Patents
Literature
228results about How to "Good specificity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
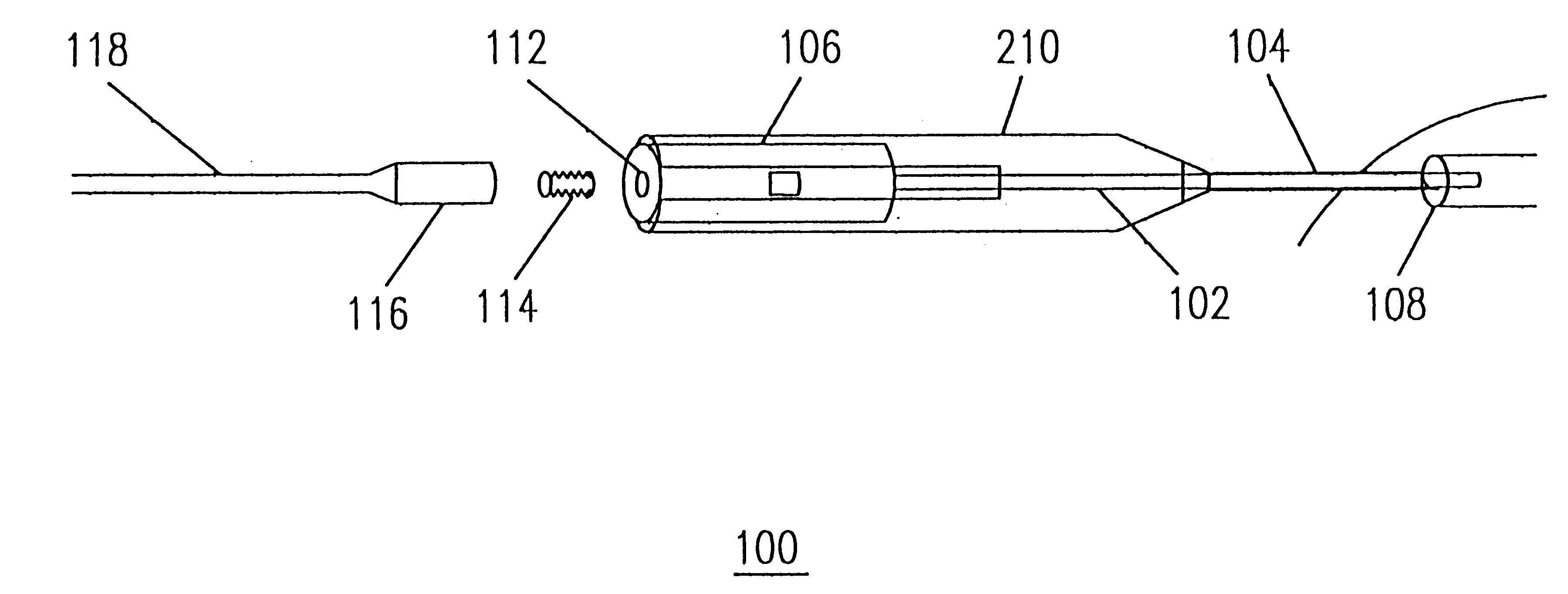
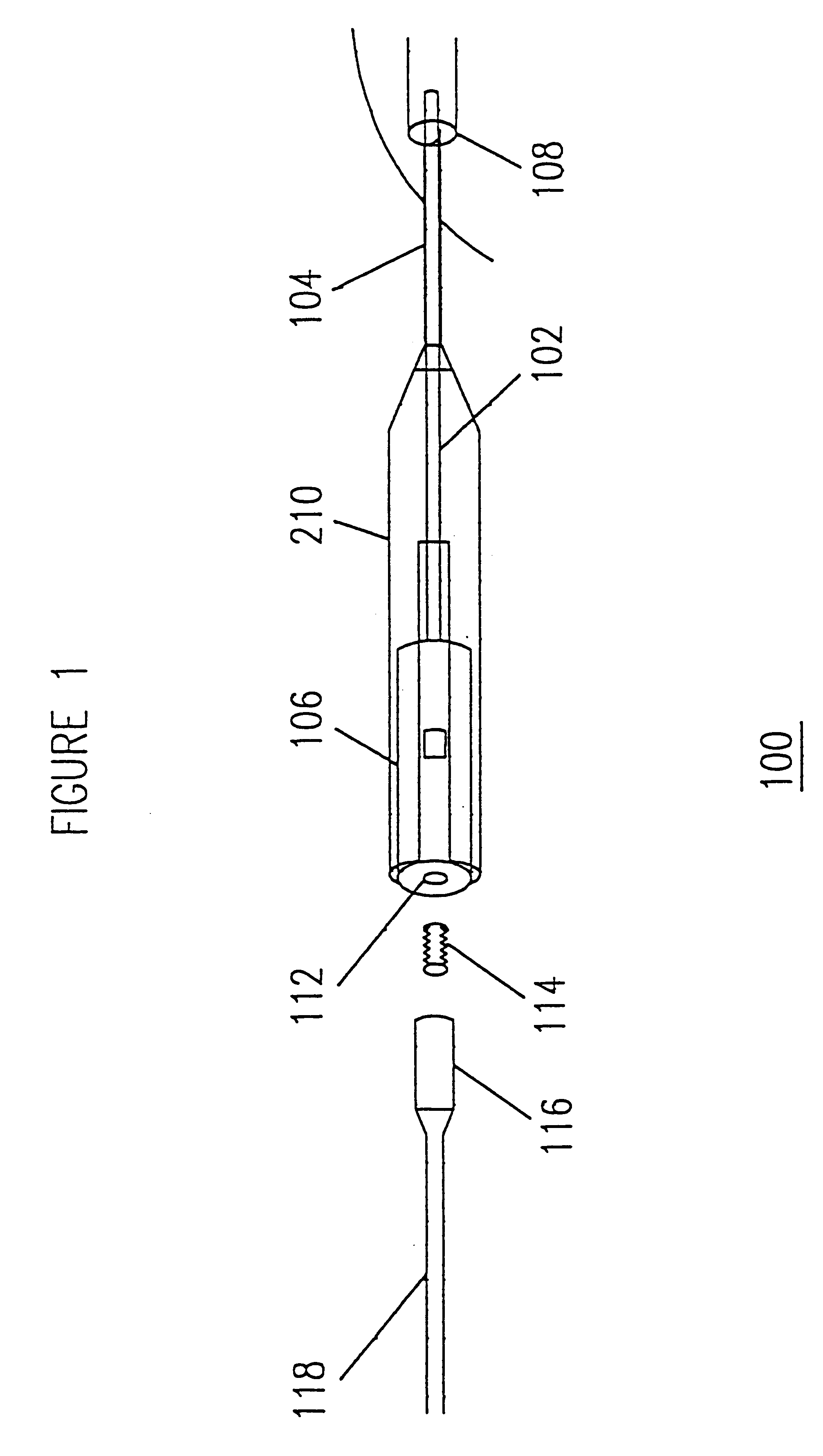
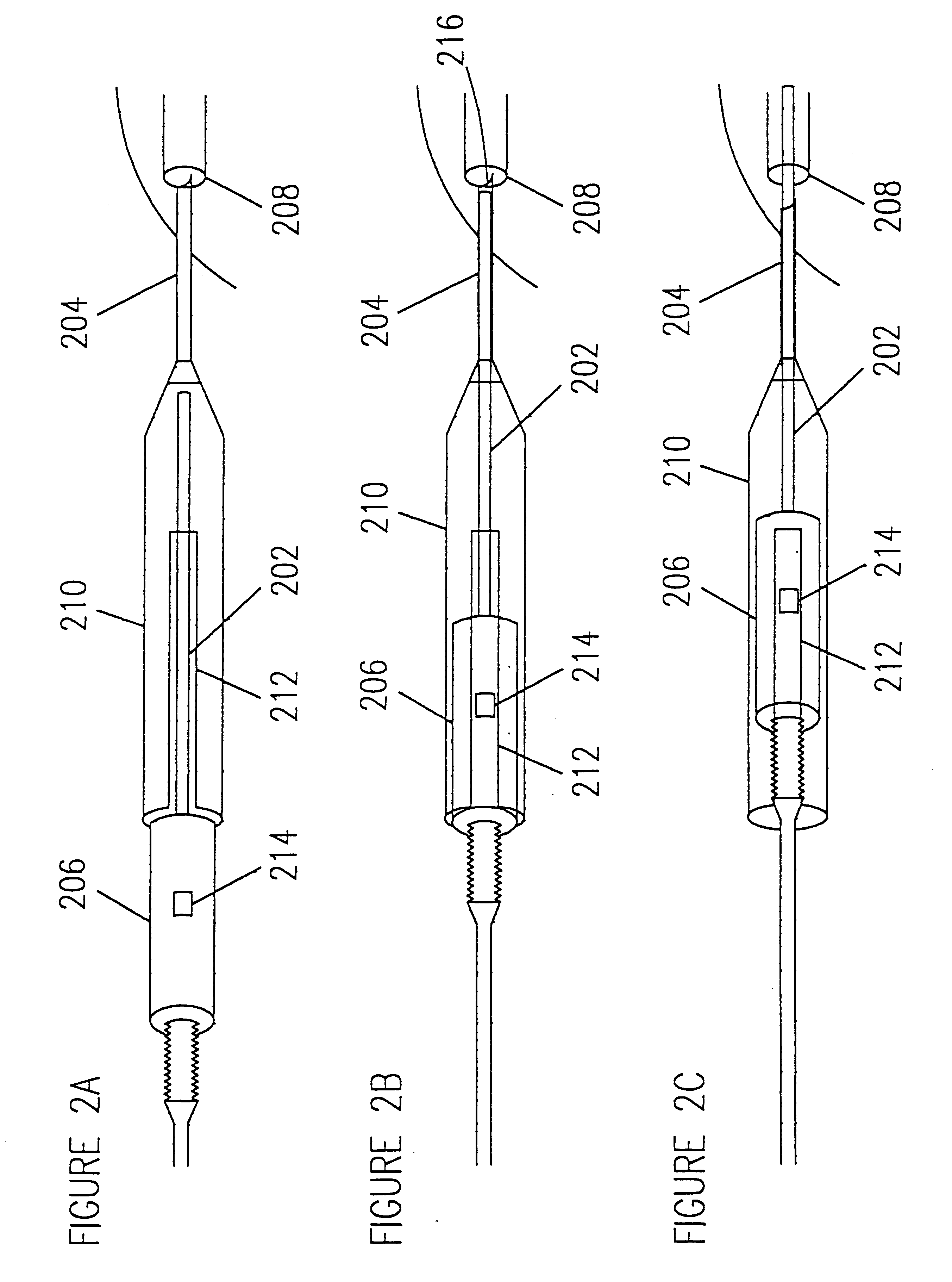
Device and method for underskin laser treatments
InactiveUS6200332B1Eradicate internal abnormalityGood specificityCatheterSurgical instrument detailsVascular structureTreatment field
A device and method for underskin laser treatment that is minimally invasive, versatile and precise, that allows for underskin laser treatment with only minimal insertions into the area of treatment. For example, an entire area may be treated with one insertion. The device and method incorporates a standard insertion component making the system inexpensive and easy for doctors to use. In addition, the the invention allows users to get in direct contact with the treatment site, eliminating deleterious side effects encountered when treatment is administered to the skin surface. The device and method has applications in several areas of treatment. First, underskin treatment of aesthetic skin blemishes such as sagging and wrinkles can be performed with minimal external effects. Laser power is delivered directly beneath the skin, bypassing harmful exposure of the skin surface to the radiation. Second, common vascular abnormalities such as capillary disorders, spider nevus, hemangioma, and varicose veins can be selectively eliminated. The device allows a simple, single insertion per treated structure and specific laser delivery. The needle is inserted into the vascular structure and any abnormalities are eradicated starting from the source and continuing through the entire structure. Third, when coupled with x-ray imaging, the present invention may be used to treat various internal body structures for example during surgery. X-ray imaging allows the user to orient the device within the body structures. Laser delivery treatment can then be administered as described above.
