A high-throughput method for absolute quantification of soil bacteria
An absolute quantitative, high-throughput technology, applied in the field of soil microorganisms, to achieve simple, reliable cross-sample, relatively accurate and reliable results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
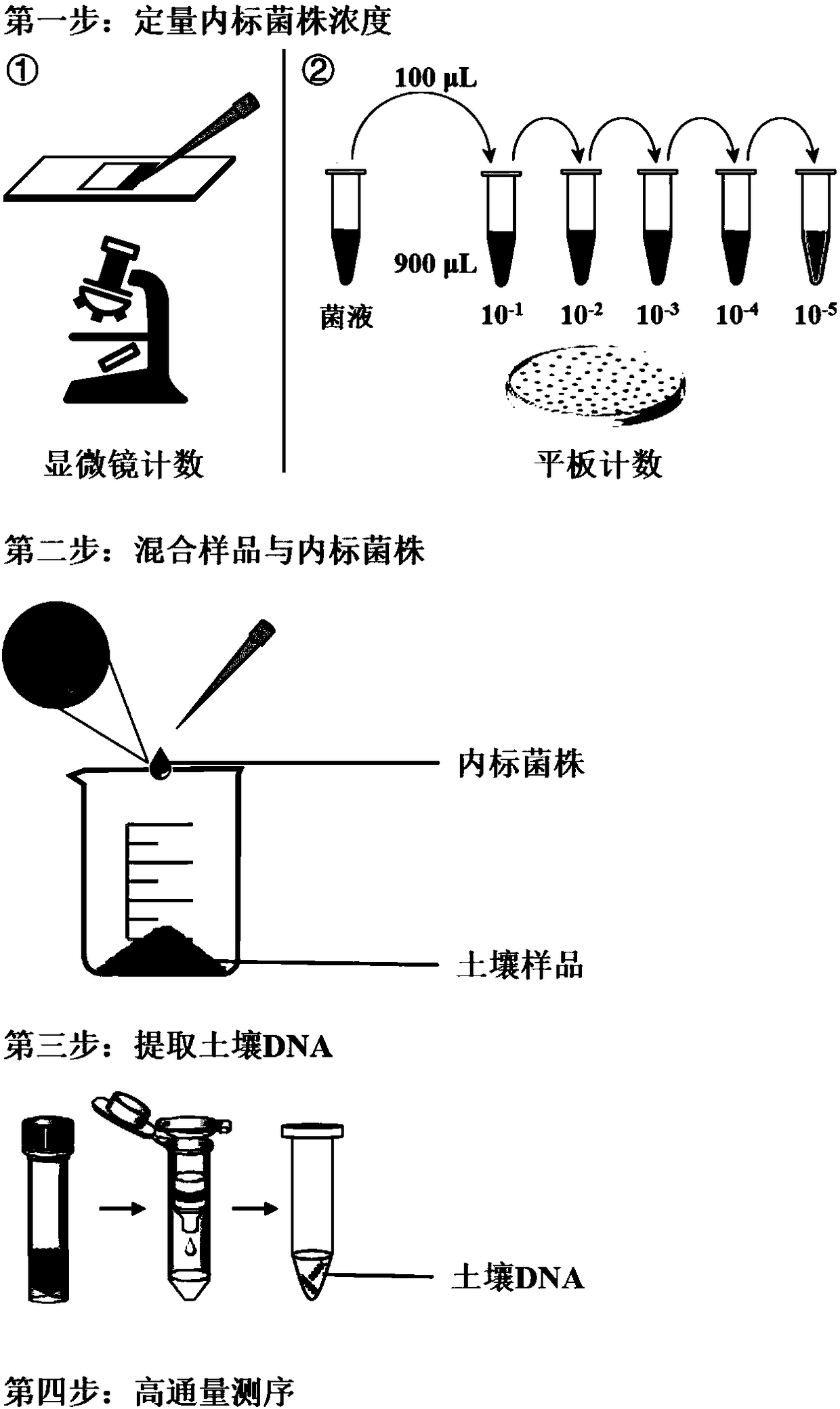
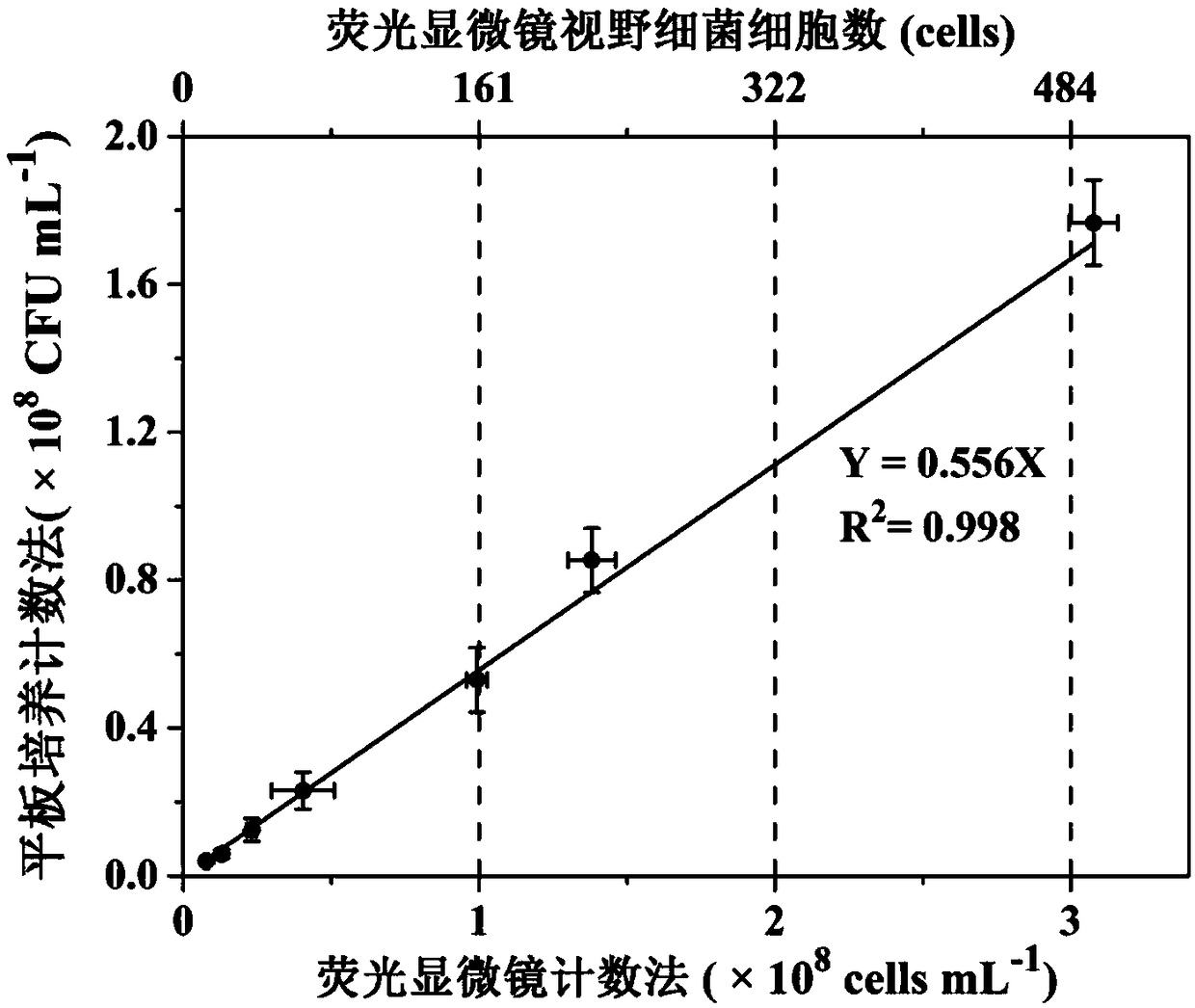
[0059] Embodiment 1, the absolute quantification of the internal standard bacterial strain HTAQ-GFP is carried out by using the fluorescence microscope counting method and the plate culture counting method, and the following steps are carried out in sequence:
[0060] 1) Preparation of 2-fold serial dilution of bacterial suspension:
[0061] Pipette 500 μL of the mother solution of the above-mentioned internal standard strain HTAQ-GFP bacteria suspension into a 1.5 mL sterilized centrifuge tube, add 500 μL of sterilized water and mix well by pipetting to make a 2-fold diluted bacterial suspension. Draw 500 μL from the 2-fold diluted bacterial suspension into a 1.5mL sterilized centrifuge tube, add 500 μL sterilized water, blow and mix well to make a 4-fold diluted bacterial suspension; and so on, make a 2-fold gradient diluted bacterial suspension solution (the mother solution is diluted 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128 times).
