Inorganic phase-change material used for air conditioner cold accumulation and preparation method thereof
An inorganic phase change material and cold storage technology, applied in heat exchange materials, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as corrosion, non-flammability, leakage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
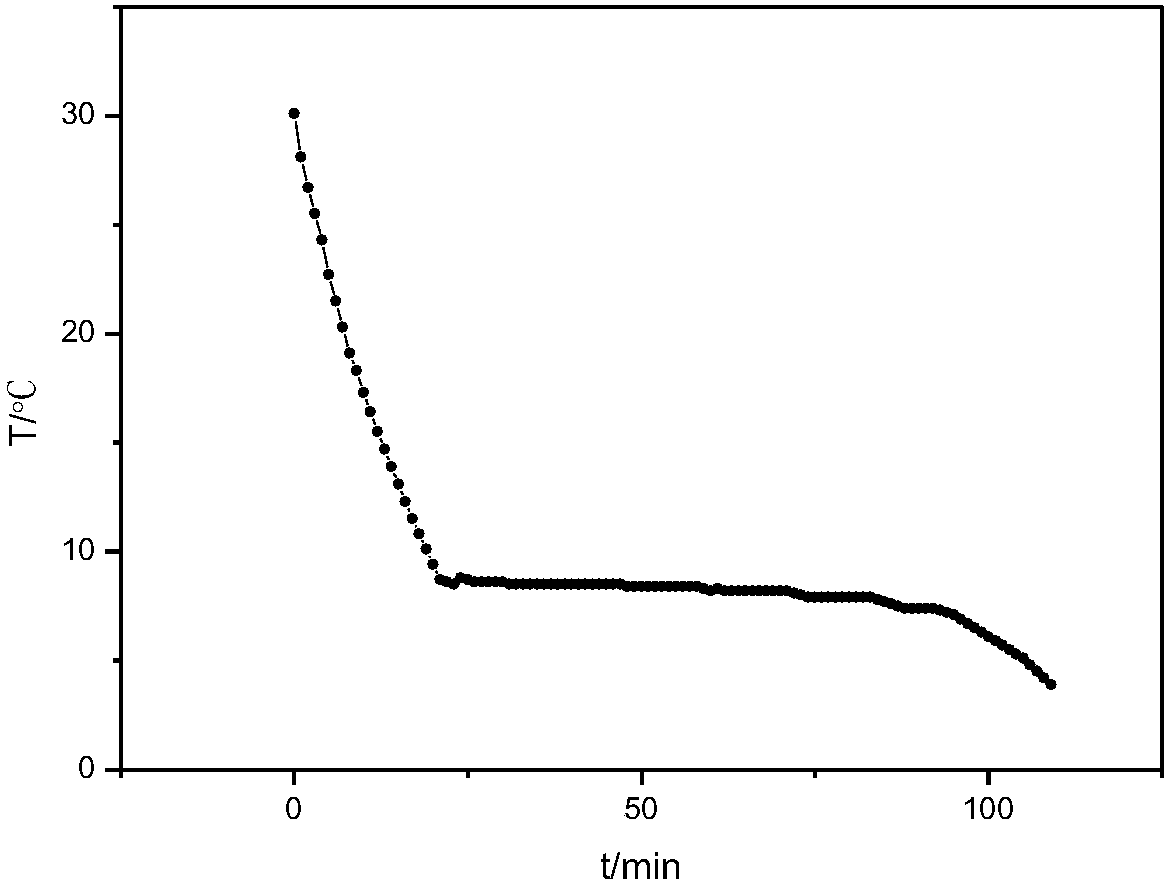
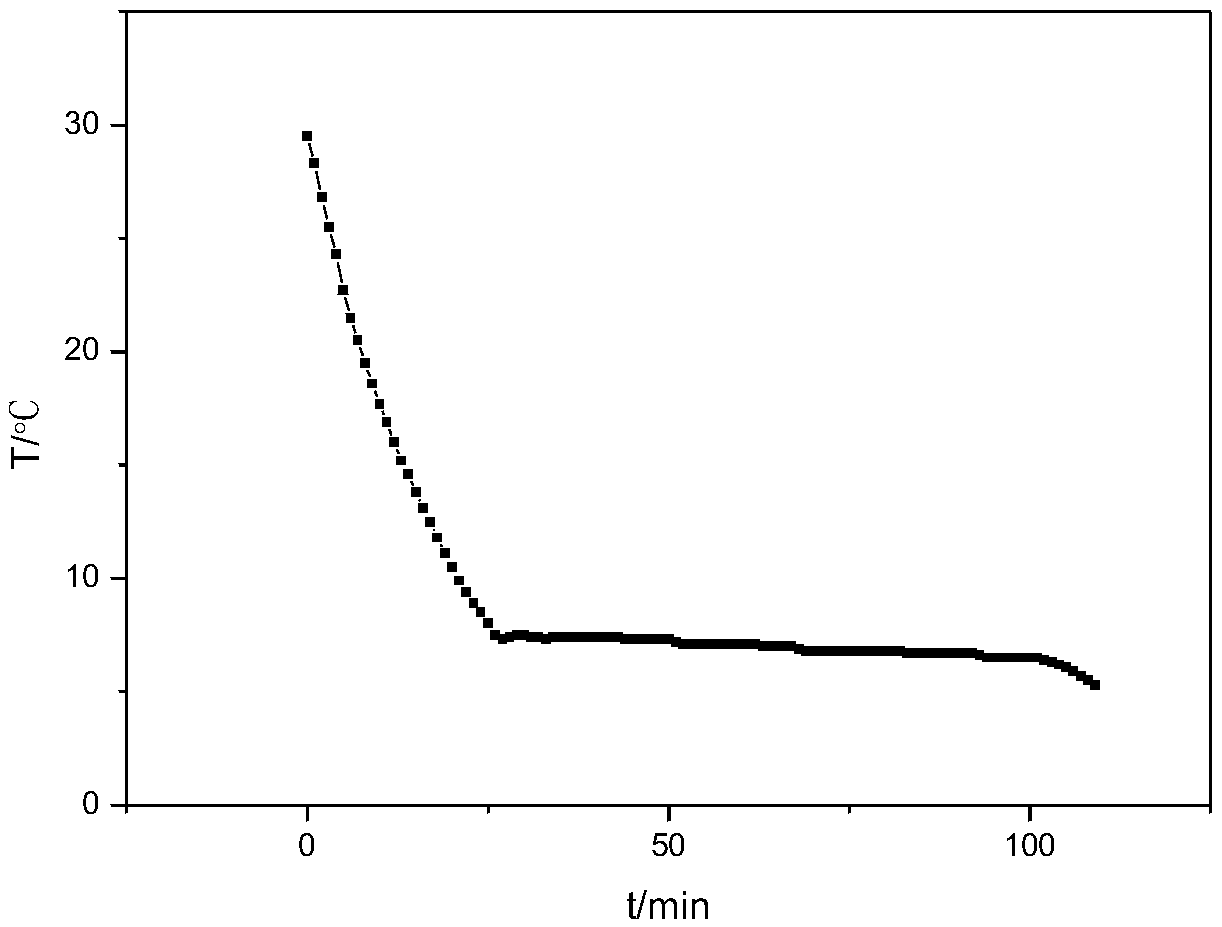
[0020] An inorganic phase-change material for air-conditioning cold storage, comprising the following components in parts by weight: 75 parts of sodium sulfate decahydrate, 7 parts of ammonium chloride, 2 parts of borax, 5 parts of hydrophilic gas-phase white carbon black, pH 2 parts of regulator and 0.1 part of conductive particles.
[0021] A preparation method for an inorganic phase-change material used for air-conditioning cold storage, comprising the following steps:
[0022] (1) Add sodium sulfate decahydrate and ammonium chloride into the mixer, start heating and stirring at the same time, and heat up to 40°C;
[0023] (2) add pH regulator and borax, stir at constant temperature, until borax is all dissolved;
[0024] (3) Add hydrophilic fumed silica into the mixer, stir at a constant temperature of 100r / min at a low speed, then add conductive particles, and then stir at a high speed of 600r / min to prepare a phase change material.
[0025] Preferably, in step (3), the...
Embodiment 2
[0030] An inorganic phase change material used for air-conditioning cold storage, comprising the following components in parts by weight: 80 parts of sodium sulfate decahydrate, 10 parts of ammonium chloride, 4 parts of borax, 8 parts of hydrophilic fumed white carbon black, pH 4 parts of regulator and 0.5 parts of conductive particles.
