A permanent magnet variable stiffness flexible joint for robots
A flexible joint and variable stiffness technology, applied in the field of flexible robots, can solve problems such as low safety and poor environmental adaptability, and achieve the effects of simple manufacturing, simple operation, and simple movement form.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. In this way, how to apply technical means to solve technical problems in the present invention, and achieve the technical process of achieving the effect can be fully understood and implemented accordingly. It should be noted that, as long as there is no conflict, each embodiment of the present invention and each embodiment Each feature can be combined with each other, and the formed technical solutions are all within the protection scope of the present invention.
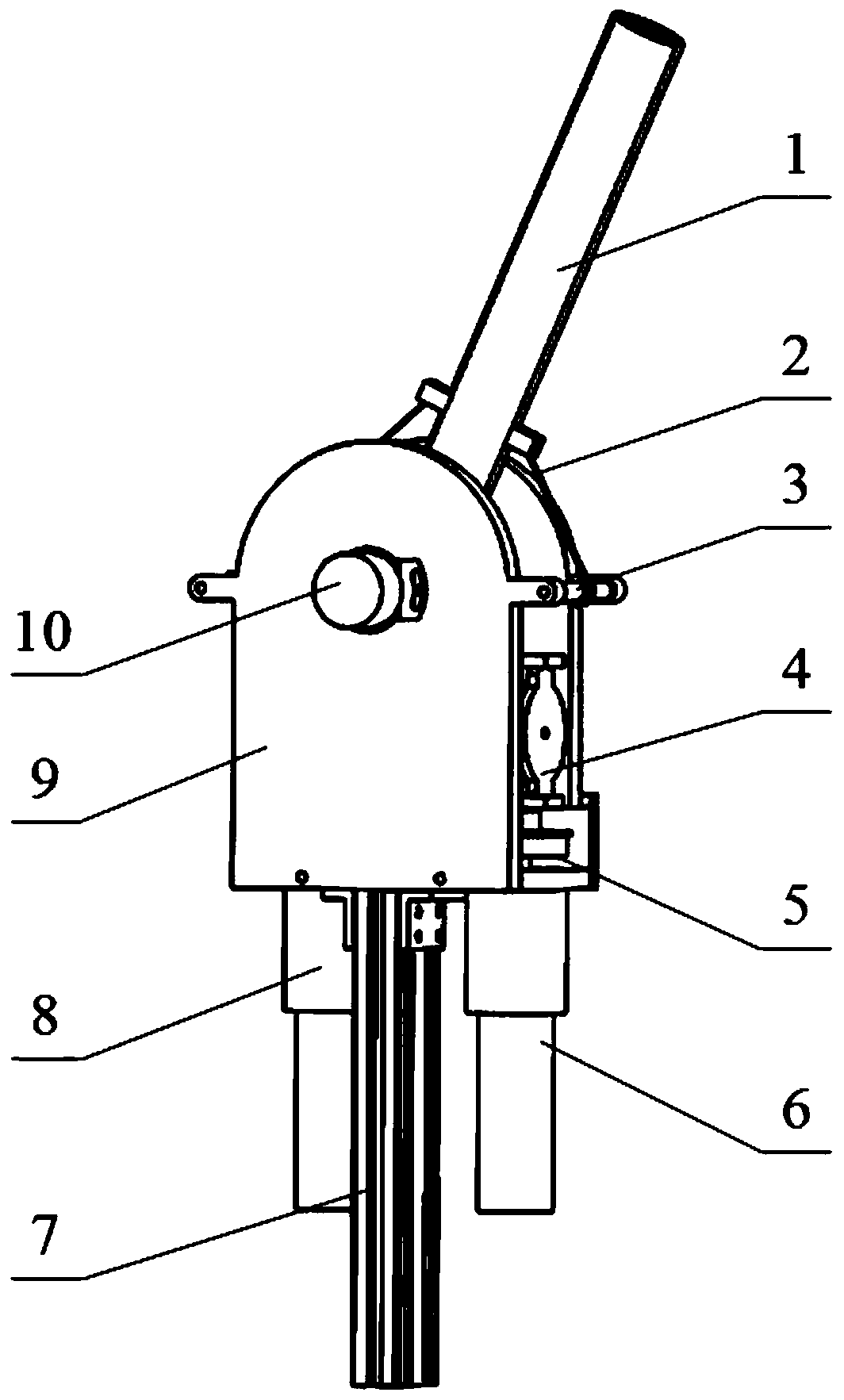
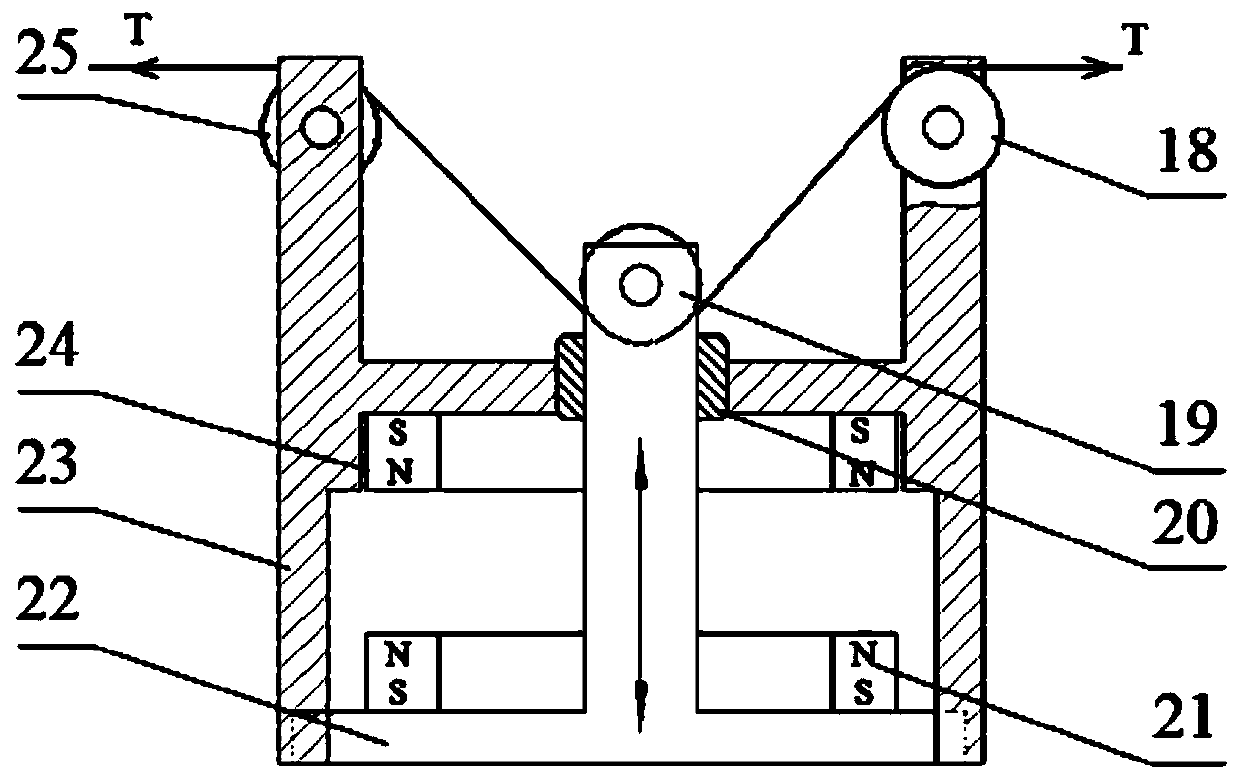
[0020] combine figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 To illustrate this embodiment, a permanent magnet variable stiffness flexible joint for a robot includes: an operating arm 1, a rope A2, a wire pulley A3, a permanent magnet variable stiffness module A4, a rope winch A5, a servo motor 6, a boom fixing frame 7, a harmonic Wave reducer 8, boom 9, encoder 10, wire pulley B11, ...
