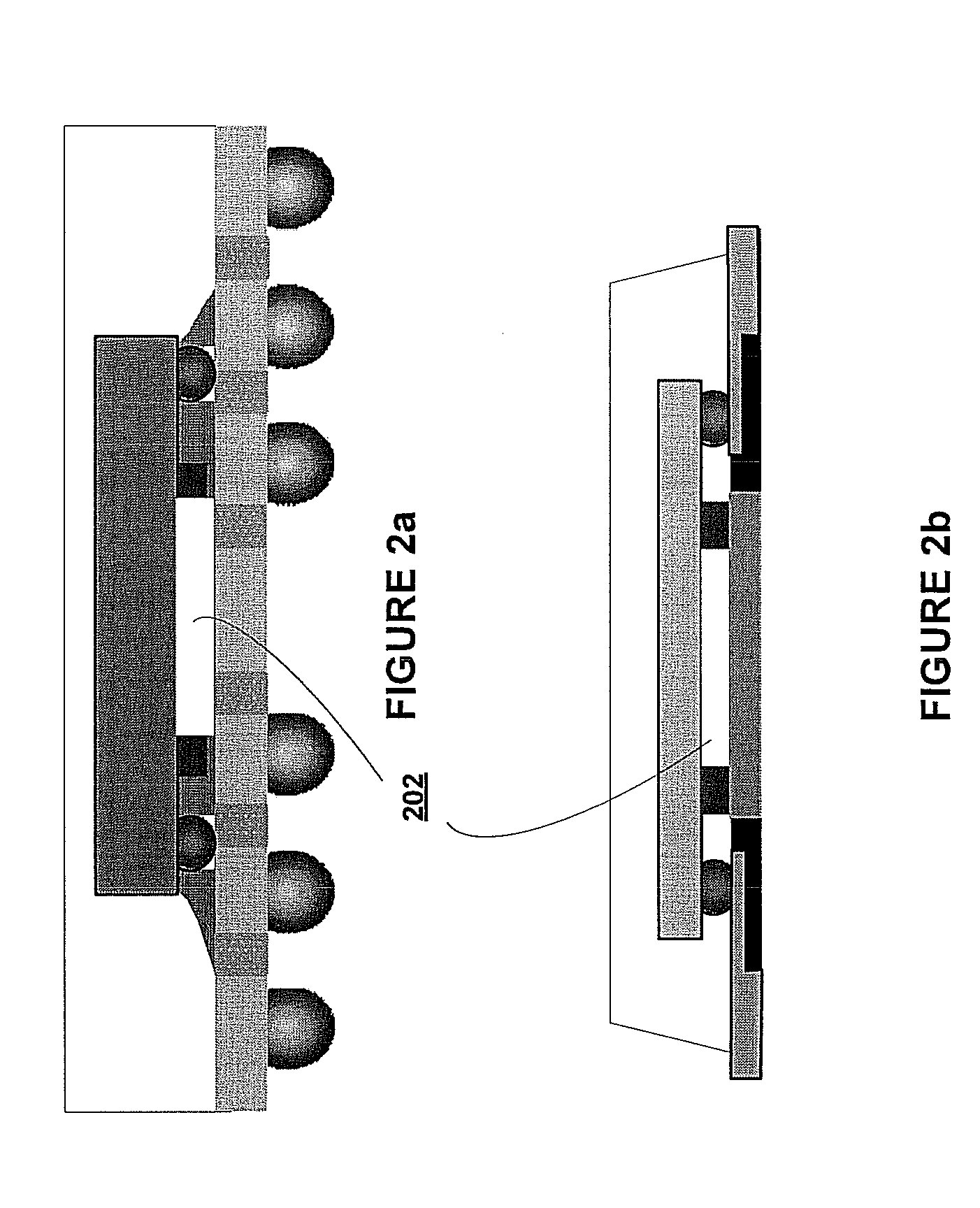
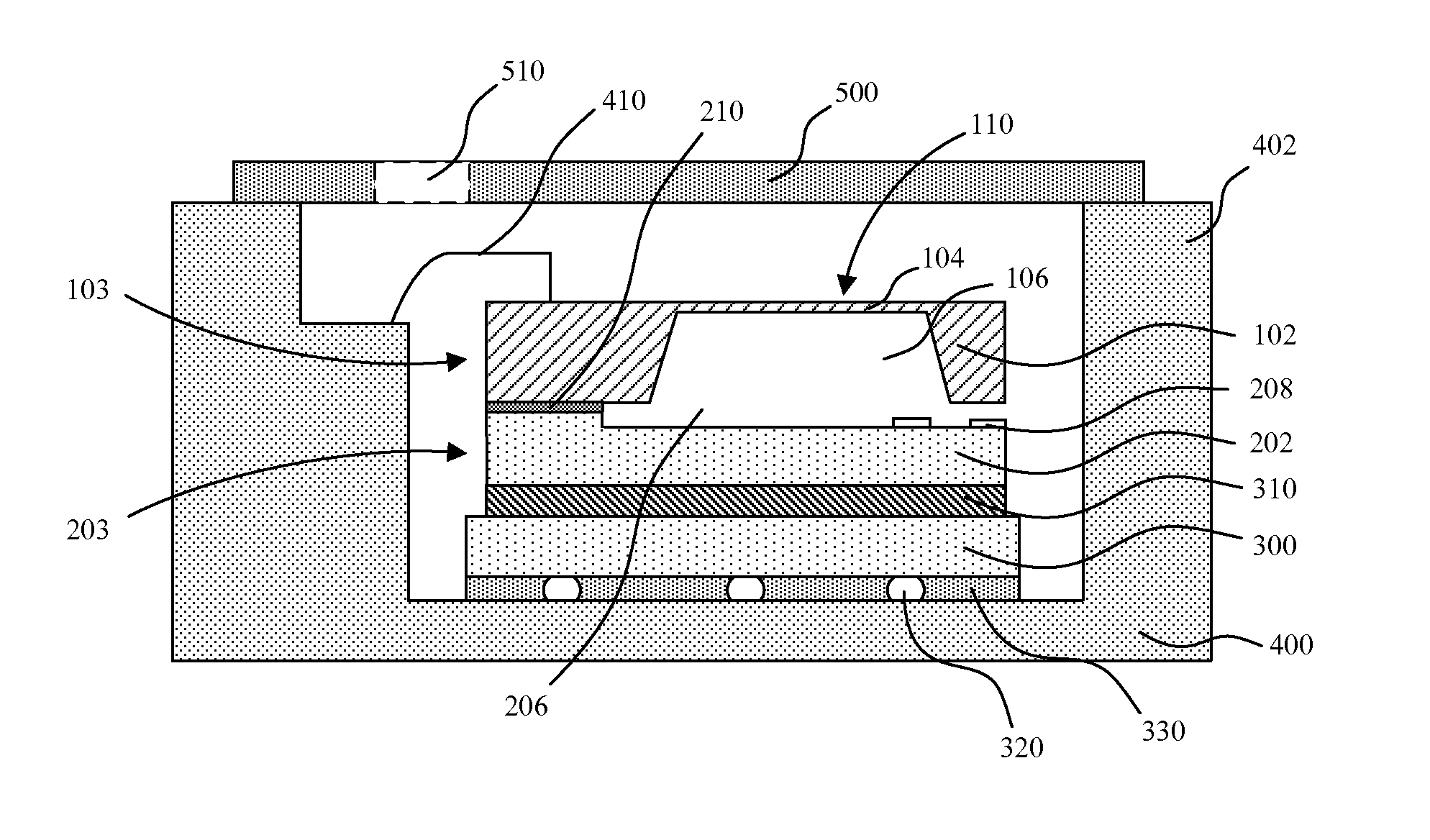
InactiveUS20080176362A1Relieve pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAnisotropic conductive filmCoupling
Various methods are described where the semiconductor die and the lead frame (or the BGA or LGA substrate) are spaced apart to reduce stress. In one scenario, an air gap is formed between the semiconductor die and the lead frame by depositing a perimeter (made, for example, using polymer) either on the semiconductor die or the lead frame. In another scenario, an anisotropic conducting film (ACF) is formed with an air gap between the semiconductor die and the lead frame (or the BGA or LGA substrate). The air gap relieves stress on the semiconductor die. Further, a lead frame-based isolator package and a BGA (or LGA) isolator package are described. A window-frame ACF-based isolation method for magnetic coupling in a lead-frame package and BGA (or LGA) package is also described.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Various stress free sensor packages using wafer level supporting die and air gap technique
ActiveUS20160061677A1Provide integrityFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsEngineeringForce sensor
Sensor packages and manners of formation are described. In an embodiment, a sensor package includes a supporting die characterized by a recess area and a support anchor protruding above the recess area. A sensor die is bonded to the support anchor such that an air gap exists between the sensor die and the recess area. The sensor die includes a sensor positioned directly above the air gap.
Owner:APPLE INC
Digitalized assembly system for bodies of large planes
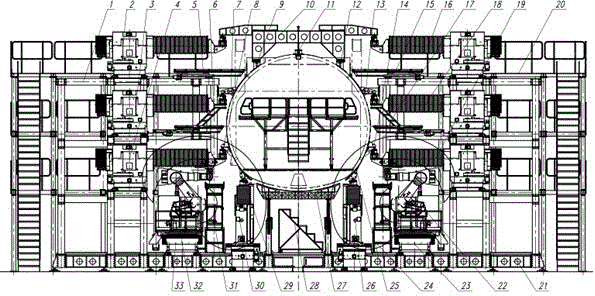
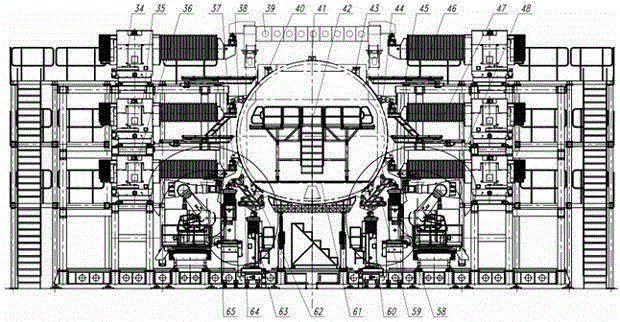
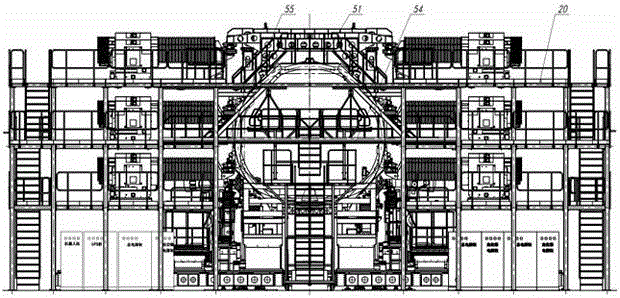
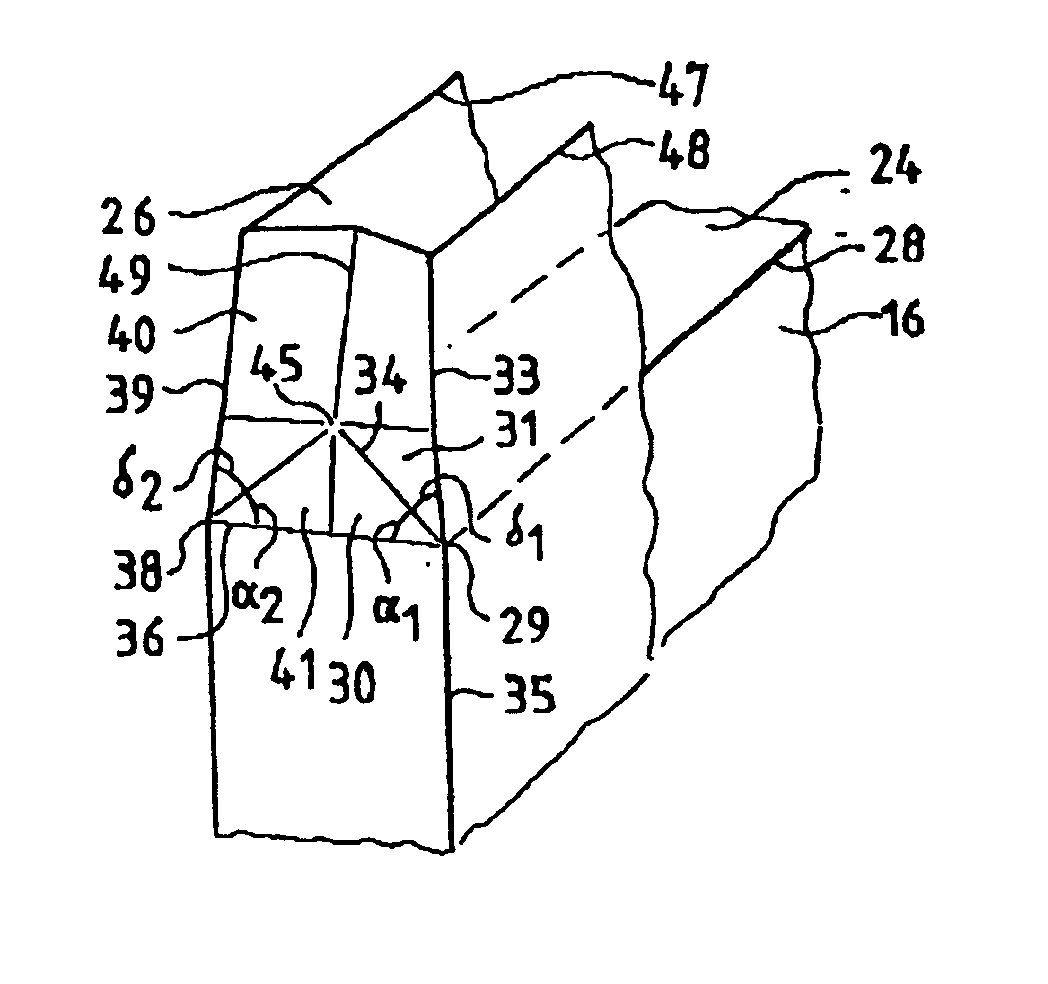
The invention discloses a digitalized assembly system for bodies of large planes. The digitalized assembly system comprises an attitude-adjusting positioning system base platform, an attitude-adjusting positioner unit, a shape-preserving frame, process connectors, end surface shape-preserving frame positioners, a process floor, a modularized external console and a robot machining plant. The digitalized assembly system integrates the numerically controlled positioners, the shape-preserving frame and the process connectors together to carry out flexible supporting, attitude adjustment and accurate positioning for each panel module and realize stress-free or low-stress assembly; the numerically controlled positioners can move in coordination to elastically restore deformed panel modules; the industrial robot holing technique and the industrial robot boring technique are adopted to increase the connection quality of opposite joint areas in body assembly, bore main intersection holes and increase the positional and surface precision of holes; the industrial robot-assisted assembly technique is adopted to accurately position and mount system parts; and by arranging the mounting positions of a plurality of numerically controlled positioners, the digitalized assembly system can be adapted to the change in the length of a body, and has certain scalability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Foil-enveloped evacuated thermal insulation elements
The invention relates, on the one hand, to a prismatic, especially panel-formed thermal insulation element which is enveloped in a gas-tight foil and evacuated, whereby a stable core pre-formed from a porous material is completely enveloped in a single cut sheet of the gas-tight foil; as well as a manufacturing process for same comprising the following steps:a) Manufacture of a prismatic core corresponding to the desired form of the thermal insulation element from a porous material;b) Enveloping of the principal faces of this core with a single sheet of the gas-tight foil;c) At least partial welding together of the foil which is drawn tight around the core along the face of the core;d) Folding-in of the welded seam area of the foil against the face of the core;e) Stress-free folding-together of the areas of the cut sheet of gas-tight foil projecting beyond the core, covering and in flat contact with the end surface(s) of the core;f) Welding together of the folded-together areas of foil on at least one end face of the core;g) Evacuation of the enveloped core;h) Complete welding closed of all remaining openings in the foil under vacuum.
