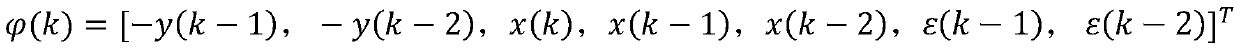A Parameter Estimation Method of Human Hand Skin-Electrode Bioimpedance Model Based on Electrotactile Device
A bio-impedance and model parameter technology, applied in electrical digital data processing, calculation, mechanical mode conversion, etc., can solve the problems of not fully considering the finger epidermis and electrode model parameters, not fully considering the human hand-skin impedance model, etc., to avoid Decreased ability of parameter correction, improved estimation accuracy, simple design effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] The invention will be further illustrated by the following examples.
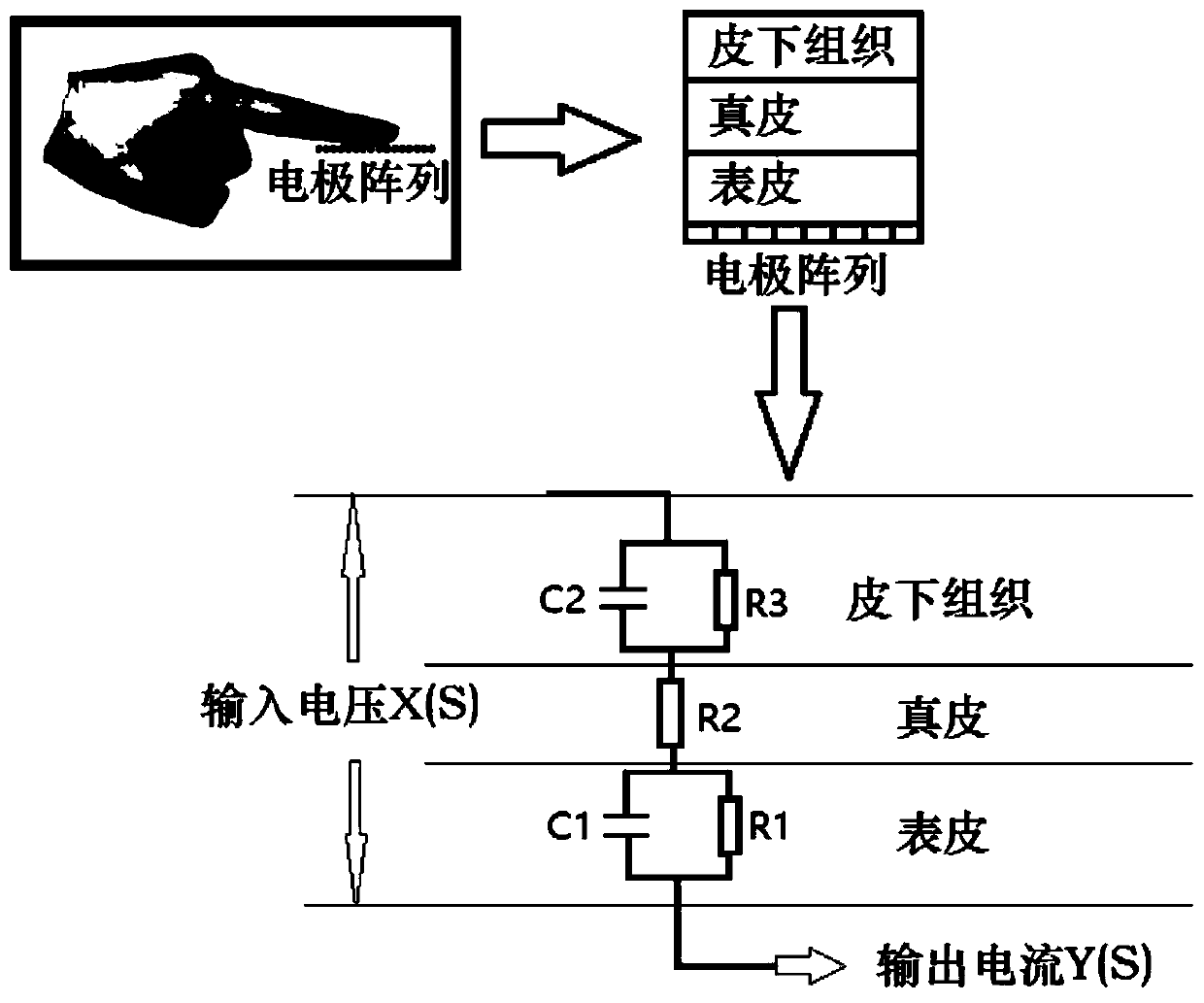
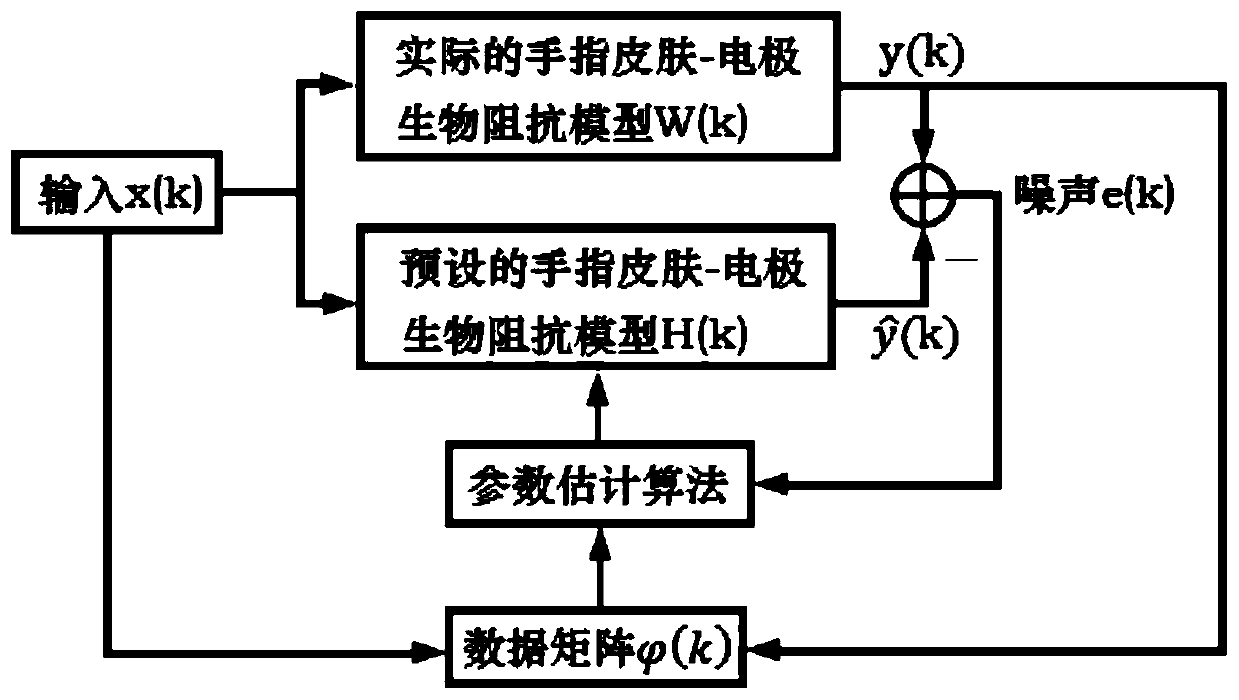
[0037] Step 1: Modeling of human hand skin-electrode bioimpedance.
[0038] (a) From the epidermis-dermis-subcutaneous tissue electrical impedance model, the Laplace transform formula can be obtained:
[0039]
[0040] in, is the Laplace transform form of the impedance model
[0041] (b) The relationship between Laplace transform and Z transform (Z=e Sτ , τ is the sampling period) to get:
[0042]
[0043] in, is the Z-transform form of the impedance model
[0044] (c) Transpose:
[0045]
[0046] (d) Do inverse Z transformation:
[0047]
[0048] rewrite it as:
[0049]
[0050] (e) The order of the finger skin-electrode bioimpedance model (that is, the least squares parameter estimation model) can be preset by the order of (4), and the preset human skin-electrode bioimpedance model is written in the form of least squares :
[0051]
[0052]
[0053] In the formula, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com