Owner:BIOLITEC UNTERNEHMENSBETEILLIGUNGS II AG
Indirect ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) method and kit for detecting haemophilus parasuis antibodies
InactiveCN101968490AGood specificityHigh sensitivityBacteria peptidesBiological testingEpidemiologic surveyEnzyme
The invention discloses indirect ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) method and kit for detecting haemophilus parasuis antibodies. The indirect ELISA method comprises the steps of: taking a haemophilus parasuis OMPP5 protein as an envelope antigen; wherein the judgment standard is as followed: OD450 value of to-be-detected serum is greater than 0.375, OD450 value of the to-be-detected serum / OD450 value of standard negative serum is greater than or equal to 2.1. The kit for realizing the method comprises an envelope buffer solution, confining liquid, a washing buffer solution, an antibody diluent, a chromogenic substrate solution and a stop solution, wherein the envelop antigen used in the method is the haemophilus parasuis OMPP5 protein. Proved by a specificity test, a blocking-up experiment, a repeatability test and clinic application detection, the invention has the characteristics of excellent specificity, high sensitiveness, good repeatability, rapidness, simpleness and accuracy, and can be used in clinic large-scale detection of haemophilus parasuis antibodies and epidemiological survey.
Owner:广东省农业科学院兽医研究所
Application of cystatin (SN)
ActiveCN103898205AHigh sensitivityGood specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPancreas CancersCystatin-SN
The invention discloses novel application of cystatin (SN), and particularly relates to application of cystatin SN to preparation of markers for diagnosing and indicating liver cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, pancreas cancer or esophagus cancer. The invention further discloses a trapping agent of the markers for diagnosing and indicating liver cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, pancreas cancer or esophagus cancer, and application of the trapping agent to preparation of a kit for diagnosing and indicating liver cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, pancreas cancer or esophagus cancer. The prepared kit has the advantages of good specificity, high sensitivity and the like, and can be used for early diagnosing liver cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, pancreas cancer or esophagus cancer, evaluating the treatment effect in the treatment process, and monitoring the transfer relapse after treatment.
Owner:SHANGHAI LIANGRUN BIOMEDICINE TECH CO LTD
Hepatitis B virus surface antigen quantitative determination kit and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104090106AHigh sensitivityGood specificityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceQuantitative determinationEnzyme
The invention belongs to the technical field of immunologic diagnosis, and particularly relates to a hepatitis B virus surface antigen quantitative determination kit and a preparation method thereof by a microparticle chemiluminescence method. The kit consists of magnetic particles for testing HBsAg (hepatitis B virus surface antigen), a tracer conjugate for testing HBsAg, a calibrator, an analysis buffer solution and sample diluent. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the quantitative determination kit. By adopting a microparticle chemiluminescence immuno assay, compared with the ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay), the sensitivity and specificity are higher, and the hepatitis B virus surface antigen quantitative determination kit and the method are suitable for the clinical auxiliary diagnosis of hepatitis B.
Owner:威海威高生物科技有限公司
Mimic electrochemical immunosensor for detecting beta-amyloid protein oligomers and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105651840AGood specificityHigh selectivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingAntibodyOxide
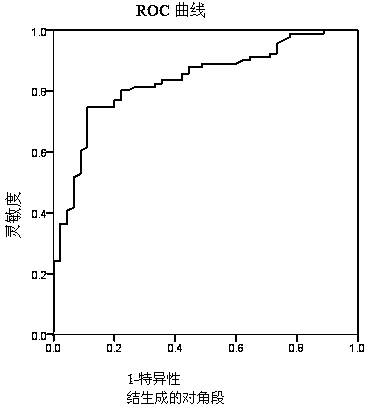
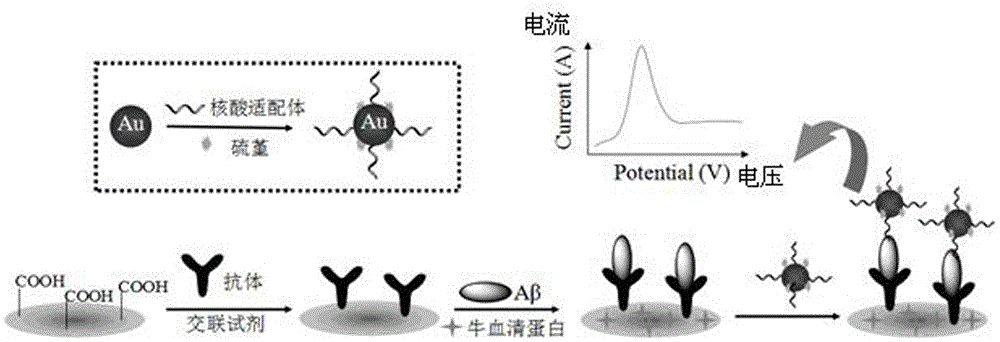
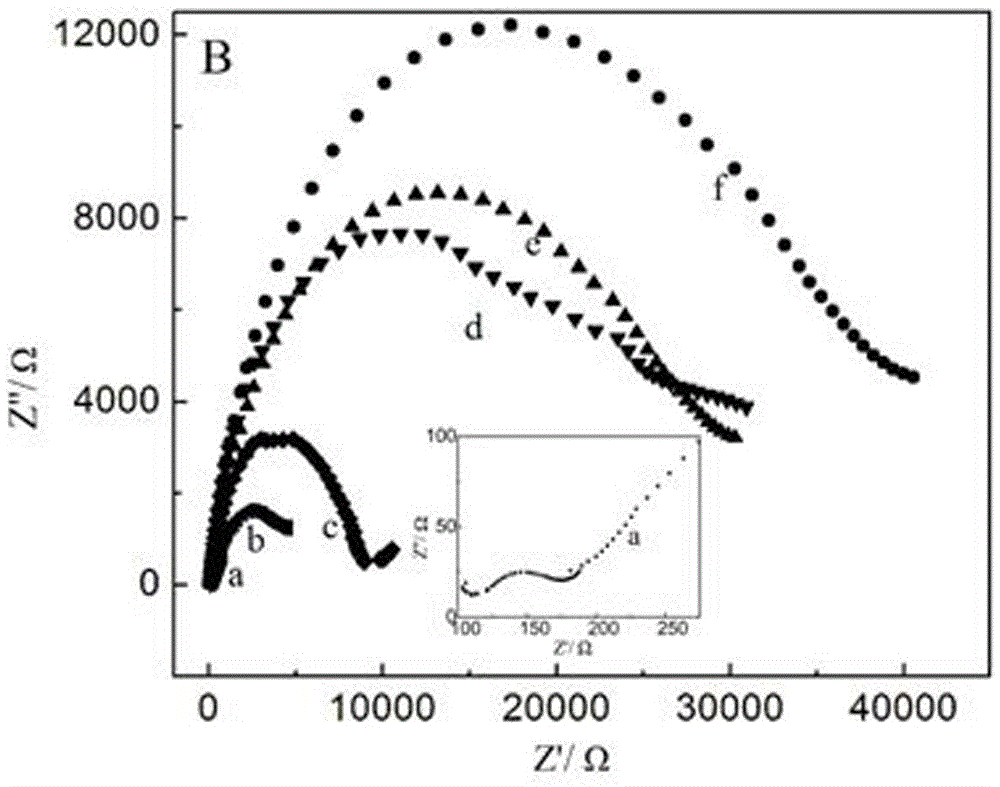
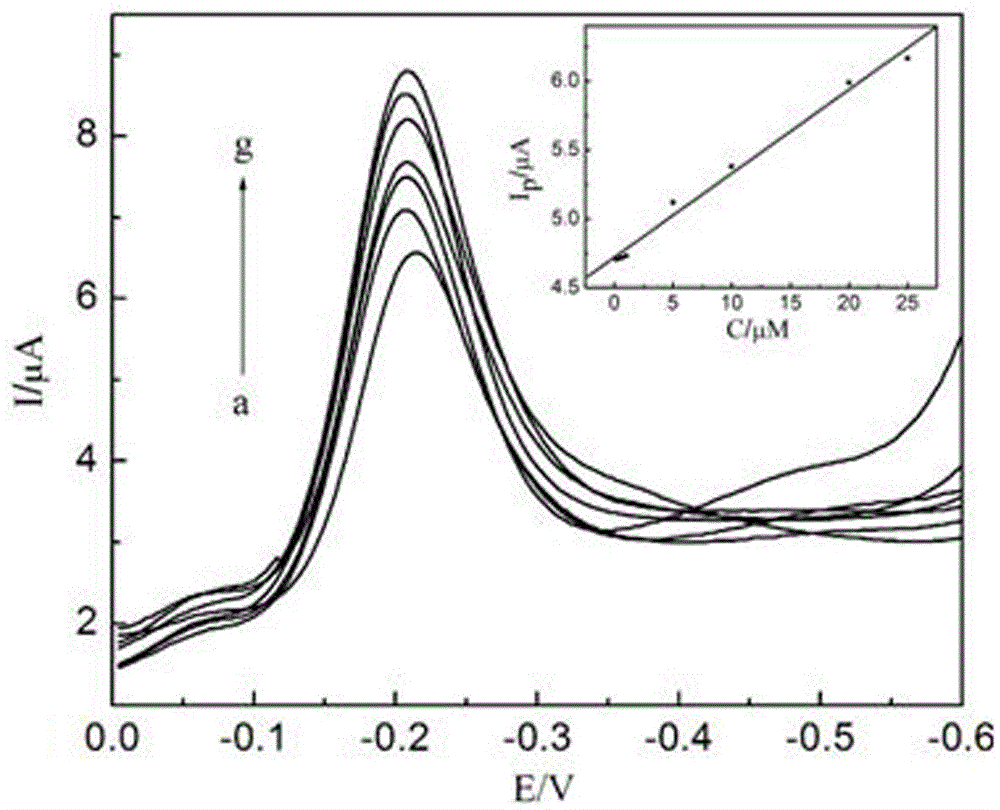
The invention relates to a mimic electrochemical immunosensor for detecting beta-amyloid protein (ABeta) oligomers and preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of biosensing and electroanalytical chemistry. gold nanoparticles jointly act with sulfhydryl-modified aptamer and thionine to form a stable nano conjugate; an antibody is fixed to the surface of a carboxylic graphene oxide modified electrode; after an ABeta oligomer is recognized, the oligomer is further connected with the aptamer modified gold nanoparticle conjugate, thus forming a sandwich mimic immunosensor; the ABeta oligomer is measured through thionine electrochemical signals. The immunosensor has high sensitivity, good specificity and high stability; compared with traditional immunosensors, the immunosensor features preparation simplicity and avoidance of the use of enzyme-labeled antibody reagents, is useful in the detection of ABeta oligomers in cerebrospinal fluid to promote early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and has clinical applicable value.
