Chemical reprogramming of human glial cells into neurons for brain and spinal cord repair
A glial cell, glial cell technology, applied in the field of chemical reprogramming of human glial cells into nerve cells for brain and spinal cord repair, can address unmet, complex risks, potential immune injection, tumor Occurrence and differentiation uncertainty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
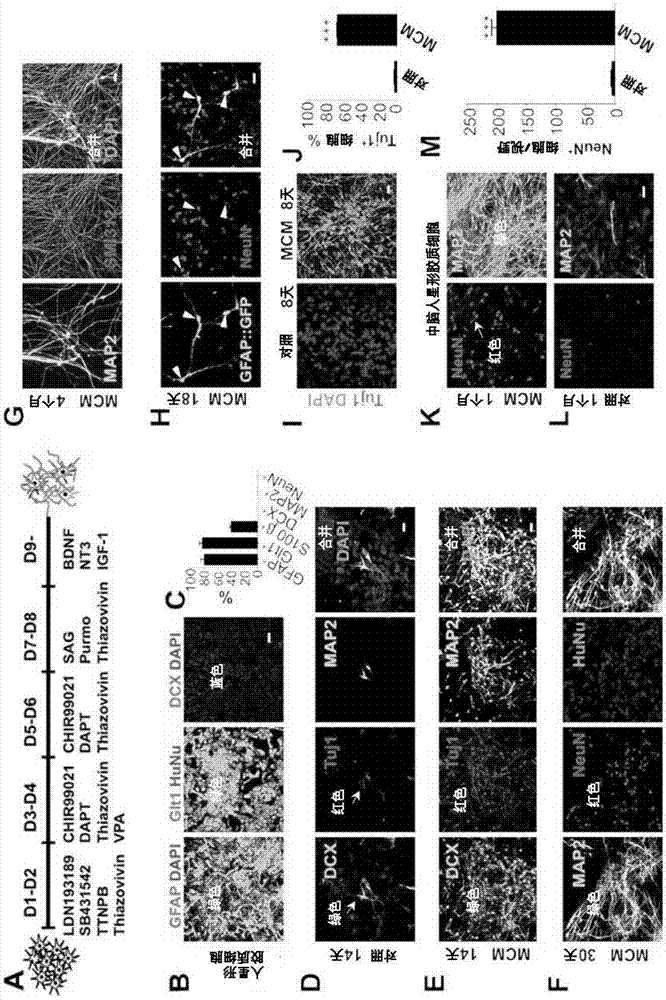
[0066] This example demonstrates the successful reprogramming of human astrocytes into neurons by small molecules as described above. These experiments are designed to develop convenient methods for reprogramming human astrocytes into neurons using small molecules such as, but not limited to, oral administration drugs that can be easily taken by patients. Therefore, we investigated whether small molecules can replace neural transcription factors to reprogram glial cells into neurons. We use human cortical astrocytes (HA1800, ScienCell, San Diego, CA, USA) in culture for chemical reprogramming for clinical applications in human brain repair. Based on two main selection criteria: one ct inhibits glial signaling pathways and the other activates neuronal signaling pathways. We selected 20 small molecules as our starting candidate library. Some molecules are included because they can modulate DNA or histone structure to improve reprogramming efficiency. The 20 small molecules sele...
Embodiment 2
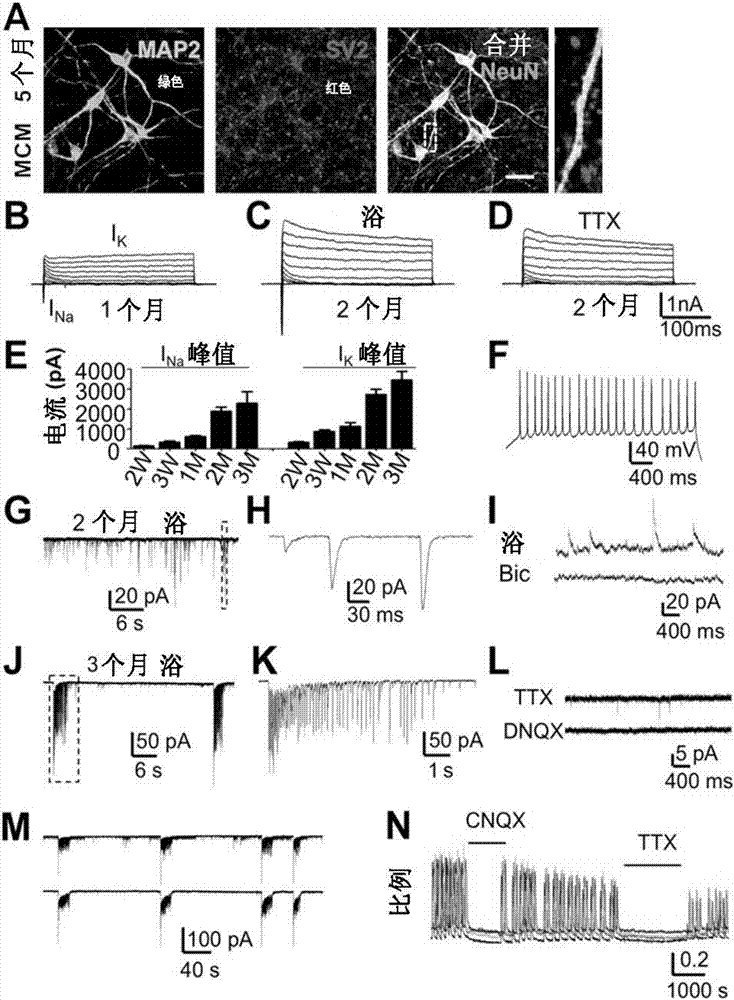
[0071] This example demonstrates that the small molecule transformed human neurons produced according to the present disclosure are fully functional in stimulating action potentials and releasing neurotransmitters. In particular, we found that neurons transformed by small molecules survived for