[0031] A preparation method for an inorganic phase-change material used for air-conditioning cold storage, comprising the following steps:
[0032] (1) Add sodium sulfate decahydrate and ammonium chloride into the mixer, start heating and stirring at the same time, and heat up to 50°C;
[0033] (2) add pH regulator and borax, stir at constant temperature, until borax is all dissolved;
[0034] (3) Add hydrophilic fumed silica into the mixer, stir at a constant temperature of 300r / min at a low speed, then add conductive particles, and then stir at a high speed of 800r / min to prepare a phase change material.
[0035] The phase change temperat...
Embodiment 3
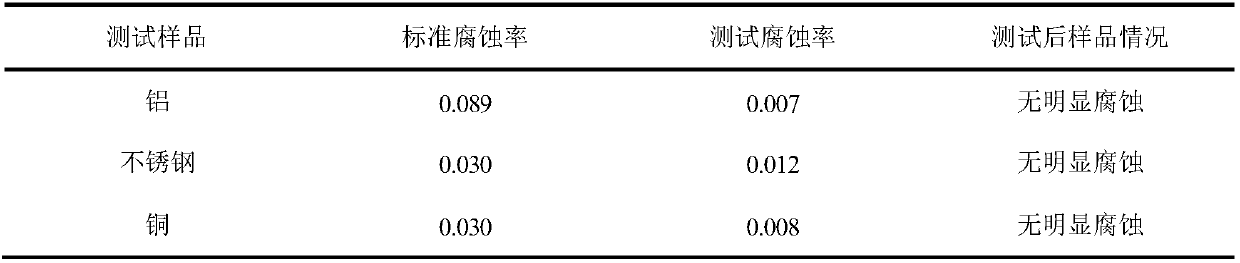
[0039] An inorganic phase-change material for air-conditioning cold storage, comprising the following components in parts by weight: 77% sodium sulfate decahydrate, 8% ammonium chloride, 4% borax, 6% hydrophilic fumed white carbon black, pH Conditioner 4% and conductive particles 0.4%. Wherein, boric acid is selected as the above-mentioned pH regulator, copper powder is selected as the conductive particle, and the pH is adjusted to 6.5.
[0040] A preparation method for an inorganic phase-change material used for air-conditioning cold storage, comprising the following steps:
[0041] (1) Add sodium sulfate decahydrate and ammonium chloride into the mixer, start heating and stirring at the same time, and heat up to 40°C;
[0042] (2) add pH regulator and borax, stir at constant temperature, until borax is all dissolved;
[0043] (3) Add hydrophilic fumed silica into the mixer, stir at a constant temperature of 200r / min at a low speed, then add conductive particles, and then s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition enthalpy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com