Owner:SHANGQIU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin positive bacteria dual fluorescent quantitative PCR rapid detection kit
ActiveCN104531867AGood specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFalse positive rateEnterotoxin
The invention relates to a fluorescent quantitative PCR rapid detection kit for specifically detecting clostridium perfringens enterotoxin positive bacteria infection. The detection kit comprises (a) a fluorescent quantitative reaction solution; (b) clostridium perfringens exotoxin cpa positive and clostridium perfringens enterotoxin cpe positive quality control substances; and (c) a negative quality control substance, wherein the fluorescent quantitative reaction solution comprises 2 pairs of primers and one pair of probes, namely a forward primer cpa01 and a reverse primer cpa02 of clostridium perfringens exotoxin cpa and a fluorescence probe cpap, as well as a forward primer cpe01 and a reverse primer cpe02 of clostridium perfringens enterotoxin cpe and a fluorescence probe cpep. The detection kit disclosed by the invention has the advantages that positive clostridium perfringens of the enterotoxin cpe can be rapidly diagnosed; the specificity is high, the sensitivity is high, and the false positive rate is low; and moreover, the detection speed is high, and only one and a half hours are needed.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Primer, probe and kit for detecting canine parvovirus and detection method
InactiveCN105803112AGood specificityEasy stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCanine parvovirusNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to a primer, probe and kit for detecting canine parvovirus and a detection method.According to the fluorogenic quantitative PCR primer for detecting canine parvovirus, an upstream detection primer CPV-F has the nucleotide sequence as shown in the SEQ ID NO.1, and a downstream detection primer CPV-R has the nucleotide sequence as shown in the SEQ ID NO.2.The probe has the nucleotide sequence as shown in the SEQ ID NO.3.The kit comprises the primer and the probe.The fluorogenic quantitative PCR primer, probe and kit for detecting canine parvovirus have the advantages that operation is easy, cost is low, sensitivity is high and specificity is high, and can guarantee clinical detection.
Owner:中国人民解放军成都军区疾病预防控制中心
Hybridoma cell line Anti-CLas McAb1 and monoclonal antibody secreted by hybridoma cell line Anti-CLas McAb1 and use thereof
ActiveCN108486064AGood specificityStrong anti-interferenceImmunoglobulins against bacteriaTissue cultureInterference resistanceCandidatus Liberibacter asiaticus
The invention provides a hybridoma cell line Anti-CLas McAb1 which is a mouse hybridoma cell (Mus musculus Hybridoma) Anti-CLas McAb1 and has a preservation number of CCTCC NO: C2017219. The inventionalso provides a preparation method of the hybridoma cell strain and a recombinant Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus CLas McAb1 monoclonal antibody secreted by the hybridoma cell strain or a passage cell thereof. The invention also provides uses of the recombinant Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus n CLas McAb1 monoclonal antibody. The uses comprise a detection kit and an immunocolloidal gold teststrip and utilizes the specific detection of the recombinant Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus CLas McAb1 monoclonal antibody. The recombinant Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus CLas McAb1 monoclonal antibody has the advantages of good specificity, strong interference resistance, low cost and wide application, and can quickly and effectively detect Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus in citrus materials.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Lily mottle virus double-antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit and preparation method
ActiveCN101915835AHigh sensitivityGood specificityImmunoglobulins against virusesFermentationPolyclonal antibodiesGenetic engineering
The invention relates to a lily mottle virus (LMoV) double-antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit and a preparation method. The assay kit comprises a 96 micropore ELISA plate, an enzyme labeled antibody, a buffer solution, a developing solution and a stop solution, wherein the 96 micropore ELISA plate is coated with an LMoV specific polyclonal antibody, and the enzyme labeled antibody is an LMoV specific polyclonal antibody labeled by horse radish peroxidase. An immunogen used in the invention is a fusion recombinant antigen of LMoV coat protein and cytoplasmic inclusion protein, which is expressed by genetic engineering. The double-antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay established by antibodies produced by the immunization can be used for detecting lily leaf specimens. Compared with other detection methods, the double-antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay has high detection sensitivity and high accuracy, and ng-level viral antigenscan be detected. The preparation method of the kit is simple, convenient, quick, economical and practical.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO-ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
Time-resolved immunochromatography kit for synchronously detecting aflatoxin and carbaryl mixed pollution, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106918704AGood specificityHigh sensitivityBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against fungi/algae/lichensFluorescenceChemistry
The invention relates to a time-resolved immunochromatography kit for synchronously detecting aflatoxin and carbaryl mixed pollution, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The kit comprises an immunochromatography time-resolved fluorescence test strip and a sample reaction bottle containing lyophilized products of an europium-labeled anti-aflatoxin monoclonal antibody and an europium-labeled anti-carbaryl monoclonal antibody, wherein the detection line of the immunochromatography time-resolved fluorescence test strip is respectively coated with an aflatoxin-bovine serum albumin conjugate and a carbaryl-ovalbumin conjugate; and the anti-carbaryl monoclonal antibody is secreted by a hybridoma cell strain Jnw1D2 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO.C201654. The kit can be used for synchronously detecting the content of aflatoxin and carbaryl in a sample, and has the characteristics of simplicity in operation, rapidness and high sensitivity.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
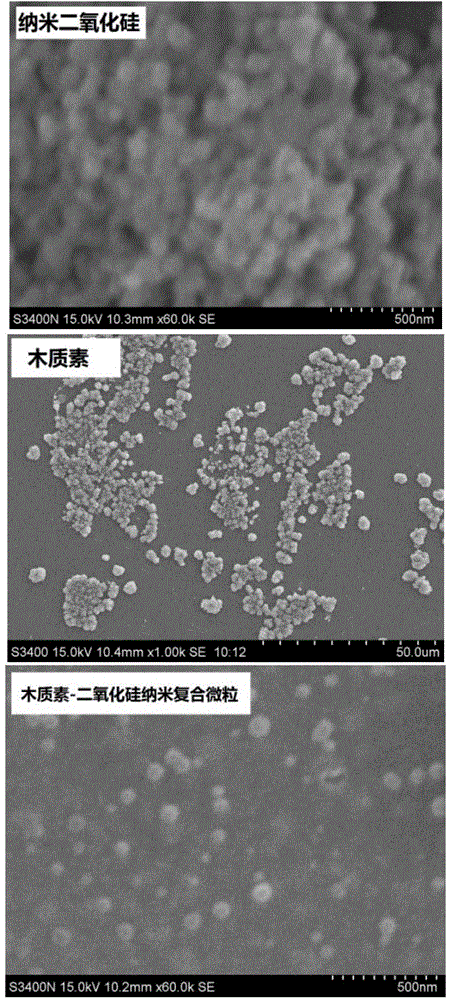
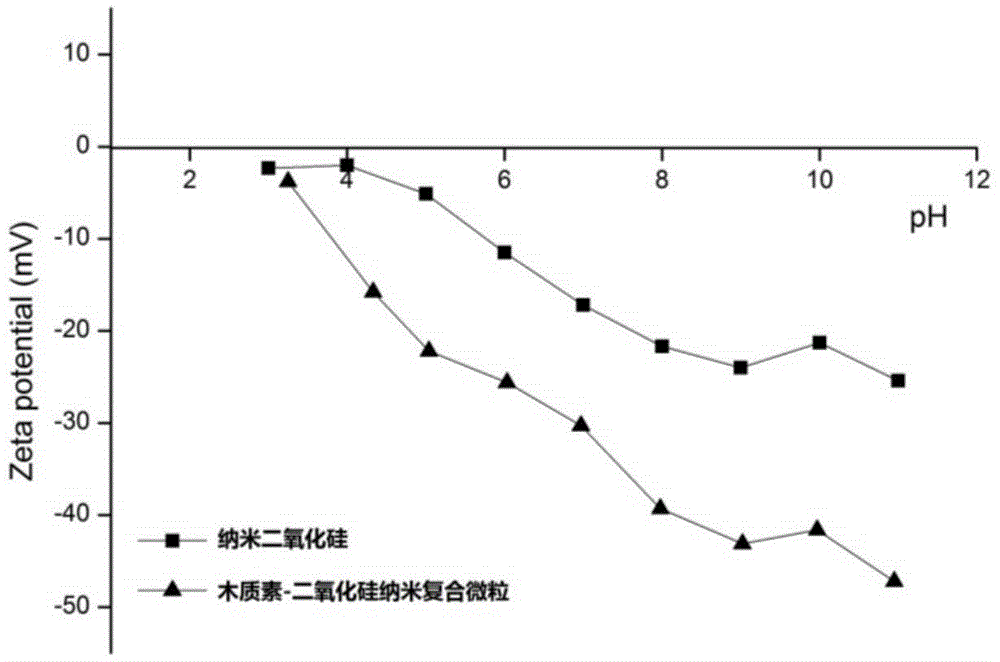
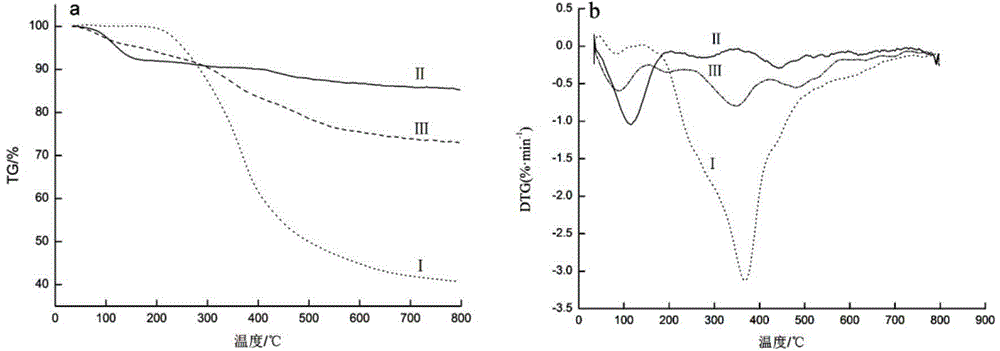
Lignin-silicon dioxide nanocomposite particle as well as preparation method and application of lignin-silicon dioxide nanocomposite particle
The invention discloses a lignin-silicon dioxide nanocomposite particle as well as a preparation method and application of the lignin-silicon dioxide nanocomposite particle. The method comprises the steps of firstly, introducing an azido structure on the surface of a nano silicon dioxide particle by virtue of alkylation reaction, and preparing alkynyl lignin from lignin; then, reacting alkynyl lignin and triazo nano silicon dioxide under the catalytic action of Cu (I) to prepare the lignin-silicon dioxide nanocomposite particle containing a triazole structural unit. The lignin-silicon dioxide nanocomposite particle prepared according to the characteristics of click reaction temperature, high speed and good specificity has favorable dispersibility and thermal stability and good selective heavy metal ion adsorption performance, has the Cu<2+> adsorption capacity of 120-135mg / g, and can be applied to the field of ion adsorption materials and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM IND OF FOREST PROD CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Gene chip for identifying capripoxvirus virus and detection method of same
ActiveCN102373303AStrong and stable hybridization signalGood specificityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementPox virusesMicroarray cgh
The invention discloses relates to a capripoxvirus virus, and provides a chip detecting device for goat pox virus, sheep pox virus and cow lumpy skin disease virus. In the invention, a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer is designed through analyzing a genome sequence of a standard virus strain; a specific probe is designed through analyzing the clone and sequencing of a target gene; and the goat pox virus, the sheep pox virus and the cow lumpy skin disease virus of capripoxvirus can be identified at the same time. The invention aims at providing a method for detecting the goat pox virus, the sheep pox virus and the cow lumpy skin disease virus of capripoxvirus by using a microarray array which has the characteristics of high sensitivity, high specificity, time saving and labor saving and is easy to observe a result.
