Method for simulating three-dimensional closed and clung cracks in rocks
A three-dimensional, crack technology, applied in the field of simulating three-dimensional sealing and close cracks inside rocks, can solve the problems of insufficient brittleness, high cost, complex technology and operation, etc., and achieve the effect of mild experimental conditions, short preparation cycle and high application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
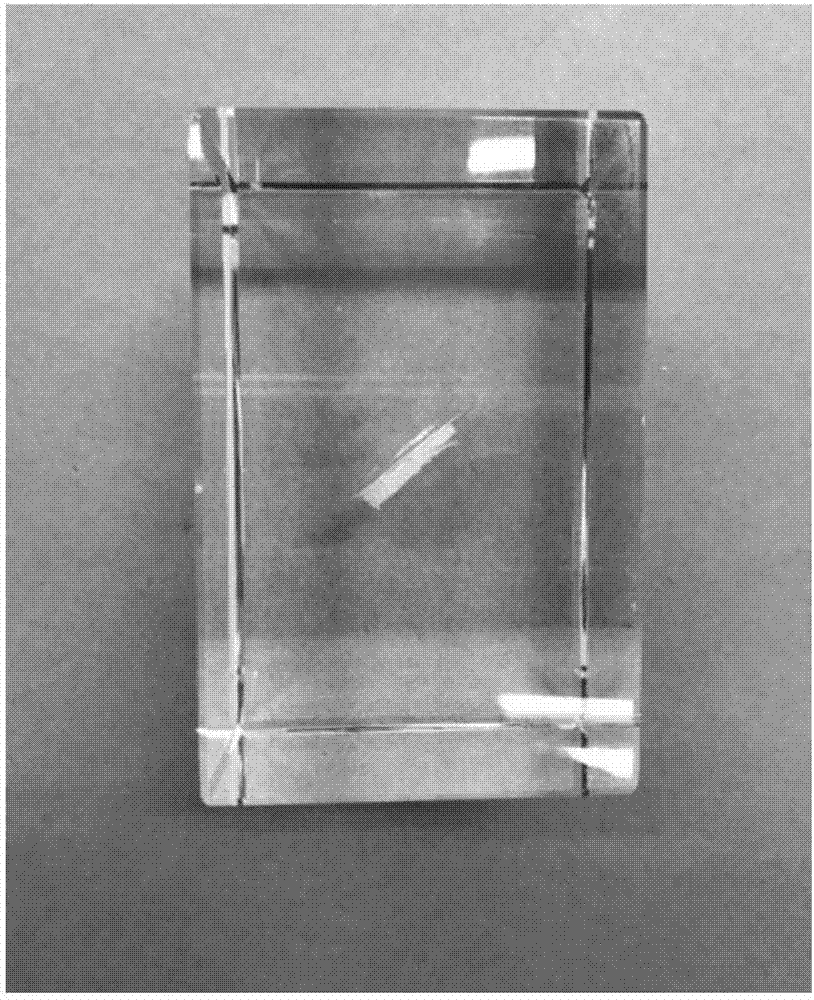
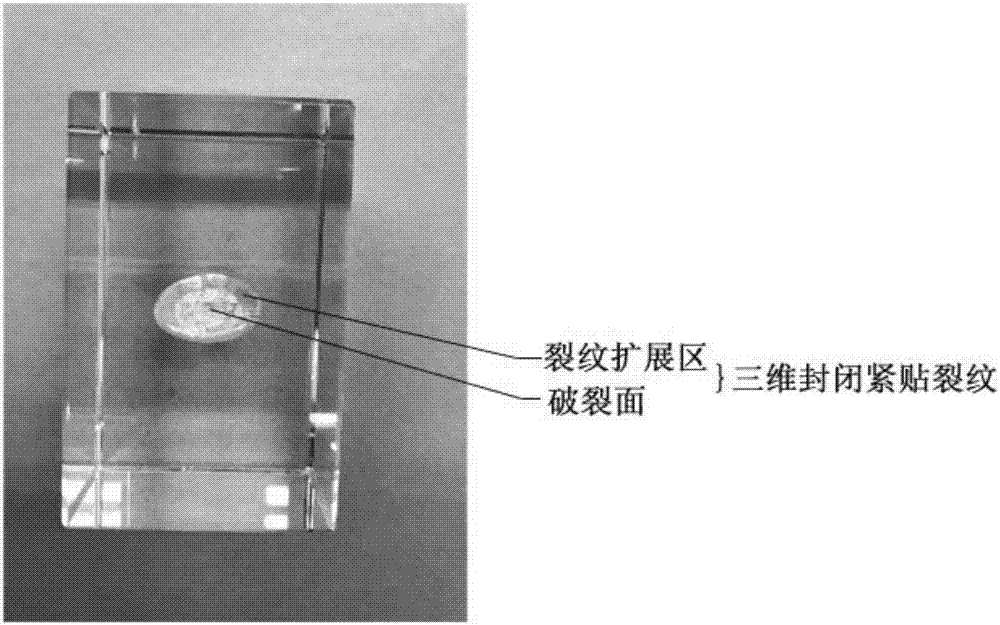
[0083] A method for simulating a three-dimensional closed crack inside a rock, comprising the following steps: taking a complete artificial crystal, selecting the position of a pre-fabricated crack, modeling the size and shape of the pre-fabricated crack; focusing a laser through a lens, and the energy of the laser The density is lower than the damage threshold of the artificial crystal before entering the artificial crystal and reaching the position of the pre-fabricated crack, and exceeds the damage threshold of the artificial crystal at the position of the pre-fabricated crack; the laser pulse causes the transparent material to be thermally ruptured, and a rupture occurs in the area covered by the pre-fabricated crack point; repeating the above process, a rupture surface consisting of a group of rupture points is formed in the covered area, and at the same time, a neat circle of crack propagation area is formed on the outer edge of the rupture surface and is connected with th...
Embodiment 2
[0091] Such as Figure 9-11 As shown, the method of Example 1 can also be used to make V, X, and Z cracks, which are used to measure the tensile and shear properties of rocks, and to explore the differences between these three types of cracks and the expansion and penetration of single cracks. Wherein, the laser wavelength is 1064 nm, the pulse width is 30 ns, and the pulse energy is 300 mJ. The size of the rupture point is 80 μm, the horizontal distance of the rupture point is 0.1 mm, and the vertical distance is 0.1 mm, and the number of layers of the rupture surface is 10 layers.
Embodiment 3
[0093] Such as Figure 12-13 As shown, the method of embodiment 1 can also be used to make cracks on the cylindrical artificial crystal, which is used to measure the influence of cracks inside the rock on its tensile strength, elastic modulus and fracture toughness, etc., to simulate cylinders, utility poles, etc. Cylindrical crack propagation and penetration. Wherein, the laser wavelength is 532nm, the pulse width is 20ns, and the pulse energy is 48.9mJ. The size of the rupture point is 20 μm, the horizontal distance of the rupture point is 0.01 mm, and the vertical distance is 0.08 mm, and the number of layers of the rupture surface is 6 layers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com