Embodiment 2
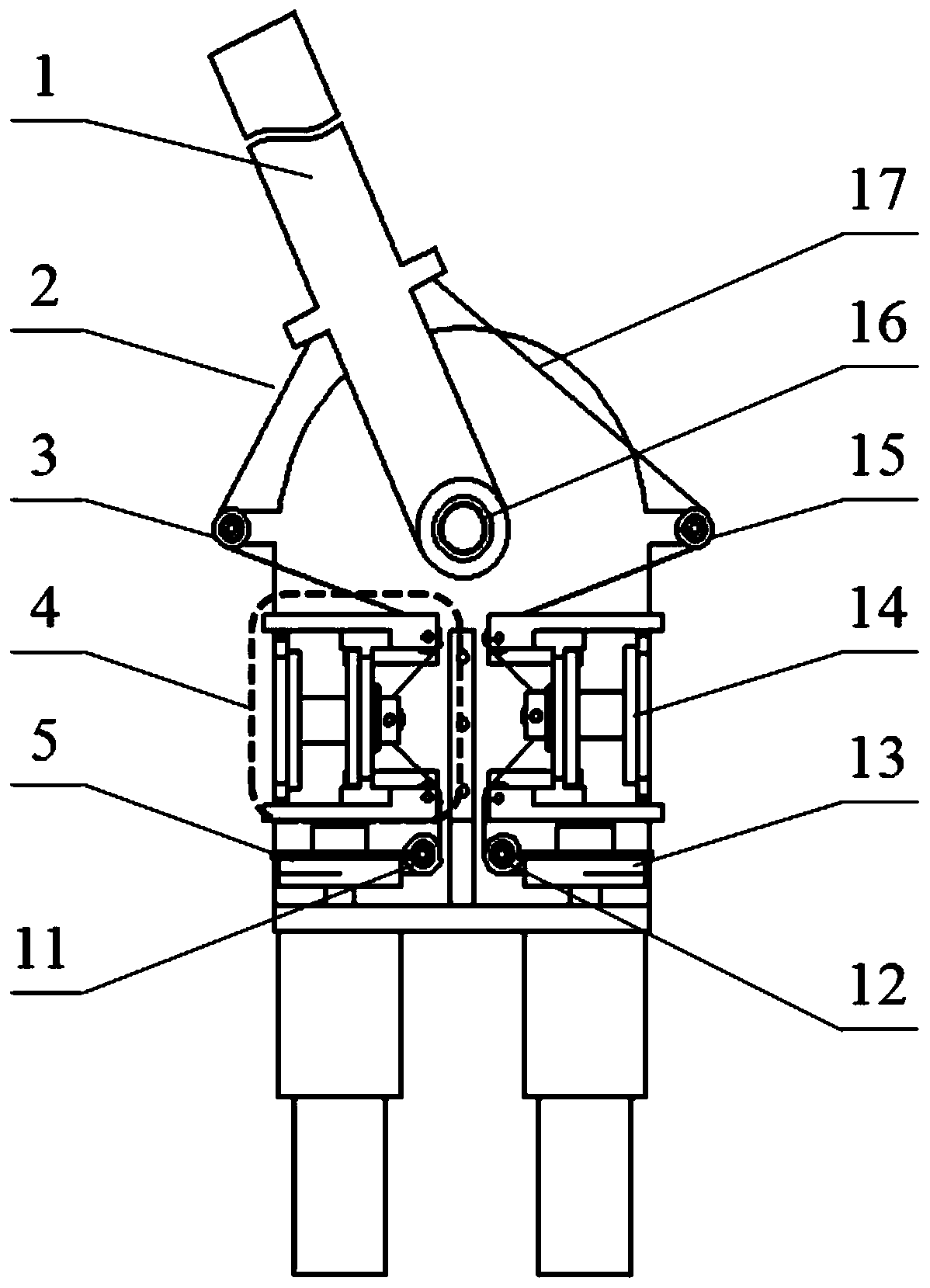
[0030] like Figure 4 As shown, it is a schematic diagram of a two-degree-of-freedom parallel variable-stiffness robot joint mechanism of the present invention, and two permanent-magnet variable-stiffness modules are symmetrically arranged in each rotational degree of freedom direction. The rotation axis of each operating arm is perpendicular to the direction of the rope pulling force of the rotation direction, thus ensuring the stiffness independence of the two rotation directions. All permanent magnet variable stiffness modules are placed behind, which reduces the mass and inertia of the operating arm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com