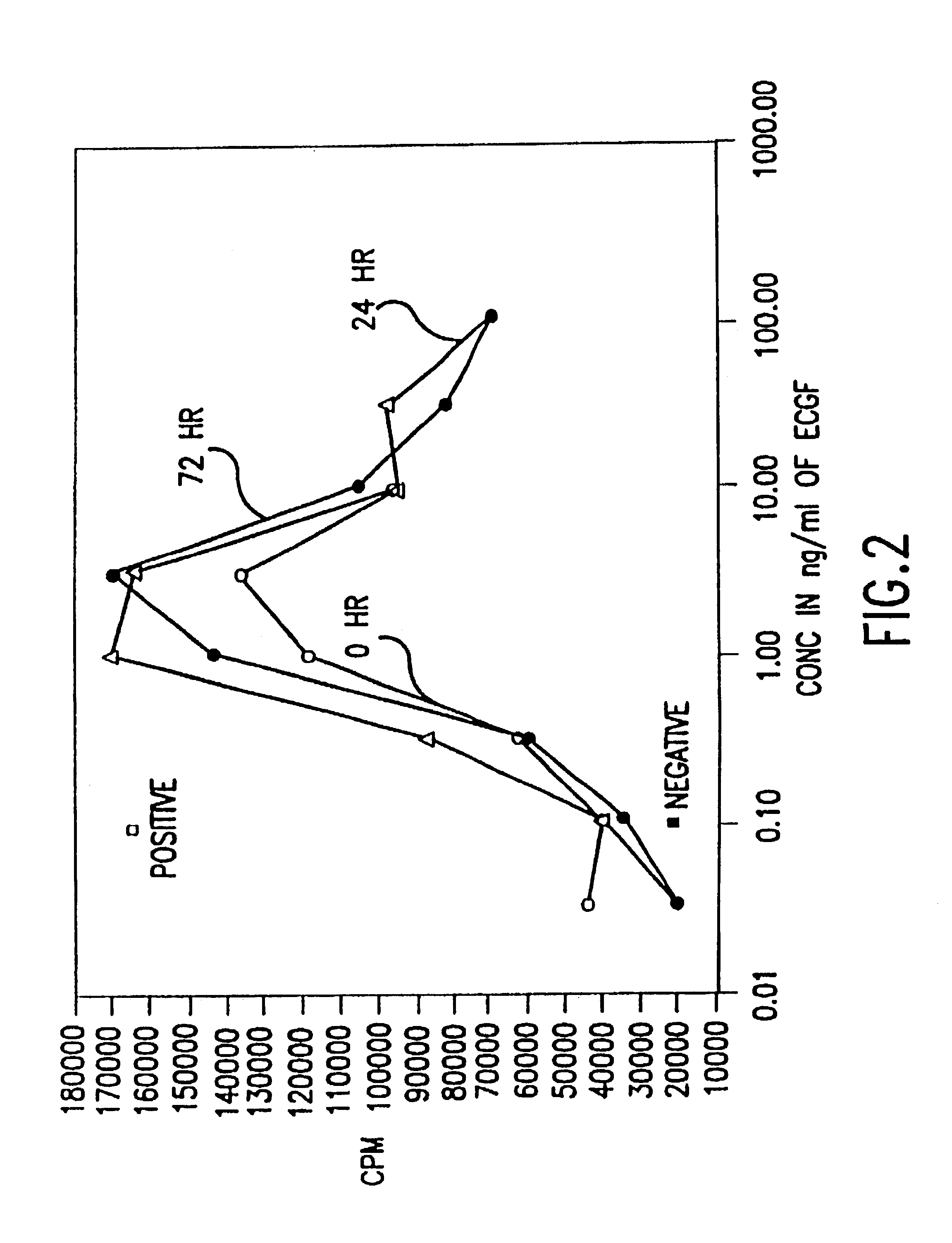
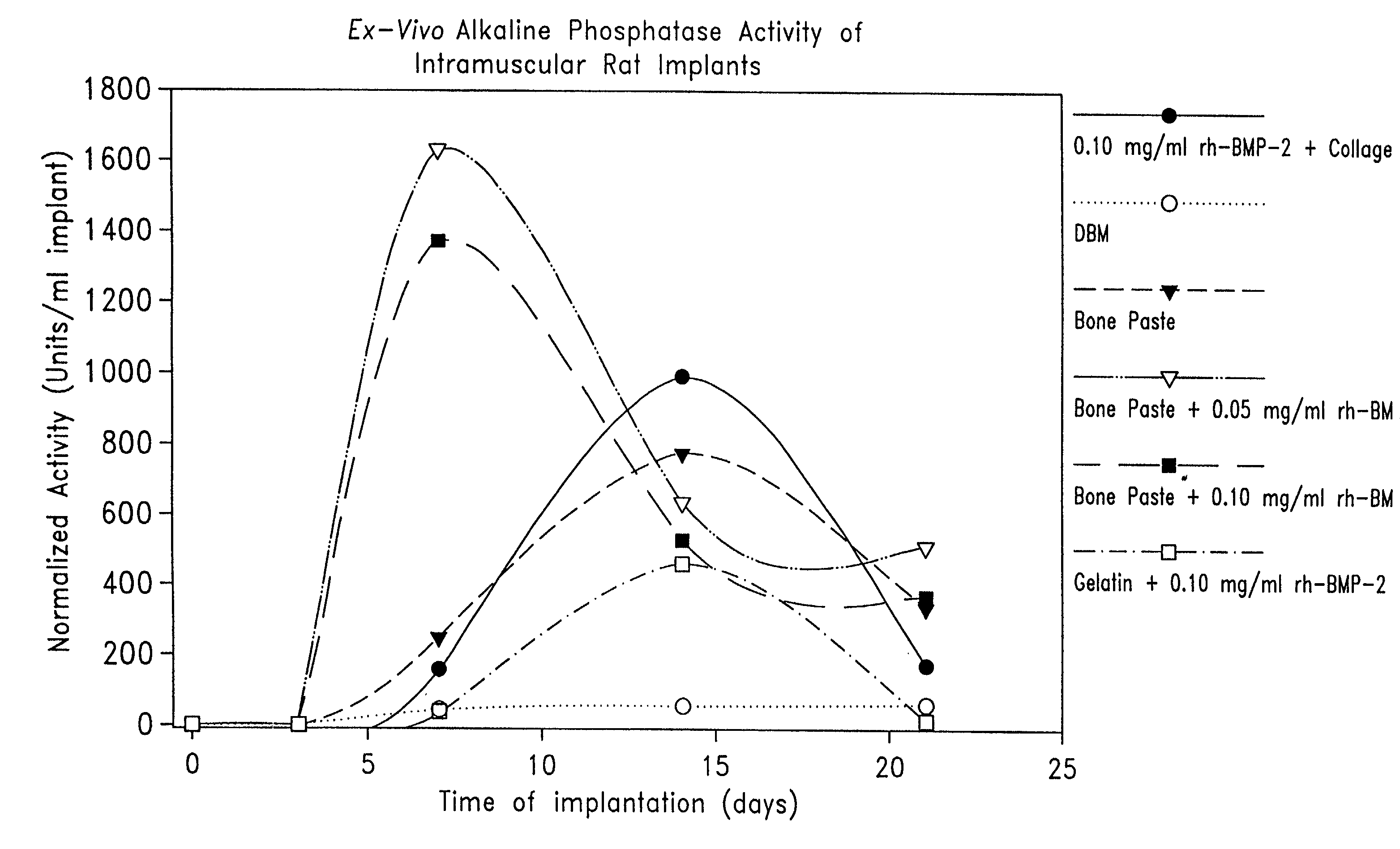
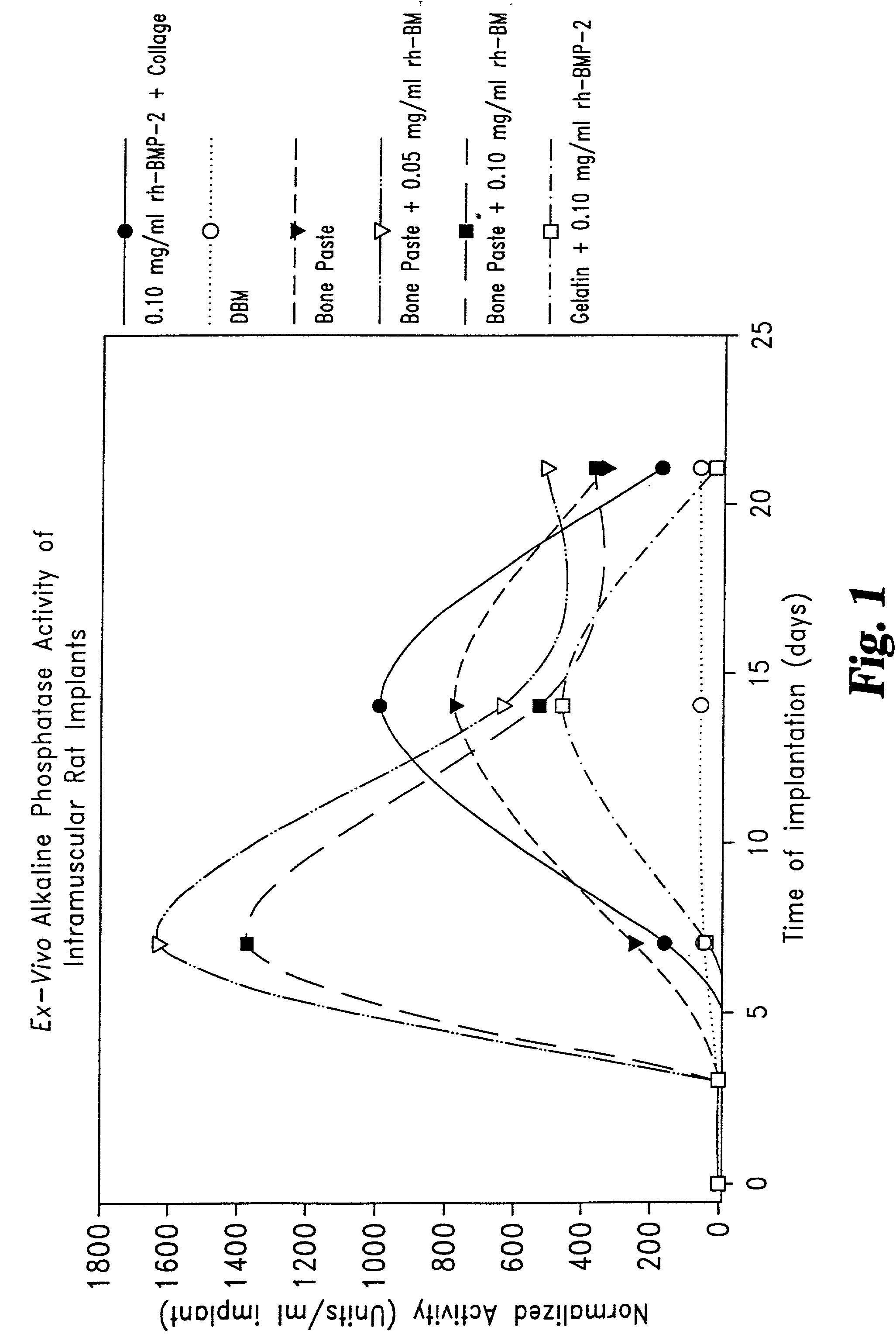
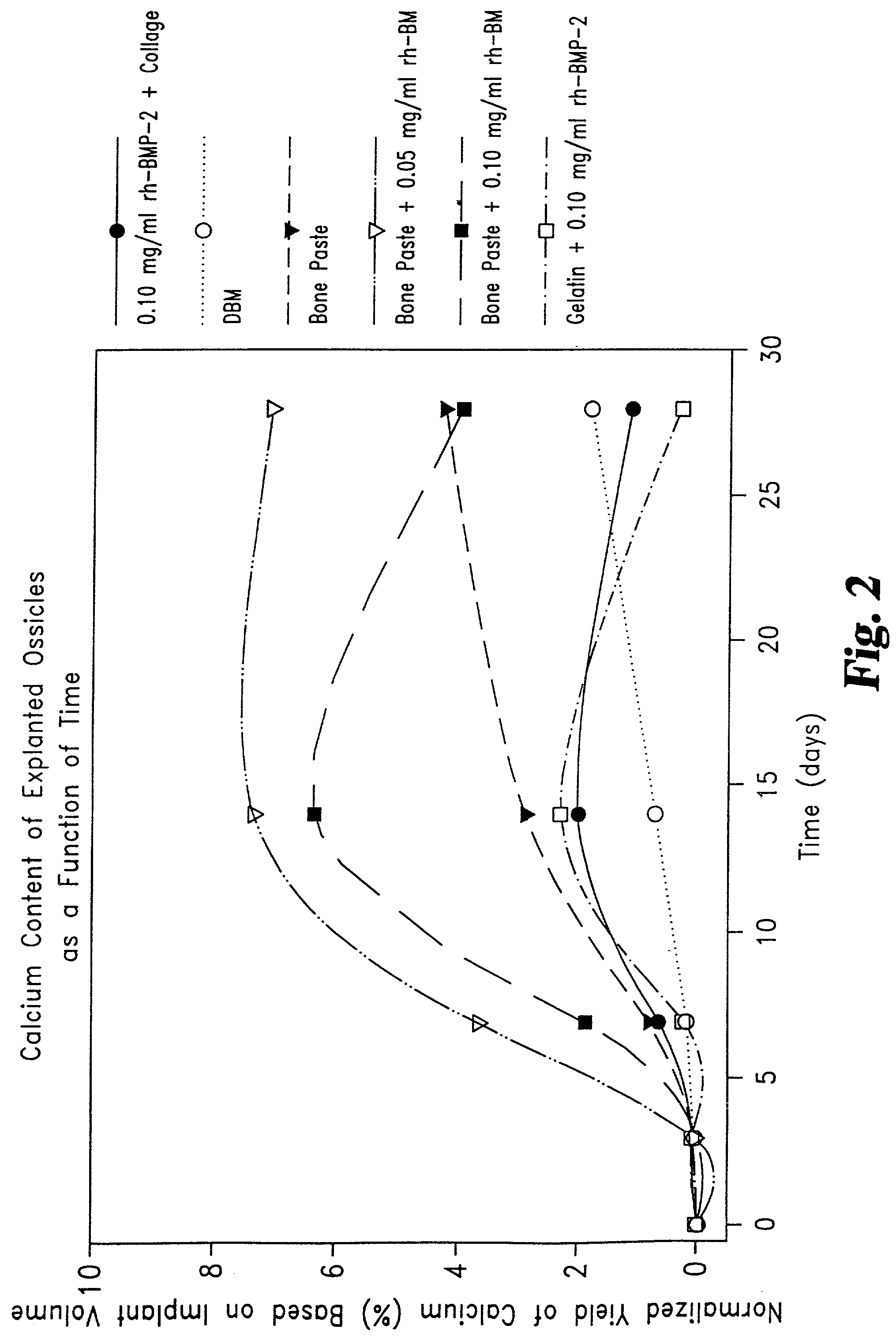
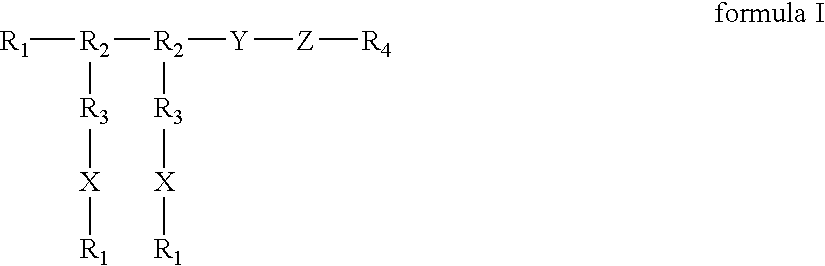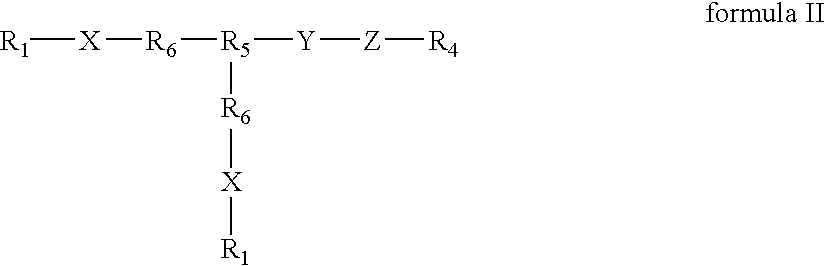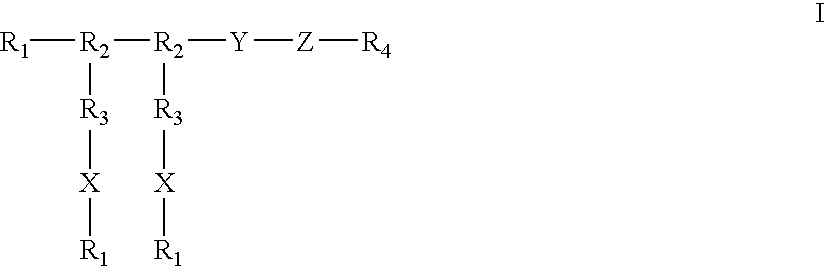Patents
Literature
504 results about "Bone morphogenesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The process in which bones are generated and organized. [GOC:dph]
Particulate acellular tissue matrix
A method of processing an acellular tissue matrix to give a particulate acellular tissue matrix includes: cutting sheets of dry acellular tissue matrix into strips; cryofracturing the dry acellular tissue matrix strips at cryogenic temperatures; separating the resulting particles by size at cryogenic temperatures; and freeze drying the fraction of particles desired size to remove any moisture that may have been absorbed to give a dry particulate acellular tissue matrix. Rehydration of the dry particulate acellular tissue matrix may take place just prior to use. The particulate acellular tissue may be applied to a recipient site, by way of injection, spraying, layering, packing, in-casing or combinations thereof. The particulate acellular tissue may further include growth and stimulating agents selected from epidermal growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, nerve growth factor, keratinocyte growth factor, platelet derived growth factor, vasoactive intestinal peptide, stem cell factor, bone morphogetic proteins, chondrocyte growth factor and combinations thereof. Other pharmaceutically active compounds may be combined with the rehydrated particulate material including: analgesic drugs; hemostatic drugs; antibiotic drugs; local anesthetics and the like to enhance the acceptance of the implanted particulate material. The particulate material product may also be combined with stem cells selected from mesenchymal stem cells, epidermal stem cells, cartilage stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells and combinations thereof.