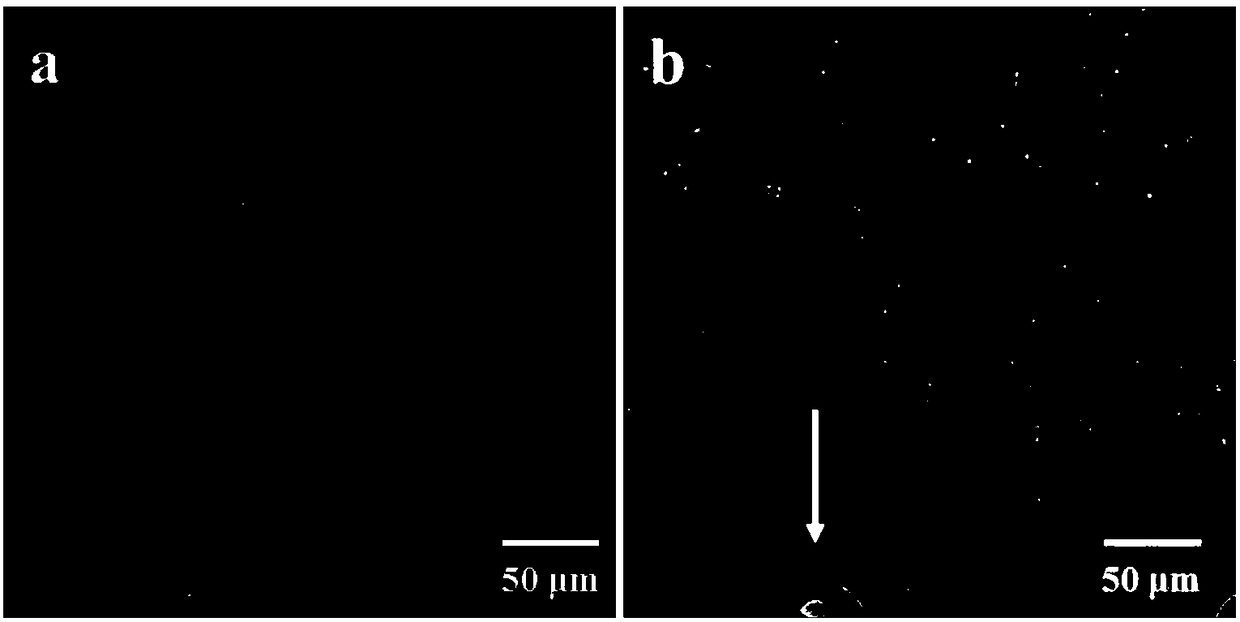
[0062] 2) Fluorescence microscope counting method:
...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Embodiment 2, add internal standard bacterial strain HTAQ-GFP, obtain soil bacteria absolute content (total amount and each classification level content)
[0072] 1) Add the internal standard strain to the sample:
[0073] Draw 200μL of the 10-fold diluted strain HTAQ-GFP bacterial suspension mother solution into a beaker containing 10g soil sample (dry soil), stir and mix for 5min under ice bath conditions, and obtain a final concentration of strain HTAQ-GFP of 10 6 cells g -1 Left and right soil samples. The soil samples added with equal volume of sterile water were used as control treatment.
[0074] 2) Extract soil DNA:
[0075] Weigh 0.25g of the soil sample obtained in step 1) to extract soil DNA. This example uses MoBio DNA extraction kit, the operation steps follow the standard procedure of the kit.
[0076] 3) High-throughput sequencing:
[0077] The soil sample DNA was subjected to high-throughput sequencing of bacterial 16S rRNA gene amplicons (Illumin...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Embodiment 3, the high-throughput absolute quantification method of soil bacteria is applied to the soil sample treated with sodium azide, and the following steps are carried out in sequence:
[0083] 1) Add 0.1% sodium azide (w / w) to the soil, culture at 28°C for 14 days, and take 10 g of soil samples from 0 and 14 days of culture for subsequent addition of internal standard strain HTAQ-GFP .
[0084] 2) Add the internal standard strain to the sample:
[0085] Draw 200μL of the 10-fold diluted strain HTAQ-GFP bacterial suspension mother solution into a beaker containing 10g soil sample (dry soil), stir and mix for 5min under ice bath conditions, and obtain a final concentration of strain HTAQ-GFP of 10 6 cells g -1 Left and right soil samples.
[0086] 3) Extract soil DNA:
[0087] Weigh 0.25g of the soil sample obtained in step 2) to extract soil DNA. This example uses MoBio DNA extraction kit, the operation steps follow the standard procedure of the kit.
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com