Semi-lignified acer rubrum shoot cuttage method
A semi-lignified and lignified technology, which is applied in the cutting of semi-lignified young shoots of Acer safflower and the breeding of Acer safflower, can solve the problems of slow plant growth, low survival rate, and short color leaf period, and achieve early germination, Fast rooting and strong growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1, a kind of semi-lignified shoot cutting method of Acer safflower, comprises the following steps:
[0031] 1. Material preparation
[0032] This experiment was carried out in the experimental nursery of Qingzhou Deli Agriculture and Forestry Technology Co., Ltd.;
[0033] In June, the semi-lignified "October Brilliant" shoots that grew vigorously, with full buds, and were basically the same in growth and thickness were selected as cuttings.
[0034] The thickness of the cuttings is 0.45 cm. Cut into sections, each section is 6 cm long, and keep 1 leaf.
[0035] 2. Treatment of cuttings
[0036] Carry out incision processing on the cuttings, wherein, the upper incision is about 1.2 to 1.8 cm away from the upper bud, and the lower incision is obliquely cut;
[0037] After the cuttings are cut, use 50% carbendazim wettable powder 500 times solution to soak the cuttings from the bottom to 1cm for 15 minutes, and then disinfect them for later use.
[0038] 3...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The experiment of the influence of the selected cuttings on the rooting rate of embodiment 2
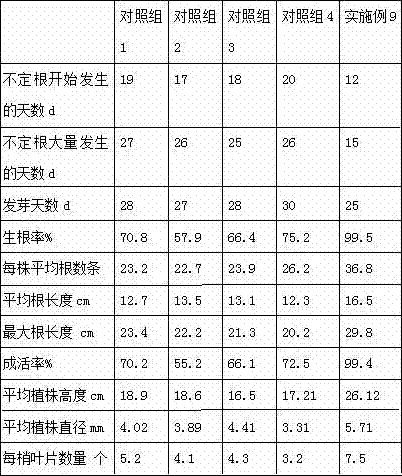
[0051] Carry out cutting seedling raising according to the method of embodiment 1, only change the thickness and the length of semi-lignified shoot cuttings selected in step 1 material preparation and carry out embodiment 2~4; See table 1 for details:
[0052] Thickness and length of semi-lignified shoot cuttings selected in table 1 material preparation
[0053]
[0054] Investigate the cutting rooting situation of embodiment 1~4 after cuttingtage 50d, rooting rate (%)=cutting root number / cutting total number×100%;
[0055] The survey results are shown in Table 2;
[0056] The rooting rate of table 2 cuttings
[0057]
[0058] Investigation result shows, the rooting rate of embodiment 2, 3 is obviously higher, is preferred embodiment; The thickness of semi-lignified new shoot cuttings selected in step 1 material preparation is preferably 0.5~0.55cm, and length is prefe...
Embodiment 5
[0059] Example 5 Effects of different cutting substrates on the survival rate of Acer safflower
[0060] Carry out cutting seedling raising according to the method of embodiment 1, only change the cutting matrix in step 4 cutting, carry out embodiment 5~8; See table 3 for details;
[0061] Table 3 Cutting substrates used
[0062]
[0063] 80 days after cutting, investigate the survival of each cutting seedling, survival rate (%)=survival number of cuttings / total number of cuttings×100%; see Table 4 for details:
[0064] Table 4 Survival rate of cuttings
[0065] Example 5 Example 6 Example 7 Example 8 Survival rate % 85.5% 90.2 95.7 80.5%
[0066] The survey results show that the survival rate of the cuttings in Example 7 is significantly higher, and the cutting substrate in the cuttings is preferably a mixed substrate of river sand, vermiculite, and pine pollen at a volume ratio of 1:1:0.2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com