Owner:LIFECELL
Antibodies specific for sclerostin and methods for increasing bone mineralization
ActiveUS20050106683A1Skeletal disorderImmunoglobulins against growth factorsGreek letter betaIncreased bone mineral density
Compositions and methods relating to antibodies that specifically bind to TGF-beta binding proteins are provided. These methods and compositions relate to altering bone mineral density by interfering with the interaction between a TGF-beta binding protein sclerostin and a TGF-beta superfamily member, particularly a bone morphogenic protein. Increasing bone mineral density has uses in diseases and conditions in which low bone mineral density typifies the condition, such as osteopenia, osteoporosis, and bone fractures.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
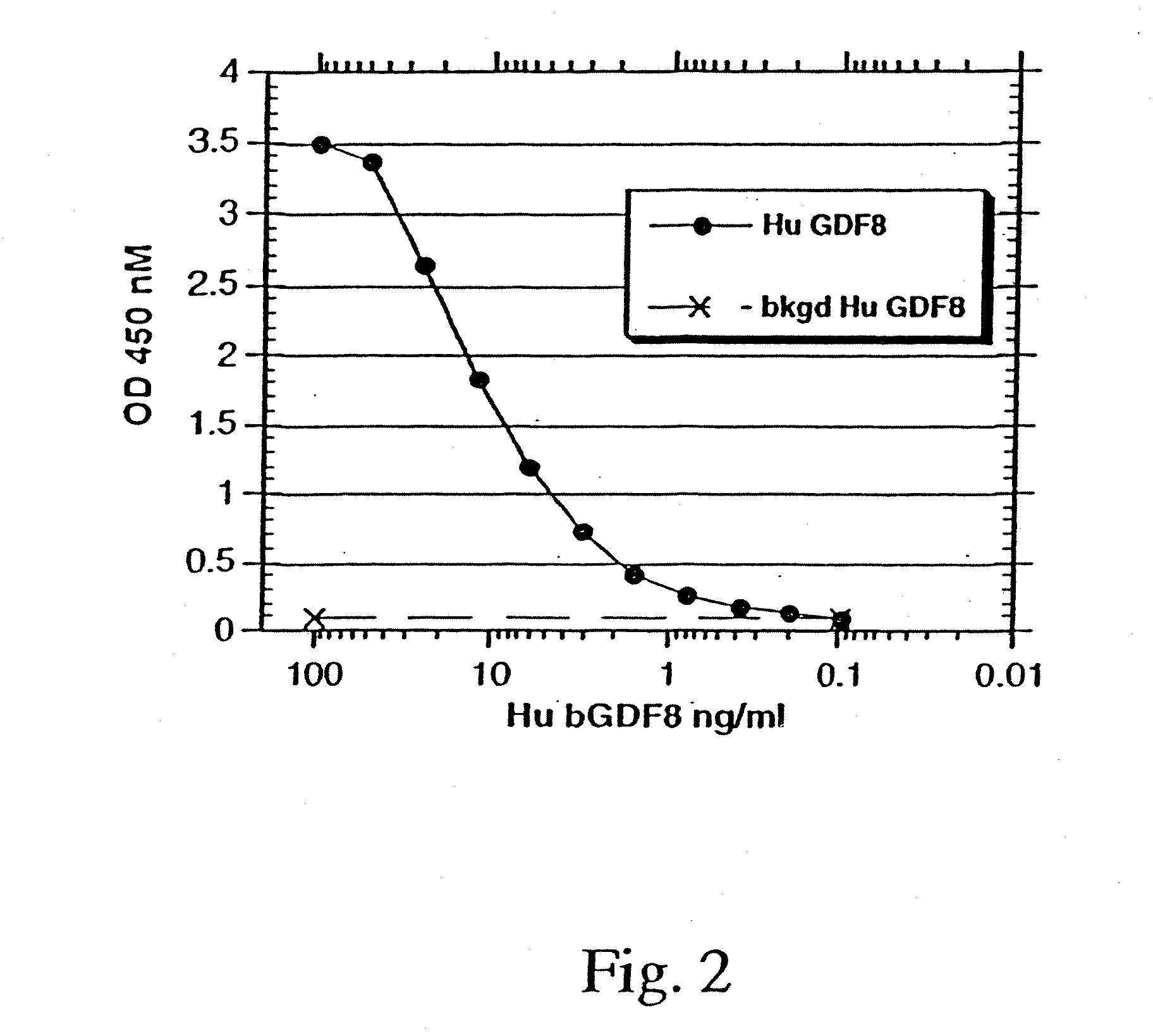
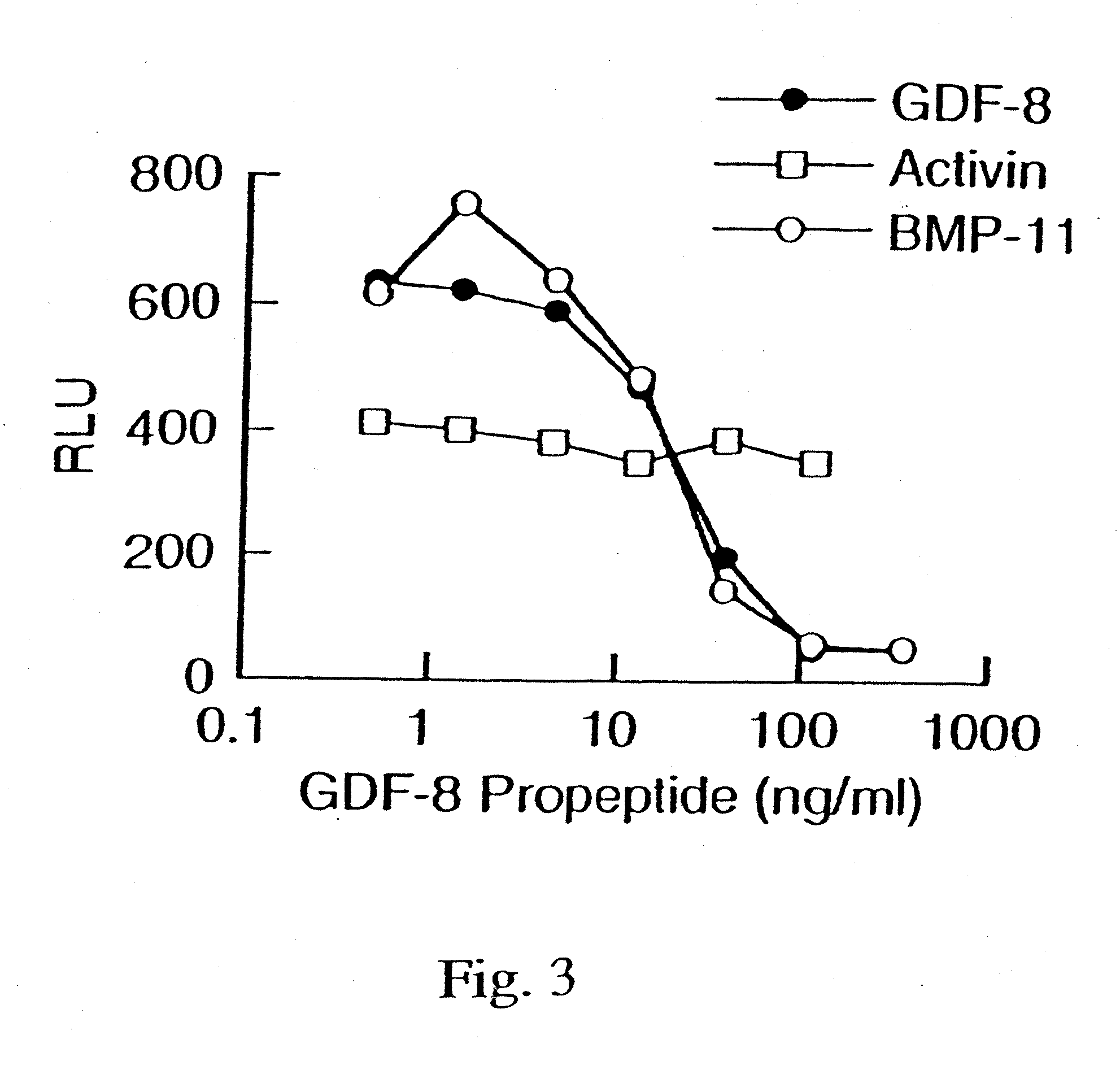
Modified and stabilized GDF propeptides and uses thereof
InactiveUS7202210B2Prevent practical therapeuticPrevent prophylactic utilityFungiBacteriaAcute hyperglycaemiaMuscle tissue
Modified and stabilized propeptides of Growth Differentiation Factor proteins, such as GDF-8 and Bone Morphogenetic Protein-11, are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for making and using the modified propeptides to prevent or treat human or animal disorders in which an increase in muscle tissue would be therapeutically beneficial. Such disorders include muscle or neuromuscular disorders (such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, muscle atrophy, congestive obstructive pulmonary disease, muscle wasting syndrome, sarcopenia, or cachexia), metabolic diseases or disorders (such as such as type 2 diabetes, noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia, or obesity), adipose tissue disorders (such as obesity), and bone degenerative diseases (such as osteoporosis).
Owner:WYETH LLC
Supplemented and unsupplemented tissue sealants, methods of their production and use
ActiveUS7189410B1Low antigenicityDecreasing thrombogenicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue sealantVascular dilatation
This invention provides a fibrin sealant bandage, wherein said fibrin sealant may be supplemented with at least one composition selected from, for example, one or more regulatory compounds, antibody, antimicrobial compositions, analgesics, anticoagulants, antiproliferatives, anti-inflammatory compounds, cytokines, cytotoxins, drugs, growth factors, interferons, hormones, lipids, demineralized bone or bone morphogenetic proteins, cartilage inducing factors, oligonucleotides polymers, polysaccharides, polypeptides, protease inhibitors, vasoconstrictors or vasodilators, vitamins, minerals, stabilizers and the like. Also disclosed are methods of preparing and / or using the unsupplemented or supplemented fibrin sealant bandage.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
Naphtholactams and lactones as bone morphogenetic protein active agents
InactiveUS6030967AHigh toxicological thresholdReduce riskBiocideOrganic chemistryActive agentCarbon chain
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 02858 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 30, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 30, 1997 PCT Filed Aug. 19, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 07705 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 26, 1998A compound of the formula: wherein Q is an optionally substituted carbon atom or N(O)p wherein p is 0 or 1; Y is an optionally substituted methylene group, S(O)q wherein q is an integer of 0 to 2, or an optionally substituted imino group; Z1 is a C1-3 alkylene group which may have an oxo group or a thioxo group and may contain etherified oxygen or sulfur within the carbon chain; Z2 is an optionally substituted C1-3 alkylene group; Ar is an optionally substituted carbocyclic group or an optionally substituted heterocyclic group; one of R1 and R2 is a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, a hydroxyl group, an optionally substituted lower alkyl group, or an optionally substituted lower alkoxy group; the other is a halogen atom, a hydroxyl group, an optionally substituted lower alkyl group, or an optionally substituted lower alkoxy group; or R1 and R2 taken together with adjacent -c=c- form a ring; and ring A is a benzene ring which may be substituted in addition to R1 and R2; or a salt thereof.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Osteogenic fusion device
InactiveUS7179293B2Support of loadMinimize radiopacityBone implantJoint implantsDevice formBone growth
An interbody osteogenic fusion device is provided that includes opposite end pieces with an integral central element. The end pieces are sized to maintain the height of an intervertebral disc space. The central element has a much smaller diameter so that the osteogenic fusion device forms an annular pocke around the central element. An osteogenic material is disposed within the annular pocket between the opposite end pieces. In one embodiment,the osteogenic material constitutes a collagen sheet soaked in asolution containing a bone morphogenetic protein. The osteogenic fusion device is configured so that the osteogenic material is in direct contact with the adjacent vertebral bone. In addition to the enhanced area of contact between the vertebral bone and the fusion material, the inventive osteogenic fusion device reduces stress-shielding and minimizes the radiopacity of the implant so that growth of the fusion mass can be continuously assessed. In yet another embodiment, the osteogenic fusion device includes at least one end piece with a truncated surface. The osteogenic fusion devices of the present invention may be combined with other fusion devices to form an implant system. The implant system includes at least one load bearing member having a truncated surface configured to nest within another load bearing member, preferably the load bearing, osteogenic fusion device of the present invention. The invention also provides implant systems comprising adjacent load bearing members connected to one another to resist lateral separation. Methods of promoting fusion bone growth in the space between adjacent vertebrae utilizing devices and systems of the invention are also described.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Supplemented and unsupplemented tissue sealants, methods of their production and use
InactiveUSRE39321E1Decreasing thrombogenicityLow antigenicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue sealantVascular dilatation
This invention provides a fibrin sealant dressing, wherein said fibrin sealant may be supplemented with at least one composition selected from, for example, one or more regulatory compounds, antibody, antimicrobial compositions, analgesics, anticoagulants, antiproliferatives, antiinflammatory compounds, cytokines, cytotoxins, drugs, growth factors, interferons, hormones, lipids, demineralized bone or bone morphogenetic proteins, cartilage inducing factors, oligonucleotides polymers, polysaccharides, polypeptides, protease inhibitors, vasoconstrictors or vasodilators, vitamins, minerals, stabilizers and the like. Also disclosed are methods of preparing and / or using the unsupplemented or supplemented fibrin sealant dressing.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
Osteogenic paste compositions and uses thereof
InactiveUS7172629B2Rapid and premature resorptionDiminish and eliminate capacityImpression capsSurgical adhesivesMineral matrixImplantation Site
Described are osteogenic paste compositions with enhanced osteoinductive properties for use in bone repair. Compositions comprising a quickly resorbable paste carrier, a more slowly resorbed mineral matrix, and Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) or other osteogenic factor are described which enable increased osteoinductive activity while retaining a reliable scaffold for the formation of new bone at the implant site. Methods for making and methods for therapeutic use of the compositions are also disclosed.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Methods for treating wound tissue and forming a supplemented fibrin matrix
InactiveUS7196054B1Low antigenicityDecreasing thrombogenicityOrganic active ingredientsSurgical adhesivesTissue sealantVascular dilatation
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
Modified and stabilized gdf propeptides and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070149455A1Avoid utilizationImproved pharmacokinetic propertiesFungiBacteriaMuscle tissueAmytrophic lateral sclerosis
Modified and stabilized propeptides of Growth Differentiation Factor proteins, such as GDF-8 and Bone Morphogenetic Protein-11, are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for making and using the modified propeptides to prevent or treat human or animal disorders in which an increase in muscle tissue would be therapeutically beneficial. Such disorders include muscle or neuromuscular disorders (such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, muscle atrophy, congestive obstructive pulmonary disease, muscle wasting syndrome, sarcopenia, or cachexia), metabolic diseases or disorders (such as such as type 2 diabetes, noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia, or obesity), adipose tissue disorders (such as obesity), and bone degenerative diseases (such as osteoporosis).
Owner:WYETH LLC
Deposition of calcium-phosphate (CaP) and calcium-phosphate with bone morphogenic protein (CaP+BMP) coatings on metallic and polymeric surfaces
InactiveUS20080097618A1Reduce the amount of solutionHigh densityImpression capsBone implantPolymeric surfaceSolubility
The invention is a medical implantable device which is coated by the method according to the invention. The surface of the substrate used for the implantable device, in the raw condition, following a cleaning regime and physiochemical pretreatments, is coated using a biomimetic process in a supersaturated calcium phosphate solution (SCPS) to obtain the desired coating coverage and morphology maintaining a ratio of calcium to phosphorus pH, as well as solution temperature plays a major role in yielding precipitation of the proper phase of CaP so that composition, morphologies, crystal structures, and solubility characteristics are optimal for the deposition process. The biomimetic coating adds the attribute of osteoconductivity to the implant device. To maximize bone growth, the implant must also induce bone growth, or possess the attribute of osteoinductivity. This attribute is acquired by the use of therapeutic agents, i.e. bone morphogenic proteins (BMP), growth factors, stem cells, etc. The preparation of the SCPS solution is slightly altered so that during the immersion of the implant in the SCPS, the therapeutic agents are co-precipitated and bonded with the CaP directly on the underlying surface of the implant device. A final dipping process into a BMP solution provides an initial burst of cellular activity. For delivering stem and / or progenitor cell, after drying the dipped solution of BMP, the cells are cultured on the surface of the implant.