Owner:重庆海关技术中心
Septin 9 gene methylation detection method and kit
PendingCN110305940AHigh detection sensitivityGood specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceEnzyme
The invention provides a Septin 9 gene methylation detection kit. The kit comprises at least one of the following three groups of specific primers and probes aiming at the detection of Septin 9-v2 exon methylation, SEQ ID NO.5-SEQ ID NO.7, SEQ ID NO.8-SEQ ID NO.10, and SEQ ID NO.11-SEQ ID.13. The invention further provides a Septin 9 gene methylation detection method and a sample pretreatment method. The Septin 9 gene methylation detection method comprises the following steps of TET enzyme oxidation; pyridine borane reaction; and multiple fluorescence PCR reaction. The kit and the detection method have the advantages of high detection sensitivity, good specificity and high detection flux.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
Method for quantitively detecting methane-oxidizing bacterium
ActiveCN102154441AFastGood specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceEnvironmental chemistryFluorescent staining
The invention discloses a method for quantitively detecting methane-oxidizing bacterium. The method comprises the following steps: sampling; washing bacterium with PBS (Phosphate Buffer Solution) by shaking samples; designing and selecting a double-layer microfiltration membrane plate with specific pores according to the number of the samples; and filtering the bacteria, passing the membrane and fixing; and conducting fluorescent dyeing and result analysis. According to the fluorescent strength of samples on the microfiltration membrane plate, the number of the methane-oxidizing bacterium in soil samples or sediment samples can be quantitively calculated, so as to provide technical support for microorganism oil-gas exploration and microorganism oil-gas reservoir characteristics.
Owner:GUANGZHOU ENENTA CHEM SCI & TECH
Goldmag particles based method for immunoprecipitation
ActiveCN101726603AGood specificityGood reproducibilityBiological testingSpecific proteinNon specific
The invention relates to a goldmag particles based method for immunoprecipitation, belonging to the field of the immunoprecipitation. The goldmag particles based method for immunoprecipitation comprises the following steps of: firstly adding an antibody to a biological sample for immunoprecipitation; and then adding a carrier fixing a protein A / G for separation, or adding a carrier fixing the antibody to the biological sample for the separation after the immunoprecipitation. The method mainly comprises the steps of antibody fixing, immunoprecipitation and elution. The invention solves the problems of nonspecific binding, a few selection varieties of adoptable antibodies and much antibody activity loss in the traditional immunoprecipitation and mainly includes an individual immunoprecipitation (IP) used for separating a known specific protein of the biological sample, a co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) used for researching an integral protein complex, testing whether two target proteins are combined in vivo or not and determining the new action cooperation of the specific protein, a chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) used for researching a protein combined with DNA, an RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) used for researching a protein combined with RNA, and the like.
Owner:XIAN GOLDMAG NANOBIOTECH
Highly specific gene fragment of Cronobacter spp. and its application
ActiveCN102816761AGood specificityHigh specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesPolymerase chain reactionBase sequence
The invention relates to a Cronobacter spp. 16S rDNA gene based sequence, and also provides a method for specific detection of Cronobacter spp. by combining magnetic beads and a nested PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology. The advantage of the invention lies in that: a specific probe and primers of the Cronobacter spp. 16S rDNA gene sequence are utilized, and magnetic beads are combined to conduct rapid and specific capture and enrichment of a Cronobacter spp. target gene in a sample, finally amplification detection is performed through the nested PCR technology, and the detection sensitivity is improved.
Owner:WUXI ZODOLABS BIOTECH
LAMP primer group and detection kit for staphylococcus aureus and use method of detection kit
