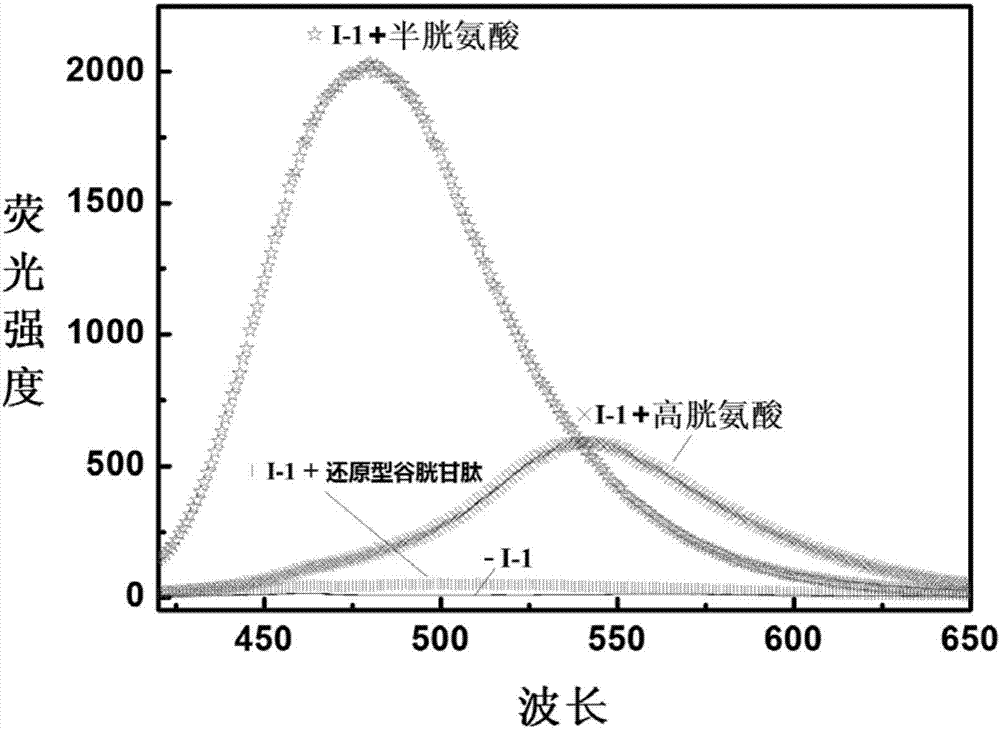
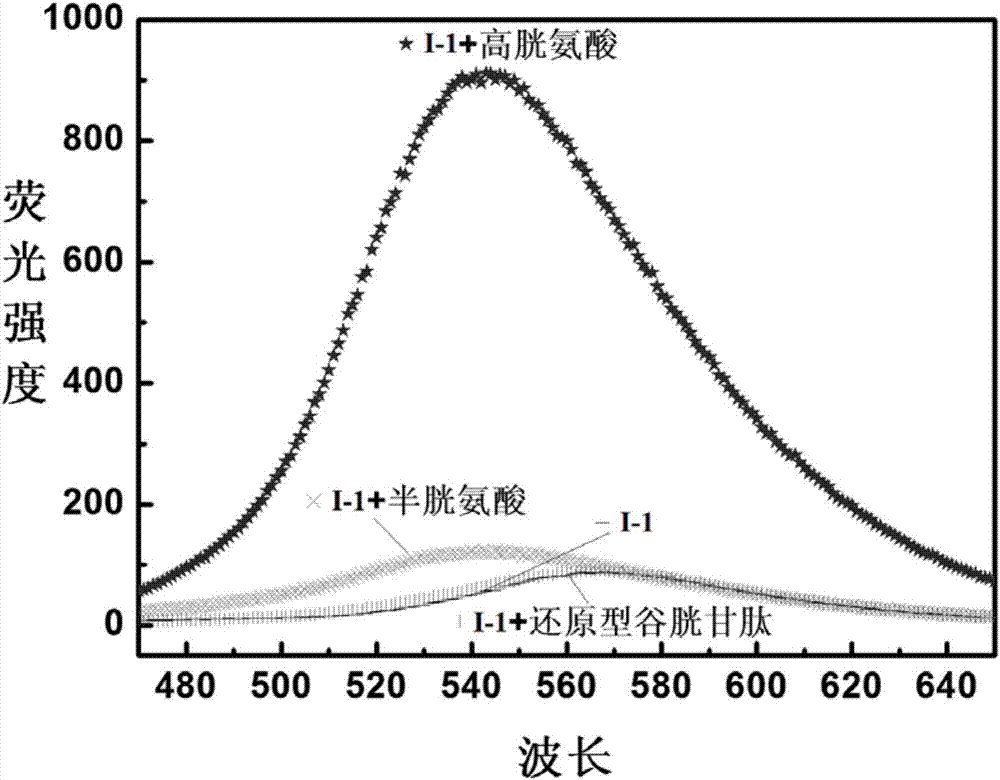
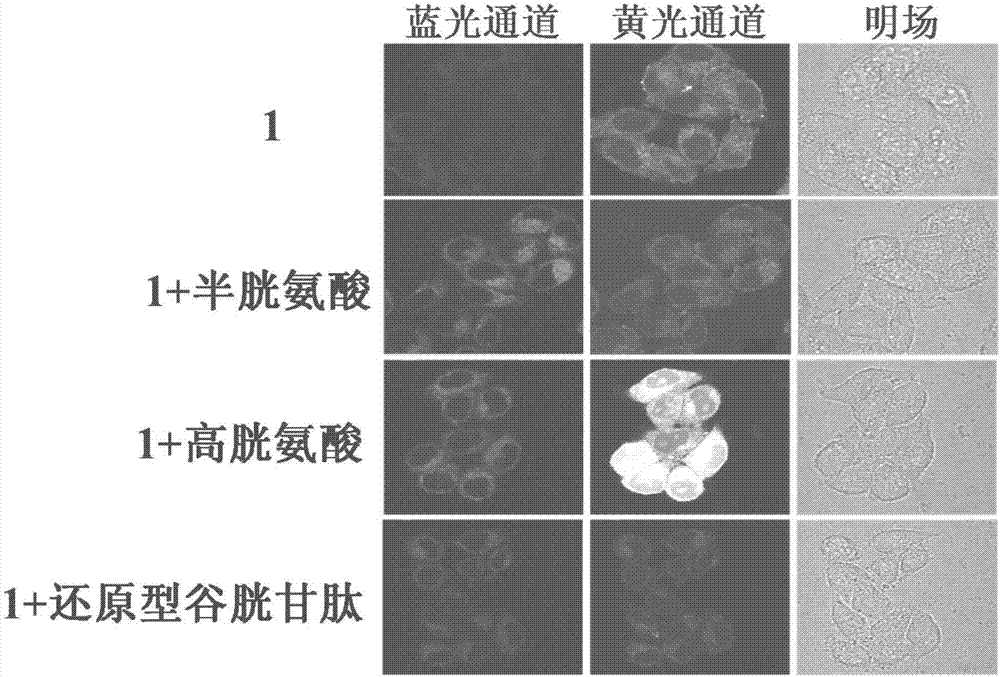
Reactive-type fluorescence probe for distinguishing sulfydryl compounds, synthesis method and application thereof
A technology of thiol compounds and fluorescent probes, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, fluorescence/phosphorescence, analytical materials, etc., to achieve the effects of small molecular weight, simple and easy preparation method, and good cell compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Synthesis of embodiment 1 fluorescent probe (I-1)
[0034] The synthetic method of fluorescent probe (I-1), comprises the following steps:
[0035] Dissolve 0.8 mM 7-julonidinecoumarin-3-aldehyde and 1 mM (1,3-dioxolan-2-yl)methyltriphenylphosphine bromide in 8 mL of dry CH 2 Cl 2 , stirred at room temperature for 0.5h; then slowly added 0.5mL of 0.3g / mL NaOH solution, stirred at room temperature for 9h; then added 1mL of concentrated HCl, stirred for 20min, and spin-dried the solvent to obtain a crude orange-yellow probe, which was analyzed by column chromatography Separation on silica gel to obtain fluorescent probe (I-1), ESI-MS: m / z[C 18 h 16 ClNO 3 +H] + :330.1.
[0036]
Embodiment 2
[0037] Synthesis of embodiment 2 fluorescent probe (I-2)