Owner:HERKOWITZ HARRY N
Compositions and methods for increasing bone mineralization
ActiveUS20060233801A1Damage formationVirusesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIncreased bone mineral densitySclerostin
A novel class or family of TGF-β binding proteins is disclosed. Also disclosed are assays for selecting molecules for increasing bone mineralization and methods for utilizing such molecules. In particular, compositions and methods relating to antibodies that specifically bind to TGF-beta binding proteins are provided. These methods and compositions relate to altering bone mineral density by interfering with the interaction between a TGF-beta binding protein sclerostin and a TGF-beta superfamily member, particularly a bone morphogenic protein. Increasing bone mineral density has uses in diseases and conditions in which low bone mineral density typifies the condition, such as osteopenia, osteoporosis, and bone fractures.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
Antibodies specific for sclerostin and methods of screening and use therefor
Compositions and methods relating to antibodies that specifically bind to TGF-beta binding proteins are provided. These methods and compositions relate to altering bone mineral density by interfering with the interaction between a TGF-beta binding protein sclerostin and a TGF-beta superfamily member, particularly a bone morphogenic protein. Increasing bone mineral density has uses in diseases and conditions in which low bone mineral density typifies the condition, such as osteopenia, osteoporosis, and bone fractures.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
Antibodies specific for sclerostin
A novel class or family of TGF-β binding proteins is disclosed. Also disclosed are assays for selecting molecules for increasing bone mineralization and methods for utilizing such molecules. In particular, compositions and methods relating to antibodies that specifically bind to TGF-beta binding proteins are provided. These methods and compositions relate to altering bone mineral density by interfering with the interaction between a TGF-beta binding protein sclerostin and a TGF-beta superfamily member, particularly a bone morphogenic protein. Increasing bone mineral density has uses in diseases and conditions in which low bone mineral density typifies the condition, such as osteopenia, osteoporosis, and bone fractures.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