Owner:VA Q TEC AG
Novel method to implement stress free polishing
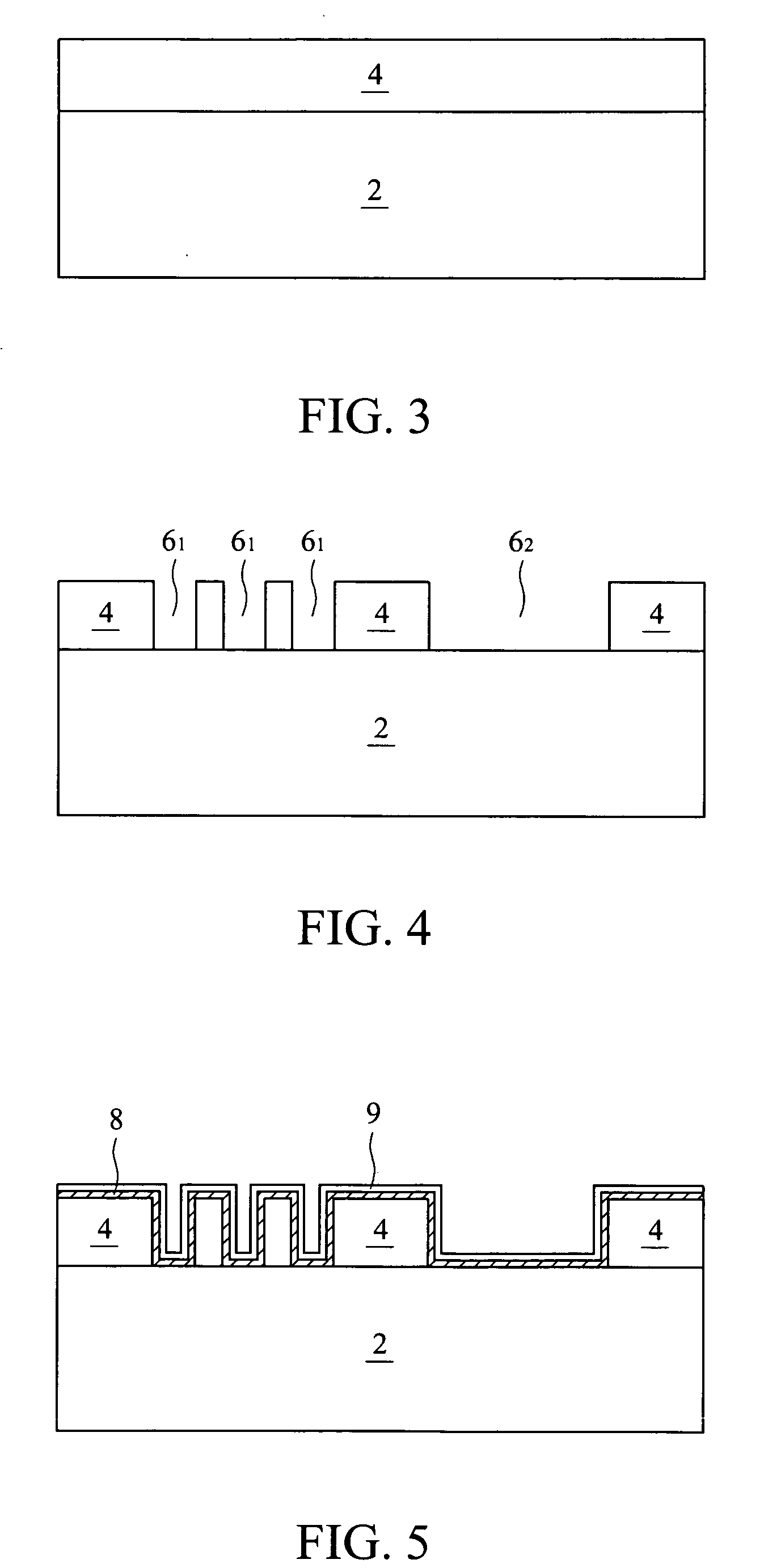
InactiveUS20060276030A1Maximum performanceLow production costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStress freeMetal
A method of forming a metal feature in a low-k dielectric layer is provided. The method includes forming an opening in a low-k dielectric layer, forming a metal layer having a substantially planar surface over the low-k dielectric layer using spin-on method, and stress free polishing the metal layer. Preferably, the metal layer comprises copper or copper alloys. The metal layer preferably includes a first sub layer having a substantially non-planar surface and a second sub layer having a substantially planar surface on the first sub layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Display element stress free at the critical layer
InactiveUS20060132030A1Avoid stress-induced damageAvoid failureDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceOperating temperature range
The invention relates to a display device, and more particularly a flexible display device comprising display component layers and display substrate such that the display remains substantially flat throughout the operating temperatures. The invention further relates a display device, and more particularly a flexible display device comprising display component layers and display substrate such that the stress in at least one layer of the light-emitting module in the display is substantially zero throughout the operating temperature range. These and other objects of the invention are accomplished by providing a flexible display, comprising at least one planar flexible substrate, at least one flexible light-emitting module deposited on the flexible substrate, the light-emitting module including at least one light-emitting layer, an anode, a cathode, and at least one top flexible superstrate on the opposite side of said display from said planar flexible substrate wherein the display is thermoelastically balanced in such a way that the display is always substantially flat, and the stress in at least one layer of the light-emitting module is substantially zero throughout the operating temperature range.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
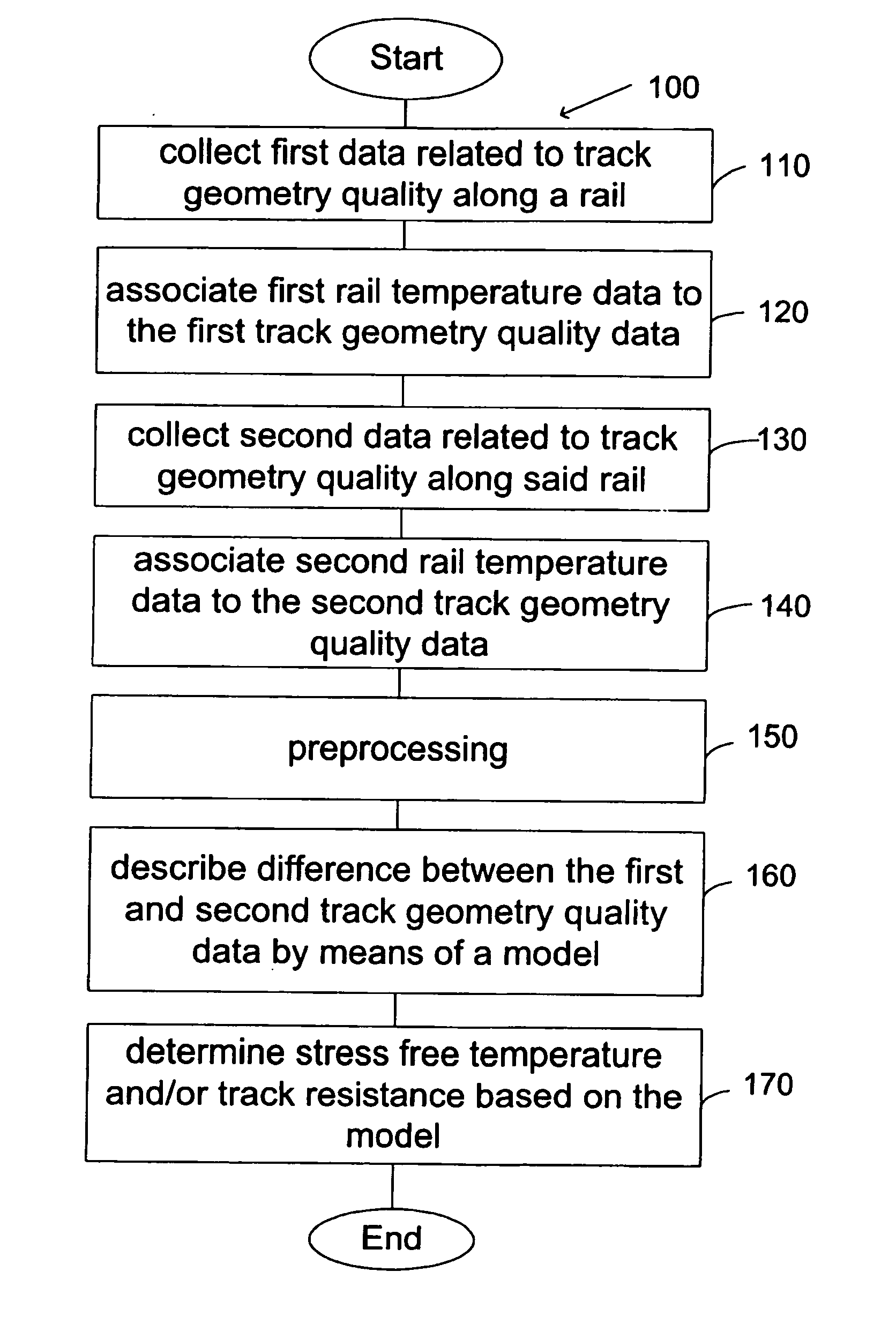
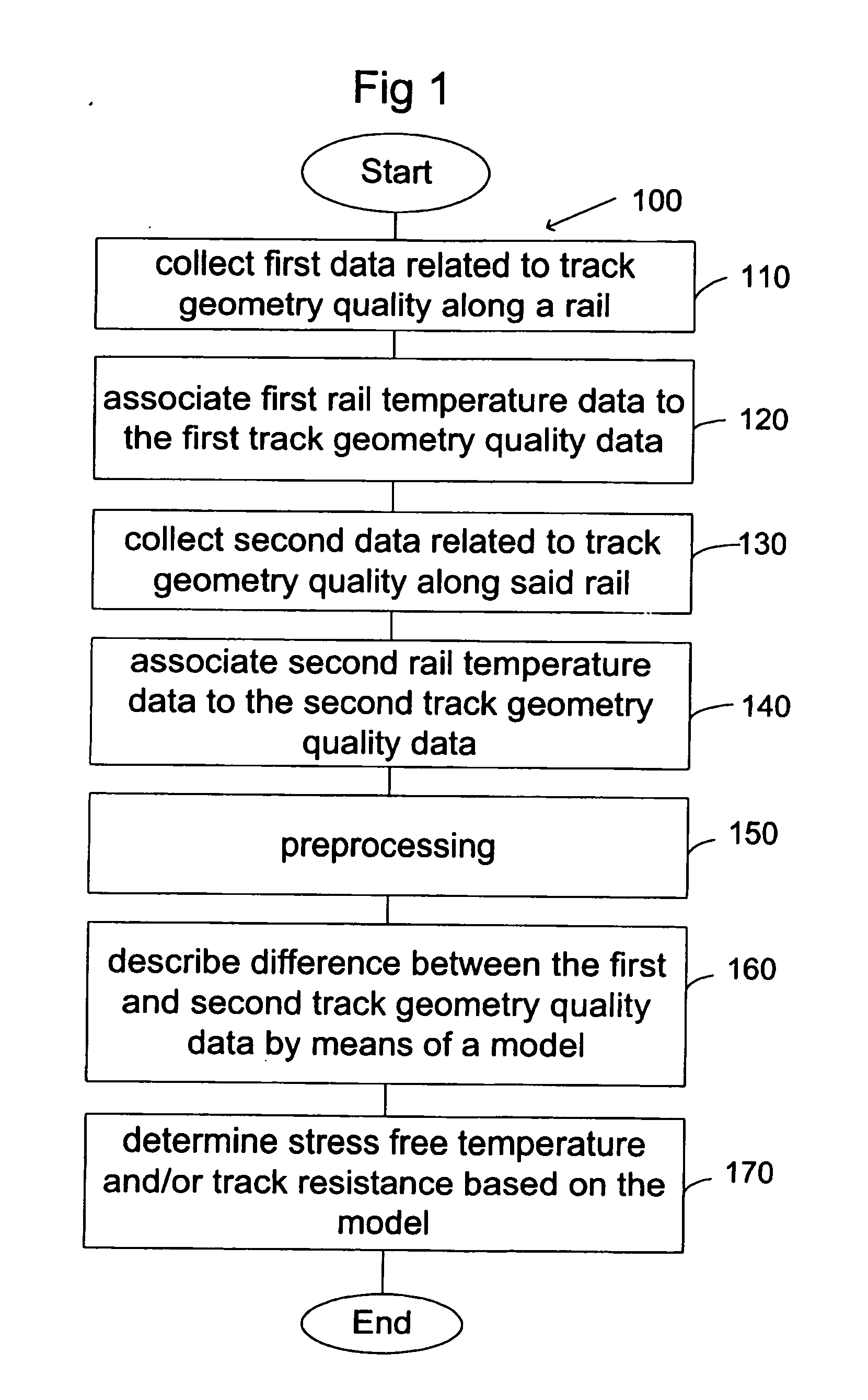
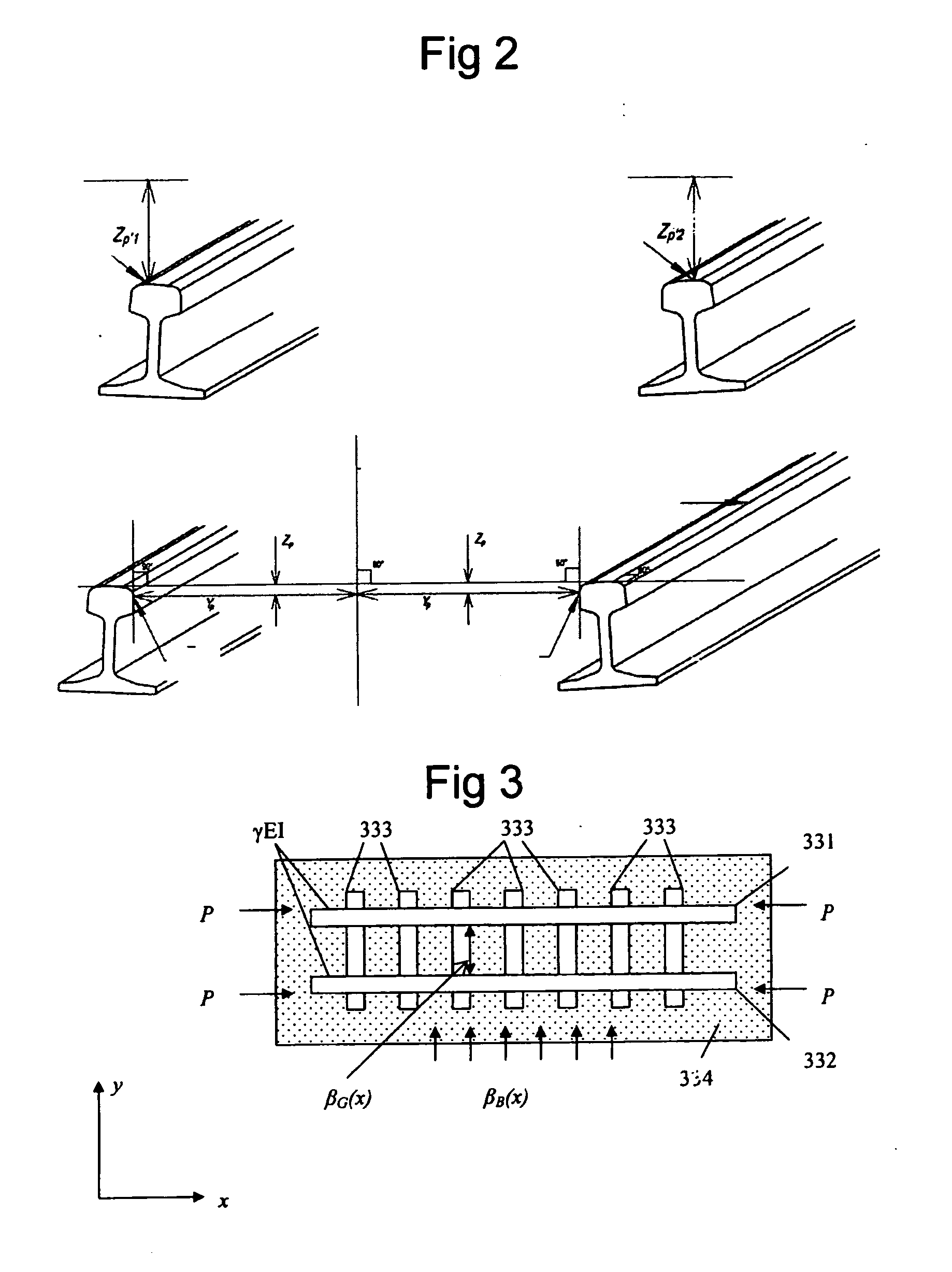
Method for determining the stress free temperature of the rail and/or the track resistance
InactiveUS20120245908A1Way of increaseComputation using non-denominational number representationMeasuring apparatusQuality dataEngineering
A method and device for determining at least a first parameter of a track. The method includes providing a first track geometry quality data associated to at least one point along a rail at a first temperature, providing a second track geometry quality data associated to at least one point at a second temperature, and describing a difference between the first and second track geometry quality data using a model. The model relates the first and second track geometry quality data with associated temperatures to stress free temperature and / or track resistance, and estimates the stress free temperature and / or track resistance in at least one point based on the model.