[0038] The synthetic method of fluorescent probe (I-2), comprises the following steps:
[0039] Dissolve 0.8 mM 7-N,N-diethylcoumarin-3-aldehyde and 1.5 mM (1,3-dioxolan-2-yl)methyltriphenylphosphine bromide in 8 mL of dry CH 2 Cl 2 , stirred at room temperature for 0.6h, then slowly added 0.23mL of 0.3g / mL NaOH solution, stirred at room temperature for 10h; then added 1.15mL of concentrated HCl, stirred for 30min, and spin-dried the solvent to obtain a crude orange-yellow probe, which was analyzed by column chromatography Separation on silica gel to obtain fluorescent probe (I-2), ESI-MS: m / z[C 16 h 16 ClNO 3 +H] + :306.1.
[0040]
Embodiment 3
[0041] Synthesis of embodiment 3 fluorescent probe (I-3)
[0042] The synthetic method of fluorescent probe (I-3), comprises the following steps:
[0043] Dissolve 0.8 mM 7-N,N-dihexylcoumarin-3-aldehyde and 2 mM (1,3-dioxolan-2-yl)methyltriphenylphosphine bromide in 8 mL of dry CH 2 Cl 2 , stirred at room temperature for 0.8h, then slowly added 0.85mL of 0.3g / mL NaOH solution, stirred at room temperature for 8h; then added 0.85mL of concentrated HCl, stirred for 22min, and spin-dried the solvent to obtain a crude orange-yellow probe. Analysis of silica gel separation, to obtain fluorescent probe (I-3), ESI-MS: m / z[C 24 h 32 ClNO 3 +H] + :418.2.
[0044]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com