Pharmaceutical agent comprising Anti-bmp9 antibody as active ingredient for treatment of anemia such as renal anemia and cancer anemia
The present invention provides an anti-BMP9 (Bone morphogenetic protein-9) monoclonal antibody or an antibody fragment thereof binding to human BMP9, a hybridoma producing the antibody or the antibody fragment, a DNA encoding the antibody or the antibody fragment, a vector comprising the DNA, a transformant obtained by introduction of the vector, a method for preparing the antibody or the antibody fragment using the hybridoma or the transformant, and a therapeutic agent comprising the antibody or the antibody fragment as an active ingredient. Further, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising the antibody or the antibody fragment as an active ingredient for the treatment of anemia such as renal anemia, cancer anemia or the like, and a method for treating anemia such as renal anemia, cancer anemia or the like using the same.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
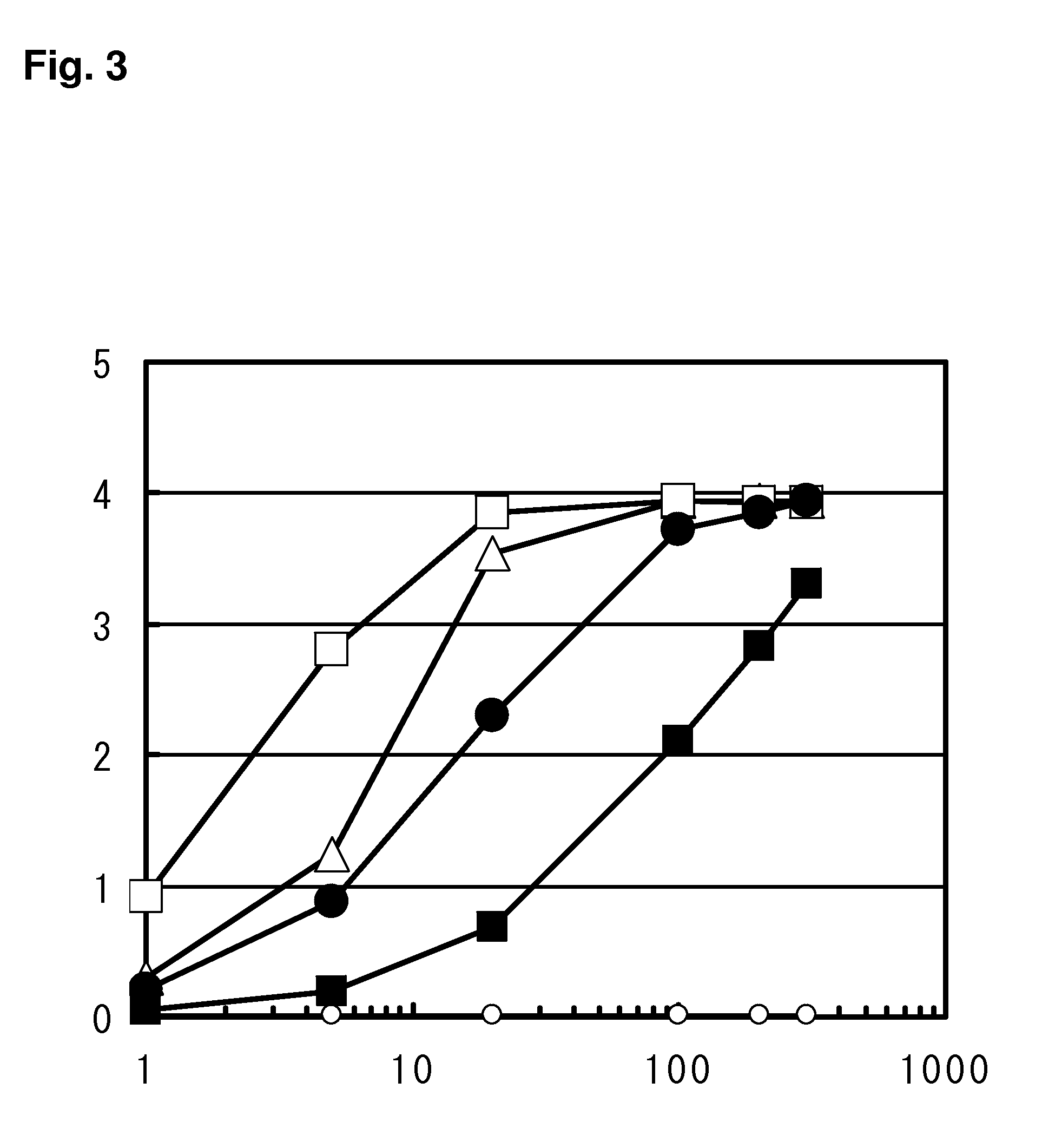
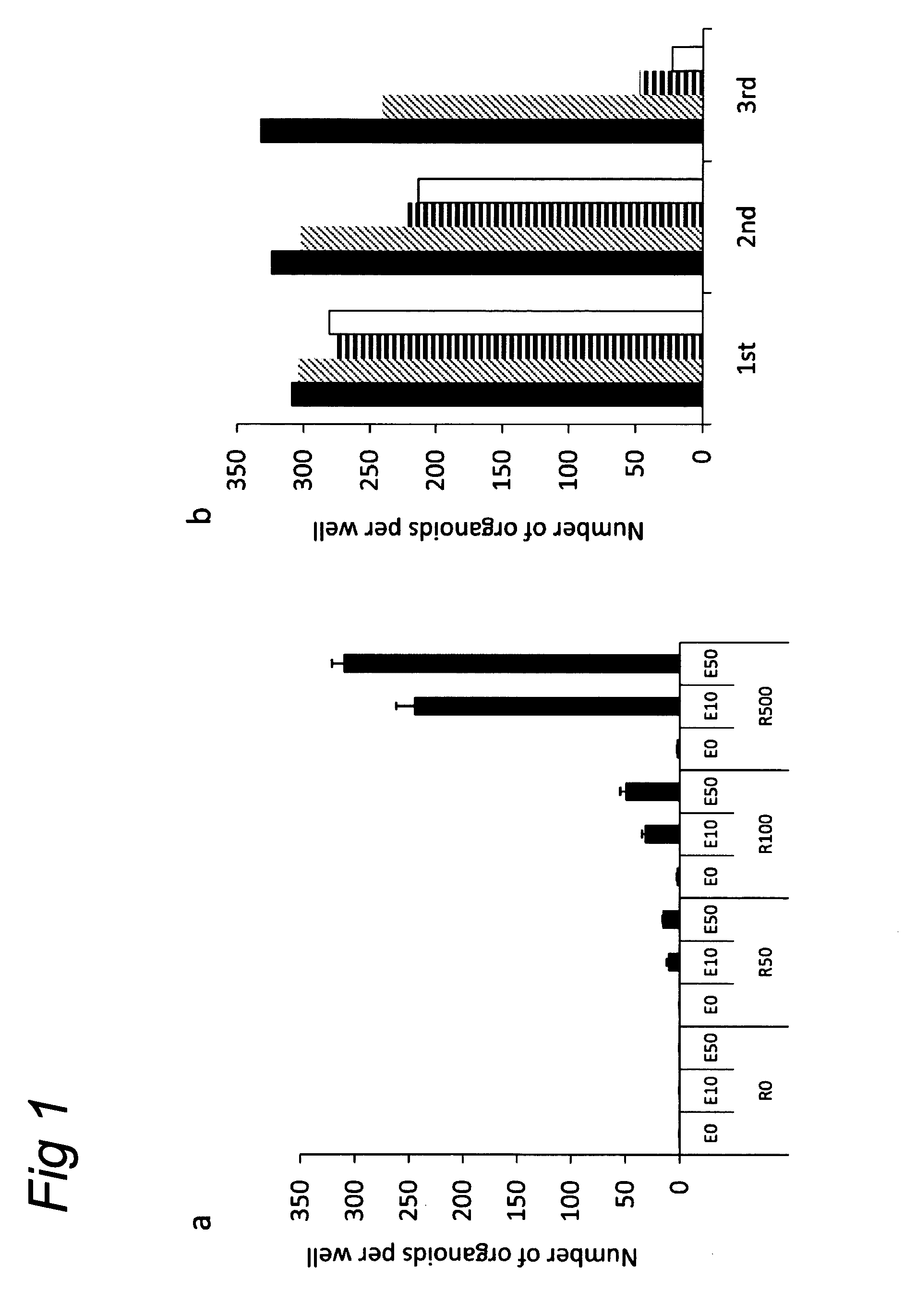
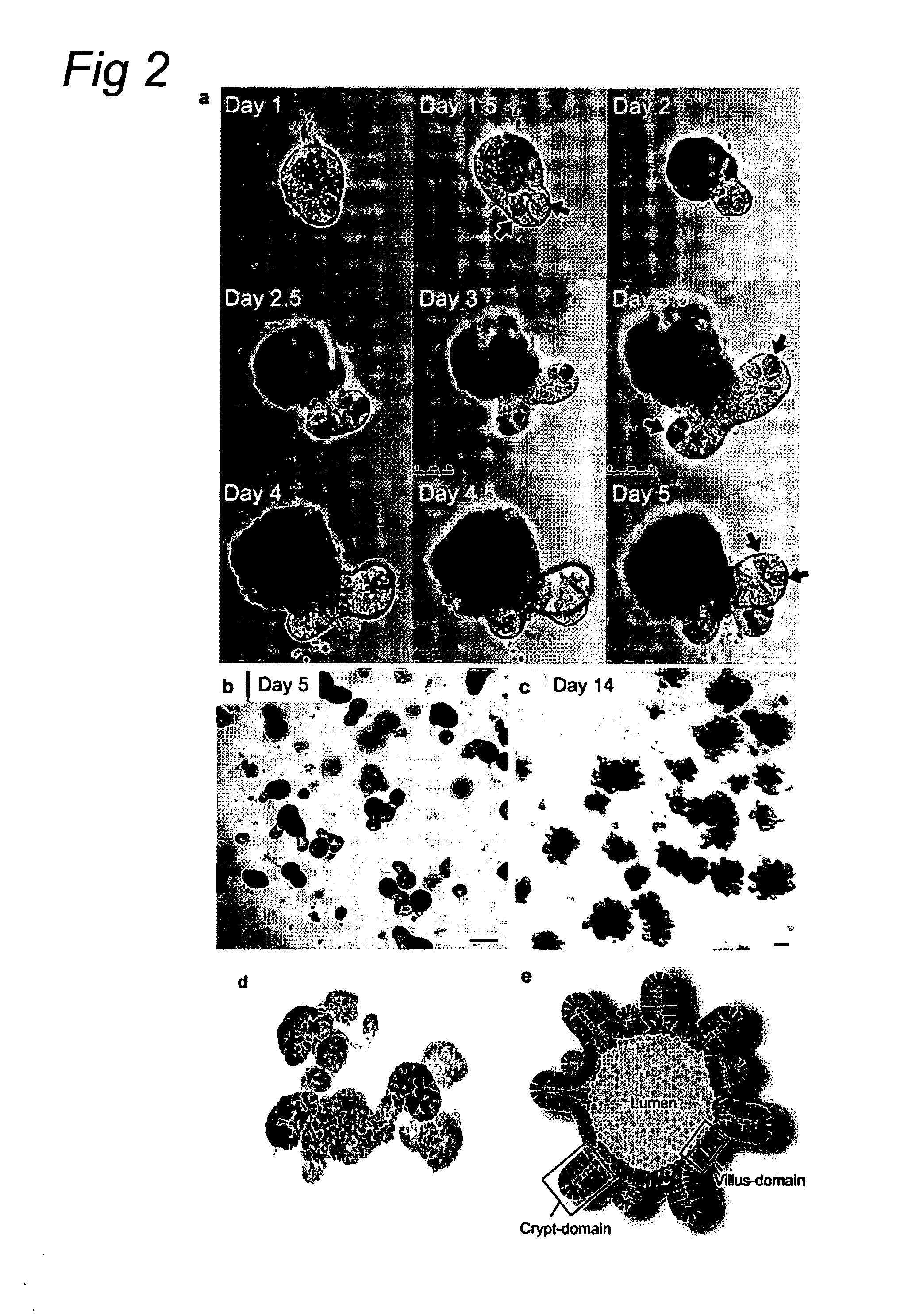
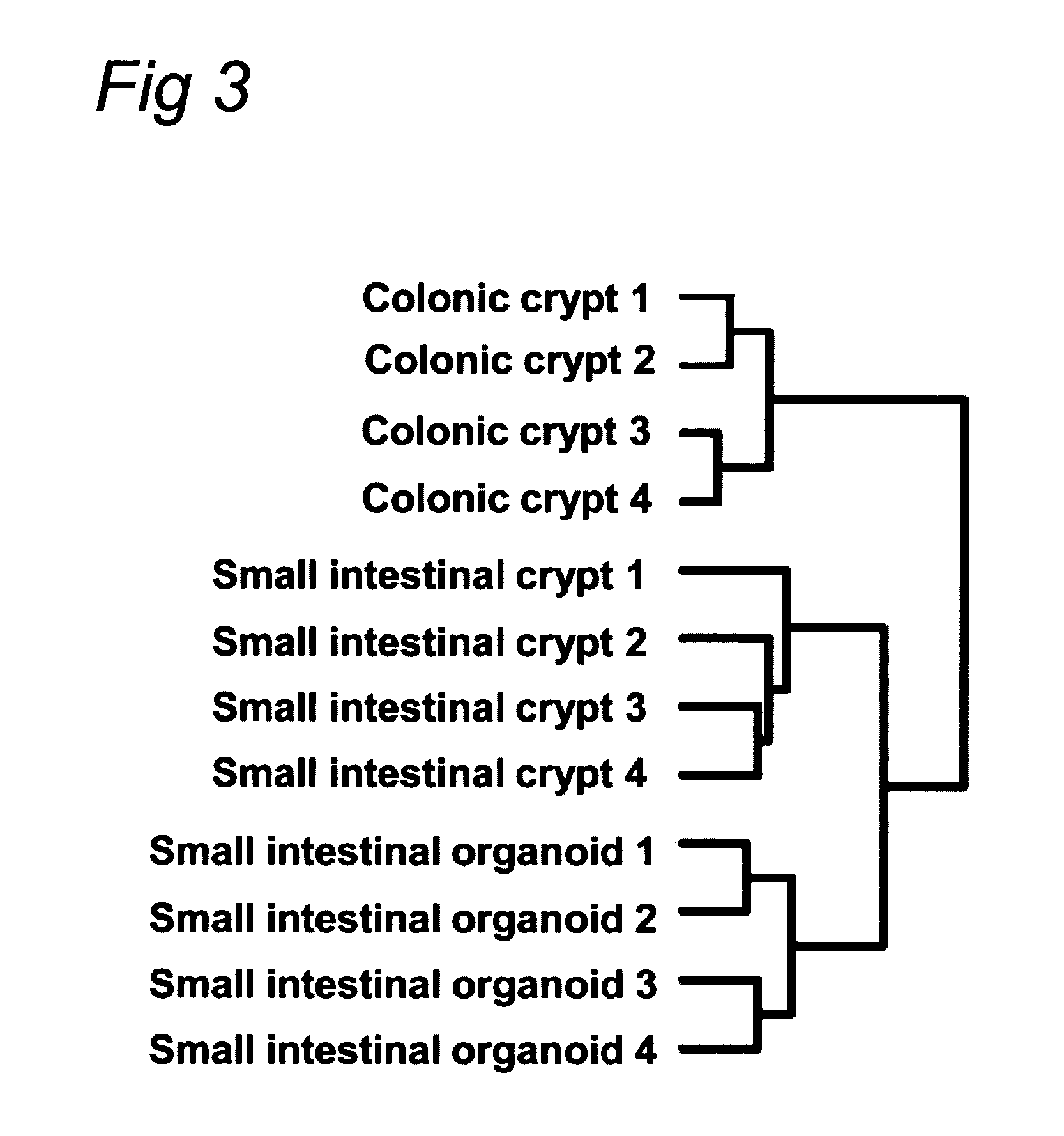
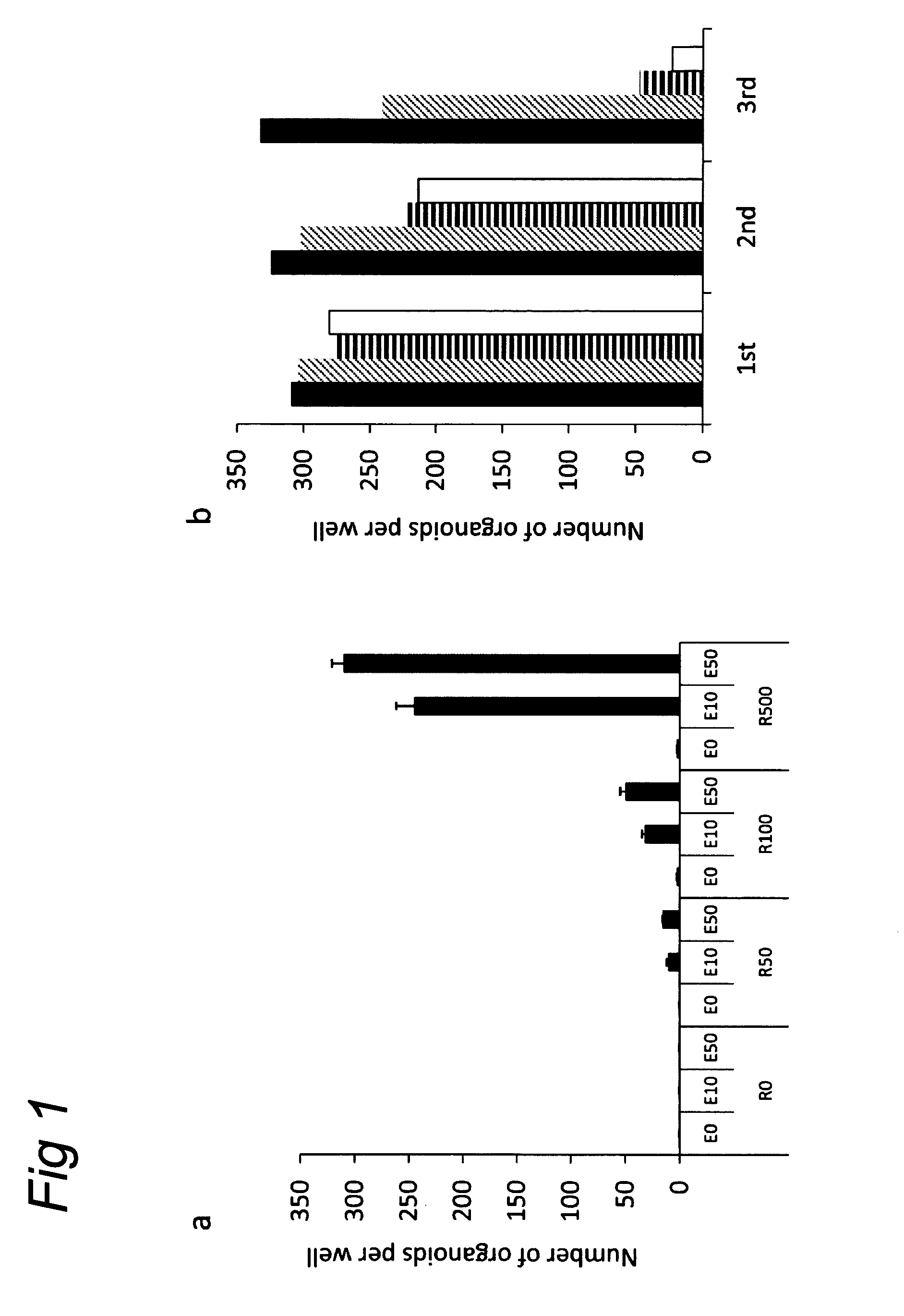
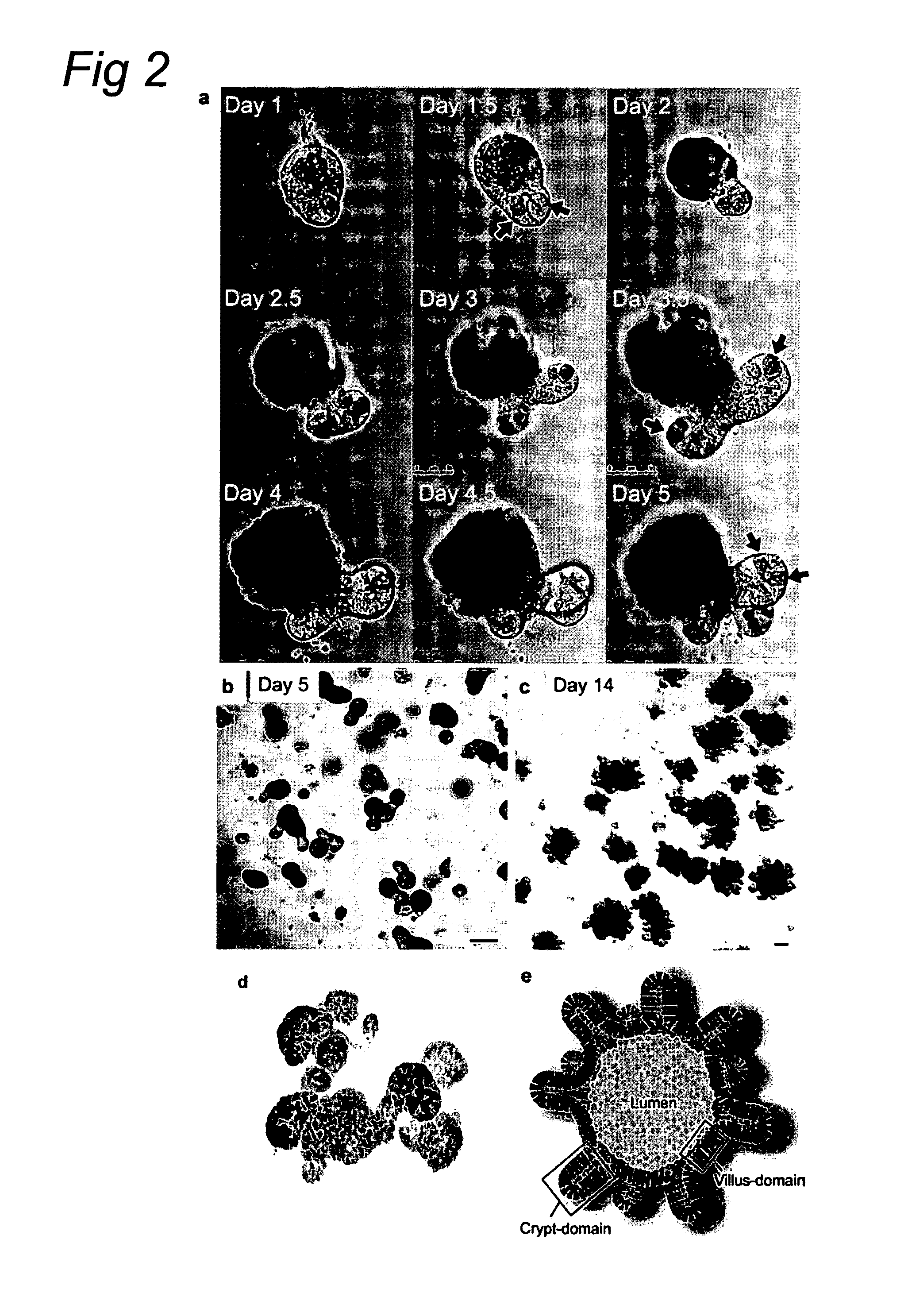
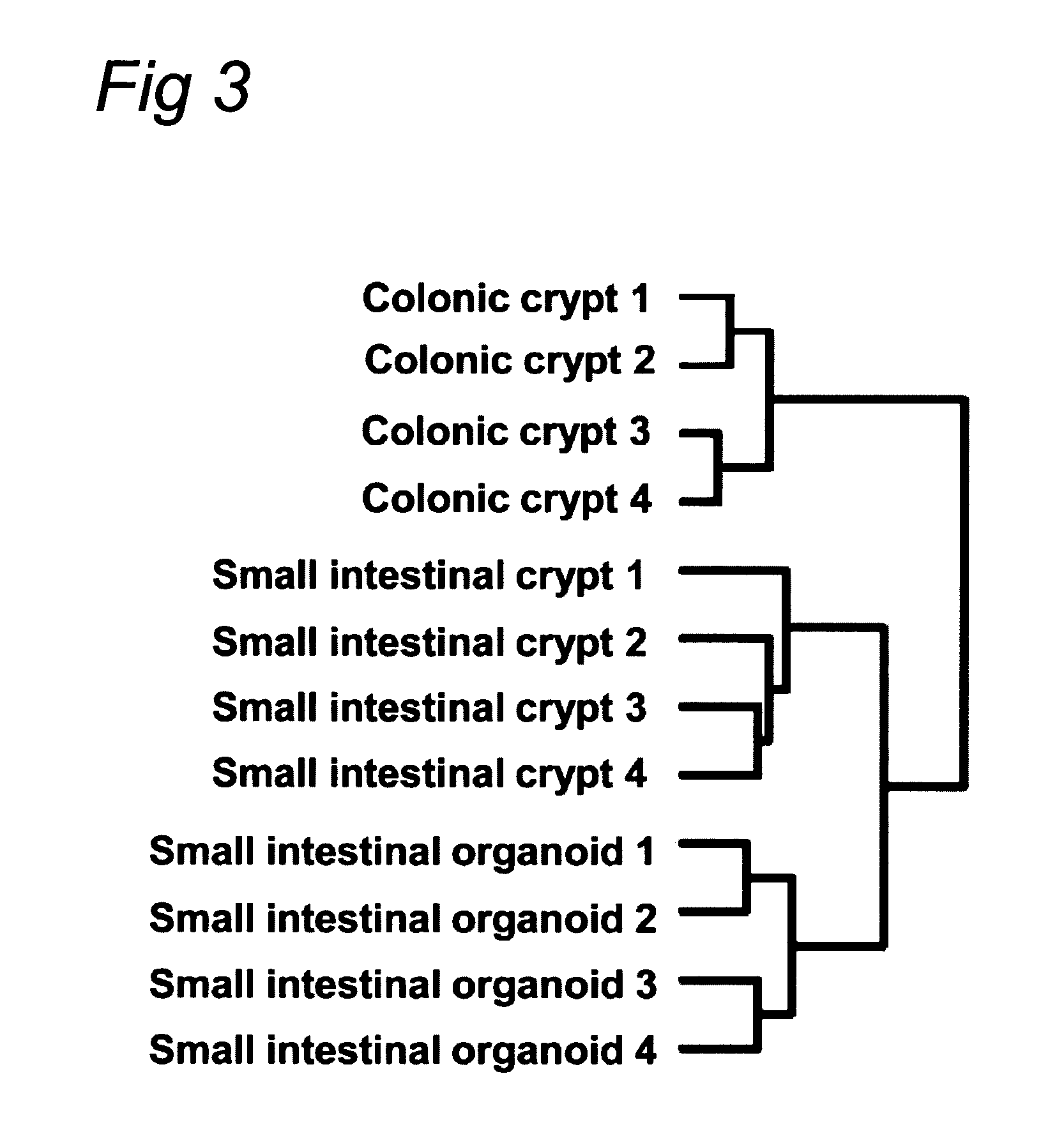
Culture medium for epithelial stem cells and organoids comprising said stem cells
ActiveUS20120028355A1Profound effectGastrointestinal cellsMetabolism disorderCell culture mediaAdenoma
The invention relates to a method for culturing epithelial stem cells, isolated tissue fragments comprising the epithelial stem cells, or adenoma cells, and culturing the cells or fragments in the presence of a Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) inhibitor, a mitogenic growth factor, and a Wnt agonist when culturing epithelial stem cells and isolated tissue fragments. The invention further relates to a cell culture medium comprising a BMP inhibitor, a mitogenic growth factor, and a Wnt agonist, to the use of the culture medium, and to crypt-villus organoids, gastric organoids and pancreatic organoids that are formed in the culture medium.
