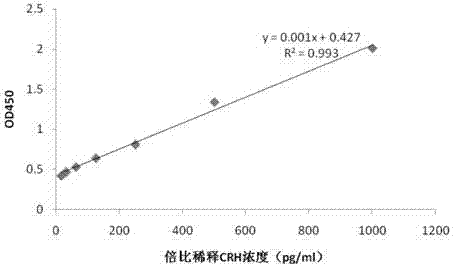
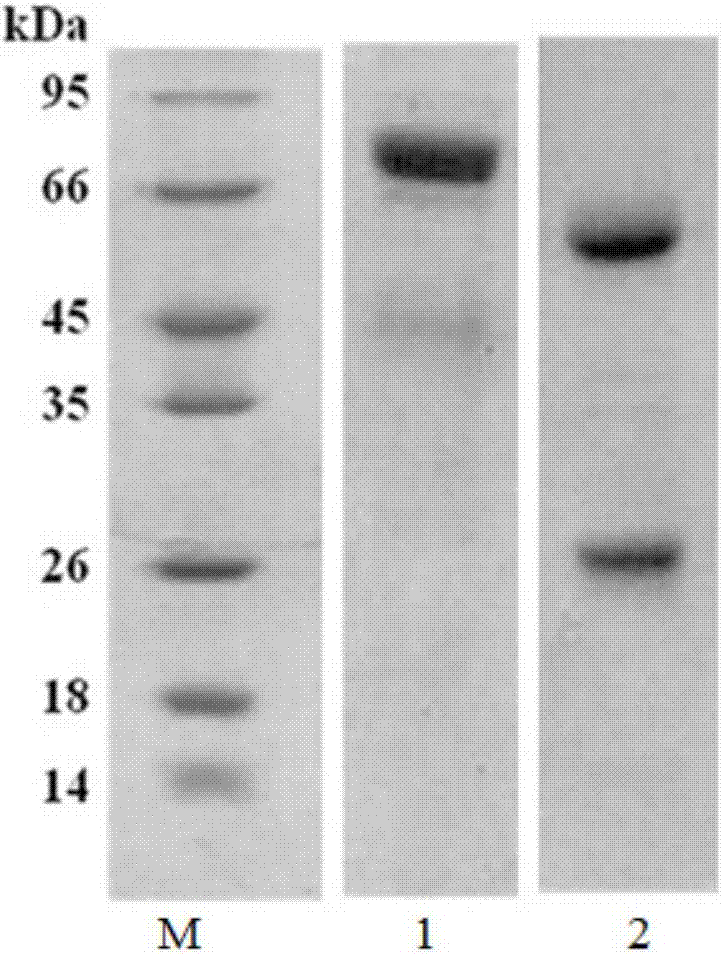
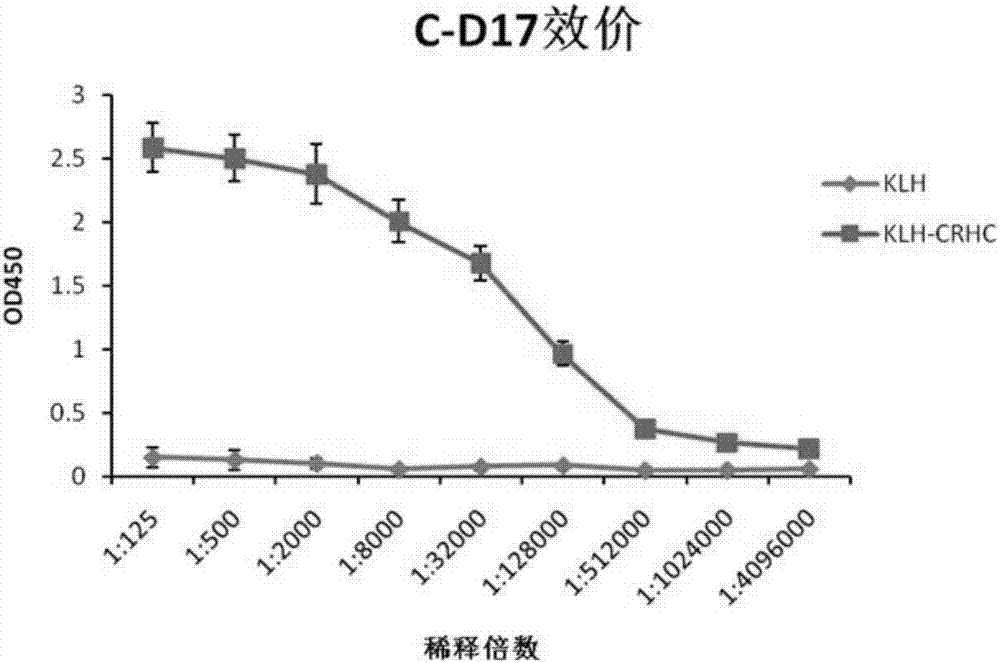
Hybridoma cell strain, anti-CRH antibody C-D17 based on hybridoma cell strain, and application of anti-CRH antibody C-D17 to detection
A hybridoma cell line and hybridoma cell technology are applied in the field of anti-adrenocorticotropin-releasing hormone monoclonal antibodies, which can solve problems such as health threats to rescue workers in plateau work, and achieve high sensitivity, low material consumption, and good specificity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1 Preparation and purification of the monoclonal antibody C-D17 of the present invention.