Owner:EBER DYNAMICS
Flywheel with self-expanding hub
A high energy storage flywheel having a rotor and annular disk which are of a composite material. A metal hub is secured to a shaft and joined to the disk at a hoop. The hub has opposite sections which are of a generally double conical shaft. A concentric rim extends around each hub section and upon rotation the hub sections expansivity deform about the rim to apply a compressive force to the disk to maintain a substantially stress free condition at the rotor and disk interface.
Owner:OPTIMAL ENERGY SYST
Method and display element with reduced thermal stress
InactiveUS20060132027A1Avoid stress-induced damage and failureDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDisplay deviceEngineering
The invention relates to a flexible display device comprising properly selected layers so that the thermal stress in the display can be reduced to avoid failure. The flexible display comprises in order a substrate layer, a conductive layer, a flexible light-emitting layer, a conductive layer, and a superstrate layer wherein the display is balanced such that the layer most subject to damage by stress is substantially stress-free. In addition, the invention provides methods of constructing such a balanced flexible display.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
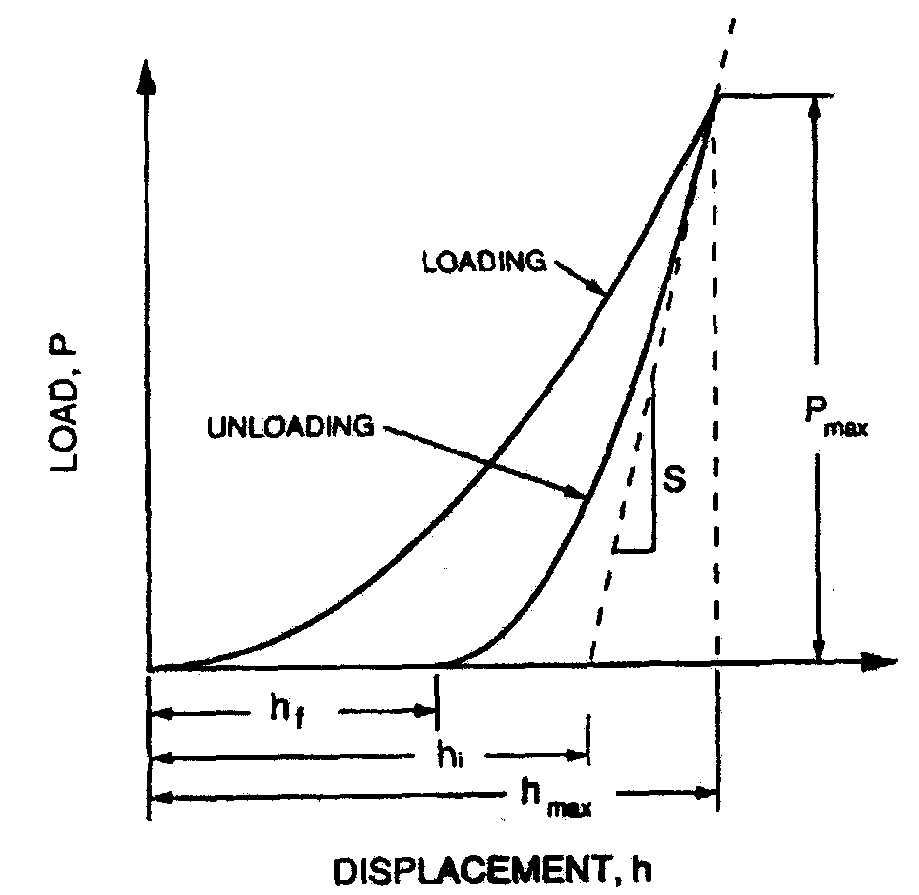
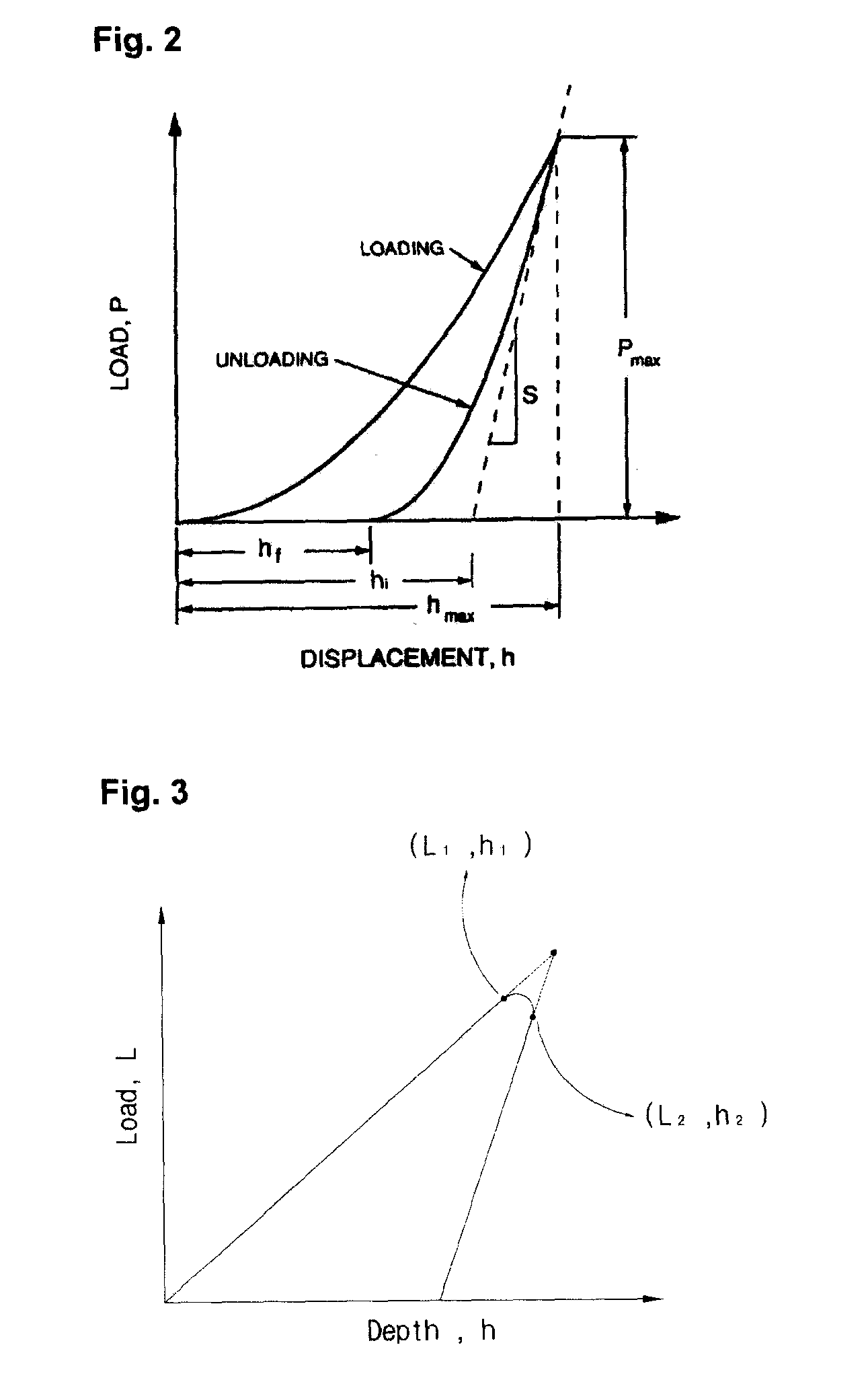
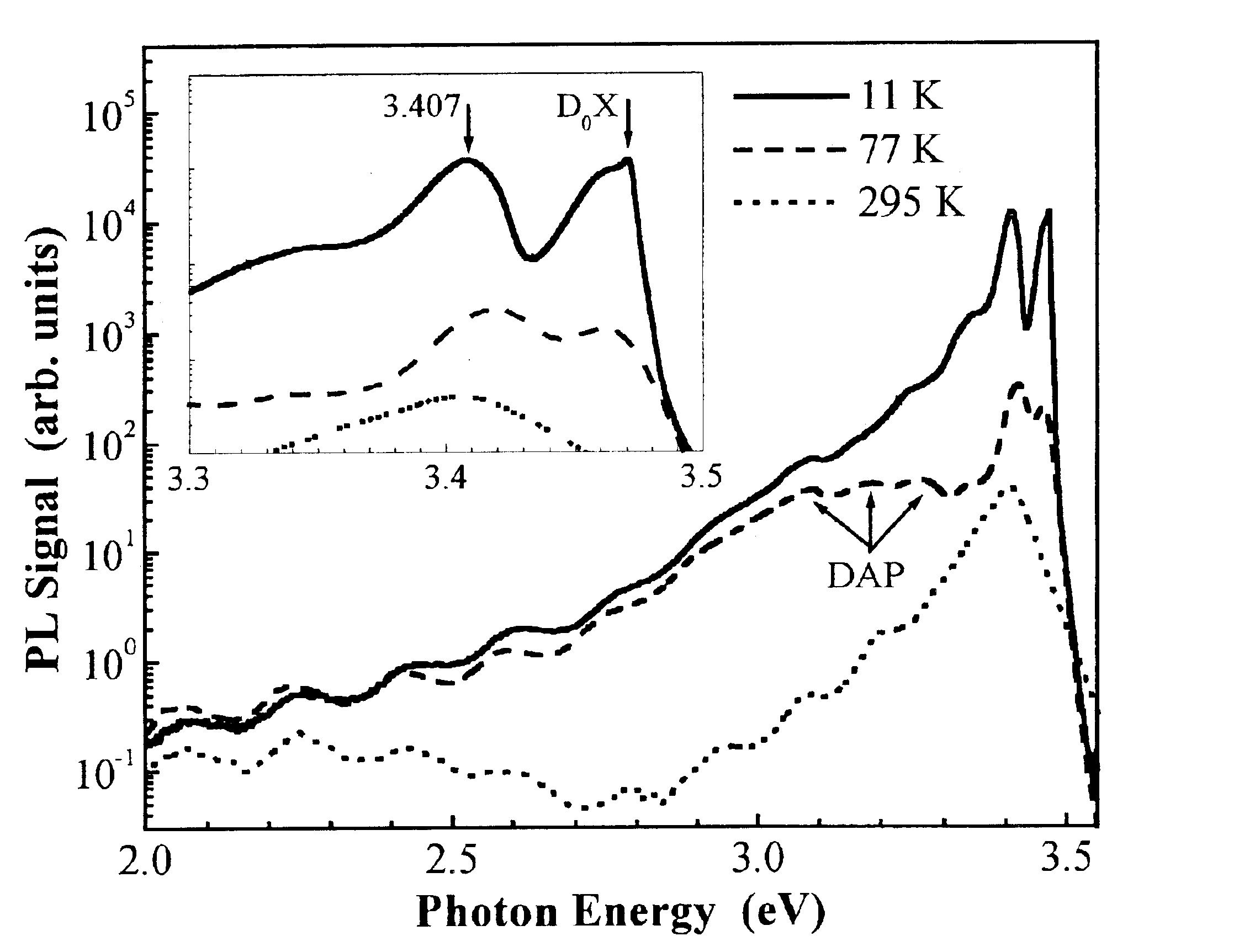
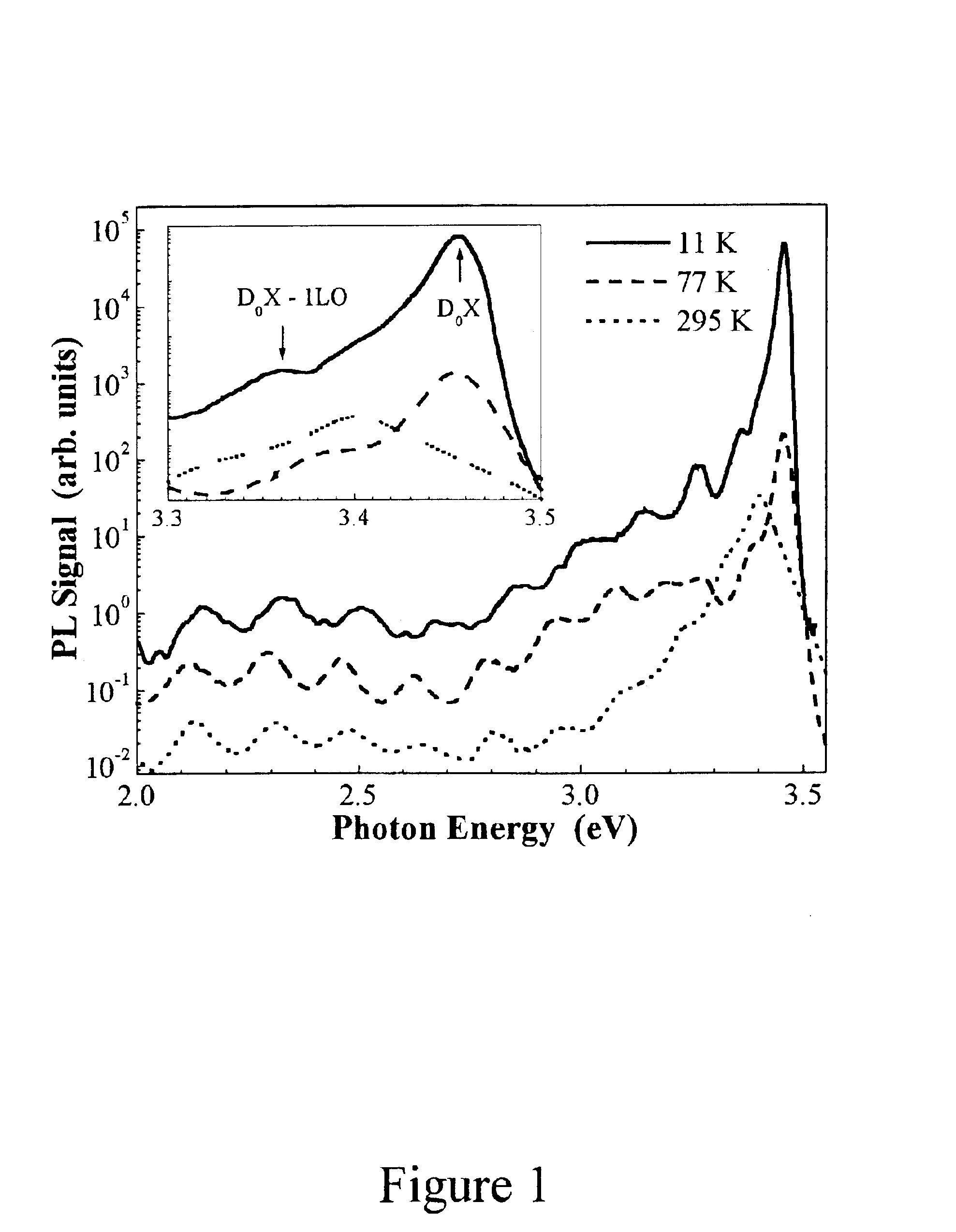
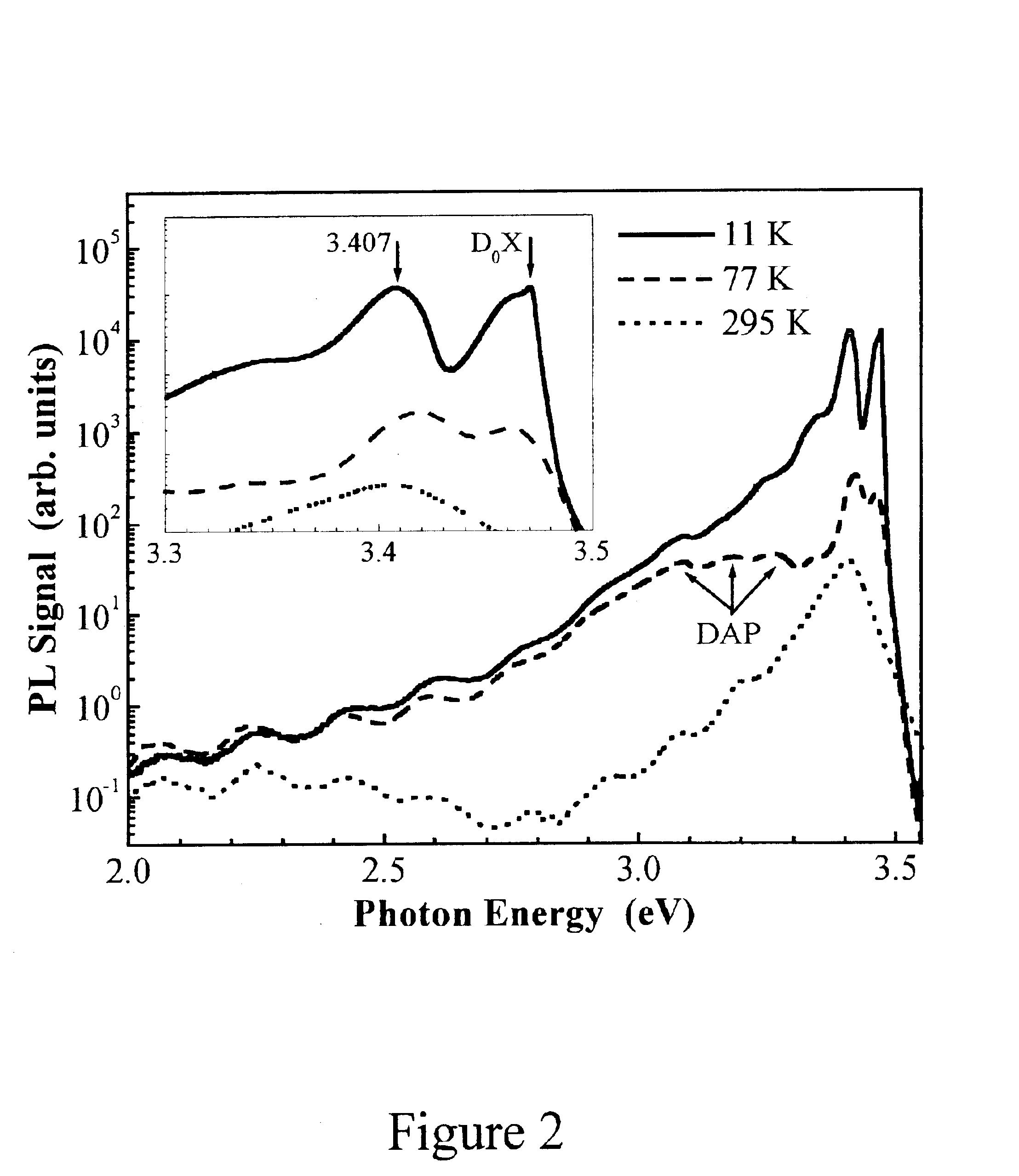
Evaluating Method of the Residual Stress Determining Method Using the Continuous Indentation Method
ActiveUS20080141782A1Error minimizationAccurate estimateAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMeasurement arrangements for variableStress freeBase metal
The present invention relates to a method of measuring residual stress and, more particularly, to a residual stress measuring method using a continuous indentation tester. Due to pile-up and sink-in of a material or a blunted tip, a conventional residual stress measuring method cannot compensate for error of a real contact (indentation) depth or directly remove stress through a thermal or mechanical technique in the conventional method of measuring residual stress of a weldment, so that it is very difficult to estimate a stress-free reference curve or to quantitatively measure residual stress. However, the present invention can precisely estimate a stress-free curve of a weldment using an indentation strength ratio (OIT ratio) of a stress-free base metal to the weldment, and compensates for error, occurring in the measurement of a material having a weldment or an anisotropic stress structure, based on the indentation strength ratio, thereby more precisely measuring residual stress. Thus, unlike the conventional method, the present method can minimize error occurring in the residual stress measuring process, and agrees with actual models.
Owner:FRONTICS +1
Laser Ultrasonic Determination Method of Metal Third-Order Elastic Constant
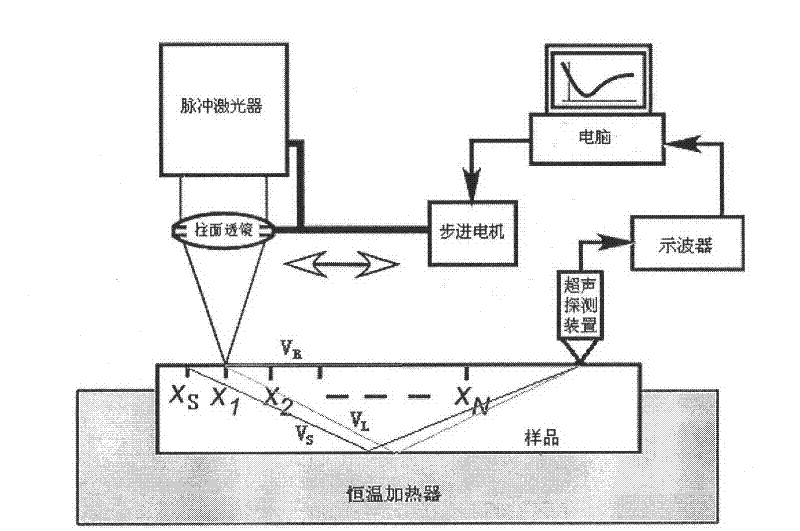
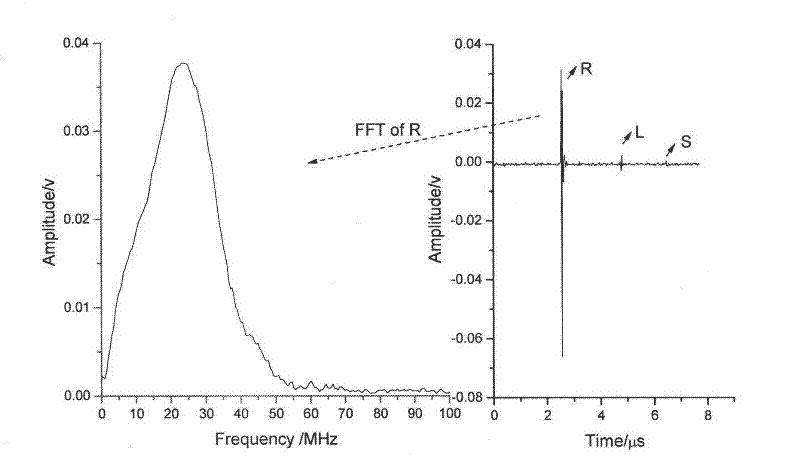
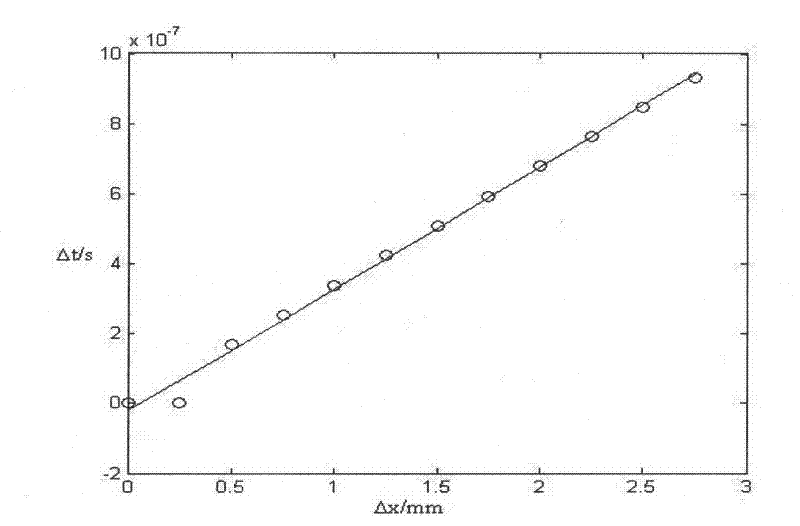
InactiveCN102297898AAvoid overheatingAvoid axial length changesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesCorrelation functionStressed state