Owner:KONINK NEDERLANDSE AKADE VAN WETENSCHAPPEN
Degradable cage for bone fusion
InactiveUS20110282392A1Improve biological activityIncrease capacityInternal osteosythesisPeptide/protein ingredientsPolycaprolactoneBiomedical engineering
A cage for facilitating fusion of bones, such as vertebrae, or fusion of adjacent bone surfaces is disclosed. In one form, the cage includes a plurality of spaced apart walls comprising a biodegradable polymeric material (e.g., polycaprolactone); an osteoconductive mineral coating (e.g., a calcium compound) on at least a portion of the walls; and a bioactive agent (e.g., a bone morphogenetic protein) associated with the polymeric material and / or the coating. The bioactive agent is present in amount that induces ossification between the bones or adjacent bone surfaces. The cage may also include a fixation plate connected to at least one of the walls.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Positive modulator of bone morphogenic protein-2
InactiveUS20050196425A1Improve biological activityMaximize bioactivityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseBone formation
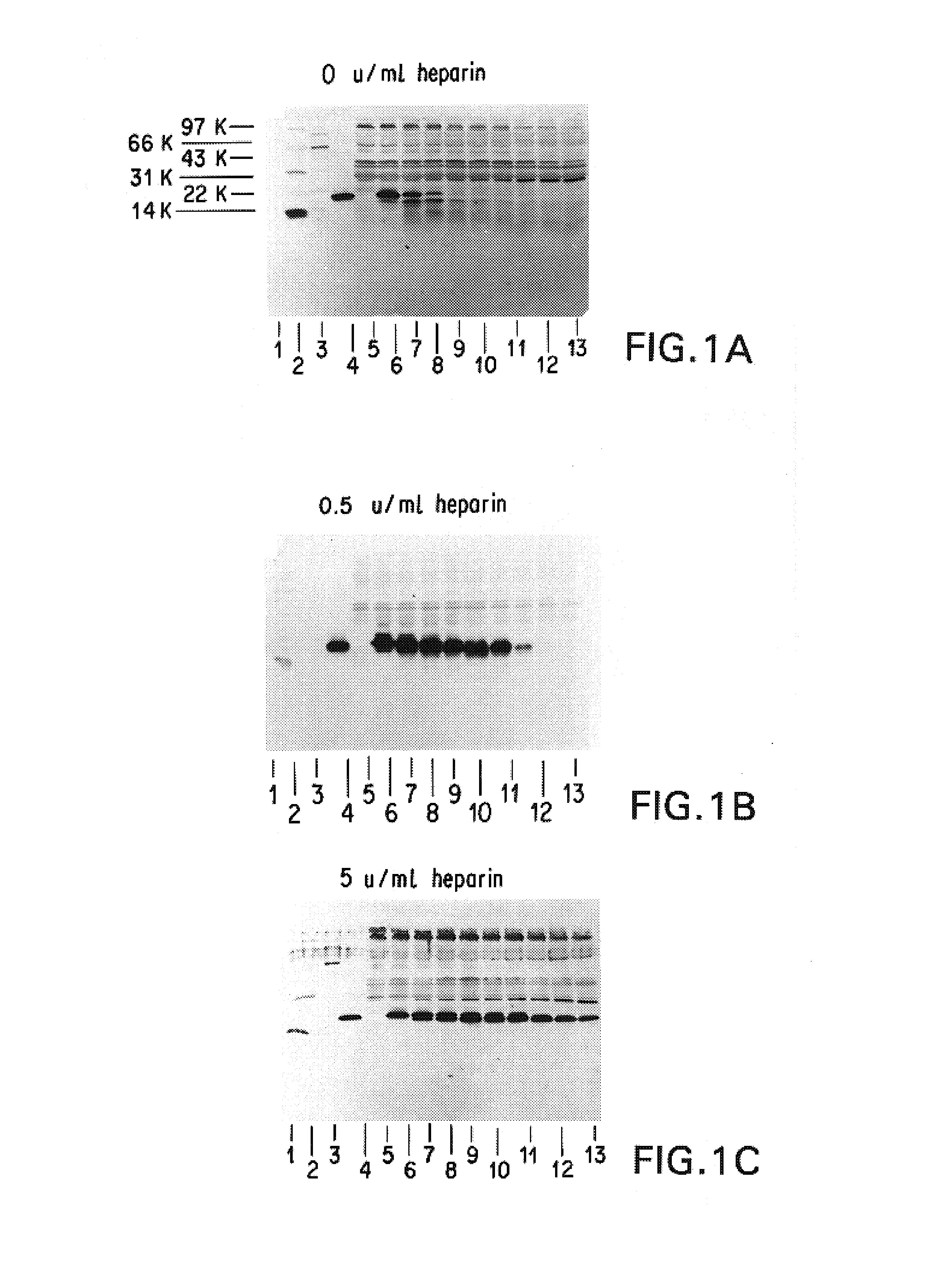
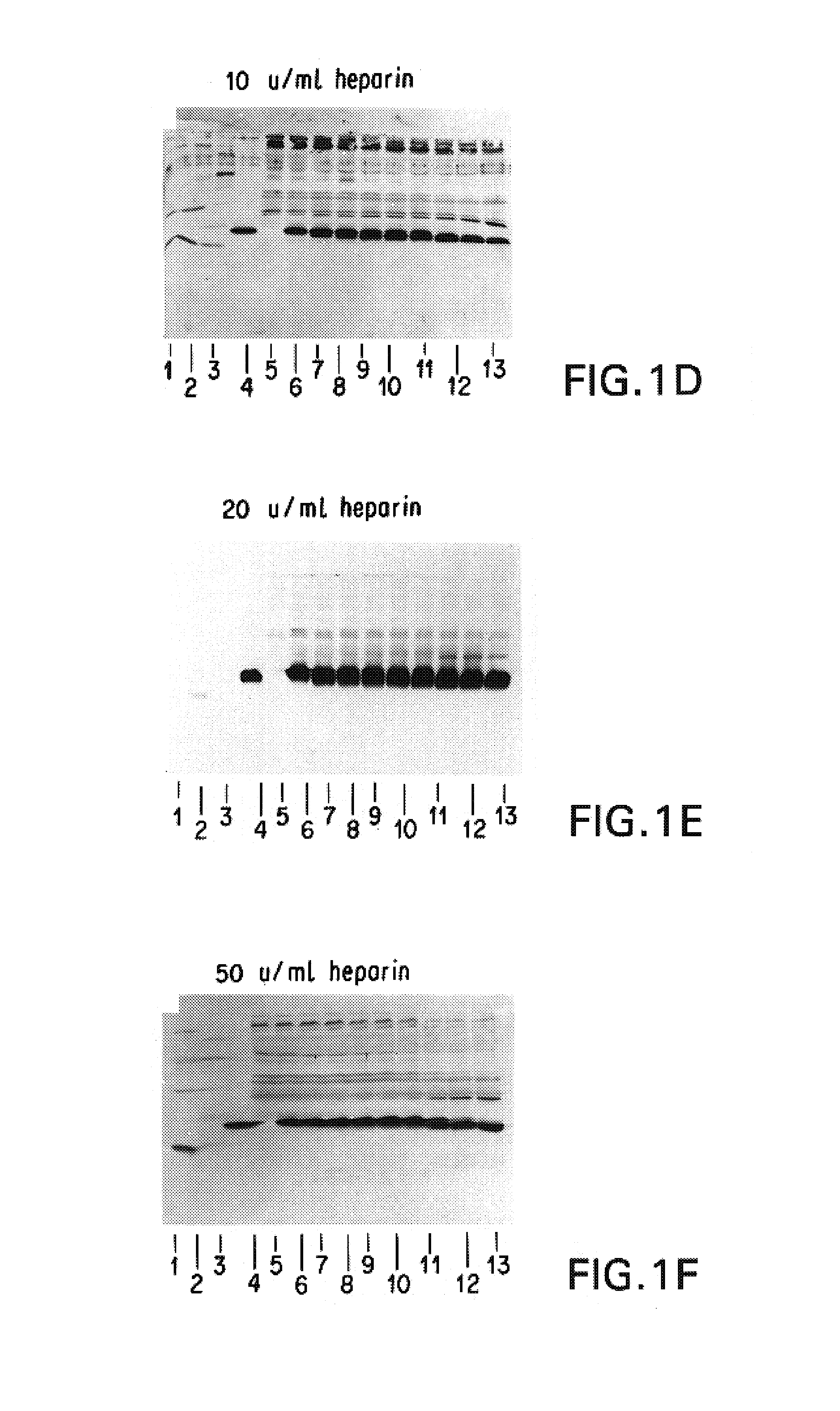
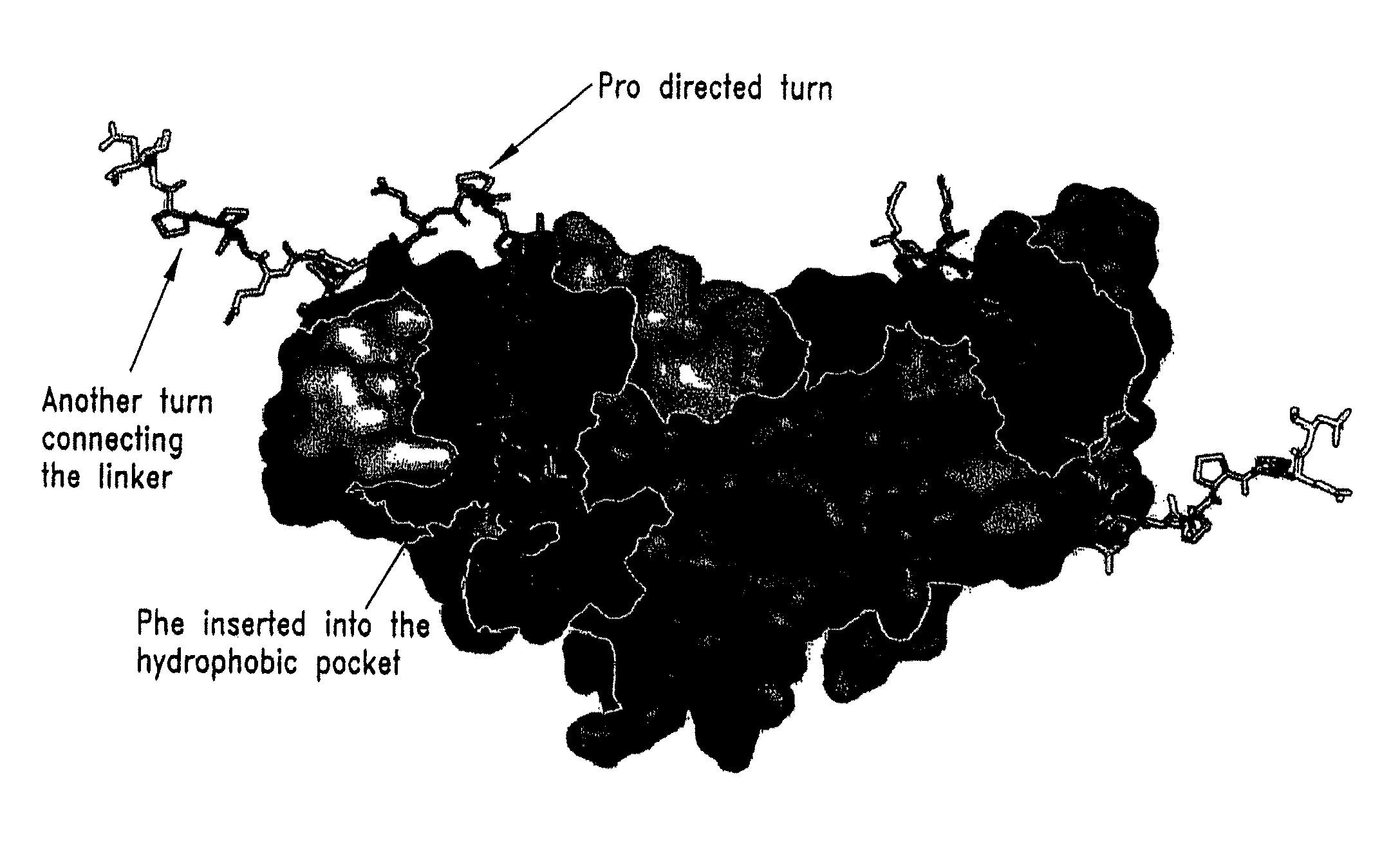
Compounds of the present invention of formula I and formula II are disclosed in the specification and wherein the compounds are modulators of Bone Morphogenic Protein activity. Compounds are synthetic peptides having a non-growth factor heparin binding region, a linker, and sequences that bind specifically to a receptor for Bone Morphogenic Protein. Uses of compounds of the present invention in the treatment of bone lesions, degenerative joint disease and to enhance bone formation are disclosed.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS +1
Bone marrow infusion chamber and method
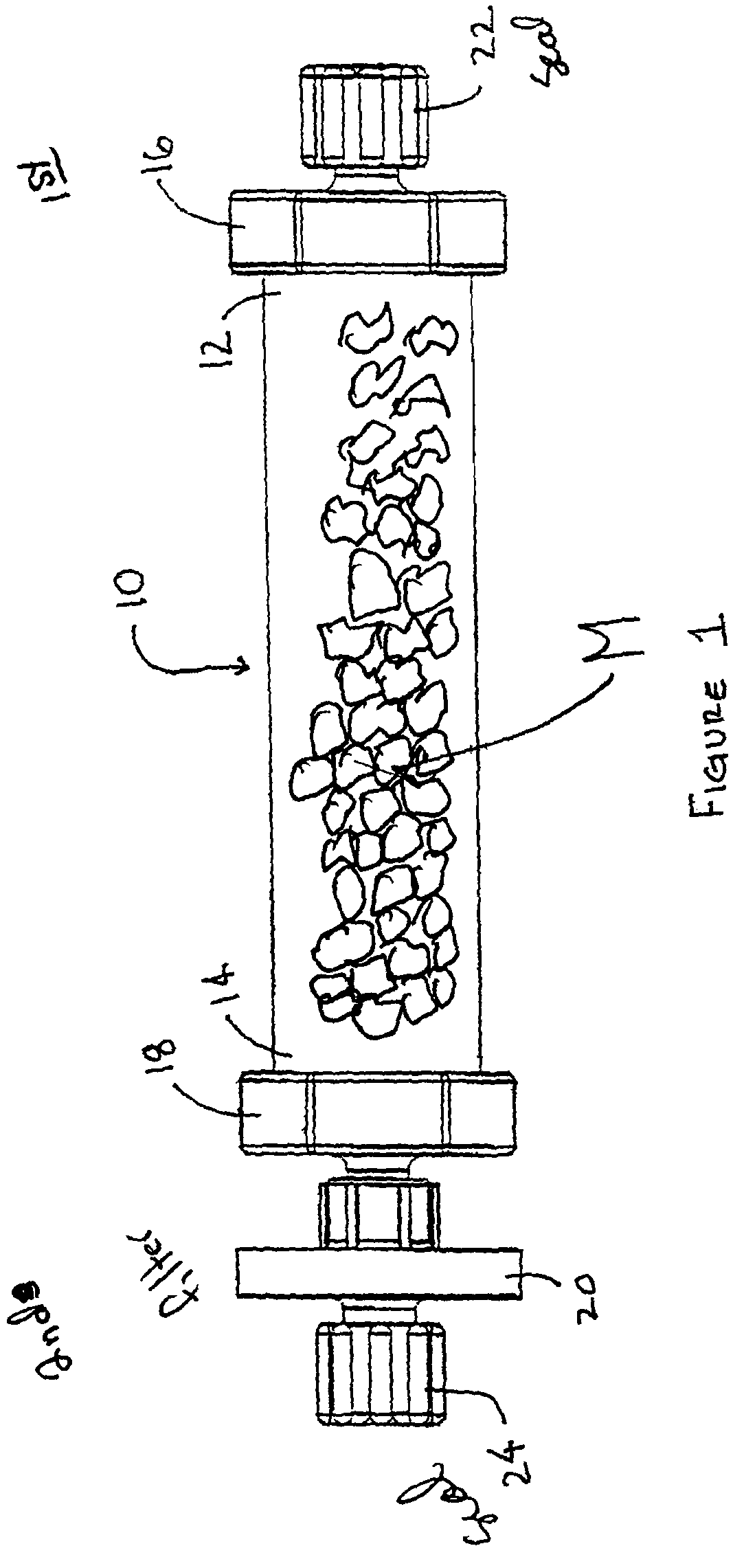
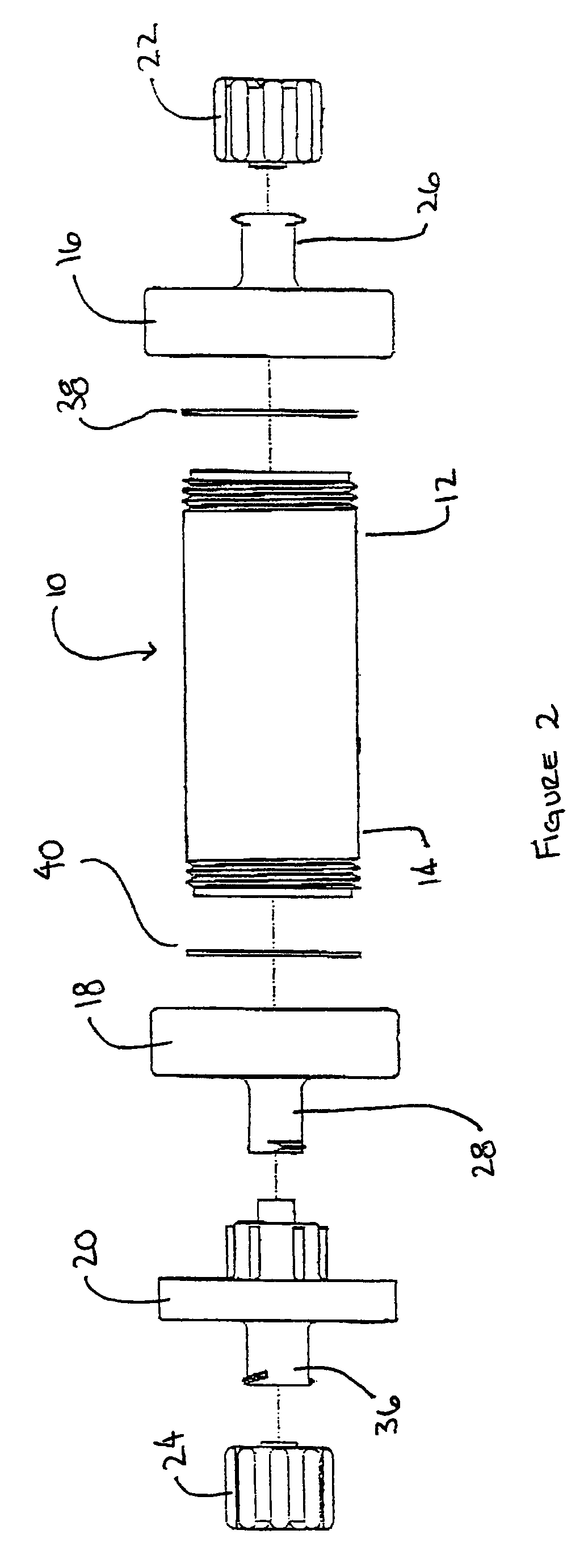
A method and apparatus for preparing a bone graft composite using an infusion chamber. A modular tube having a porous material contained therein and having removable end caps is provided. Bone marrow aspirate or other bone morphogenic protein containing suspensions may be infused into the tube. A filter on one end of the tube prevents the fluid from escaping while permitting air to be expelled from the tube as it is filled with bone marrow aspirate. Once infused into the tube, the bone marrow aspirate is allowed to settle to a putty or paste-like consistency, the putty and material together forming a bone graft composite.
Owner:WRIGHT MEDICAL TECH
Methods for treating anemia
InactiveUS20150266950A1Degrade cellReduced activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsGDF1Antagonist
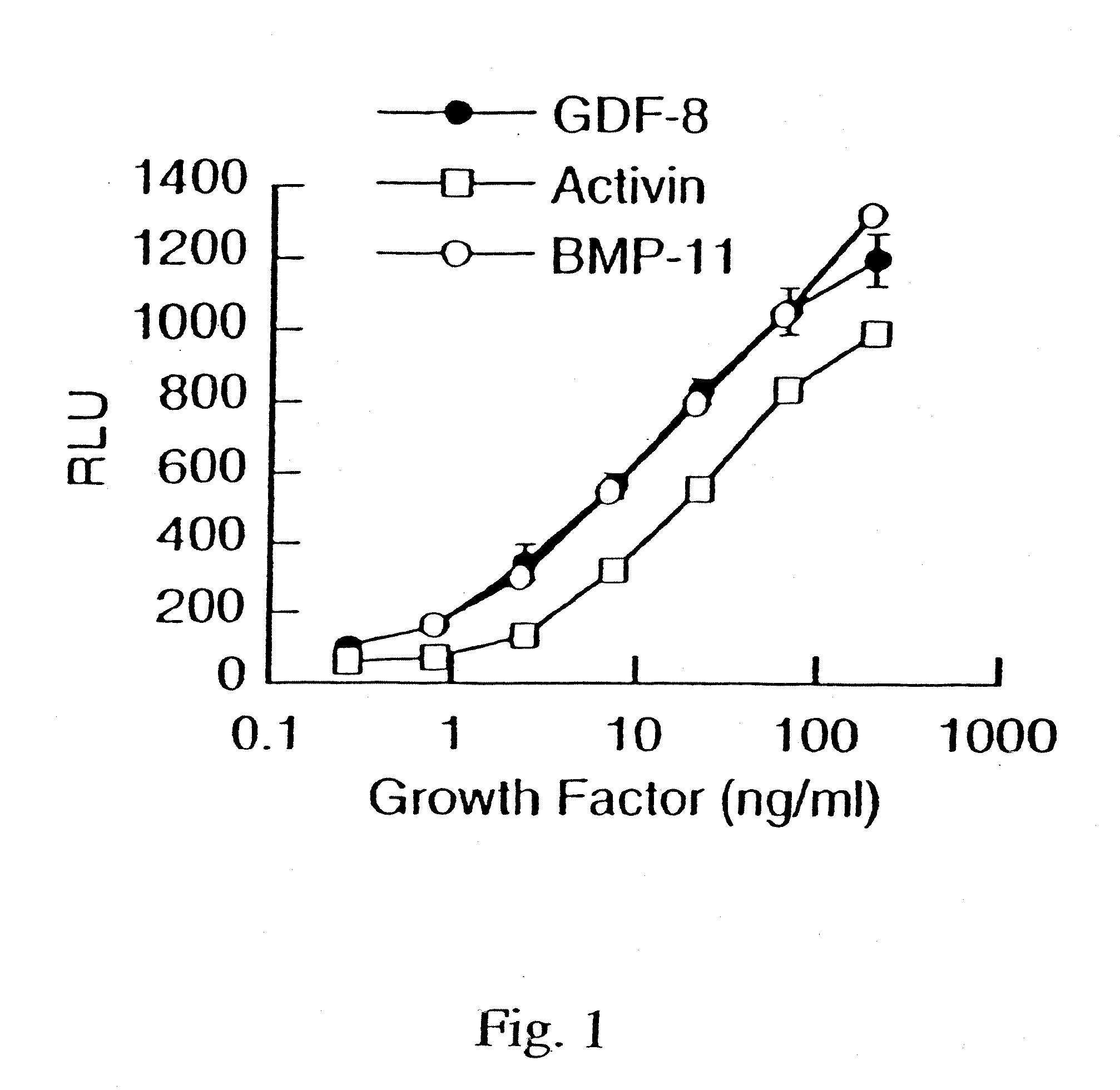
Provided herein are methods for the treatment of anemia, wherein the methods comprise administration of antagonists of Growth differentiation factor 11 (GDF1 1; also known as bone morphogenetic protein 11 (BMP11)) to a subject in need of the treatment.
