Feeding algae to cattle at low doses to produce high omega 3 levels in beef
An algal, horizontal technology, applied in the field of feeding algae to cattle at low doses to produce high omega 3 levels in beef, can solve problems such as not being sustainable in the long term
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
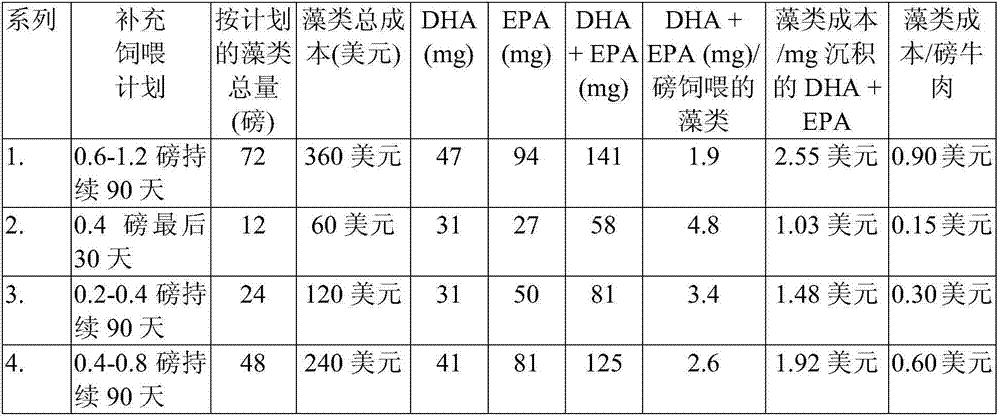
[0027] Three beef cattle were fed a standard ration consisting of corn, corn bran, hay and minerals. Control animals were fed standard diet only. In addition to the standard diet, the second animal received 80% water and a 20% slurry of Nannochloropsis algae (equivalent to 0.2 lb algae / day) administered directly into the gut via cannula of the rumen. A third animal was fed a standard diet and also received 0.2 lbs. of dried schizochytrium algae per day via cannula directly into the rumen. Animals were fed for 8 days (from December 24 to January 1). December 23 is the date before feeding begins. On January 1, using a cannula, samples of intestinal solids and fluids were collected and subsequently analyzed for combined DHA and EPA content (as percentage of omega-3 acids present). Omega-3 acids in rumen fluid are released from damaged algal cells. The omega-3 acids in rumen solids are acids from undamaged whole algal cells. The results of the analysis are shown below in tab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com