The invention discloses a method for utilizing a laser ultrasonic wave to precisely measure a third order elastic constant of metal. The method comprises the following steps: respectively measuring wave velocities of a longitudinal wave, a transverse wave and a surface wave excited by a laser under stress-free state and stress state; utilizing the wave velocities of the longitudinal wave, the transverse wave and the surface wave measured under stress-free state to calculate a second order elastic constant and a density of metal according to a sonic elasticity theory and a Rayleigh equation; utilizing the ultrasonic wave velocities of the longitudinal wave, the transverse wave and the surface wave measured under stress state to introduce an equivalent second order elastic constant and an independently measured linear coefficient of thermal expansion; and lastly, calculating the third order elastic constant according to the sonic elasticity theory. According to the method, a pulse laser source is utilized to excite a sound surface wave, non-contact exciting is performed under a thermal elastic system and an overheated phenomenon of materials is avoided, so as to realize nondestructive measurement. A large amount of sound surface wave data spread for different distances is collected and a correlation function is utilized to calculate a wave velocity of the sound surface wave and a spread distance of sound wave, thereby greatly reducing error of arriving time value of the sound surface wave and promoting the measuring precision of a sound wave velocity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
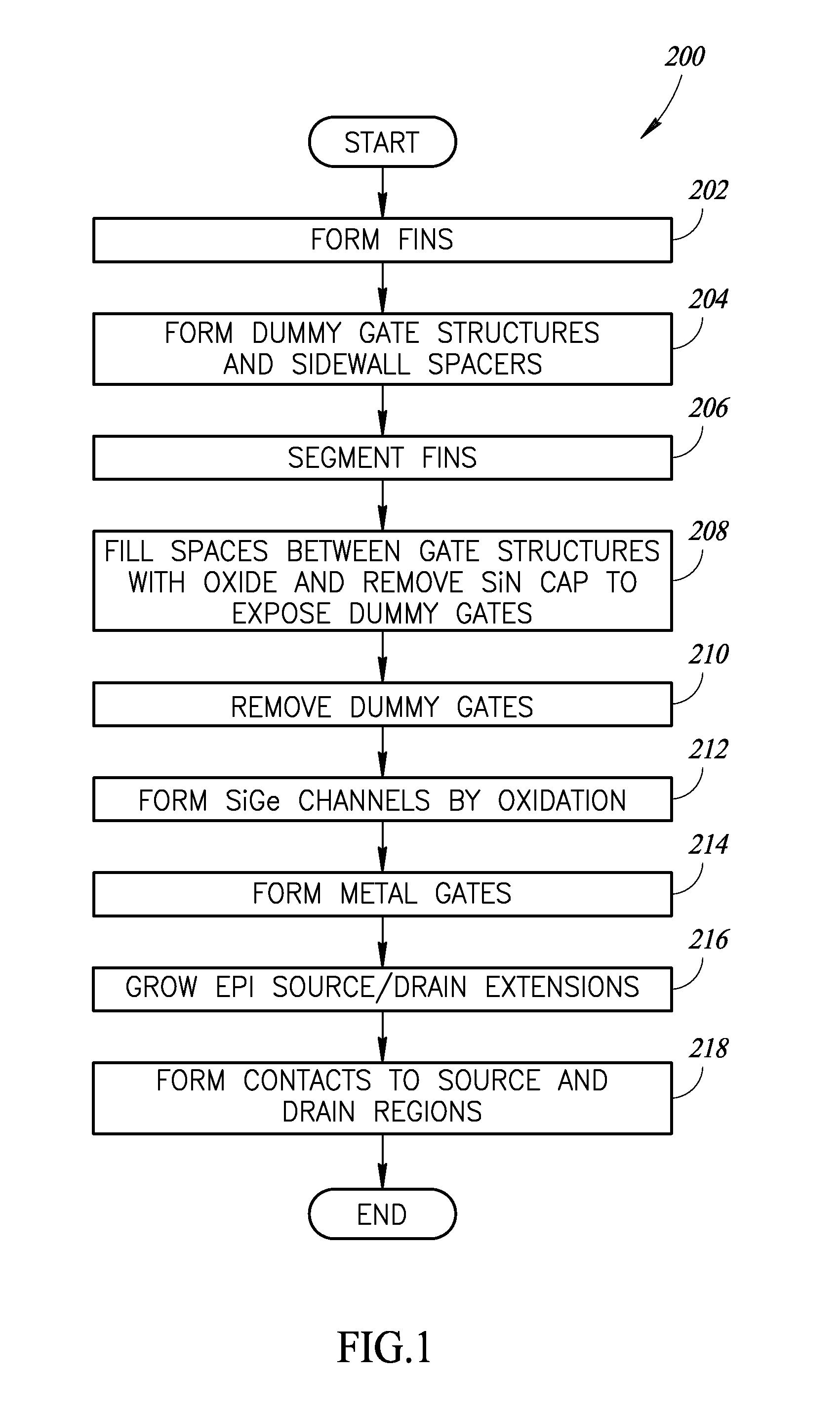
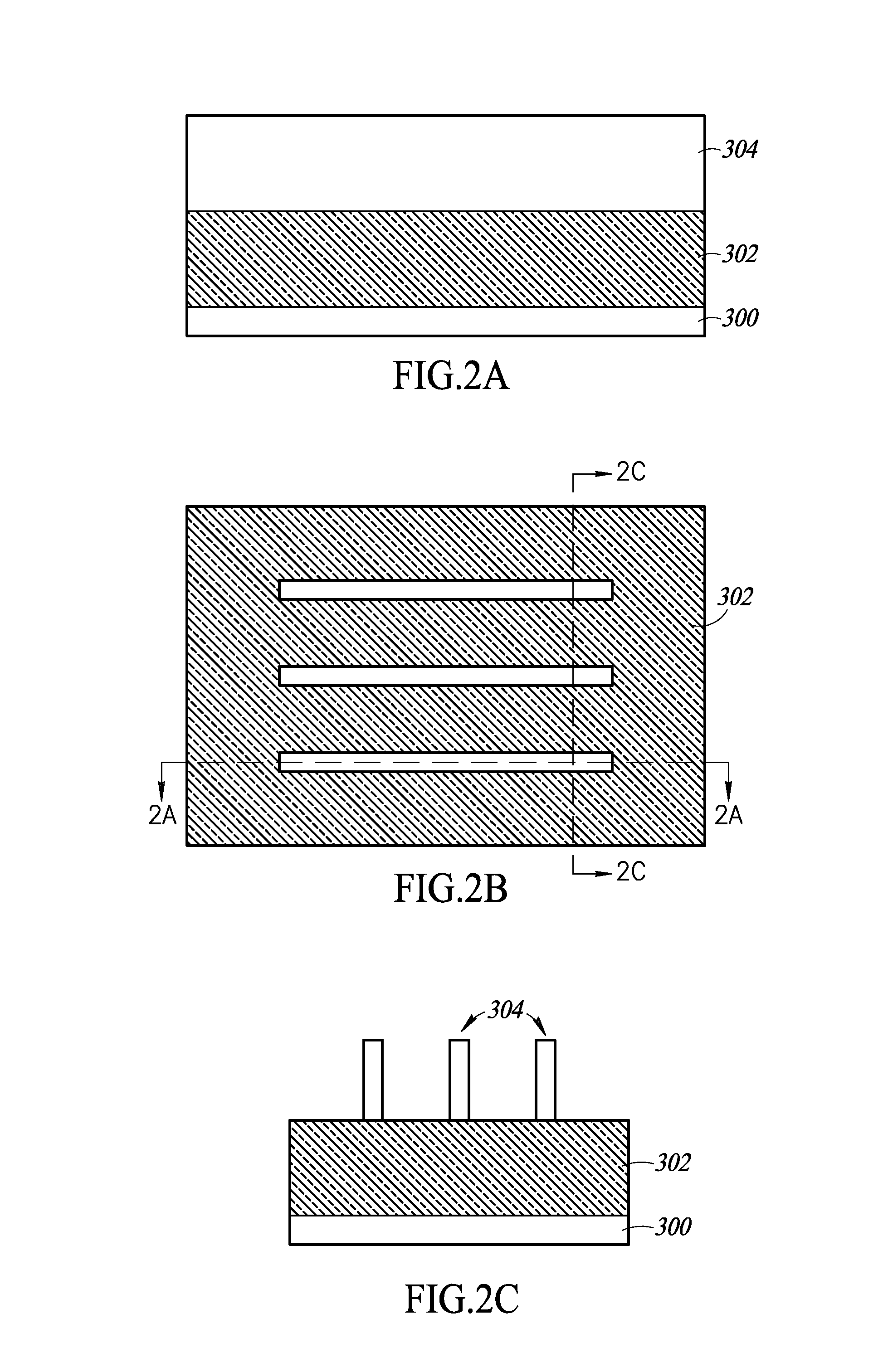
Method of using a sacrifical gate structure to make a metal gate finfet transistor
ActiveUS20170005169A1High electron mobilitySmall footprintSemiconductor devicesEngineeringStress free
A self-aligned SiGe FinFET device features a relaxed channel region having a high germanium concentration. Instead of first introducing germanium into the channel and then attempting to relax the resulting strained film, a relaxed channel is formed initially to accept the germanium. In this way, a presence of germanium can be established without straining or damaging the lattice. Gate structures are patterned relative to intrinsic silicon fins, to ensure that the gates are properly aligned, prior to introducing germanium into the fin lattice structure. After aligning the gate structures, the silicon fins are segmented to elastically relax the silicon lattice. Then, germanium is introduced into the relaxed silicon lattice, to produce a SiGe channel that is substantially stress-free and also defect-free. Using the method described, concentration of germanium achieved in a structurally stable film can be increased to a level greater than 85%.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
Clamp and clamping method for large-diameter plane optical element
ActiveCN102615567AReduced precision requirementsSmall clamping deformationOptical surface grinding machinesOptical engineeringEngineering
Provided are a clamp and a clamping method for a large-diameter plane optical element. The clamp comprises a large-diameter plane optical element press plate, an elastic pivot, a transformation thin plate frame, an inner hexagonal cylindrical head screw, a boss, a lens frame, a rotational shaft and a support. The clamp and the clamping method utilize a metal structure to directly clamp the large-diameter optical element, can produce no optical element clamping stress under the condition that surface processing accuracy of a metal clamping frame is reduced and the optical element is in any inclination angle. Simultaneously, the metal structure is utilized to conduct direct clamping, thereby well avoiding organic pollution caused by stress-free clamping of tradition organics. The clamp the clamping method can be widely applied to clamping of the large-diameter plane optical element in optical engineering and optical experiment devices and has strong practicability.