Owner:CELGENE CORP
Use of morphogenetic proteins to treat human disc disease
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are introduced into an affected intervertebral disc without the inclusion of disc cells. The inventions applies to all known and yet-to-be developed or discovered BMPs, including BMP-1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, -7, -8, -9, -10, . . . BMPn. The BMP(s) may be obtained from natural and / or recombinant sources. The BMP(s) may be introduced using any surgical technique, including percutaneous or laparoscopic approaches. As one delivery mechanism, a passageway may be formed through the annulus, with the substances then being introduced through the passageway. Alternatively, a carrier may be sewn or otherwise adhered to the inside or outside of the existing annulus using standard surgical procedures. Additional therapeutic substances such as culture medium, growth factors, differentiation factors, hydrogels, polymers, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, or immunosuppressive medications could be introduced in conjunction with the BMP(s).
Owner:ANOVA
Biodegradable osteogenic porous biomedical implant with impermeable membrane
InactiveUS20100161074A1Facilitate mechanical shaping and fillingFacilitate and enhance proliferationDental implantsSurgical adhesivesBone tissueBone growth
A biomedical implant is disclosed with osteogenic factors and a solid impermeable membrane occluding a portion of its surface for the generation of new bone growth at the target site of the implant. The implant is porous, bioresorbable, and forms a three dimensional architectural scaffold for the formation of new bone tissue. The implant is formed with a polymer or collagen, bone morphogenetic protein and ceramic particles.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Bone Morphogenetic Protein Compositions
InactiveUS20100015230A1Improve stabilityEfficient preparationPowder deliverySenses disorderDiseaseSkeletal tissues
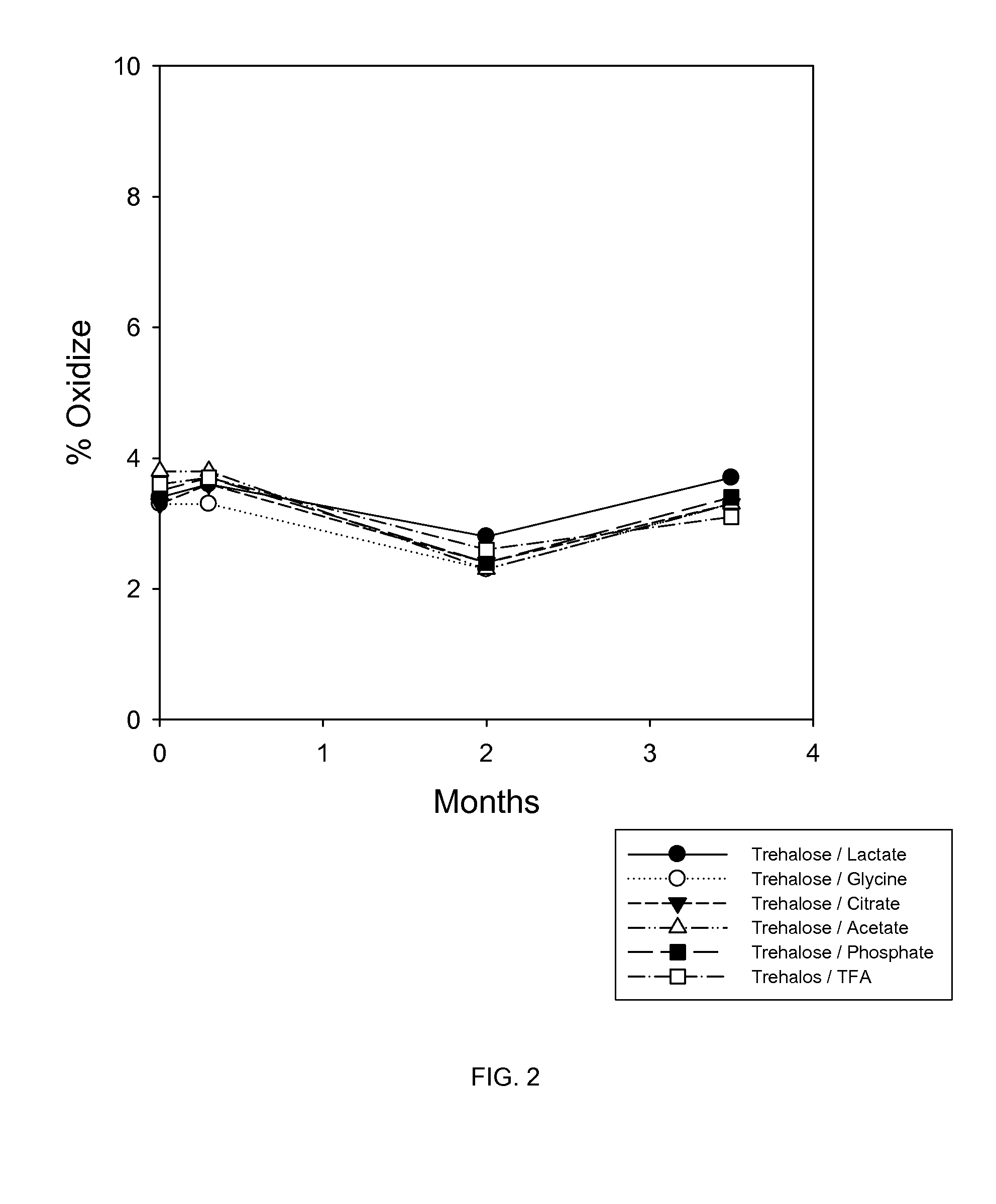
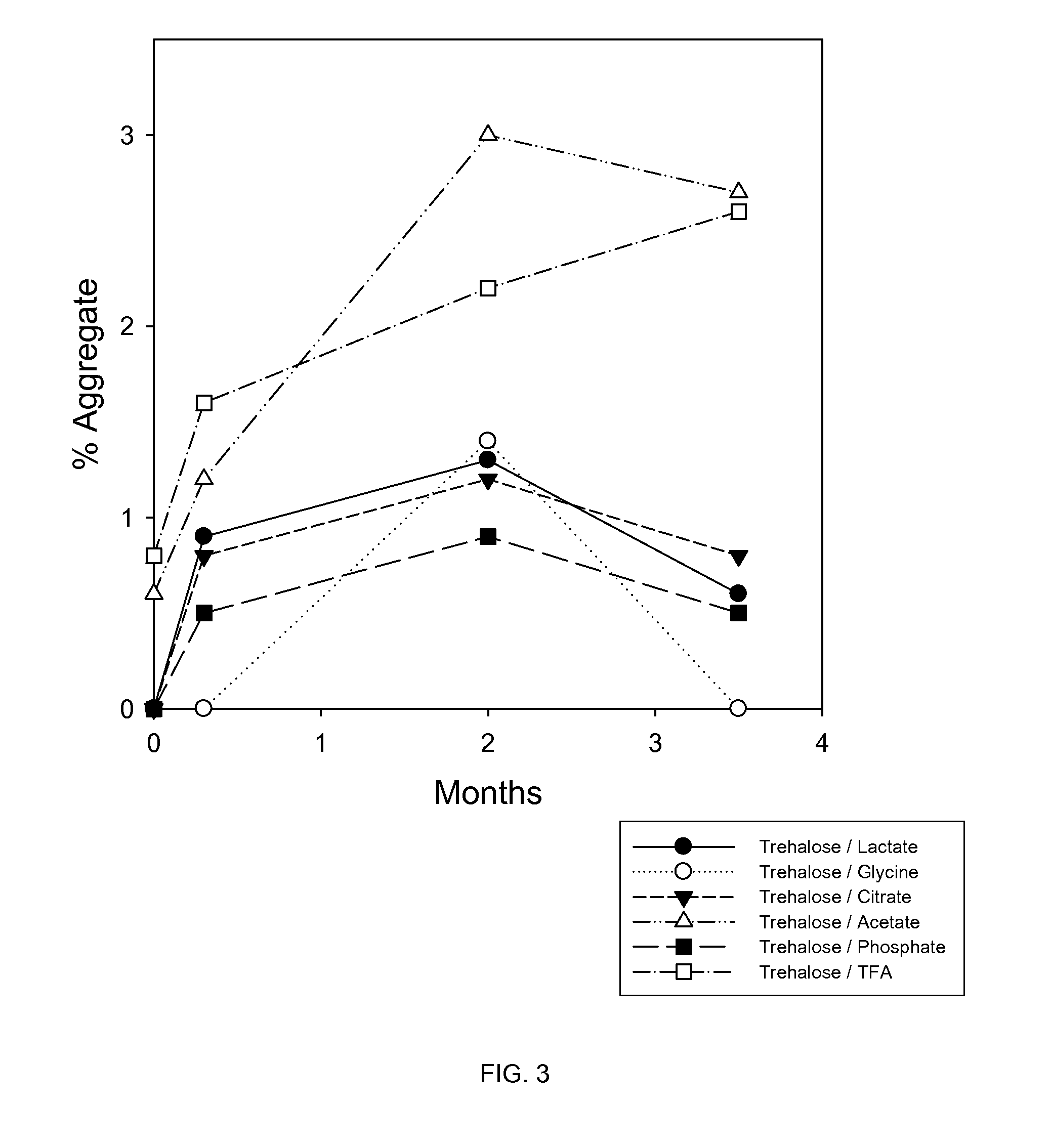
The present invention relates to compositions of bone morphogenetic proteins, particularly solid and liquid formulations of such proteins comprising one or more stabilizing excipients. The invention further provides methods of producing the compositions, kits comprising the compositions and methods of using the compositions in the treatment of diseases of skeletal and non-skeletal tissues.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Antibodies specific for sclerostin and methods for increasing bone mineralization
InactiveUS20090117118A1Peptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderDiseaseIncreased bone mineral density
Compositions and methods relating to antibodies that specifically bind to TGF-beta binding proteins are provided. These methods and compositions relate to altering bone mineral density by interfering with the interaction between a TGF-beta binding protein sclerostin and a TGF-beta superfamily member, particularly a bone morphogenic protein. Increasing bone mineral density has uses in diseases and conditions in which low bone mineral density typifies the condition, such as osteopenia, osteoporosis, and bone fractures.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