InactiveCN106434917AGood specificityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesThermostable NucleaseMolecular level
The invention discloses an LAMP primer group and an LAMP detection kit for staphylococcus aureus and a use method of the detection kit. The LAMP primer group for staphylococcus aureus comprises a pair of outer primers, a pair of inner primers and a pair of loop primers. According to the LAMP primer group, the LAMP detection kit and the use method, loop-mediated isothermal amplification primers are designed according to the sequences of the conservative regions of the heat-resistant nuclease genes (nuc) of staphylococcus aureus, the specific regions of target genes are amplified by adopting the LAMP technology, thus the rapid detection for staphylococcus aureus is realized from the molecular level, and an effective and rapid nucleic acid screening detection method is provided for detecting staphylococcus aureus.
Owner:中华人民共和国广州机场出入境检验检疫局 +2
Melamine hapten, melamine complete antigen and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101955468AGood specificityHigh sensitivityOvalbuminSerum albuminChemical structureChemistry
The invention discloses a melamine hapten, a melamine complete antigen and a preparation method thereof, wherein, the melamine complete antigen has a structure as follows: the complete antigen can maintain better physicochemical properties of the original compound such as a chemical structure, charge distribution, a space structure and the like and obtain an antibody with good specificity and high sensitivity while immunizing an experimental animal, thus laying a foundation for subsequent establishment of a rapid, sensitive and efficient ELISA melamine detection method.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Method for detecting activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase on basis of single quantum dot
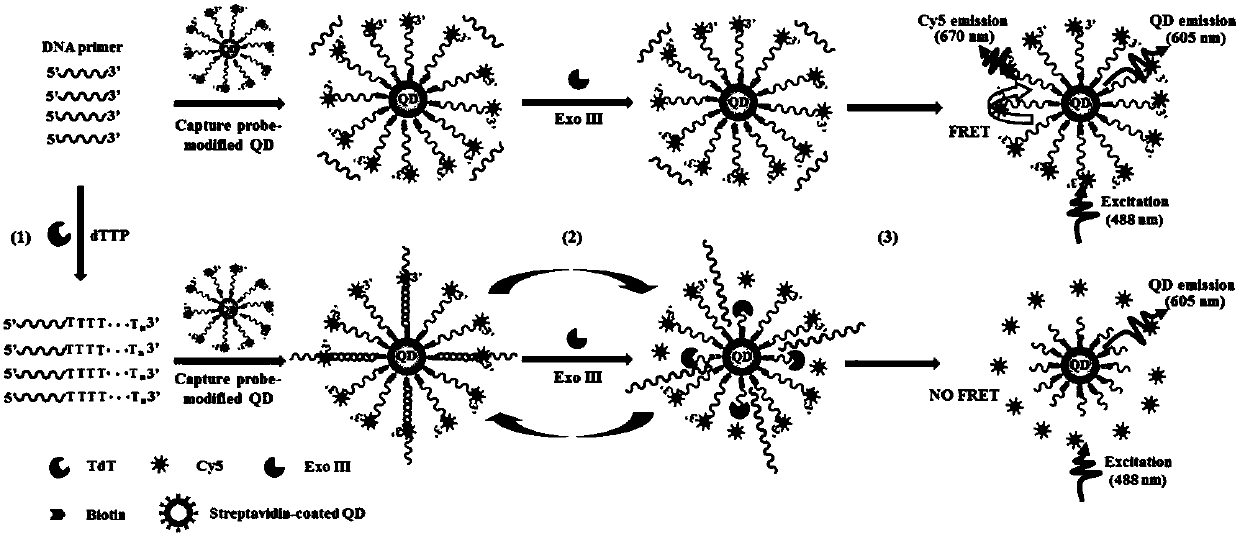
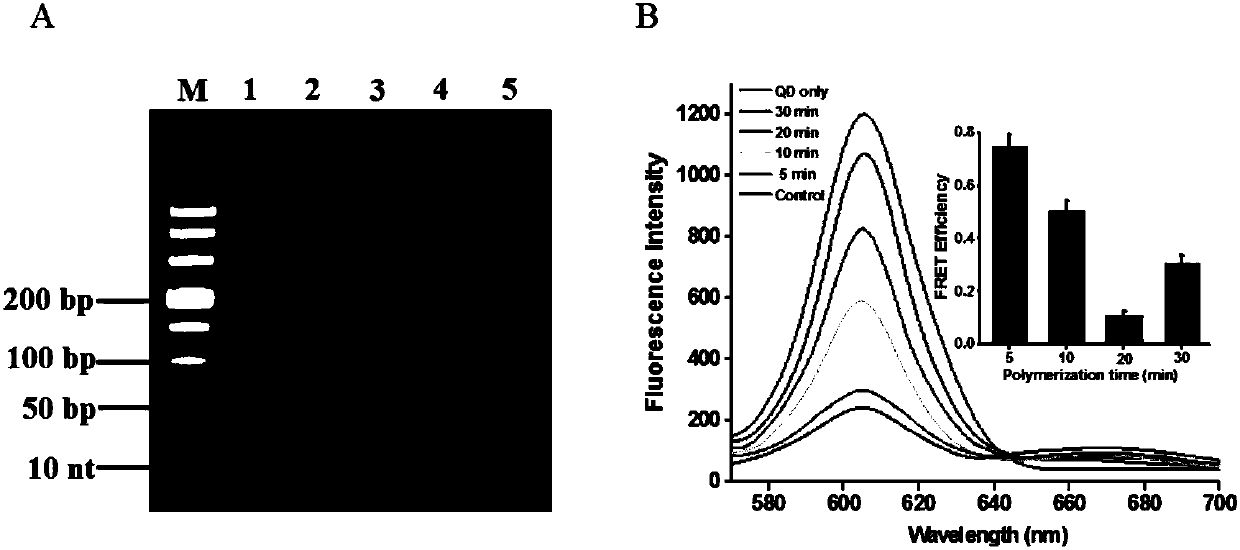
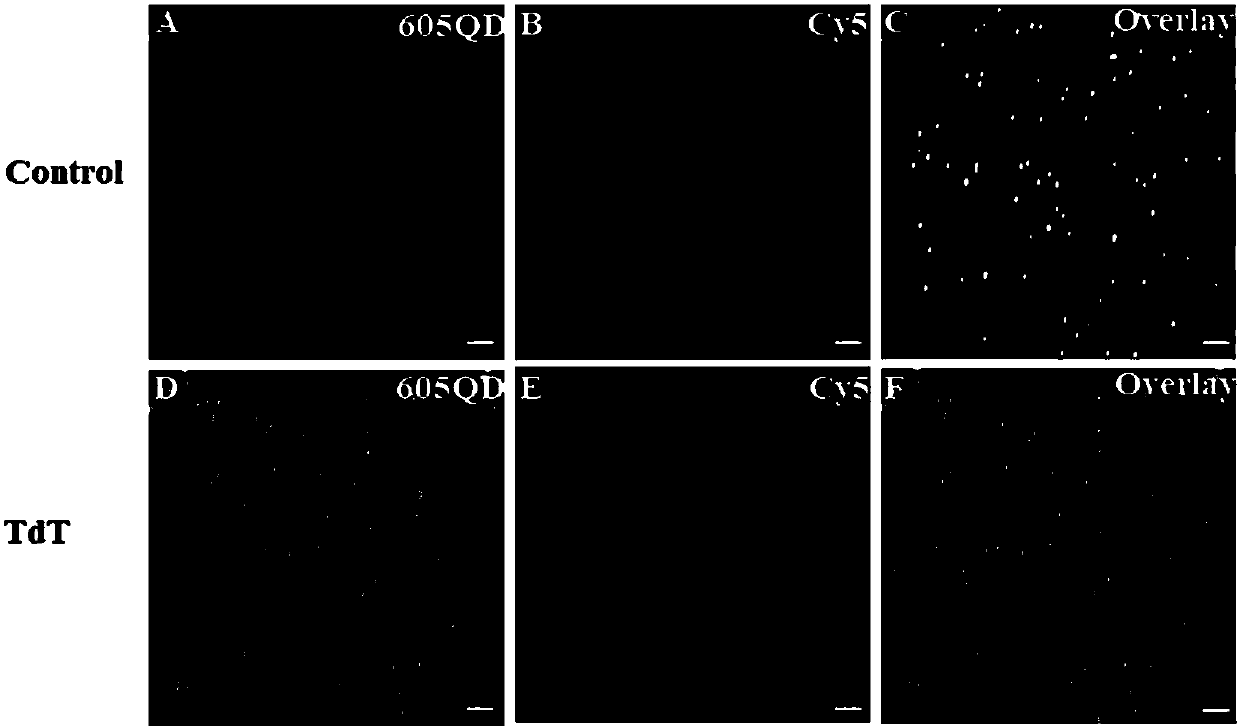
PendingCN107604042AEfficient cycle digestionGood specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceDouble strandedBiotin-streptavidin complex
The invention discloses a method for detecting activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase o on the basis of a single quantum dot. A nano sensor adopted by the method comprises a capture probe,a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) primer, a quantum dot QD, and a nucleotide excision enzyme, wherein the capture probe comprises Cy5, biotin and single-stranded DNA1; a 3' terminal of the single-strandedDNA1 is connected with Cy5; a 5' terminal of single-stranded DNA1 is connected with the biotin; the quantum dot QD is a streptavidin bound quantum dot; the capture probe is modified to the surface ofthe quantum dot QD by a streptavidin-biotin interaction; the DNA primer is a DNA sequence; deoxynucleotide can be added to the 3' terminal of the DNA sequence by the action of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase for polymerization and extension to form single-stranded DNA2; single-stranded DNA2 can be hybridized with single-stranded DNA1 to form double-stranded DNA; the nucleotide excision enzyme is an enzyme capable of digesting single-stranded DNA1 in the double-stranded DNA from a 3' hydroxyl terminal. The nano sensor can simply, quickly and sensitively detect the activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
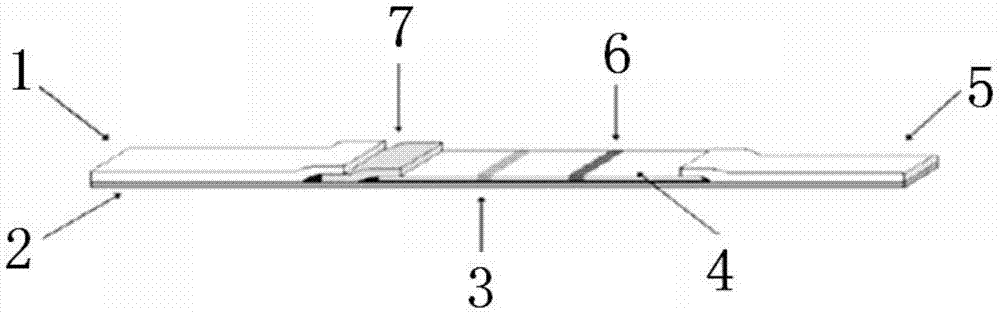
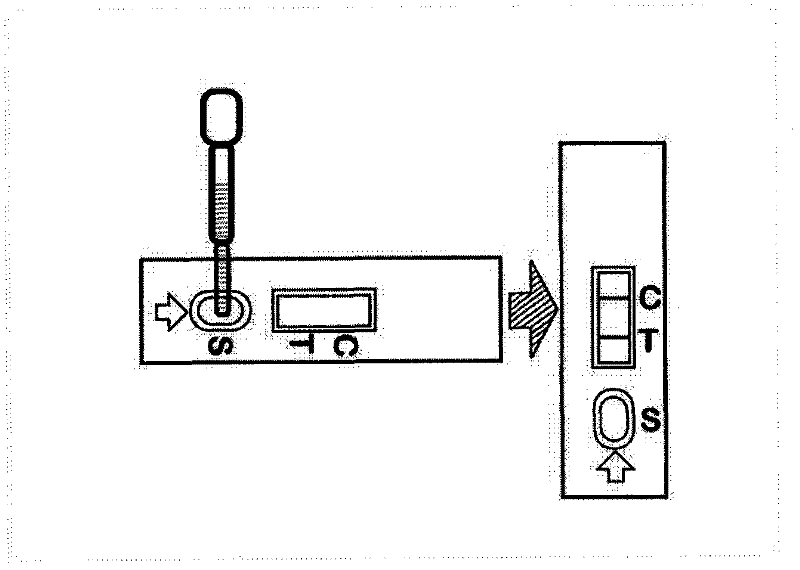
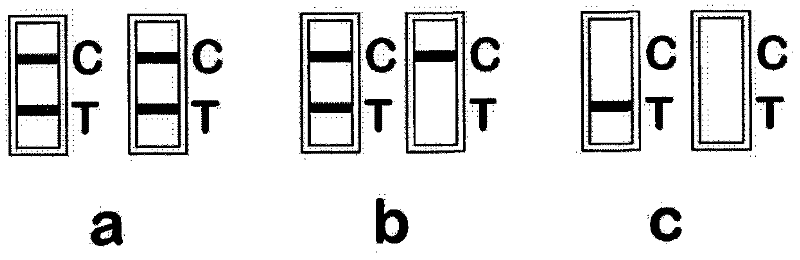
Rapid diagnosis test strip of cow mastitis candida albicans
The invention discloses a rapid diagnosis test strip of cow mastitis candida albicans. The test strip comprises an absorbent paper, an analysis membrane, a gold-labelled antibody joint pad, a sample pad and a base plate, wherein the analysis membrane contains a detection line and a quality control line; the detection line is enveloped by a candida abbicans monoclonal antibody; the quality control line is enveloped by goat anti-rabbit IgG; a colloidal gold-labelled anti-rabbit polyclonal antibody of the candida albicans is enveloped by the gold-labelled antibody joint pad. The rapid diagnosis test strip is applied to detection of cow mastitis pathogens, so that the rapid diagnosis test strip is specific, accurate, rapid, simple to operate and the like, and is applicable to basic livestock breeding, husbandry technology popularization, and animal husbandry and animal quarantine inspection. Therefore, the rapid diagnosis test strip has important value on rapid diagnosis of dairy cow mastitis.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Fast detection method of nitrofuran metabolites in aquatic products