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bistable microelectromechanical system based structures, systems and methods
InactiveUS6828887B2Increase flexibilityReduce potential out-of-plane bucklingElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysCoupling light guidesStable stateThermal impact
A bistable microelectromechanical system (MEMS) based system comprises a micromachined beam having a first stable state, in which the beam is substantially stress-free and has a specified non-linear shape, and a second stable state. The curved shape may comprises a simple curve or a compound curve. In embodiments, the boundary conditions for the beam are fixed boundary conditions, bearing boundary conditions, spring boundary conditions, or a combination thereof. The system may further comprise an actuator arranged to move the beam between the first and second stable states and a movable element that is moved between a first position and a second position in accordance with the movement of the beam between the first and second stable states. The actuator may comprise one of a thermal actuator, an electrostatic actuator, a piezoelectric actuator and a magnetic actuator. The actuator may further comprise a thermal impact actuator or a zippering electrostatic actuator.
Owner:XEROX CORP
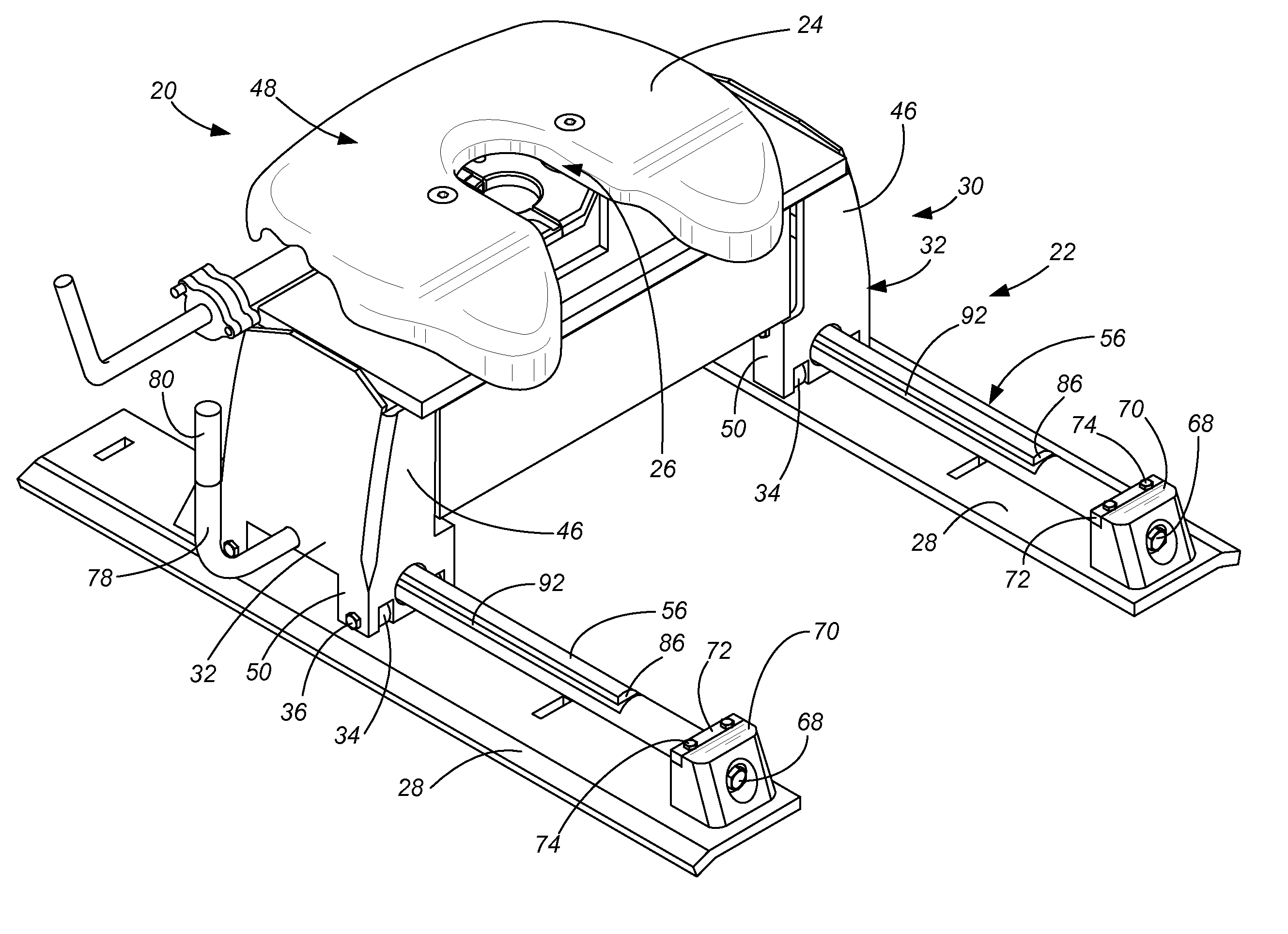
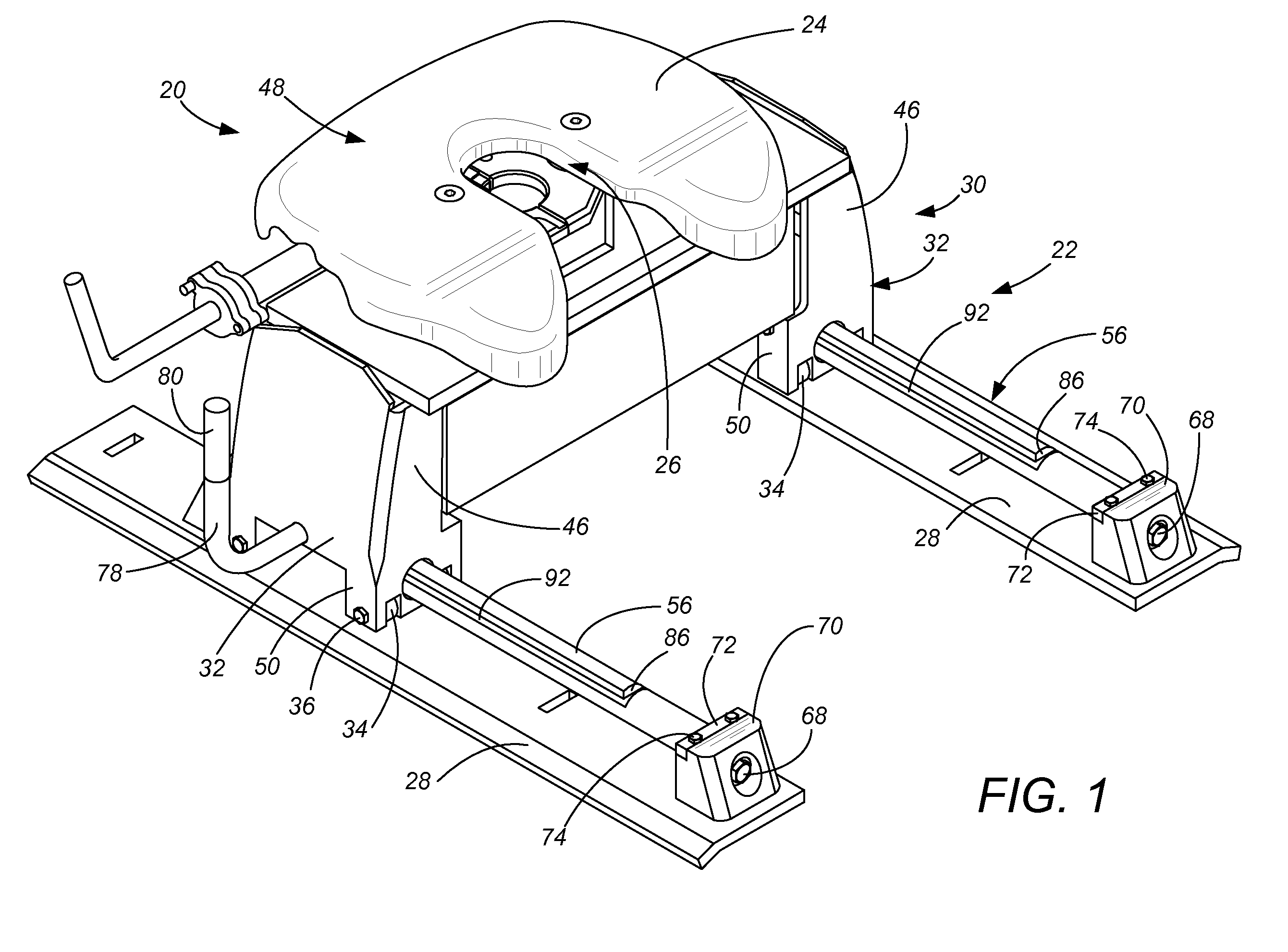
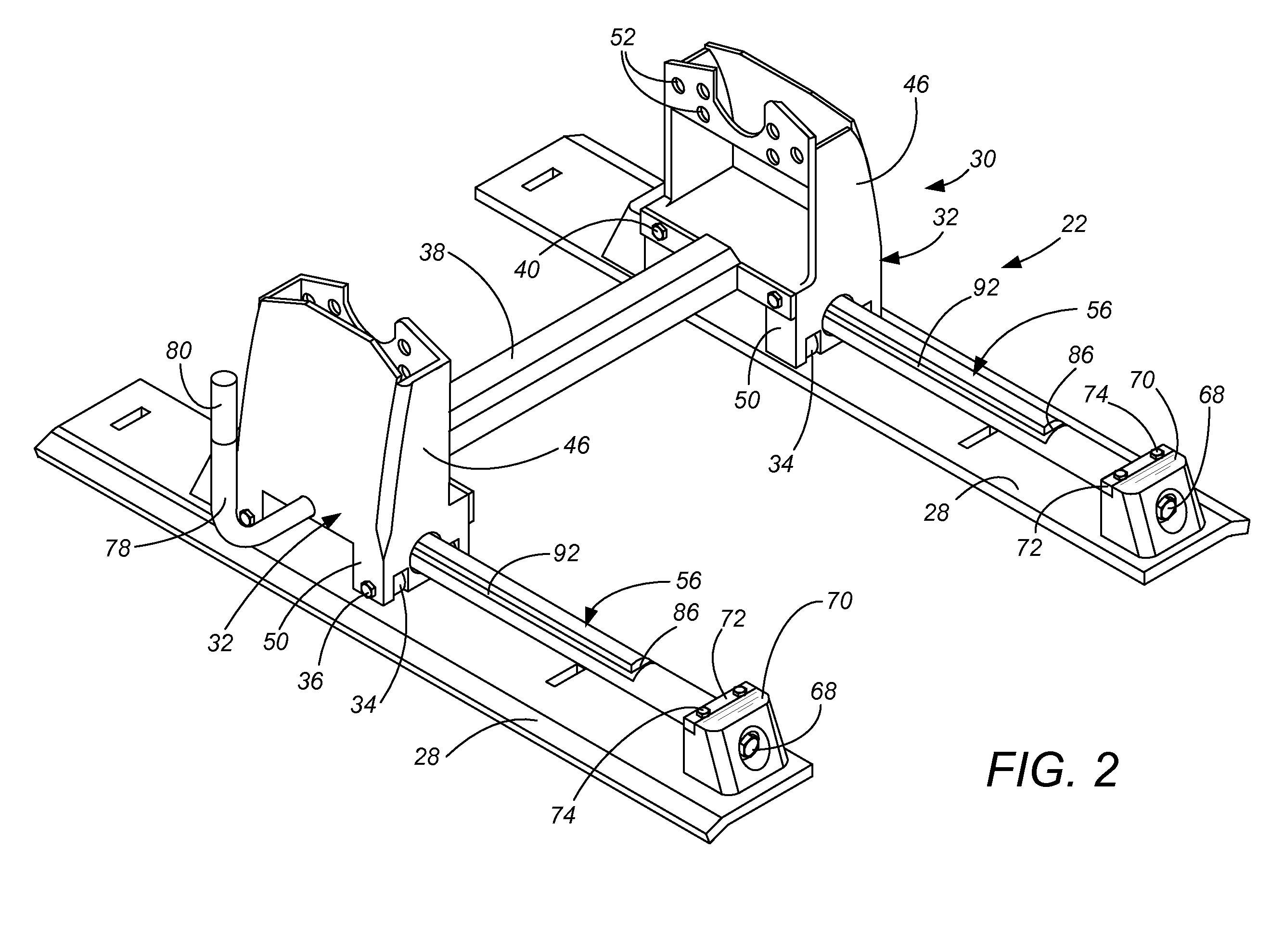
Moveable hitch with stress-free elevated bearing guide
A bearing guide for a hitch allows lateral movement of the hitch. The bearing guide is elevated relative to the bearing surface. Two trucks roll on wheels each about their own elevated guide for fore-and-aft rolling of the hitch point. The bearing guide also provides a keyway which receives a locking key. The locking key is supported on both sides of the keyway by a plunger control rod, and can be unlocked by pulling and rotating a handle. When the towing vehicle is driven to relocate the hitch point, the locking key reengages itself into a different keyway on the bearing guide.
Owner:CURT MFG
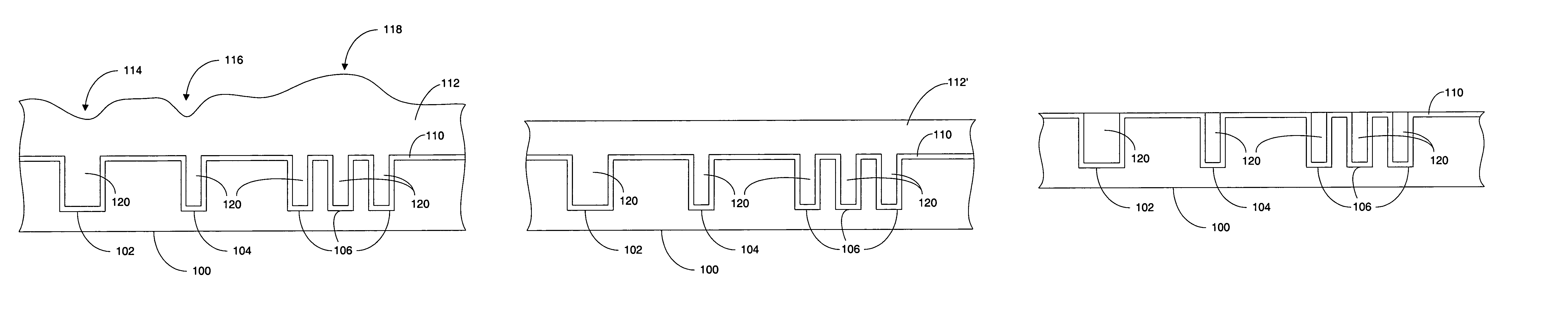
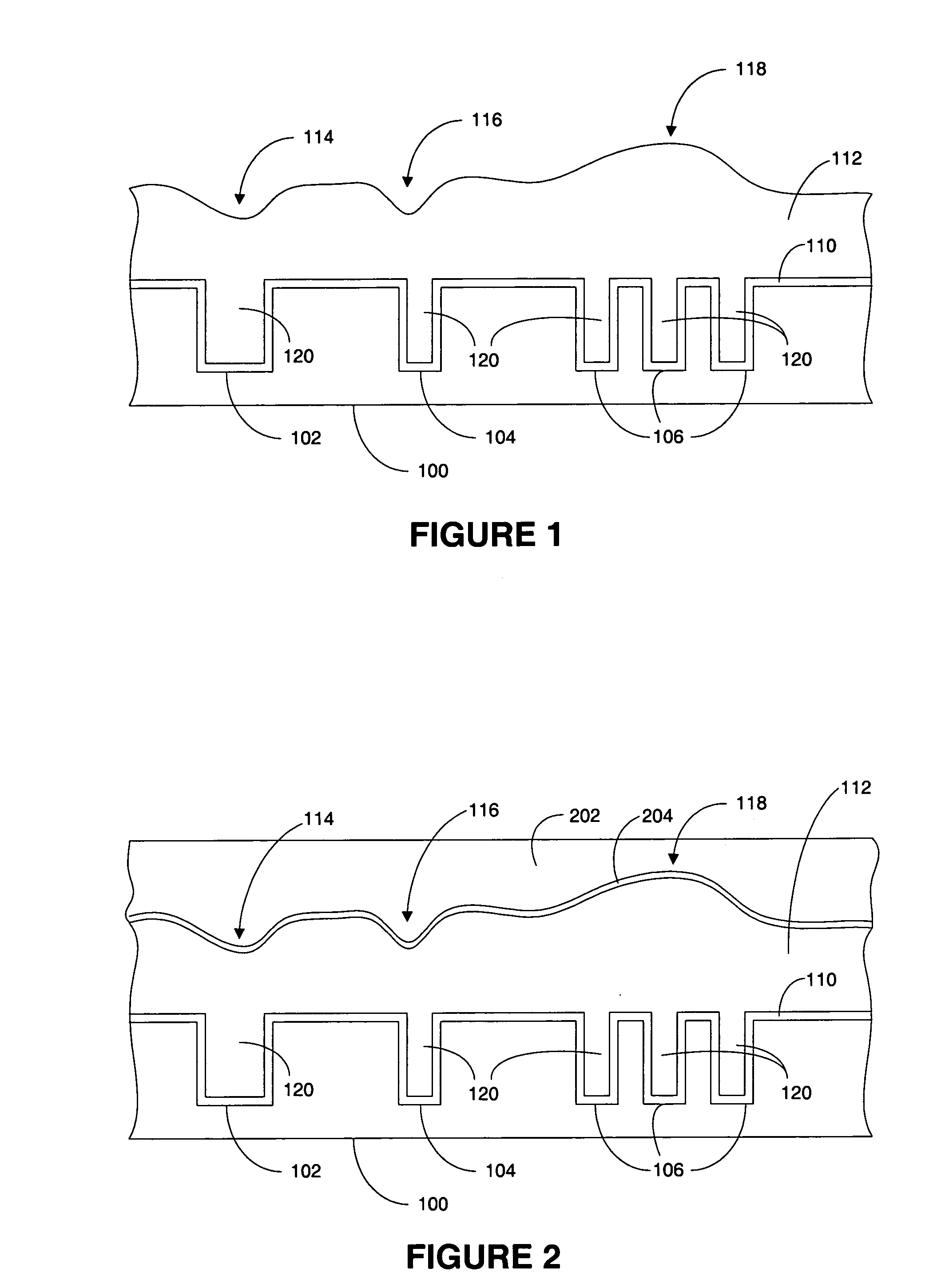
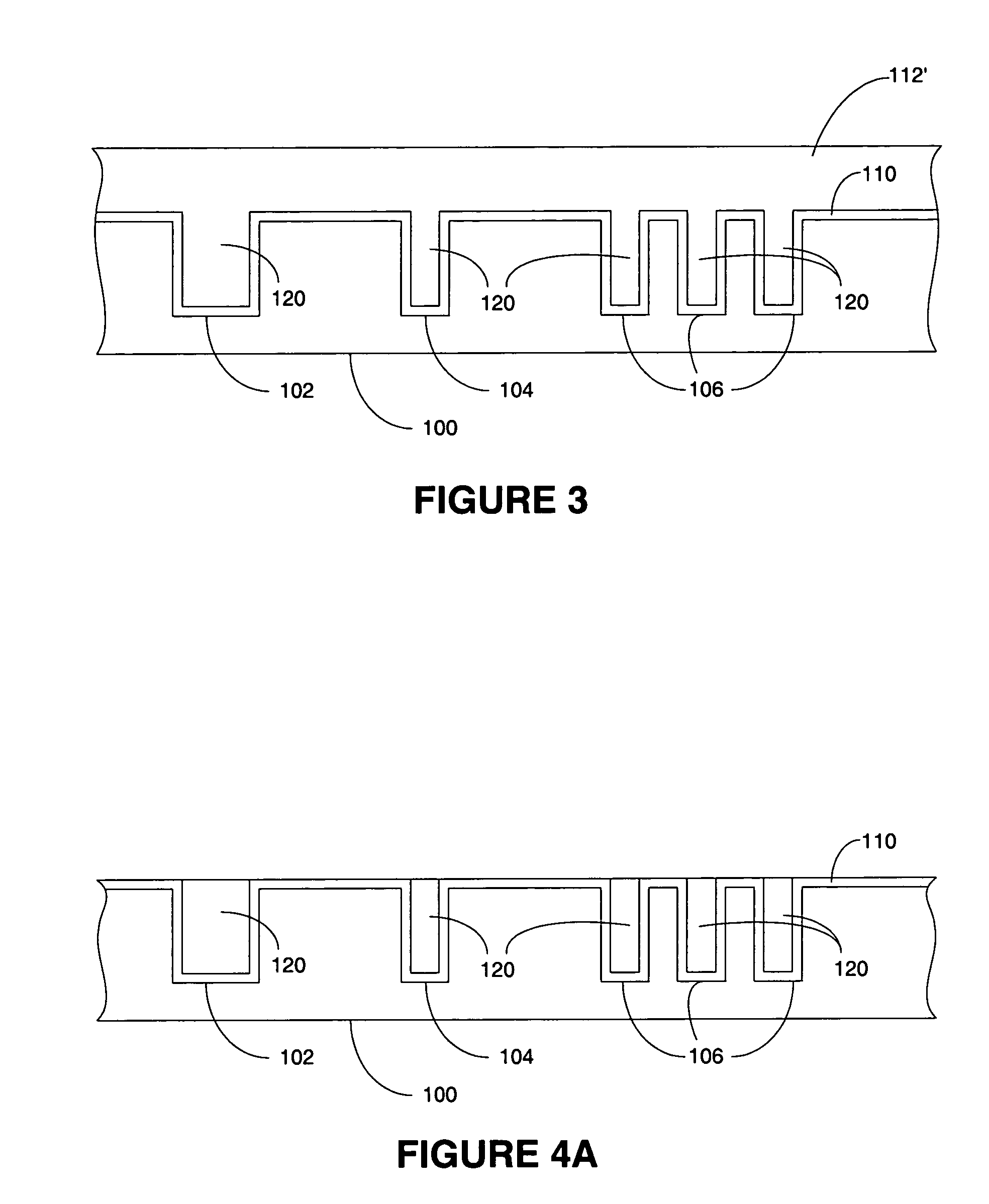
System and method for stress free conductor removal
InactiveUS7217649B2Improve flatnessPrecise applicationElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringDielectric layer
A system and method for forming a semiconductor in a dual damascene structure including receiving a patterned semiconductor substrate. The semiconductor substrate having a first conductive interconnect material filling multiple features in the pattern. The first conductive interconnect material having an overburden portion. The over burden portion is planarized. The over burden portion is substantially entirely removed in the planarizing process. A mask layer is reduced and a subsequent dielectric layer is formed on the planarized over burden portion. A mask is formed on the subsequent dielectric layer. One or more features are formed in the subsequent dielectric layer and the features are filled with a second conductive interconnect material.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