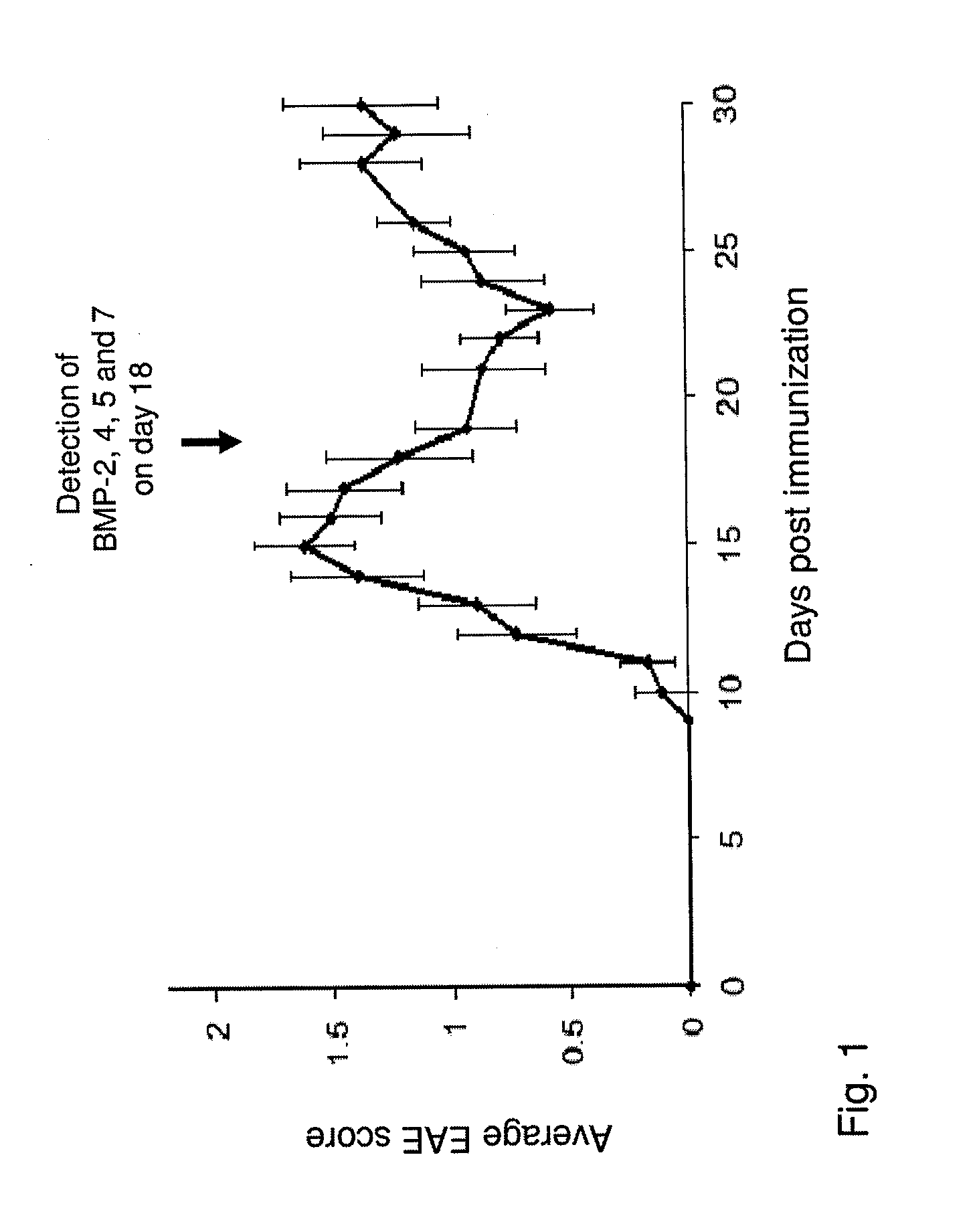
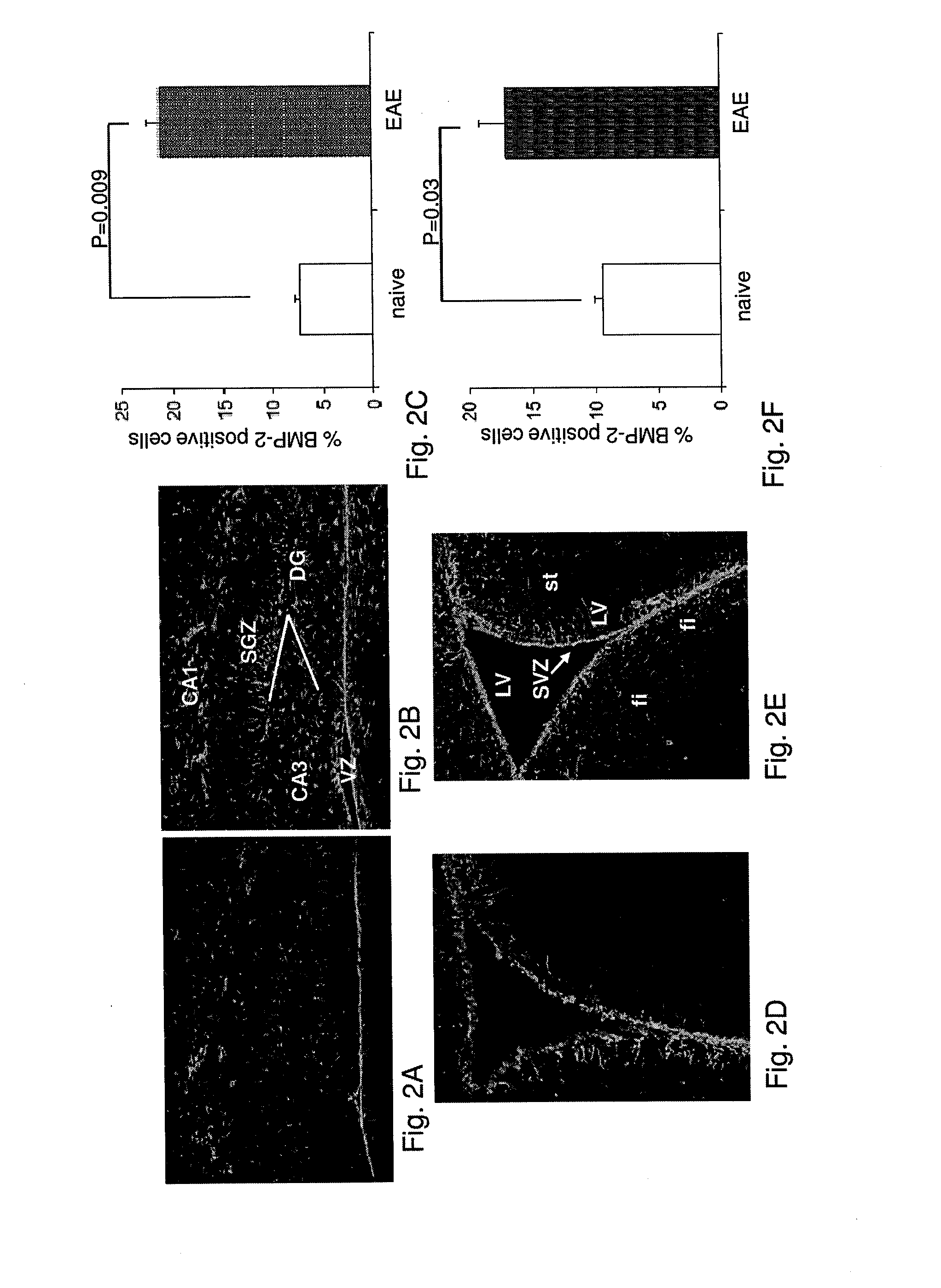
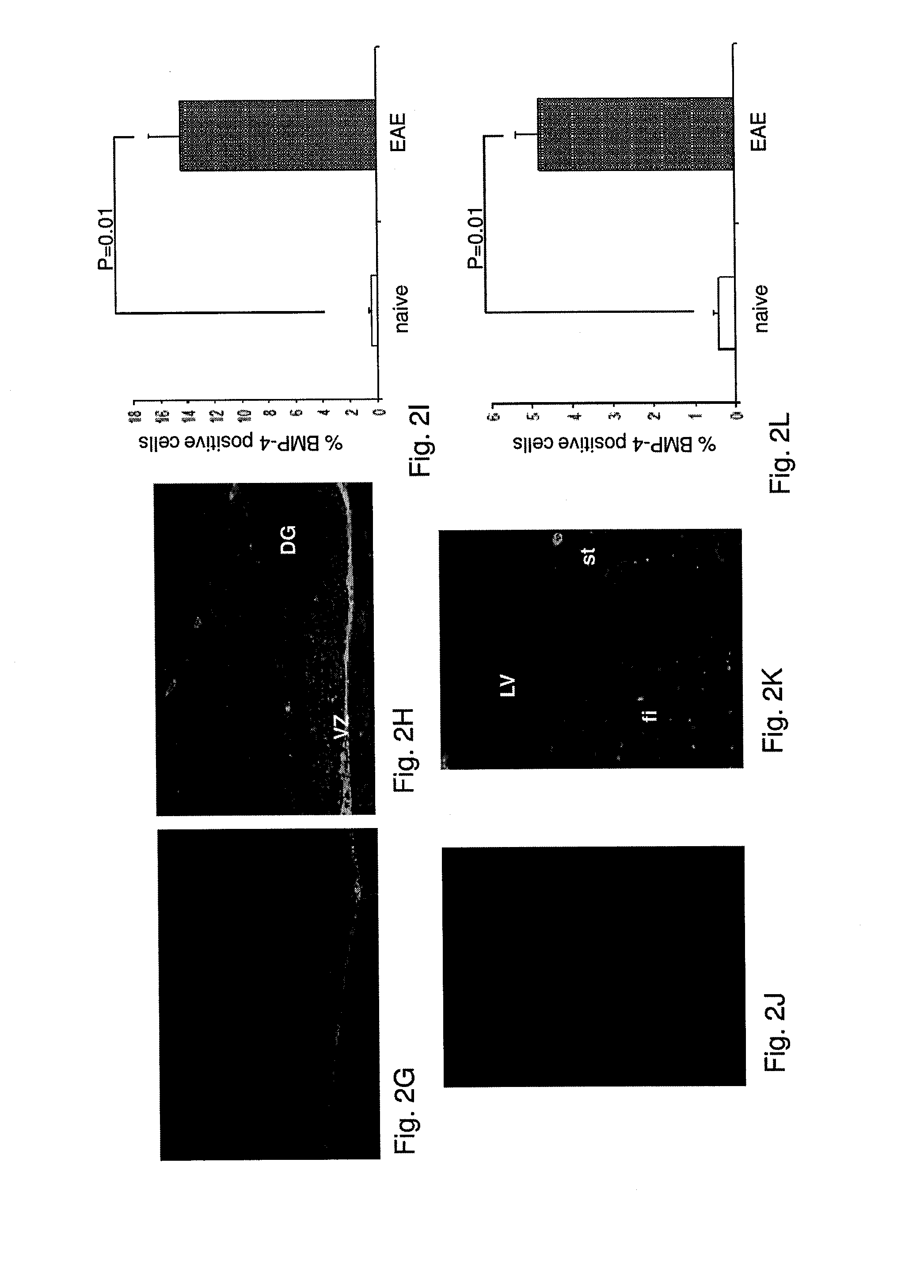
Use of blocking agents of bone morphogenic protein (BMP) signalling for the treatment of neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases
The invention provides pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of neuroinflammatory or neurodegenerative diseases comprising a single or a combination of several blocking agent(s) of Bone Morphogenic Protein (BMP) signaling. The invention further provides methods of treatment of neuroinflammatory or neurodegenerative diseases comprising administering to a patient in need thereof the pharmaceutical compositions of the invention.
Owner:THE MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & HEALTH SERVICES FUND OF THE TEL AVIV MEDICAL CENT
Culture medium for epithelial stem cells and organoids comprising the stem cells
The invention relates to a method for culturing epithelial stem cells, isolated tissue fragments comprising the epithelial stem cells, or adenoma cells, and culturing the cells or fragments in the presence of a Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) inhibitor, a mitogenic growth factor, and a Wnt agonist when culturing epithelial stem cells and isolated tissue fragments. The invention further relates to a cell culture medium comprising a BMP inhibitor, a mitogenic growth factor, and a Wnt agonist, to the use of the culture medium, and to crypt-villus organoids, gastric organoids and pancreatic organoids that are formed in the culture medium.
Owner:KONINK NEDERLANDSE AKADE VAN WETENSCHAPPEN
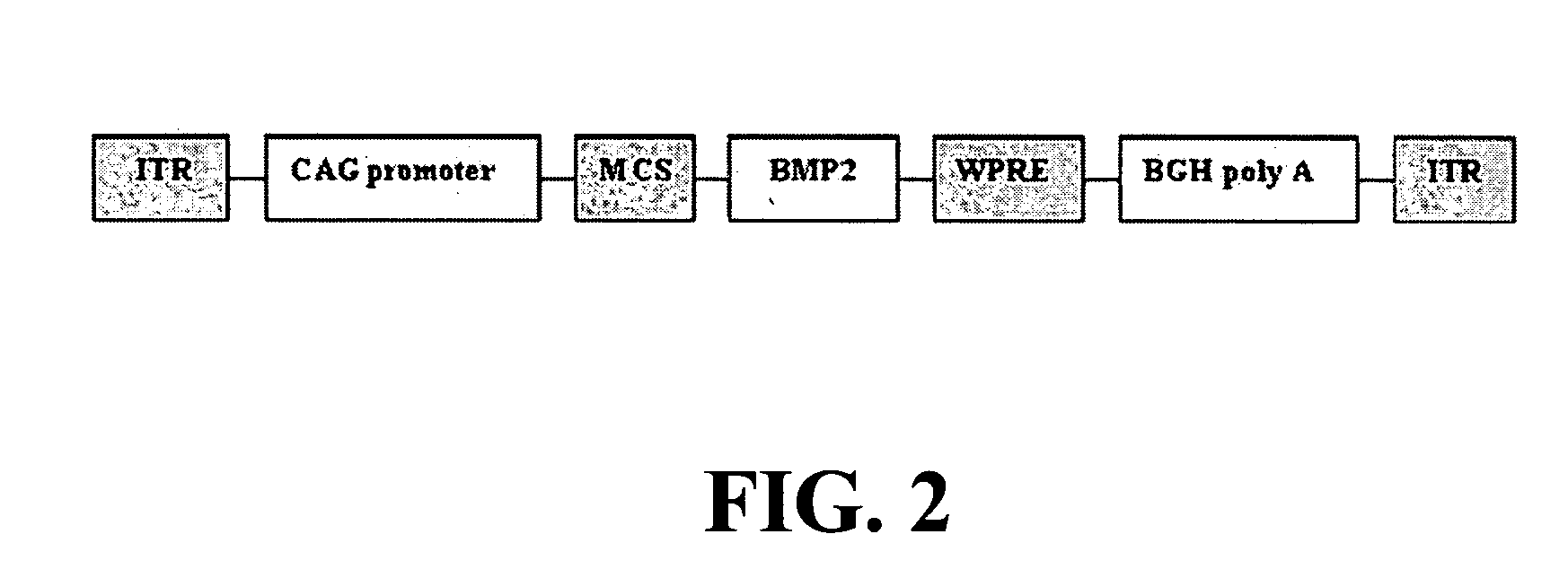
Combined adeno-associated virus and adenovirus cocktail gene delivery system for high efficiency gene expression without eliciting immune response in immuno-competent subjects
InactiveUS20040223953A1Efficient deliveryBone formationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryDisease
The present invention provides an efficient gene delivery system using Adeno-Associated Viral (AAV) vector in gene therapy. Furthermore, the invention provides a combined AAV and Adenovirus (Adv) cocktail gene delivery system which is even more efficient in in vivo gene delivery and expression without eliciting any significant immune responses in an immunocompetent subject. In particular, the invention provides a therapeutic agent and methods for preventing, treating, managing, or ameliorating various diseases and disorders including, but not limited to, bone diseases, by delivering Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 (BMP-2) for new bone formation via gene therapy using said system. The invention provides a nucleic acid molecule comprising an AVV vector and a promoter operably linked to a sequence encoding BMP-2; and a nucleic acid molecule comprising an Adv vector and a promoter operably linked to a sequence encoding BMP-2, as well as vectors and host cells comprising said nucleic acid molecules, respectively.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Systems and methods to affect anatomical structures