The invention relates to a fast detection method of nitrofuran metabolites in aquatic products, specifically relating to a fast detection method for detecting furazolidone metabolites, furantoin metabolites, furacillin metabolites and furaltadone metabolites in aquatic products. An immune colloidal gold fast detection reagent board is prepared in the invention; the reagent board comprises upper and lower plastic templates and a backing; and a sample pad, a colloid gold combining pad, a nitrocellulose membrane and an absorbent pad are tightly attached on the backing in turn. The nitrocellulose membrane is sprayed with a detection line and a quality control line in a direction from the sample pad to the absorbent pad in turn; and the reaction result can be represented with a macroscopic colour. The reagent board can perform semi-quantitative visual detection; the whole operation procedure only needs 2 hour; and expensive experimental auxiliary facilities are not needed. The method is in favour of screening massive samples, and is suitable for performing massive fast detection of nitrofuran metabolites in aquatic products by industrial and commercial administrations, disease inspection organizations, and aquaculture and processing enterprises.
Owner:杭州南开日新生物技术有限公司
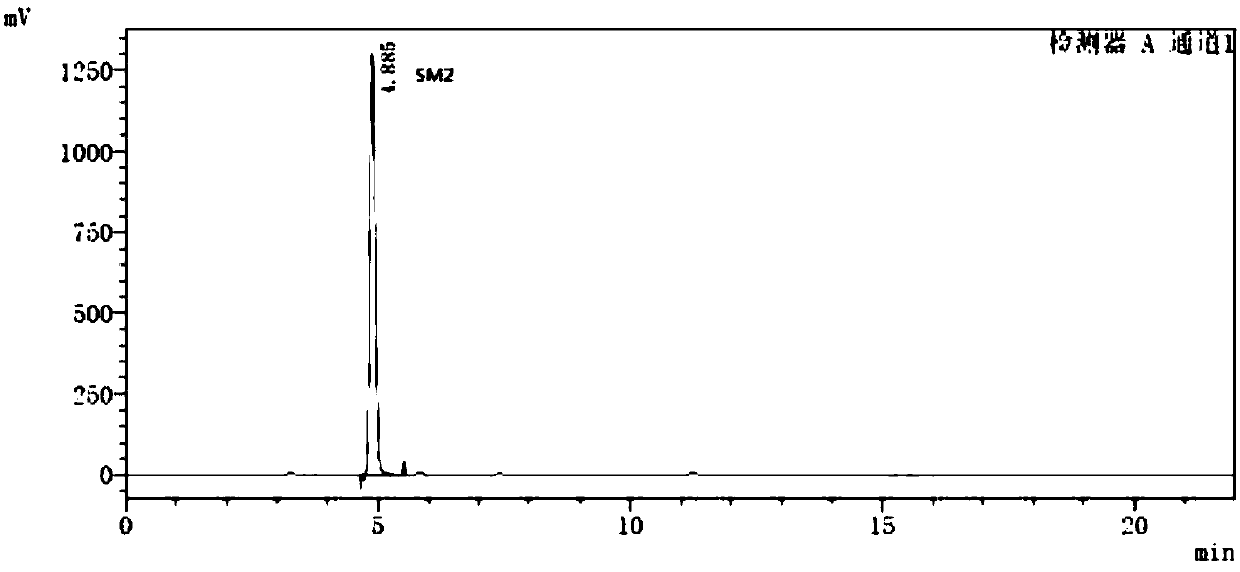
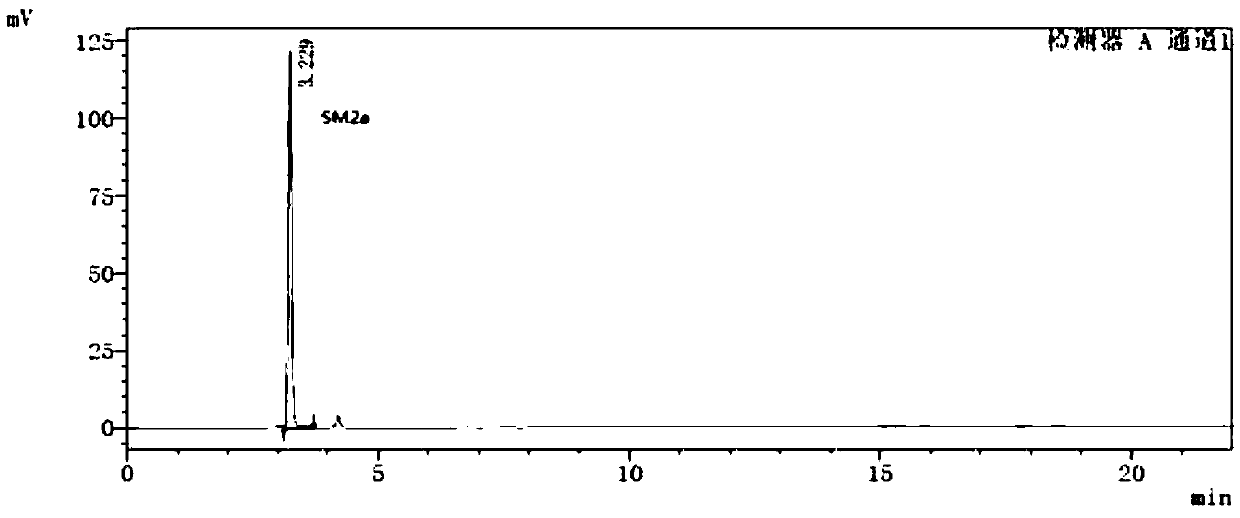
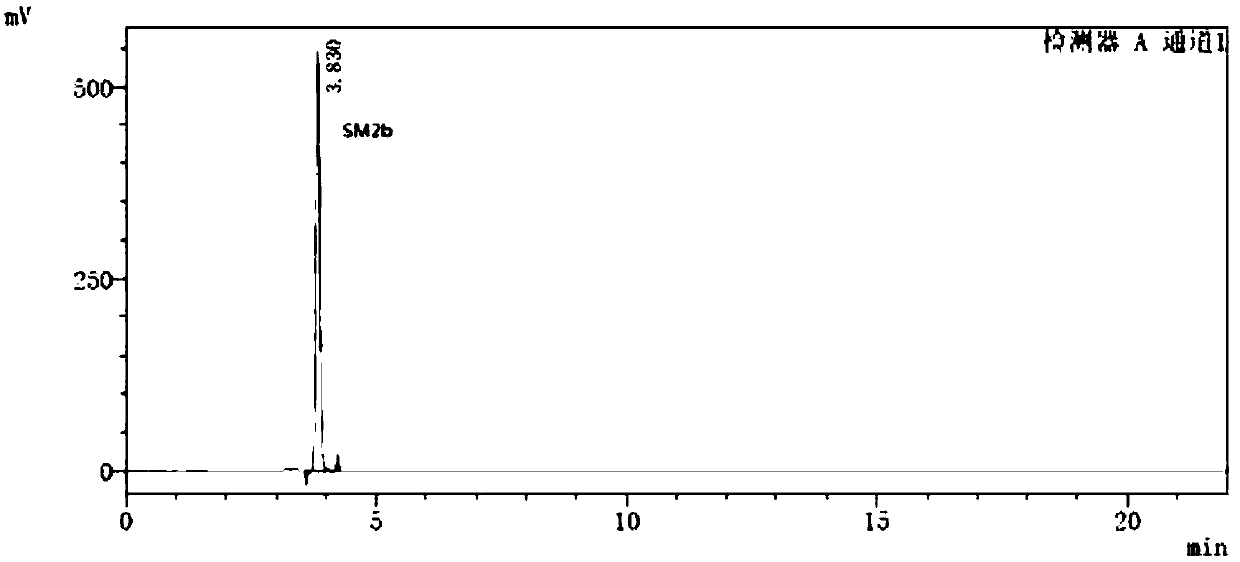
Method for separately determining dutasteride starting material SM2 and related impurities thereof through HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) method
ActiveCN108051513AGood specificityStrong specificityComponent separationAmount of substanceChemistry
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry and in particular relates to a method for separately determining a dutasteride starting material SM2 and related impurities thereof through an HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) method. A chromatographic column adopted by the method takes octadecyl silane bonded silica gel as filling, and a mixed solution of n-hexane and isopropyl alcohol is used as a mobile phase for eluting and enters a detector to be detected; the related impurities comprise one or more of SM2a, SM2b, SM2c, SM2d, SM2e and SM2f. The method provided by theinvention can realize effective separation of the impurity SM2a, the impurity SM2b, the impurity SM2c, the impurity SM2d, the impurity SM2e and the impurity SM2f in the SM2, has good specificity and free from interference by a blank and other impurities; the separation degree between each two impurity peaks is greater than 1.5 and meets related material requirements. The method has extremely important meanings on realization of quality control of the dutasteride starting material SM2 and dutasteride.
Owner:CHONGQING HUAPONT PHARMA
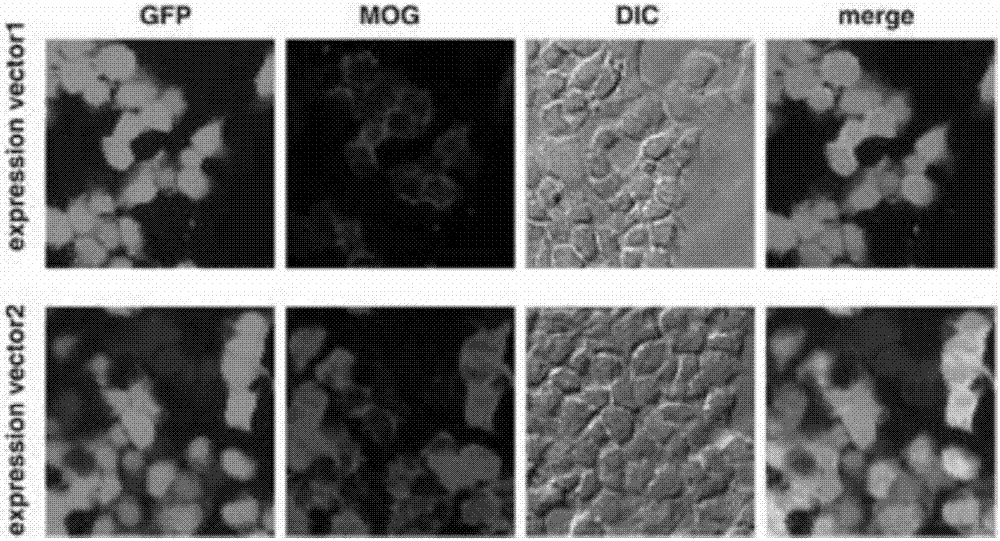
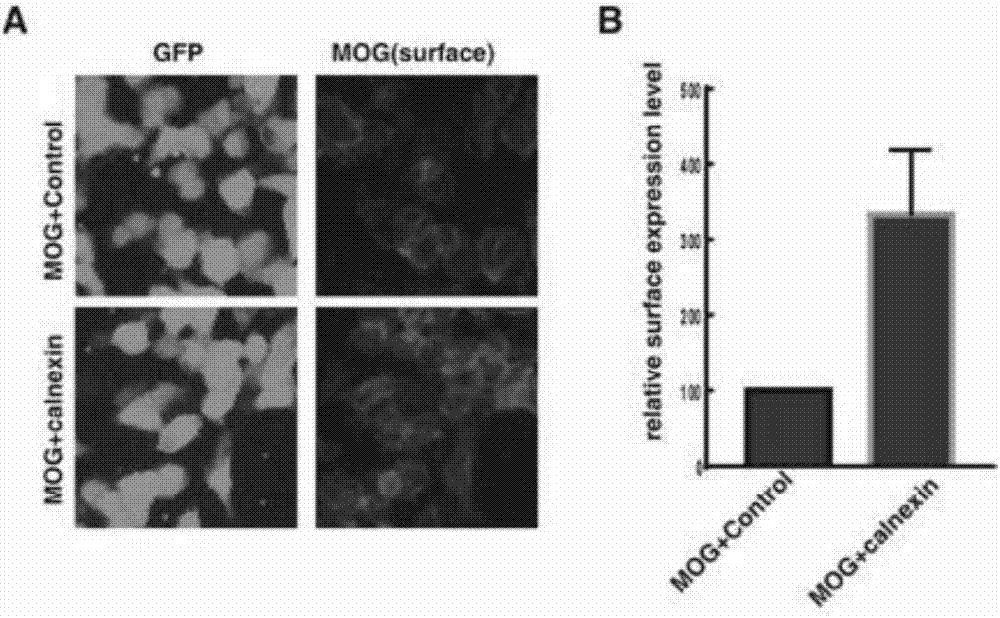
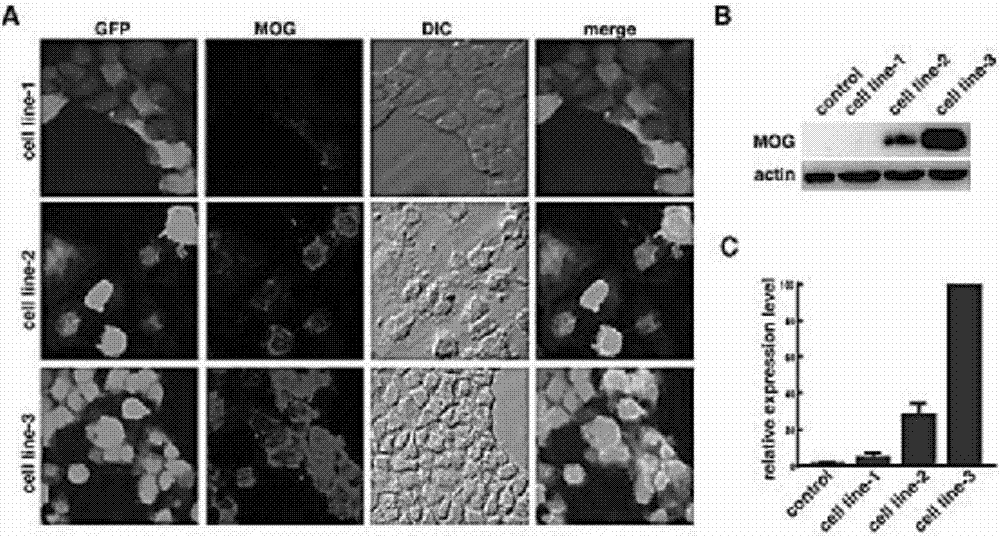
Detection method of human myelin oligodendroglia glycoprotein self immune antibody
ActiveCN107271680AImprove detection efficiencyGood specificityDisease diagnosisBiological testingGlycoproteinAntigenic protein
The invention discloses a detection method of a self immune antibody. The method comprises the following steps of performing cotransfection cells by expression vectors of allergen protein of an antibody to be detected and a chaperone protein expression vector; after the transfected cells are fixed and after washing, adding serum to be tested for incubation; adding second antibodies for incubation; then, performing analysis, wherein the antigen protein of the antibody to be detected is MOG protein. The detection method has the characteristics of high detection efficiency, high specificity and high sensitivity. The common problem of false positive or false negative detection result in the immunoblotting and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay are successfully solved; very important study and practical values are realized.
