Olive salting liquid and method for preventing production of olive precipitate
A technology for salting liquid and precipitates is applied in the field of olive salting liquid and preventing the production of olive precipitates, and can solve the problems of affecting the surface color and luster of the olive candied fruit quality, affecting the absorption of nutrients of the olive candiing fruit, reducing the edible value of the olive candiing fruit and the like. , to achieve the effect of preventing the production of olive precipitates, being conducive to preservation, and shortening the salting time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0034] Further, the olives from which the waxy layer of the epidermis has been removed in step 1 are prepared by the following method: the olives that have been graded and the rotten fruit removed are added with coarse salt and whipped until the waxy layer of the olive epidermis is removed.
[0035] It can be seen from the above description that the beneficial effect of the present invention is that the olives are beaten with coarse salt to remove the waxy layer on the surface, so that the olive brine can quickly penetrate into the olives to replace the active ingredients in the olives, thereby realizing the preservation of the olives.
[0036] Further, in step 2, the solid-liquid ratio of the olives to the olive salting liquid is 1:1-1.5.
[0037] It can be seen from the above description that the beneficial effect of the present invention is that the solid-liquid ratio of olives and olive salting liquid is 1:1 to 1.5 to ensure that the olive salting liquid can cover the olive...
Embodiment 1
[0048] 1 Materials and methods
[0049] 1.1 Materials
[0050] fresh olives;
[0051] Reagents such as sodium chloride, calcium chloride, citric acid, and sodium metabisulfite are all food grade and meet national hygiene standards.
[0052] 1.2 Main instruments
[0053] WGZ-100 scattering photoelectric turbidimeter, Shanghai Precision Instrument Factory;
[0054] BAS224S electronic analytical balance, Sartorius Scientific Instruments (Beijing) Co., Ltd.
[0055] 1.3 Test method
[0056] 1.3.1 Preparation of olive salt germ
[0057] Step 1: Add coarse salt (accounting for about 5% of olive weight) to the olives that have been graded and remove rotten fruit, and beat until the waxy layer of the olive skin is removed, then wash with water, and then prick the olives that have removed the waxy layer of the skin hole;
[0058] Step 2: Configure the olive salting solution: add 13g sodium chloride, 0.6g sodium metabisulfite, 0.1g calcium chloride and 0.2g citric acid in every 1...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Repeat the process of embodiment 1, just each component of olive salting liquid has been changed, and beginning olive salting liquid is to add 13g sodium chloride, 1.5g sodium pyrosulfite, 0.15g calcium chloride and 0.6g citric acid in every 100g water, Allocate 10kg olive salting liquid according to this ratio (the pH value of this olive salting liquid is about 2.25); The osmotic pressure of the olive brine is too high, so the salinity is continuously adjusted on the second and third day after the olives and the olive brine are poured into the PC bucket. 20g, the soaking time is 20 days.
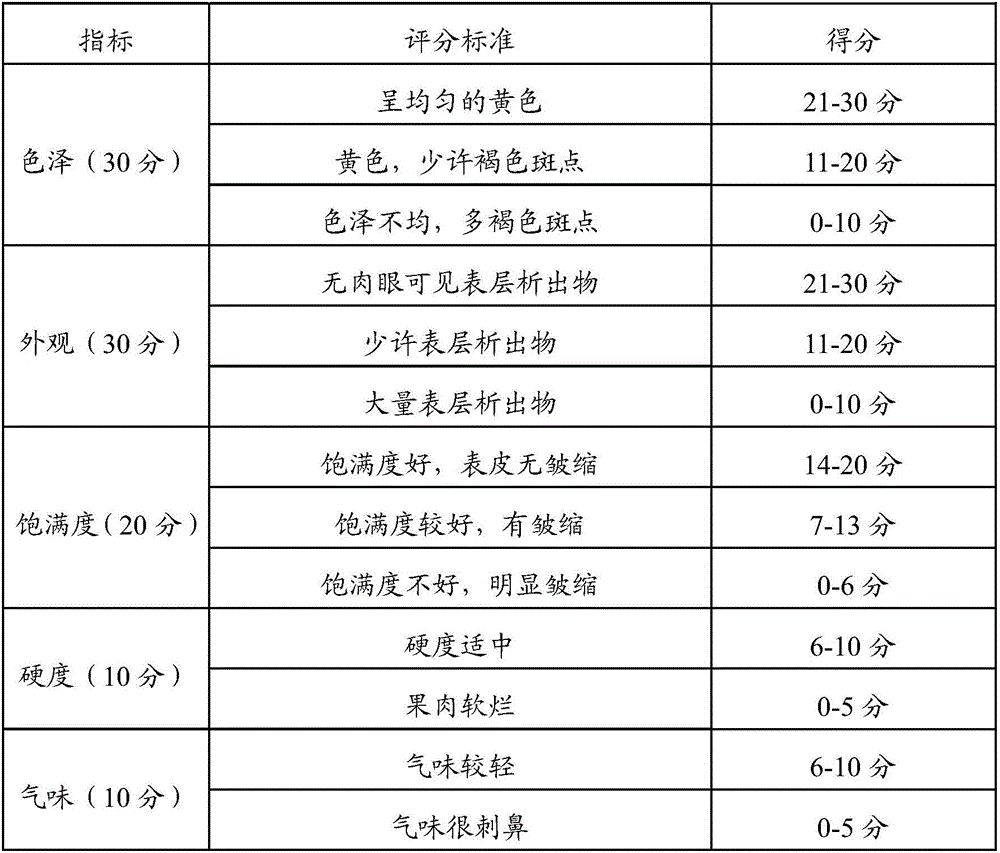
[0073] The evaluation method of olive salt germ quality is the same as that in Example 1, and the evaluation results of olive salt germ quality are shown in Table 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com