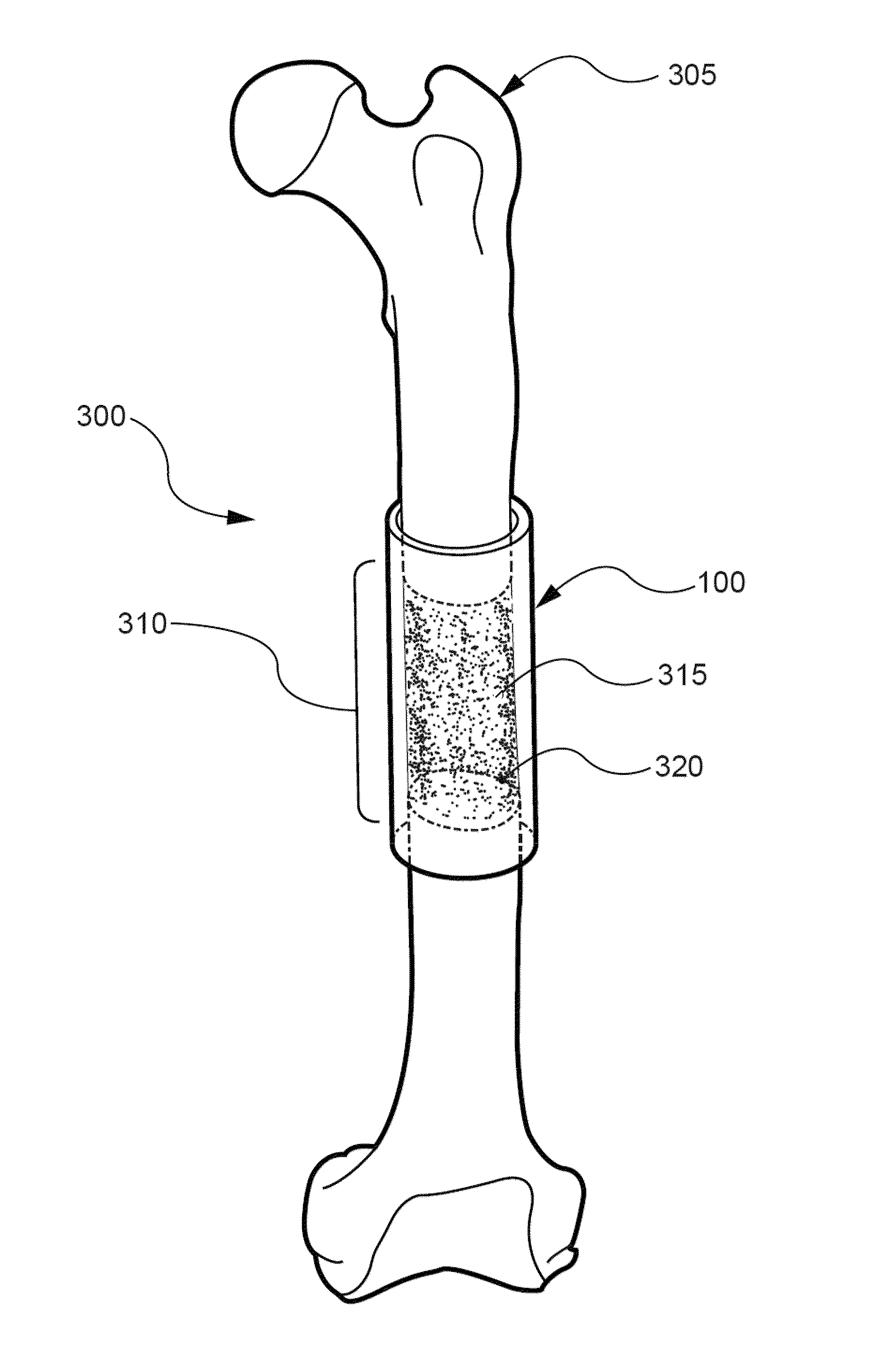
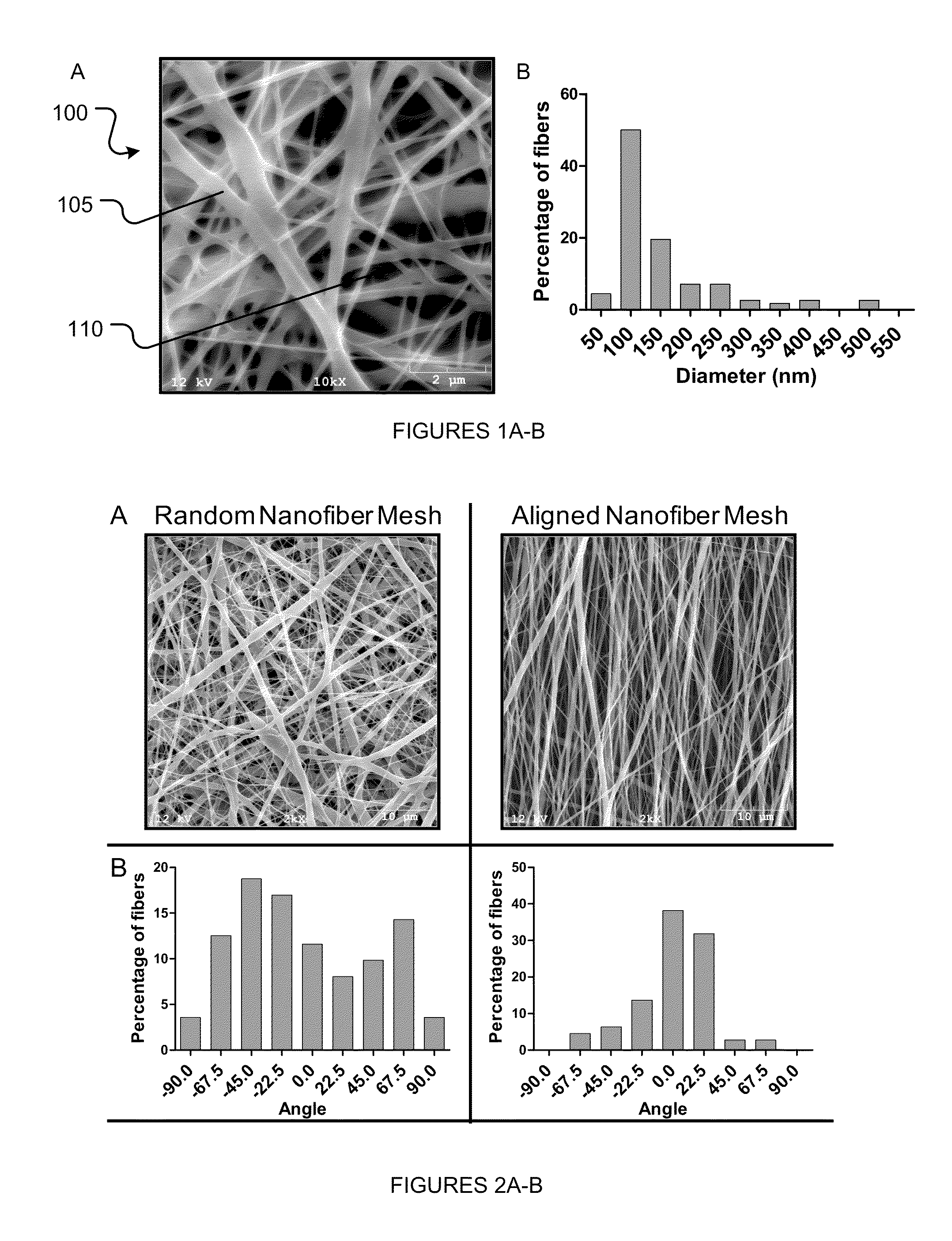
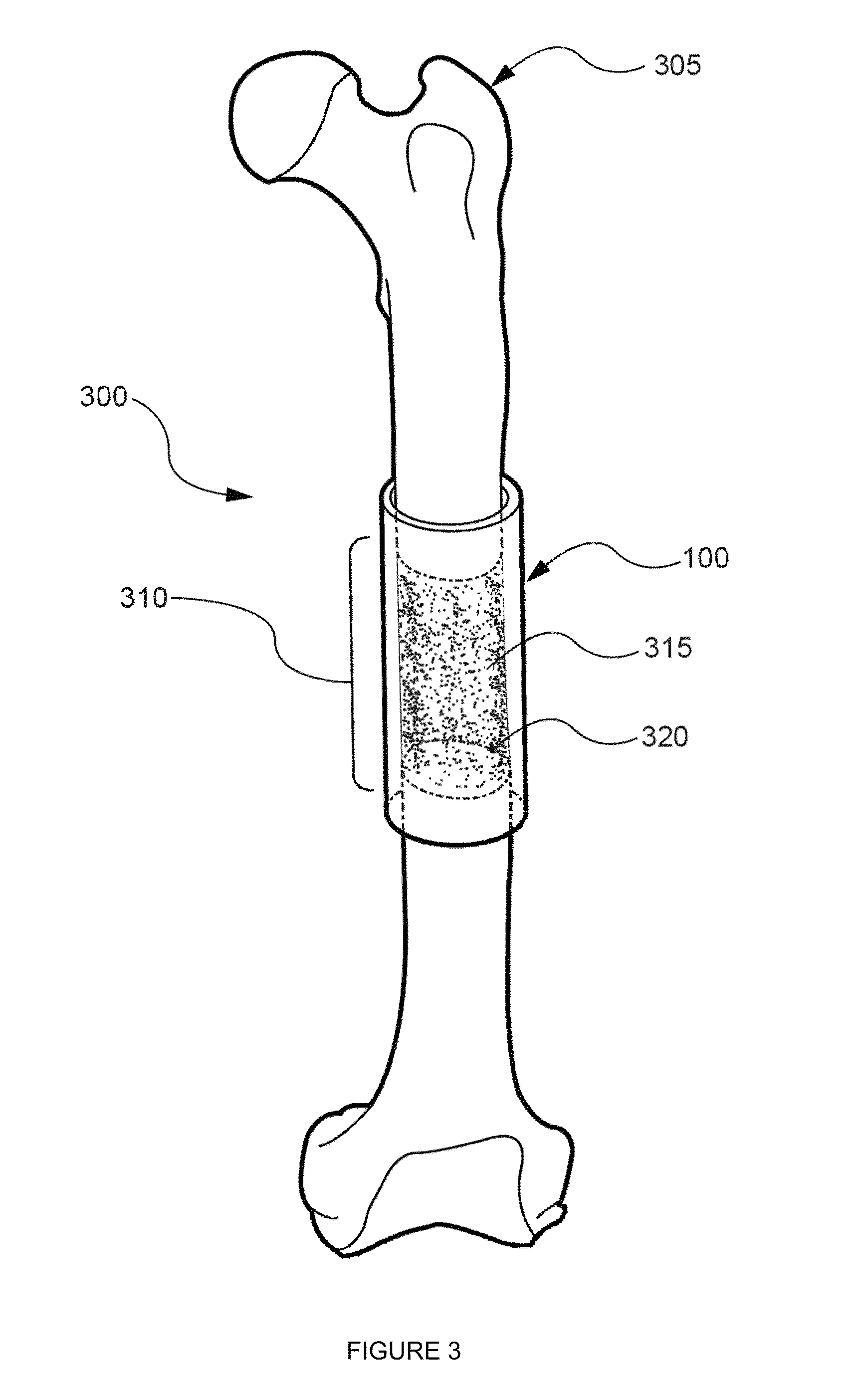
ActiveUS20100168771A1Pharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationAnatomical structuresActive agent
The various embodiments of the present invention are generally directed to systems and methods to affect anatomical structures. More particularly, the various embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems and methods to regenerate bone. An aspect of the present invention comprises a system for affecting an anatomical structure, comprising: a nanofiber mesh configured to substantially conform to an anatomical structure, wherein at least a portion of the nanofiber mesh defines a fillable space; a carrier substance comprising an active agent, such as a bone morphogenetic protein, wherein the carrier substance is disposed within the fillable space.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
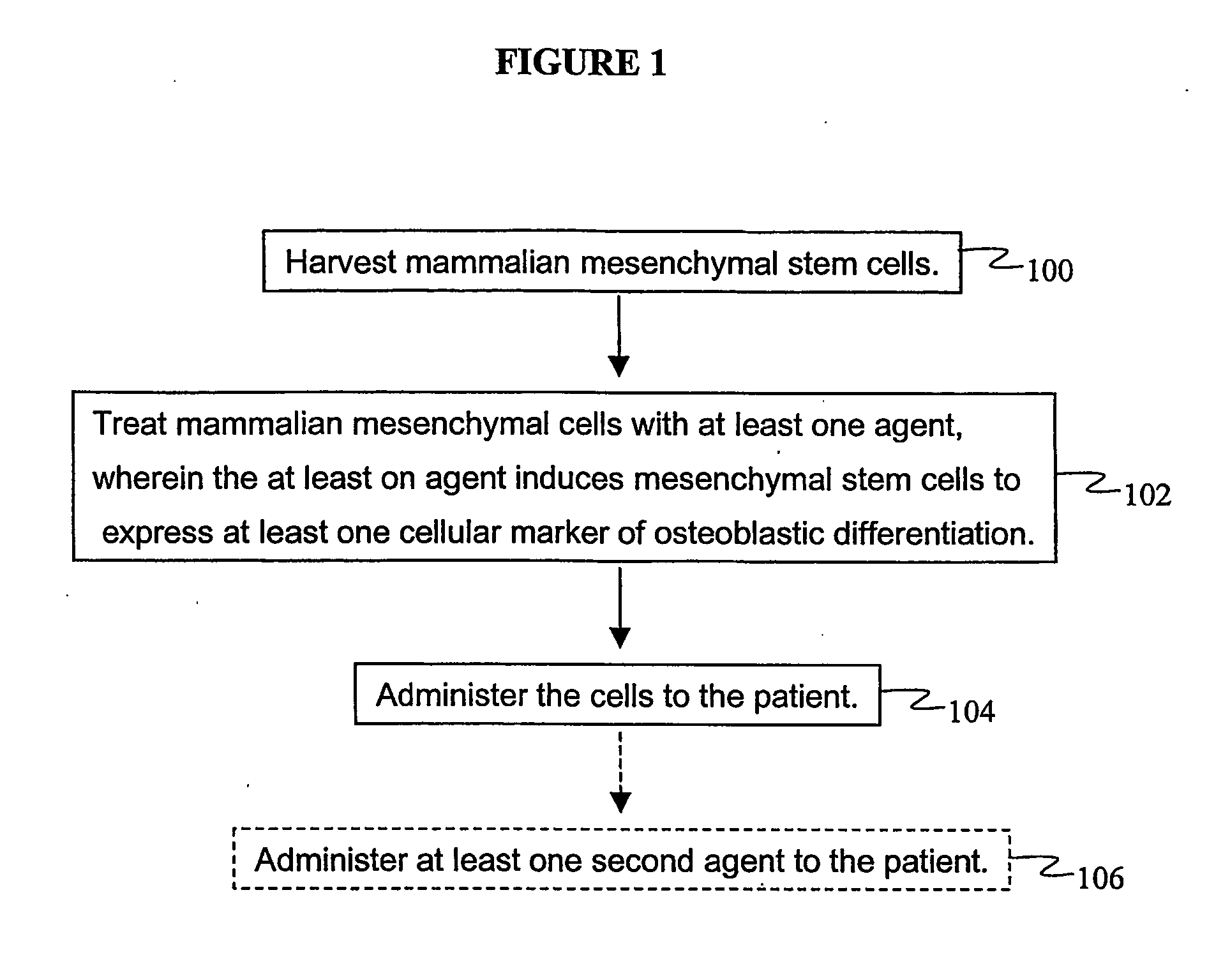
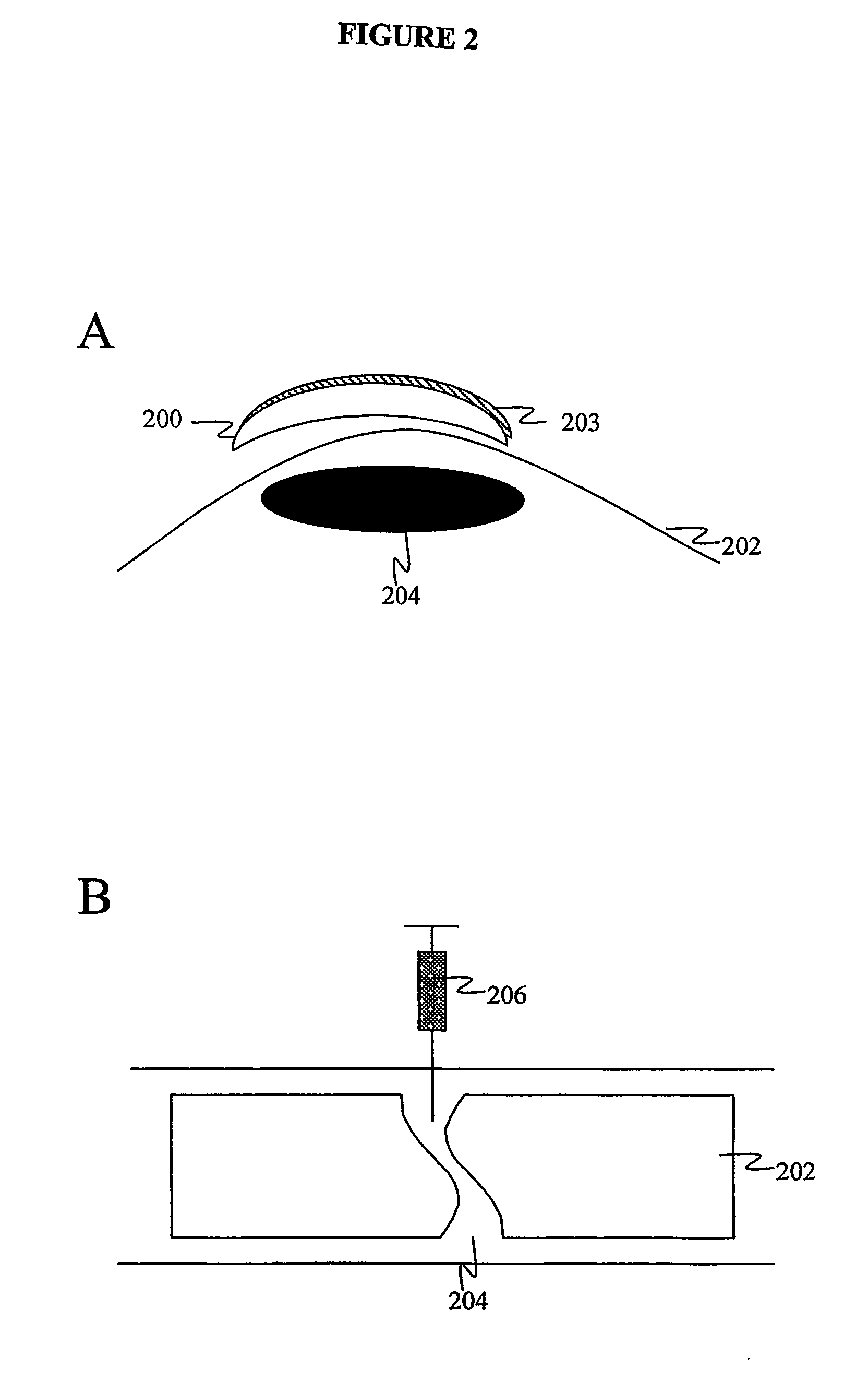
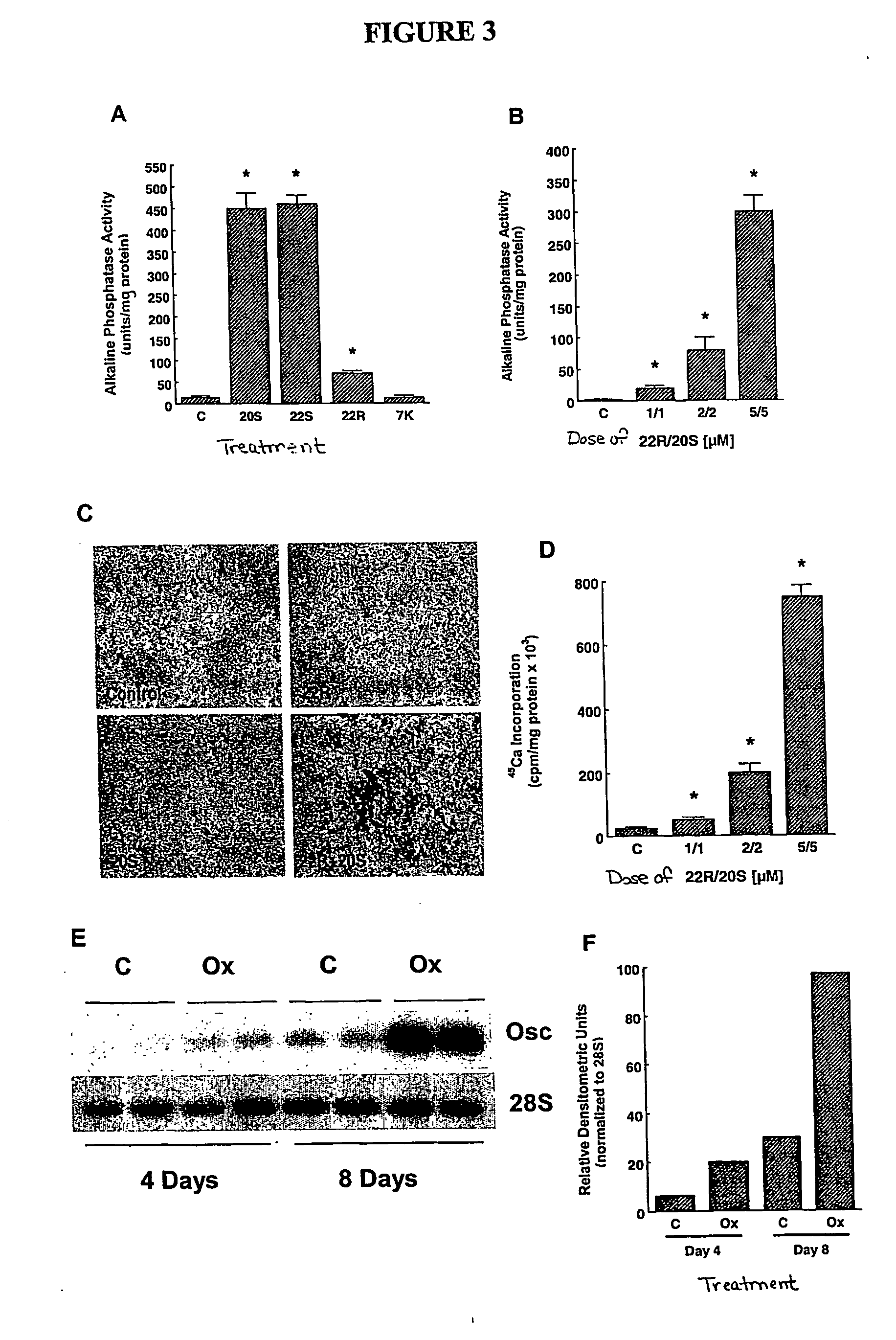
Agents and methods for enhancing bone formation by oxysterols in combination with bone morphogenic proteins
The present invention discloses agents and methods for inducing osteoblastic cellular differentiation, as well as the use of such agents and methods to treat patients to maintain bone mass, enhance bone formation and / orbone repair. Exemplary agents include oxysterols, alone or in combination with particular oxysterols, or other agents, such as bone morphogenic proteins, known to assist in bone formation. The invention further includes medicaments including oxysterols for the treatment of bone disorders and implants to facilitate bone repair.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Supplemented and unsupplemented tissue sealants, methods of their production and use
InactiveUSRE39192E1Increased longevityImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryTissue sealantVascular dilatation
This invention provides supplemented tissue sealants, methods for their production and use thereof. Disclosed are tissue sealants supplemented with at least one cytotoxin or cell proliferation inhibiting composition. The composition may be further supplemented with, for example, one or more antibodies, analgesics, anticoagulants, anti-inflammatory compounds, antimicrobial compositions, cytokines, drugs, growth factors, interferons, hormones, lipids, deminearlized bone or bone morphogenetic proteins, cartilage inducing factors, oligonucleotides polymers, polysaccharides, polypeptides, protease inhibitors, vasoconstrictors or vasodilators, vitamins, minerals, stabilizers and the like.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com