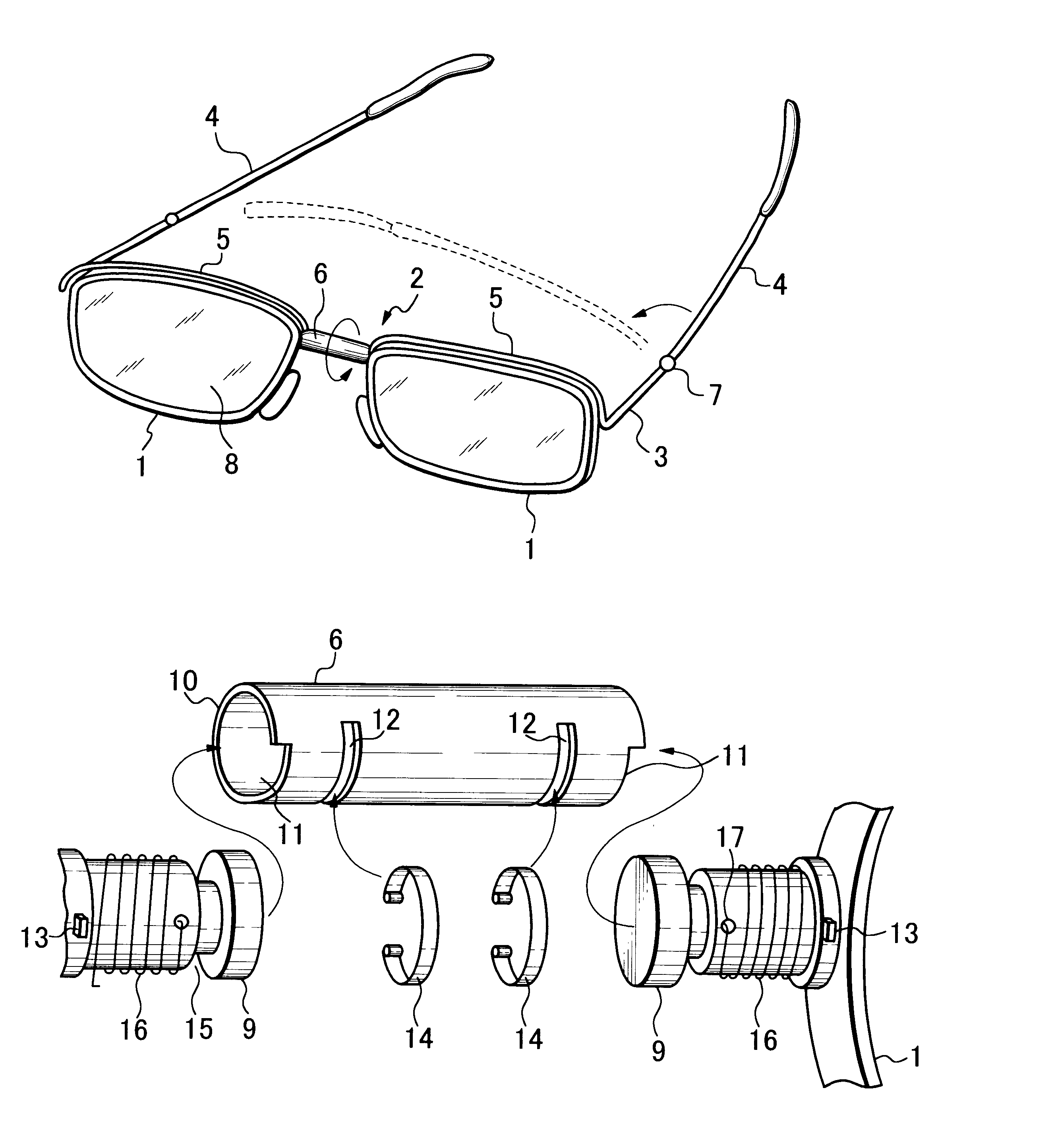
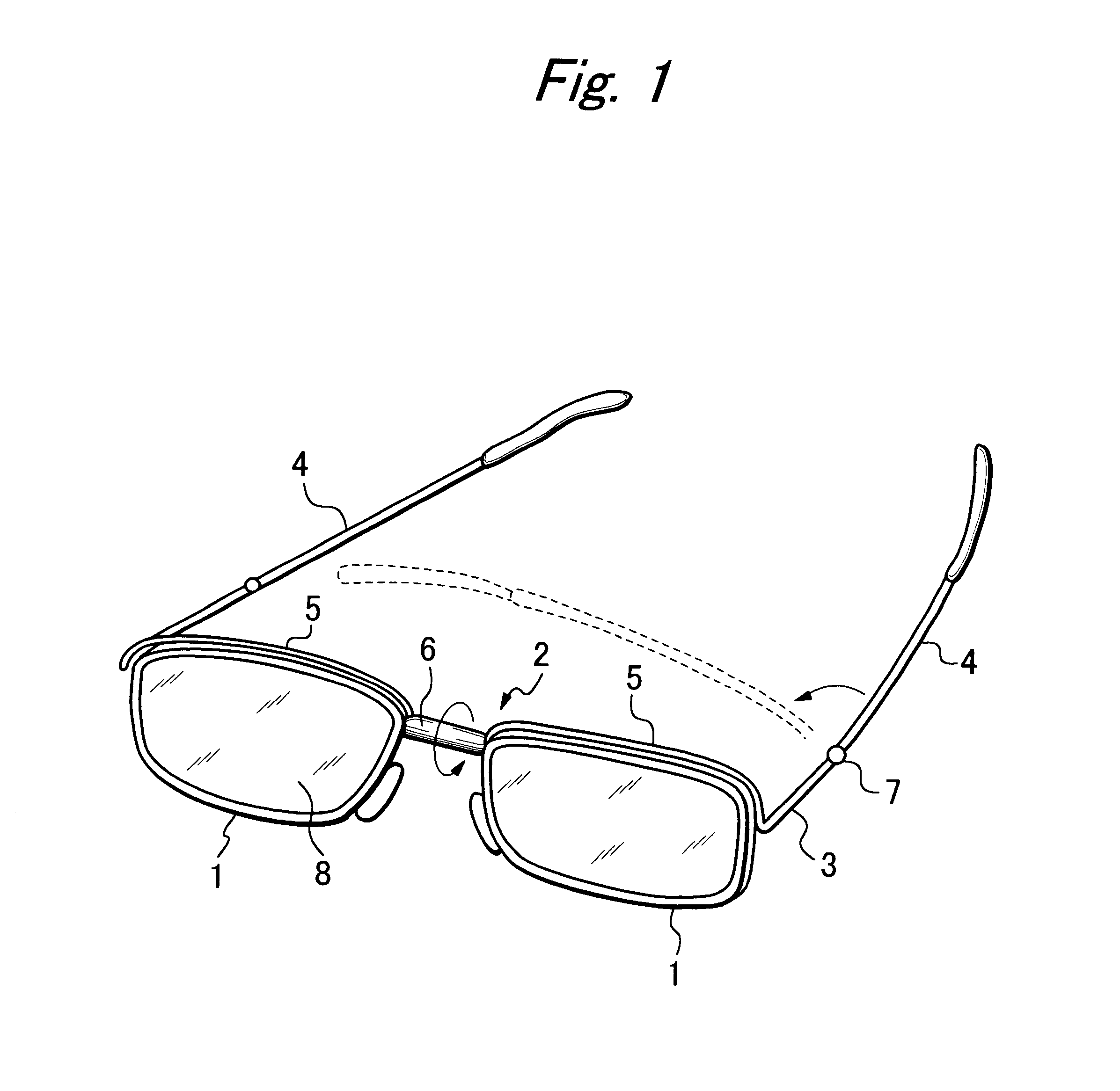
Double-foldable eyeglasses
Disclosed is a double foldable eyeglasses whose opposite temples can be folded toward the front, and then turned downward, thereby laying the folded temples below the front to be coplanar therewith. The front of the eyeglasses has two traverses integrally connected to the opposite ends of the bridge and to the opposite perpendicular joint pieces, and the opposite temples are hinged to the perpendicular joint pieces. The bridge comprises a hollow tube, and two opposite axles each integrally connected to one or the other rim are fitted in the hollow tube. Each axle has a coiled spring wound therearound, one end of the coiled spring being fixed to the axle, and the other end being fixed to the bridge. Each axle has a retainer formed thereon to be caught by catch means formed in the hollow tube. A resilient force to be applied to the rim increases with the increase of the angular rotation of the rim through the agency of coiled springs. With this arrangement the eyeglasses can be double-folded with its temples folded and laid below the front while being spring-biased toward the stress-free position, in which the eyeglasses are unfolded.
Owner:UMEDA
Method for preparing transmission electron microscope sample of soft brittle phototransistor
InactiveCN102023111AProtection from being brokenAvoid breakingPreparing sample for investigationAdhesiveProtection layer
The invention belongs to the technical field of the preparation of transmission electron microscope samples of soft brittle phototransistors, and relates to a method for preparing a transmission electron microscope sample of a soft brittle phototransistor, in particular to a method for preparing a transmission electron microscope sample of a soft brittle photo semiconducting transistor. The method is characterized in that a hard brittle semiconductor with micro Vickers hardness of over 8 GPa is used as a protective layer of the soft brittle phototransistor, wherein the roughness Ra of the ultra-smooth surface of the protective layer is below 1 nanometer, and the thickness is below 650 micrometers; sand paper of 120 to 800 meshes is adopted in the coarse grinding stage, and a membrane is ground by adopting diamond of between 0.1 and 30 micrometers in the accurate grinding stage; the protective layer is bonded with the sample by adopting a hot setting adhesive which is insoluble in an organic solvent, and a first surface of the ground transmission electron microscope sample is bonded with a substrate by adopting a hot setting adhesive which is soluble in the organic solvent; and in the final stage of accurate grinding, the transmission sample and a thin area of the protective layer are obtained by a stress-free grinding method. The method has the advantages that the preparation of the transmission electron microscope sample of the soft brittle phototransistor is realized, and high-resolution transmission electron microscope atomic images are obtained.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip and grain-oriented electrical steel strip obtained according to said process
InactiveUS20170283903A1Simple stepsReduce oxidationInorganic material magnetismSolid state diffusion coatingThin slabWater vapor