Owner:广州敏特生物技术有限公司
MLPA (multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification) identification kit capable of detecting multiple pathogens causing sudden death of pigs
ActiveCN108220479AGood specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPathogenPolymerase chain reaction
The invention relates to a biological detection technology and aims to provide an MLPA (multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification) identification kit capable of detecting multiple pathogens causing sudden death of pigs. The kit comprises an RT (reverse transcription) and pre-amplification primer mixed liquid, a probe mixed liquid, an MLPA buffer solution, a ligation buffer solution A, a ligation buffer solution B, ligase Ligase-65, a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) mixed liquid, SALSA polymerase, negative control and positive control. Compared with the prior art, the kit has the characteristics of high throughput, good specificity and high sensitivity. The kit can detect 6 pathogens causing sudden death of pigs simultaneously and can detect 96 samples simultaneously each time by useof a full-automatic nucleic acid analyzer. Through probe design, sequence comparison and blast analysis, a probe is ensured to be only bound with a target gene. During detection, all that is requiredis to amplify a target fragment in a corresponding size from a corresponding template, and other pathogens are not amplified. The target gene is enriched through the added step of RT-PCR, and one copied target gene can be detected to the minimum.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
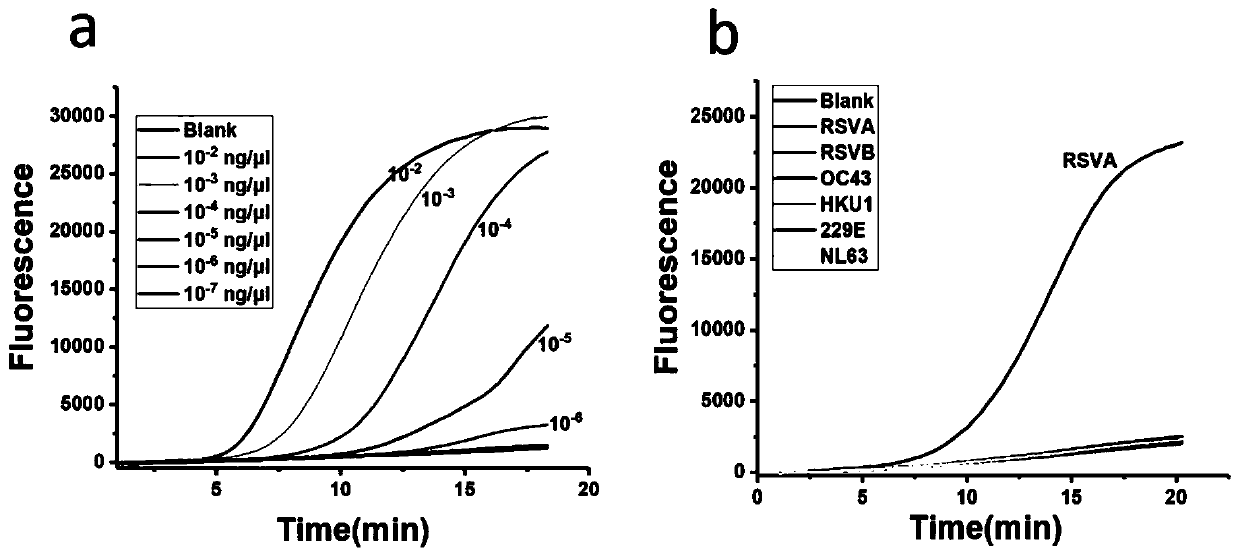
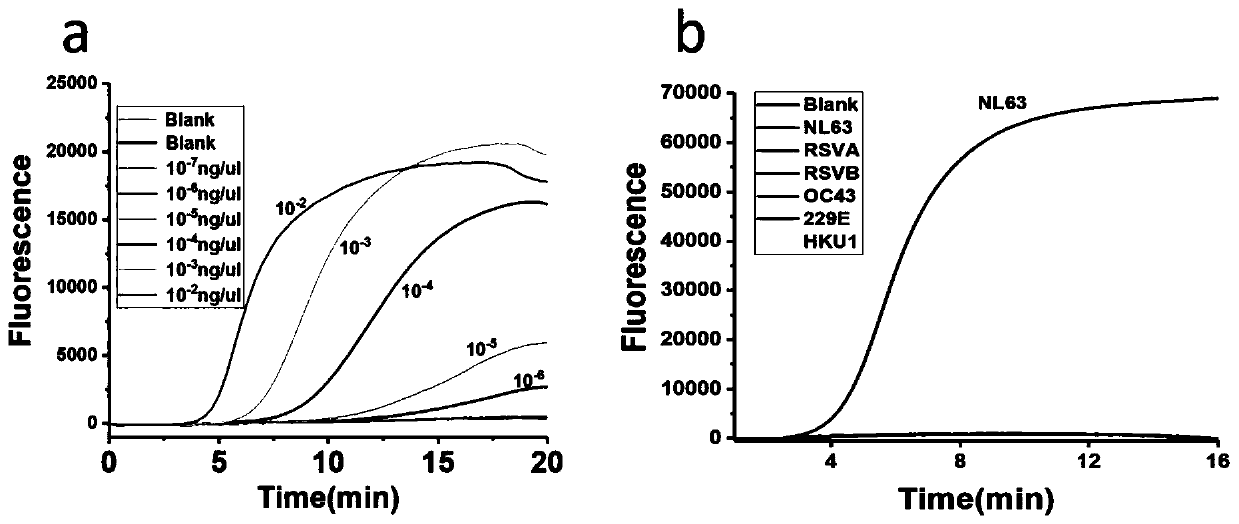
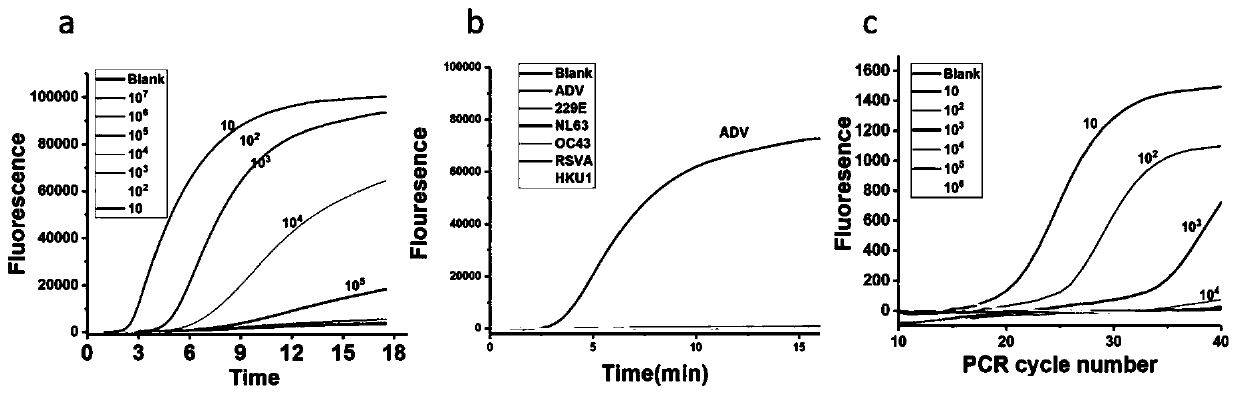
RPA primers, probe sets and kit for detecting respiratory viruses
PendingCN110499391AGood specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesFluorescenceRespiratory virus
The present invention provides RPA primers, probe sets and a kit for detecting respiratory viruses, and belongs to the technical field of virus detection. The respiratory viruses include respiratory syncytial virus type A, coronavirus NL63 and adenovirus-7. Sequences of an upstream primer, a downstream primer and a fluorescent probe for detecting the respiratory syncytial virus type A are shown inSEQ ID No.1-3; sequences of an upstream primer, a downstream primer and a fluorescent probe for detecting the coronavirus NL63 are shown in SEQ ID No.4-6; and sequences of an upstream primer, a downstream primer and a fluorescent probe for detecting the adenovirus-7 are shown in SEQ ID No.7-9. The primers and probe sets have advantages of good specificity and high sensitivity, and can be used toquickly detect the respiratory syncytial virus type A, coronavirus NL63 and adenovirus type 7 on sites.
Owner:中国人民解放军疾病预防控制中心
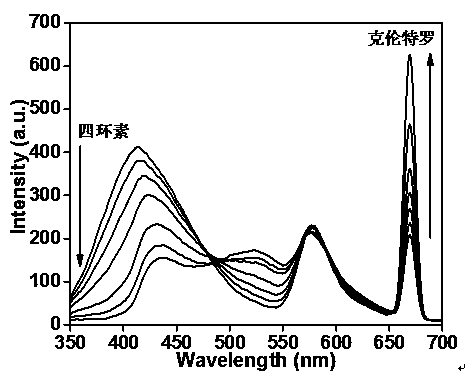
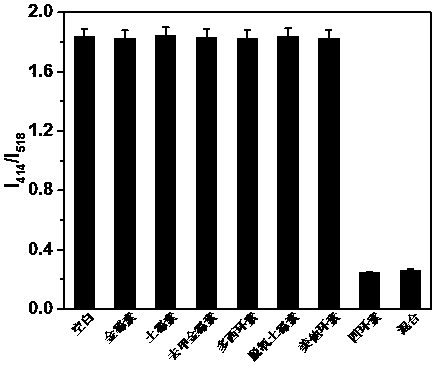
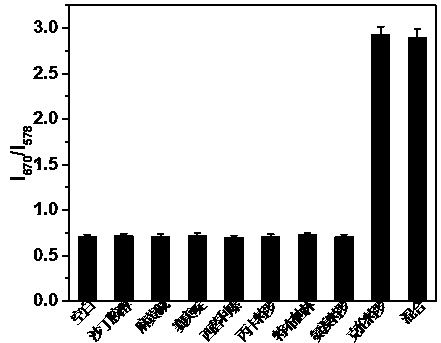
Method for detecting tetracycline and clenbuterol by carbon dot-rhodamine B bifluorescence system proportional fluorescence probe
PendingCN110441280AHigh sensitivityGood specificityNanoopticsNano-carbonCarbon sourcePhenylboronic acid
The invention discloses a method for detecting tetracycline and clenbuterol by a carbon dot-rhodamine B bifluorescence system proportional fluorescence probe. In the method, phenylboronic acid and 3-aminopropyl triethoxy silane are used as a carbon source and a silicon source; boron and silicon doped fluorescence carbon dots are compounded by a hydrothermal method; a bifluorescence system is formed by the compounded boron and silicon doped fluorescence carbon dots and rhodamine B, three transmission wavelengths of 414nm, 578nm and 670nm are generated, and a double proportion fluorescence probedetection system is formed by the double wavelength of the boron and silicon doped fluorescence carbon dots and rhodamine B serving as reference fluorescence. The tetracycline and clenbuterol respectively have linear fluorescence quenching and fluorescence sensibilization effects on the double proportion fluorescence probe detection system, and thus the proportional fluorescence probe detection method for detecting the tetracycline and clenbuterol is built. The method has the characteristics of being high in sensitivity, strong in specificity, simple to operate and rapid.
Owner:云南健牛环境监测有限公司
Primer, probe and kit for detecting genotype of HPV (Human Papillomavirus) and usage method of kit
PendingCN108060268AGood specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceBiology
The invention discloses a primer, a probe, a kit and a usage method of the kit. A primer, a probe and a kit for detecting a genotype of HPV (Human Papillomavirus) and a usage method of the kit can beused for simultaneously detecting multiple HPV subgenotypes; through using a real-time fluorescence PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification technique, the nucleic-acid extraction only needs to be carried out once; a PCR detection reaction also needs to be carried out once in each group; the usage method of the kit is quick, simple and convenient; moreover, the specificity is good; other HPVsubgenotypes or other microbes and the like cannot be detected out; therefore, a false positive problem difficultly appears; moreover, the sensitivity is high, and can reach 400copies / ml; a detectionrange is 400copies / ml to 4.00E+09copies / ml, and a detection range is wide.
