Method for manufacturing microporous fiber bar
A production method and technology of fiber rods, which are applied in the direction of household components, applications, and conjugated synthetic polymer artificial filaments, etc., can solve the problems of large energy consumption, short service life, and unsatisfactory use effects, so as to avoid pollution and save energy waste, long service life, good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
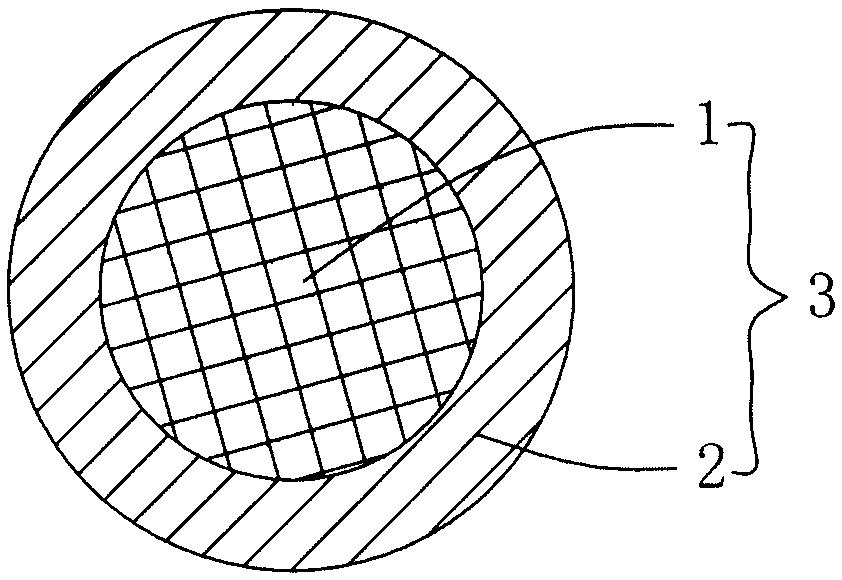
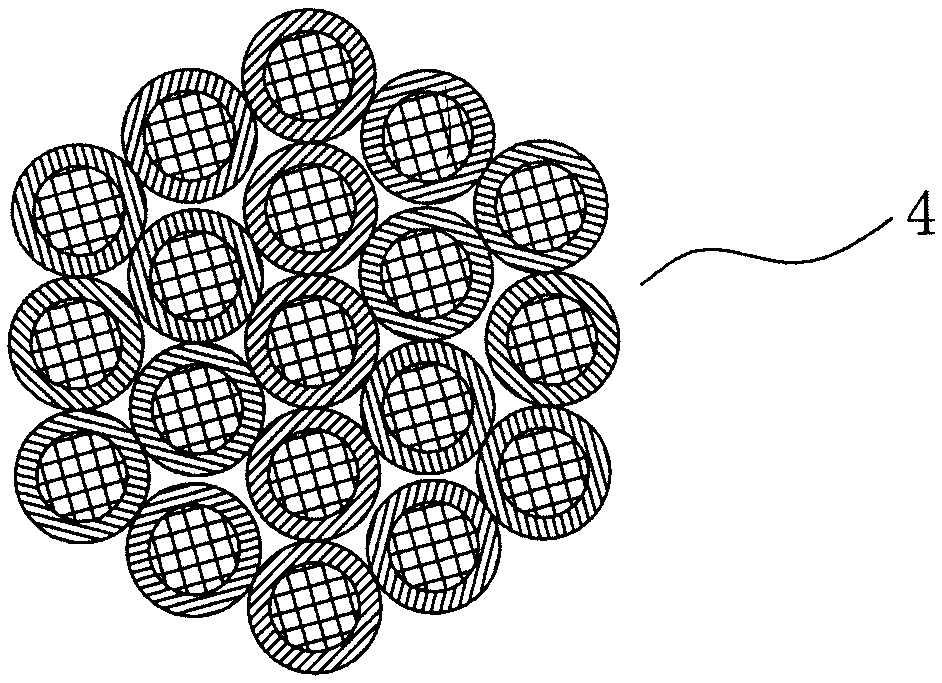
[0025] A method for making a microporous fiber rod stock, comprising the following steps: in the first step, two component polymers respectively form composite fibers of a skin layer and a core layer continuously along the fiber longitudinal direction, wherein the melting point of the skin material is lower than the The melting point of the core layer material; the mass ratio of the skin layer polymer material is 15% to 45%; 2, the core-skin composite fiber filament 3 is made, and the cross-section of the core-skin composite fiber filament 3 is a concentric circle (see figure 1 ) or an eccentric circle, wherein the melting point of the skin layer material 2 is lower than the melting point of the core layer material 1, and the mass ratio of the skin layer polymer material is 15% to 45%; specifically, the core layer is made of polyethylene terephthalate It is made of glycol ester material, and the skin layer material is made of copolyester material with a melting point of 160°C-2...
Embodiment 2
[0027] A method for making a microporous fiber rod stock, comprising the following steps: in the first step, two component polymers respectively form composite fibers of a skin layer and a core layer continuously along the fiber longitudinal direction, wherein the melting point of the skin material is lower than the The melting point of the core layer material; the mass ratio of the skin layer polymer material is 15% to 45%; 2, the core-skin composite fiber filament 3 is made, and the cross-section of the core-skin composite fiber filament 3 is a concentric circle (see figure 1 ) or an eccentric circle, wherein the melting point of the skin layer material 2 is lower than the melting point of the core layer material 1, and the mass ratio of the skin layer polymer material is 15% to 45%; specifically, the core layer is made of polyamide material, The skin layer material is made of copolyester materials with a melting point of 160° C. to 230° C. and a mass ratio of 15% to 45%. In...
Embodiment 3
[0029] A method for making a microporous fiber rod stock, comprising the following steps: in the first step, two component polymers respectively form composite fibers of a skin layer and a core layer continuously along the fiber longitudinal direction, wherein the melting point of the skin material is lower than the The melting point of the core layer material; the mass ratio of the skin layer polymer material is 15% to 45%; 2, the core-skin composite fiber filament 3 is made, and the cross-section of the core-skin composite fiber filament 3 is a concentric circle (see figure 1 ) or an eccentric circle, wherein the melting point of the skin layer material 2 is lower than the melting point of the core layer material 1, specifically, the core layer is made of polyacrylonitrile (PP) material, and the melting point of the skin layer material is 160 ° C ~ 230 ℃, the mass ratio is 15% to 45% of the copolyester material. In the second step, a number of core-skin composite fiber filam...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com