A process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip by means of thin slab continuous casting, comprising the following process steps: a) smelting a steel, b) continuously casting the smelt by thin slab continuous casting, c) heating up the thin slabs and subjecting the slabs to homogenization annealing at a maximum temperature of 1250° C., d) heating to a temperature between 1250° C. and 1350° C., e) continuously hot rolling the thin slabs to form a hot-rolled strip, f) cooling and reeling the hot-rolled strip to form a coil, g) annealing the hot-rolled strip after reeling and prior to a subsequent cold rolling step, h) cold rolling the hot-rolled strip to the nominal usable thickness, i) subjecting the cold-rolled strip to recrystallization, decarburization and nitridation annealing, j) applying an annealing separator (non-stick layer) to the strip surface of the cold-rolled strip, k) subjecting the cold-rolled strip to secondary recrystallization annealing, forming a finished steel strip having a pronounced Goss texture, and l) stress-free annealing the finished steel strip, which has been coated with an insulating layer, provides an improved process for producing grain-oriented electrical steel strip by means of thin slab continuous casting. This is achieved in that the recrystallization, decarburization and nitridation annealing of the cold-rolled strip in process step h) comprises a decarburization annealing phase and a subsequent nitridation annealing phase, with an intermediate reduction annealing phase being interposed between the decarburization annealing phase and the nitridation annealing phase, and carried out at a temperature ranging from 820° C.-890° C., for a maximum period of 40 seconds, with a dry, gaseous annealing atmosphere, which contains nitrogen (N2) and hydrogen (H2) and acts on the cold-rolled strip, and which has a water vapor / hydrogen partial pressure ratio pH2O / pH2 of less than 0.10.
Owner:SMS GRP GMBH
Hafnium nitride buffer layers for growth of GaN on silicon
InactiveUS6929867B2Improve the immunityCloser conductivityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrack freeHafnium
Gallium nitride is grown by plasma-assisted molecular-beam epitaxy on (111) and (001) silicon substrates using hafnium nitride buffer layers. Wurtzite GaN epitaxial layers are obtained on both the (111) and (001) HfN / Si surfaces, with crack-free thickness up to 1.2 m. However, growth on the (001) surface results in nearly stress-free films, suggesting that much thicker crack-free layers could be obtained.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Coupling structure mountable to a rotatable shaft
A coupling structure capable of being removed in an undamaged condition from a rotatable shaft. The coupling structure includes a metallic insert and a polymer hub surrounding the metallic insert. The metallic insert features a sleeve and a flange at the leading edge of the sleeve remote from the opening into which the shaft is inserted. Forces applied to the flange are preferentially transferred to the metallic insert such that the polymer hub remains substantially stress-free. The coupling structure may be incorporates into a torsional vibration damper that further includes an inertia member encircling the polymer hub and an elastomer layer situated between the inertia member and the polymer hub. The coupling structure permits the torsional vibration damper to be removed undamaged from a crankshaft.