[0039] 1. Preparation of immunogen
[0040] 1.1 Preparation of CRHC synthetic peptide: Synthesize the C-terminal epitope of CRH, the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, and the purity is greater than 99%.
[0041] 1.2 Obtaining of KLH-CRHC coupled peptide: Weigh 3 mg m-maleimide benzoic acid-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester (MBS) and dissolve it in 200 μL dimethylformamide (DMF), and take 1.5 mg KLH Dissolve in 0.5ml 0.05mol / L phosphate buffer (pH 7.0), add 70μL of prepared MBS solution to it, stir at room temperature for 30min; Buffer (pH 6.0) to elute, and collect 3.5mL of purified KLH / MBS; add 0.5mL of deionized water, 5mg of CRHC synthetic peptide dissolved in 100μL of DMF, quickly add 1mL of purified KLH / MBS, shake quickly and immediately wash with 2N Adjust the pH to 7.0-7.2 with NaOH, and place the mixed solution at 4°C overnight; finally add 3mL 0.1mol / LNH 4 HCO 3 , ly...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Example 2 Preparation and purification of the monoclonal antibody N-D19 of the present invention.
[0064] 1. Preparation of immunogen
[0065] 1.1 Preparation of CRHN synthetic peptide: Synthesize the N-terminal epitope of CRH, the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the purity is greater than 99%.
[0066] 1.2 Obtaining of KLH-CRHN coupling peptide: Weigh 3 mg m-maleimide benzoic acid-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester (MBS) and dissolve it in 200 μL dimethylformamide (DMF), and take 1.5 mg KLH Dissolve in 0.5ml 0.05mol / L phosphate buffer (pH 7.0), add 70μL of prepared MBS solution to it, stir at room temperature for 30min; Buffer (pH 6.0) to elute, and collect 3.5mL of purified KLH / MBS; add 0.5mL of deionized water, 5mg of CRHN synthetic peptide dissolved in 100μL of DMF, quickly add 1mL of purified KLH / MBS, shake quickly and immediately wash with 2N Adjust the pH to 7.0-7.2 with NaOH, and place the mixed solution at 4°C overnight; finally add 3mL 0.1mol / LNH 4 HCO 3 ,...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Embodiment 3 The present invention detects the composition of the double antibody sandwich ELISA kit of CRH and optimal working concentration detection
[0089] 1. Preparation of HRP-labeled anti-human CRH monoclonal antibody C-D17 or N-D19
[0090] The method for HRP-labeled monoclonal antibody C-D17 or N-D19 is as follows: First, weigh 10 mg of HRP dry powder, fully dissolve it in 5 mL double-distilled water, and add freshly prepared 0.2 mol / L NaIO 4 Solution 0.5mL, shake gently on a horizontal shaker at 4°C for 30min in the dark, add 10mg of monoclonal antibody C-D17 or N-D19 antibody that has been dialyzed into carbonate buffer, mix well, and fill the solution with molecular weight cut-off Dialyze it against 0.05mol / L pH9.6 carbonate buffer at 4°C in a 50kDa pre-treated dialysis bag, change the dialysate every 6h, and dialyze four times; after the dialysis, take out the dialysis bag Liquid in the bag, to which NaBH was added at a concentration of 5 mg / mL 4 100μL,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com