a long time (> 5 months), and showed strong synapses along the dendrites ( figure 2 A). Similarly, neurons reprogrammed from midbrain human astrocytes and Gibco human astrocytes also survived more than 2 months in culture, with many synapses along the dendrites ( Picture 10 F, I). Patch-clamp recordings showed obvious sodium and potassium currents in neurons transformed by astrocytes, which gradually increased during the maturation of neurons ( figure 2 B-E; 2 months: I Na =1889±197Pa, n=10; I K =2722±263Pa, n=10). These neurons can trigger repetitive action potentials ( figure 2 F). More importantly, neurons transformed by small molecules showed strong spontaneous synaptic activit...
Embodiment 3
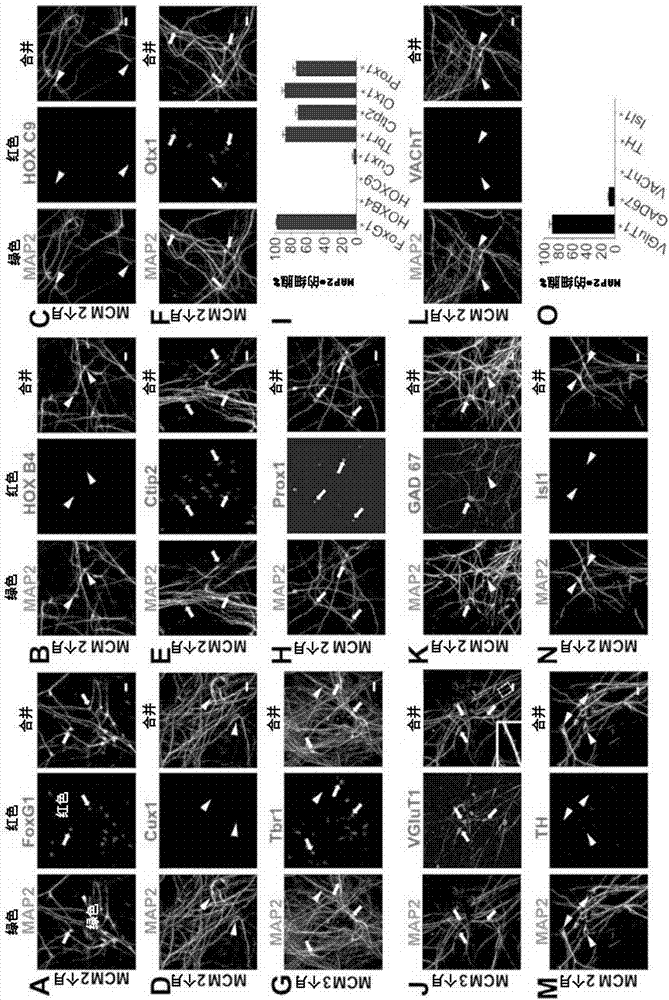
[0073] This example demonstrates that the small molecules described herein reprogram human astrocytes into forebrain glutamatergic neurons. In order to characterize the neuronal characteristics after reprogramming induced by small molecules, we examined neuronal markers expressed in the nervous system from the front to the back. We found that most of the neurons transformed by astrocytes were immunopositive for the forebrain marker FoxG1 (97.1±1.1%, image 3 A, n=3 batches), but it was negative for the hindbrain and spinal cord markers HoxB4 and HoxC9 ( image 3 B-C, n=3 batches). We next performed a series of immunostaining with various cortical neuron markers. We found that most of the neurons transformed by human astrocytes were immunonegative to the cortical surface marker Cux1 ( image 3 D), but for the deep marker Ctip2( image 3 E, 71.4±3%, n=5 batches) and Otx1( image 3 F) It is immunopositive. Transformed neurons from human astrocytes are paired with forebrain neuron...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com