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH
CyHV-2 (Cyprinid herpesvirus II) LAMP (loop-mediated isothermal amplification) detection kit and detection method
InactiveCN103045764AGood specificityReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementLoop-mediated isothermal amplificationSYBR Green I
The invention discloses a CyHV-2 (Cyprinid herpesvirus II) LAMP (loop-mediated isothermal amplification) detection kit and detection method. The CyHV-2 LAMP detection kit comprises the following components: 10*ThermoPol Reaction buffer solutions, Bst DNA polymerase, dNTPs, outer primers F3 and B3, inner primers FIP and BIP, Betaine, MgCl2 and 1000*SYBR Green I. The invention has the characteristics of convenience, quickness and high specificity and sensitivity; and the CyHV-2 in a sample can be accurately detected within 2 hours by means of a water bath or metal bath alone, CyHV-2 infected sick fish tissues can be detected, and CyHV-2 infected cells can be detected, thereby ensuring that the invention is very applicable to on-site quick CyHV-2 detection.
Owner:YANGTZE RIVER FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
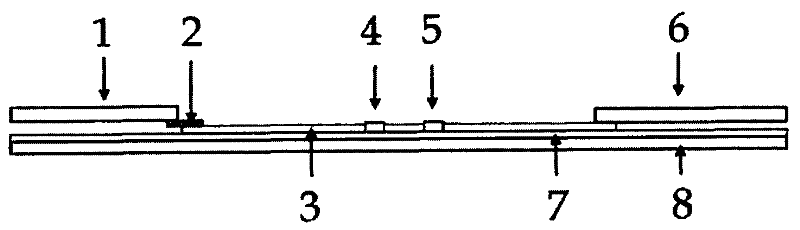
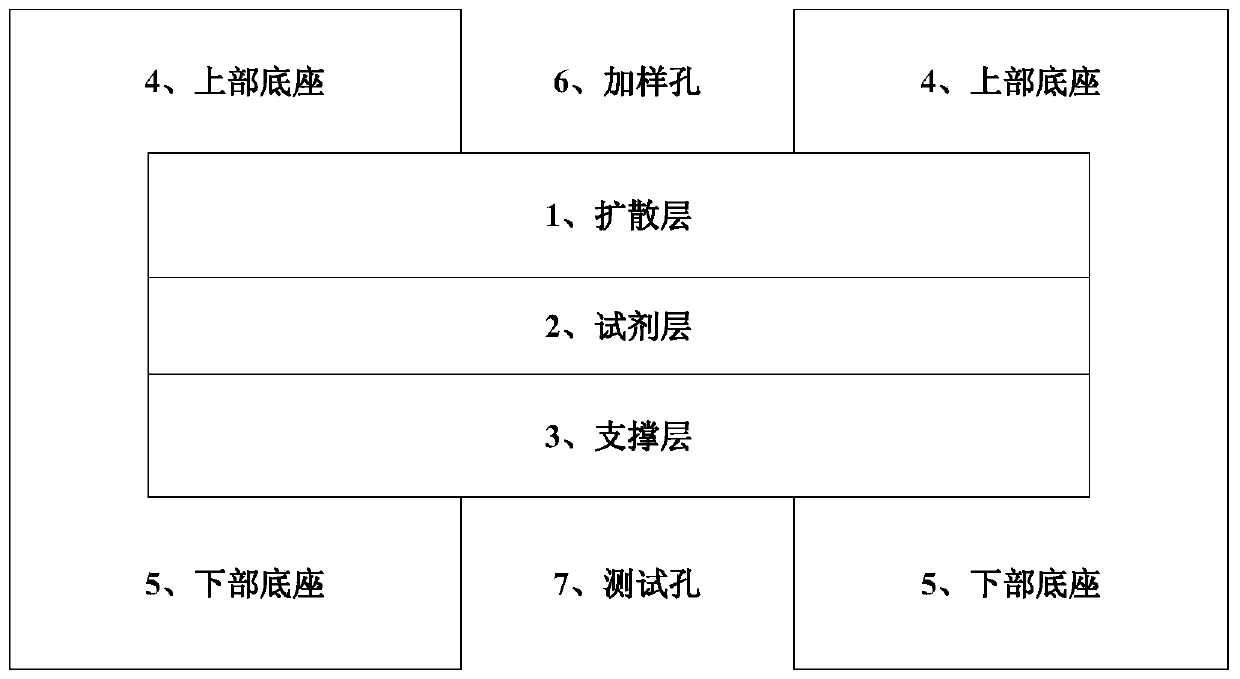
Multilayer dry slides for measuring content of high-density lipoprotein (HDL)
PendingCN110172496AGood specificityStrong anti-interference abilityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemistryLDL - Low density lipoprotein
The invention relates to multilayer dry slides for measuring the content of high-density lipoprotein (HDL). The multilayer dry slides are characterized in that the multilayer dry slides comprise a lower dry slide base (5), a supporting layer (3), a reagent layer (2), a diffusion layer (1) and an upper dry slide base (4), wherein the lower dry slide base (5) is integrally bonded with the upper dryslide base (4), and a loading hole (6) and a test hole (7) are formed in the same positions up and down. The multilayer dry slides involved in the invention have good specificity and strong anti-interference capacity, can resist the interference of hemoglobin, bilirubin and ascorbic acid, are suitable for full-automatic analyzers, and have a relatively large clinical application value; meanwhile,the multilayer dry slides are easy to store and transport, reasonable in design, strong in practicability and wide in application range.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Mercury ion detection method based on nucleic acid probe head-to-tail complementation strategy, and mercury ion detection kit based on nucleic acid probe head-to-tail complementary strategy
ActiveCN104977280AHigh sensitivityGood specificityFluorescence/phosphorescenceSYBR Green IDouble strand
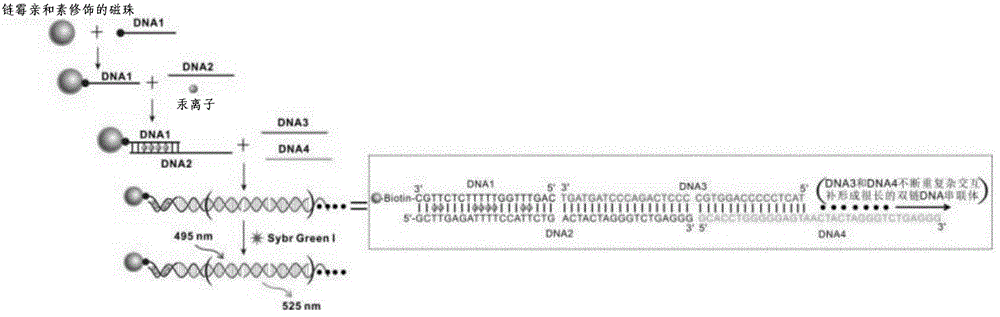
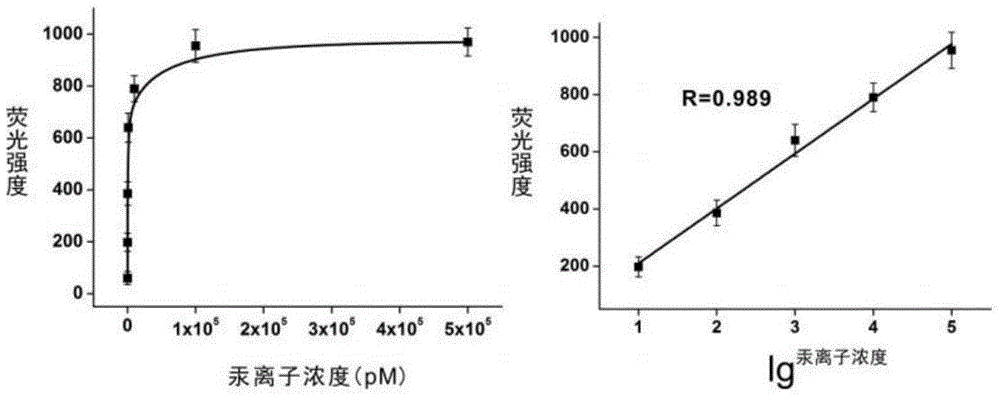
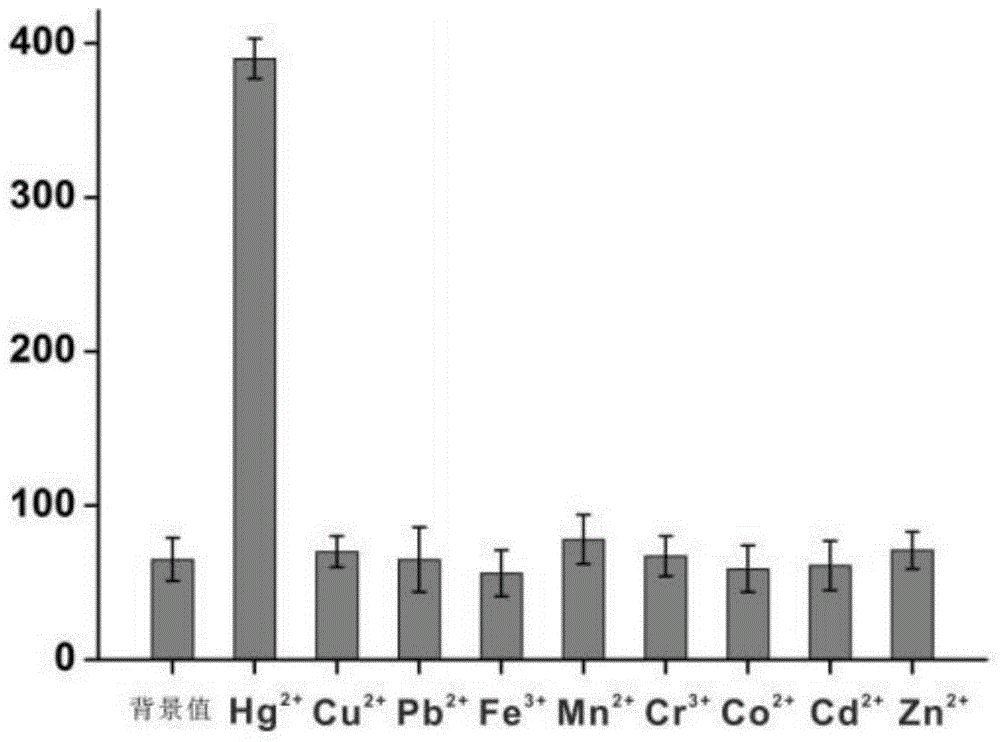
The present invention discloses a mercury ion detection method based on nucleic acid probe head-to-tail complementation strategy, and a mercury ion detection kit based on nucleic acid probe head-to-tail complementation strategy. According to the present invention, T base-rich nucleic acid is designed as a molecule recognition element, and is combined with a capture probe through T-Hg<2+>-T pairing so as to be immobilized on magnetic beads, two nucleic acid probes having head-to-tail complementation are added after the magnetic beads are separated, the long double-stranded DNA is formed through continuous hybridization complementation, a fluorescent intercalator Sybr Green I is added after the magnetic beads are separated, the fluorescent intercalator Sybr Green I has strong fluorescence property after being combined with the double-stranded DNA, and the fluorescence intensity and the mercury ion concentration have the good correlation so as to achieve the purpose of mercuric ion detection; the detection method and the detection kit have high sensitivity, the detection limit on Hg<2+> is 2 pM, the good specificity is provided, and other common interference ions do not affect the detection; and the signal amplification process is derived from the continuous head-to-tail complementation of the DNA probe without protease, the operation is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com