Owner:DAYCO IP HLDG
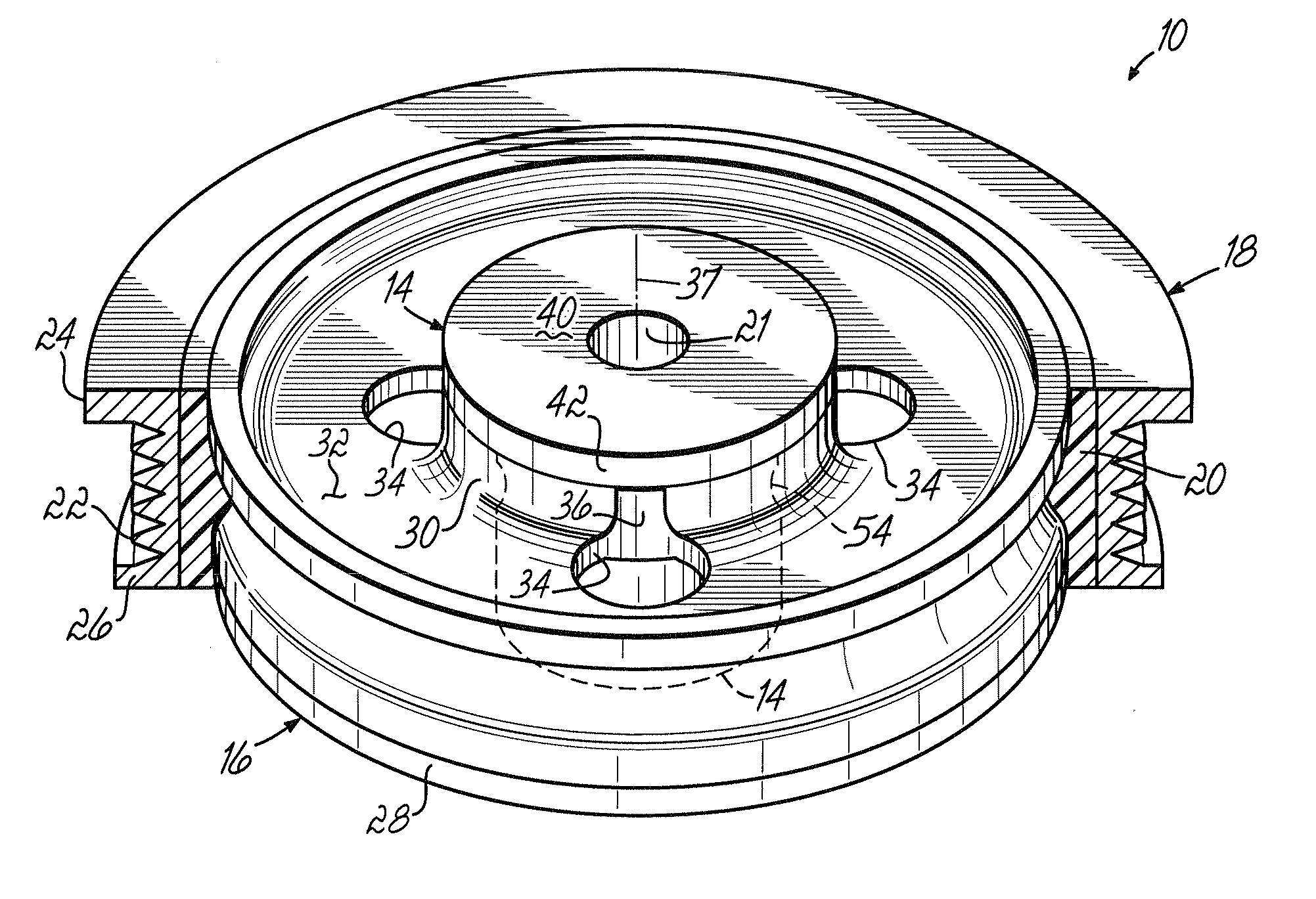
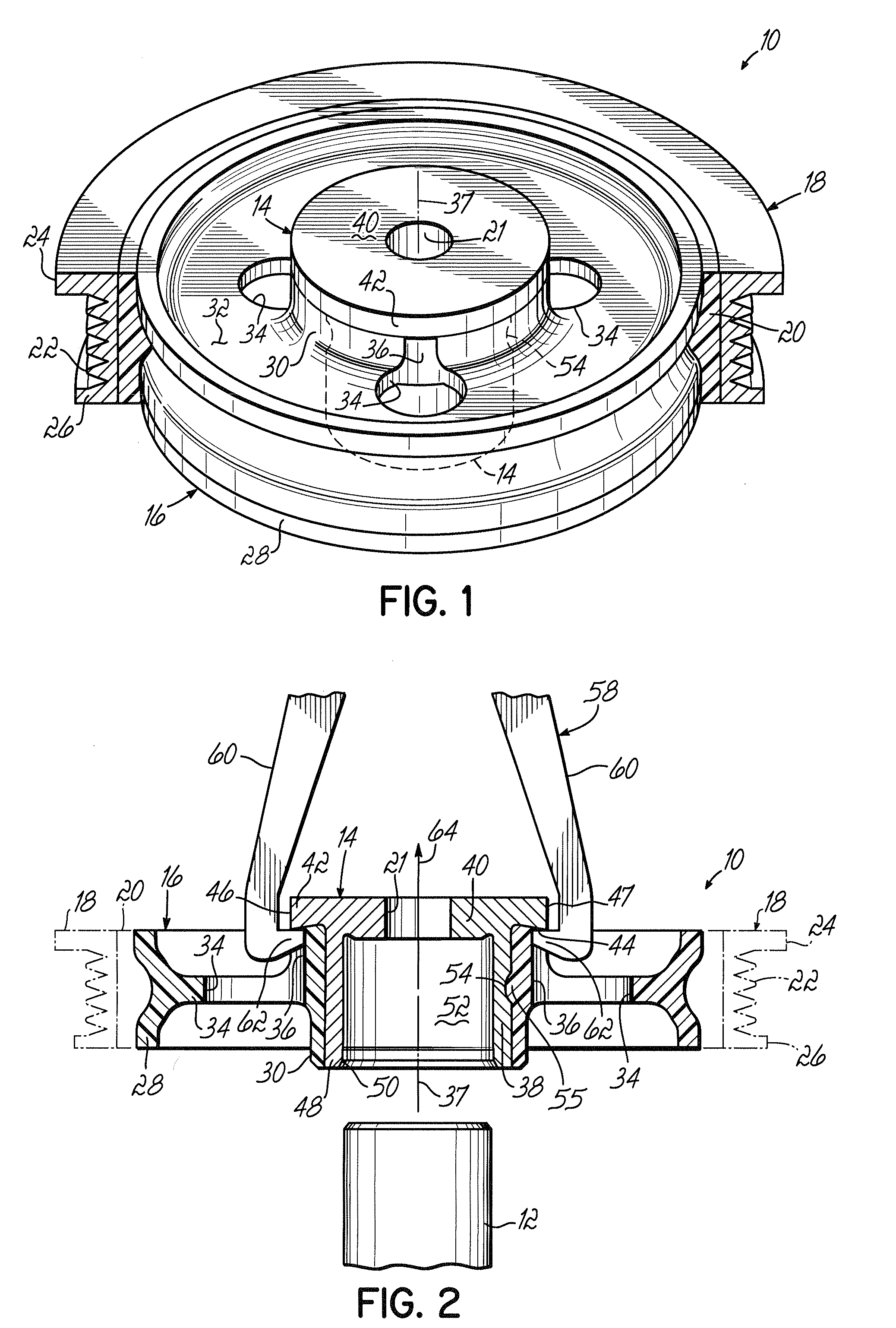
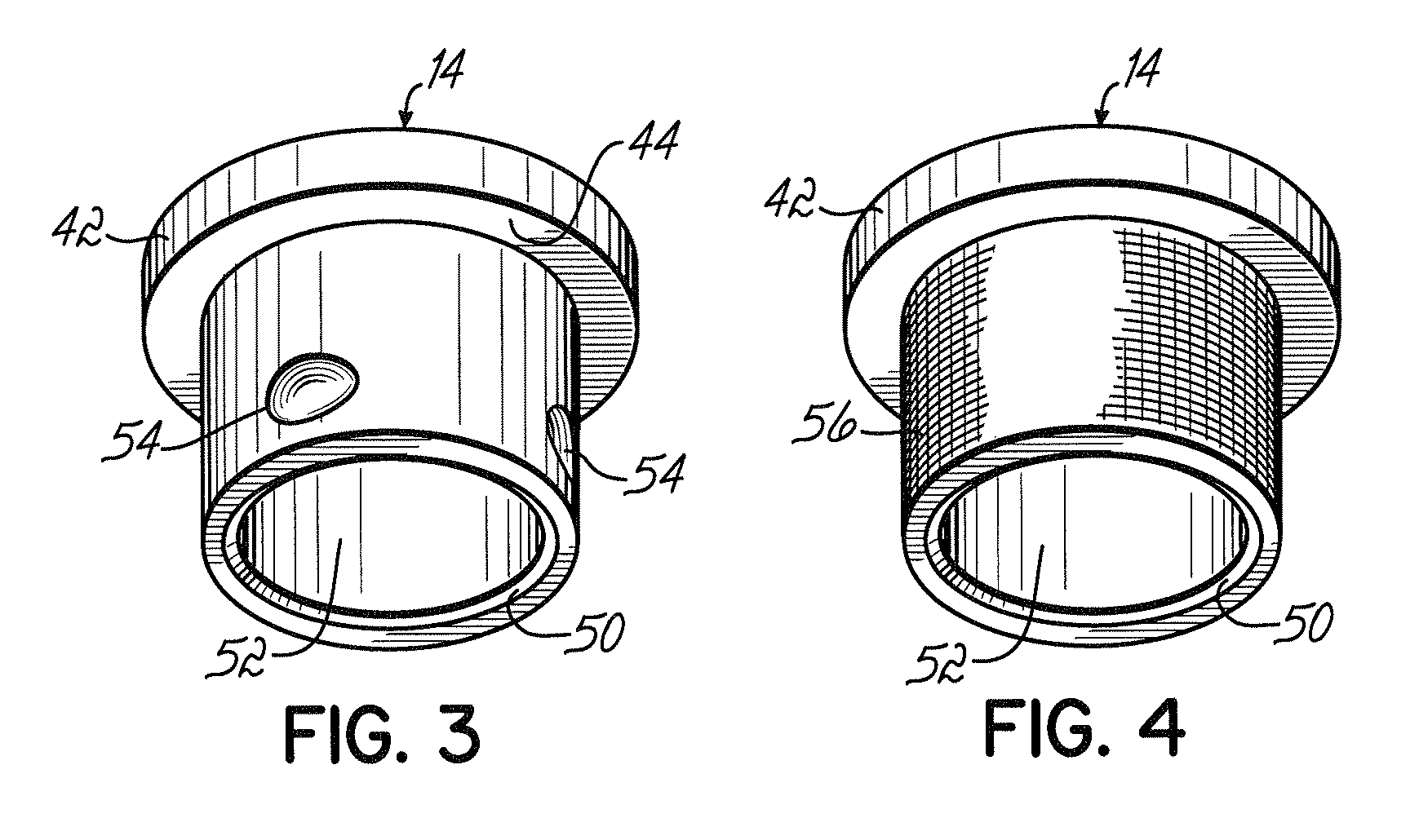
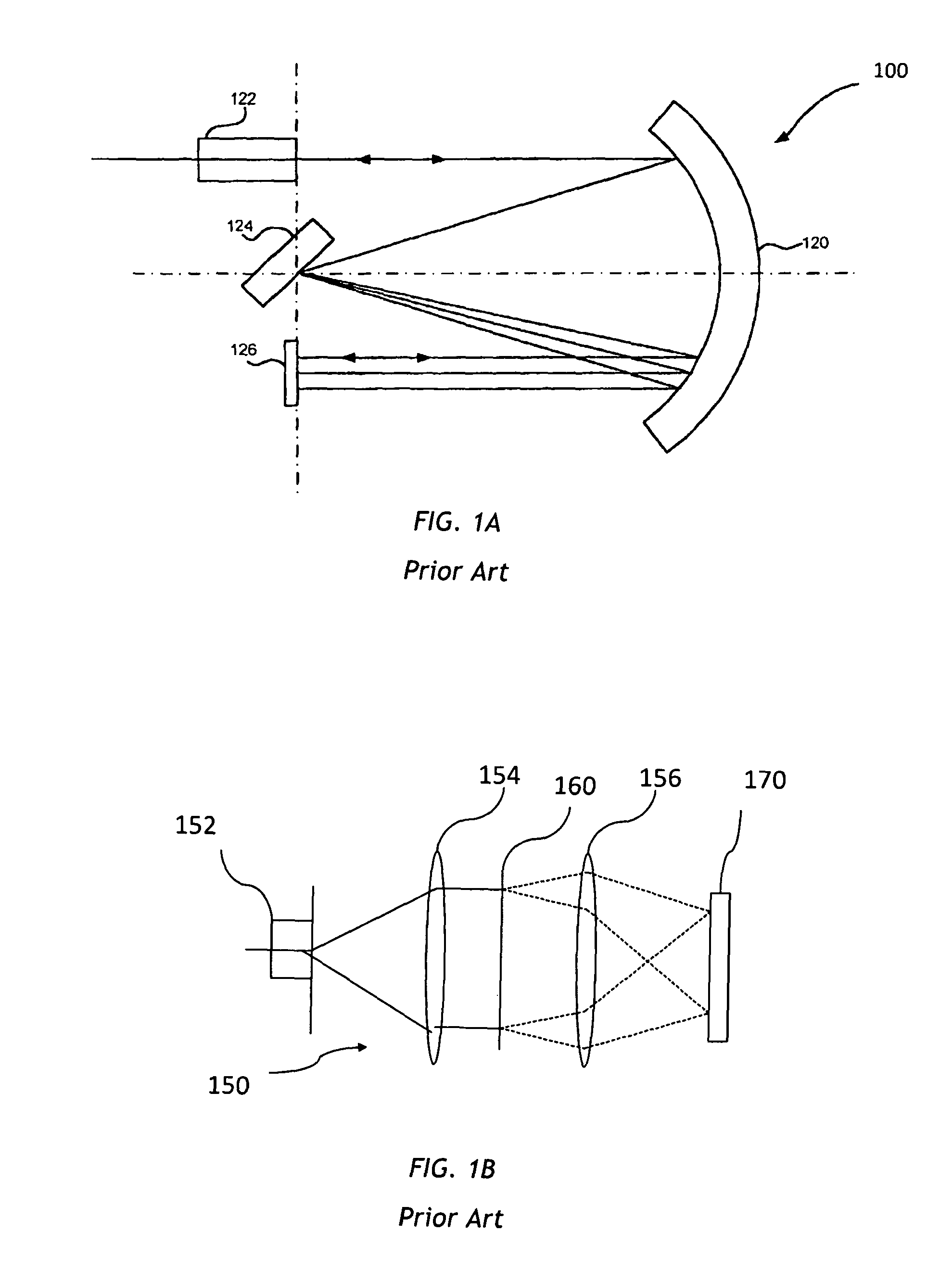
Stress free mounting of optical bench for WSS
ActiveUS8036502B2Restrict movementCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideEngineeringOptical table
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com