Radix et rhizoma ginseng, radix panacis quinquefolii and radix notoginseng solid fermentation processing method
A technology of solid fermentation and processing method, which is applied in the fields of pharmaceutical formula, medical preparations containing active ingredients, food science, etc. It can solve the problems of low bioavailability, low content of rare ginseng saponins, etc., and achieve the effect of low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
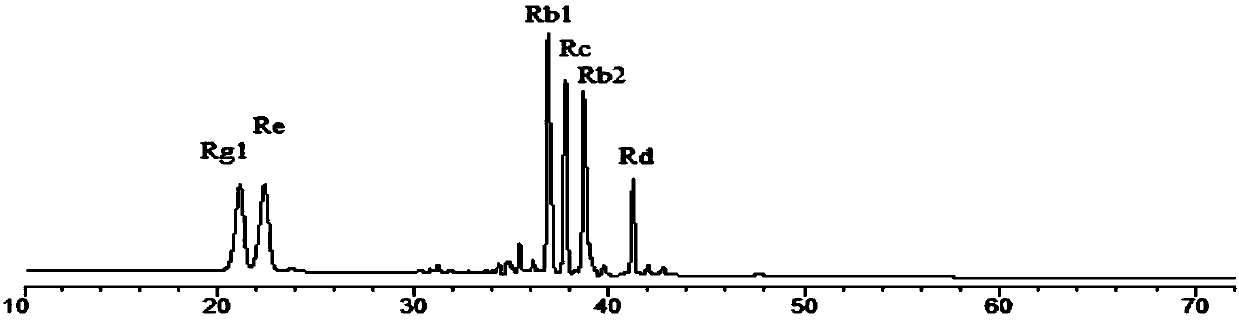
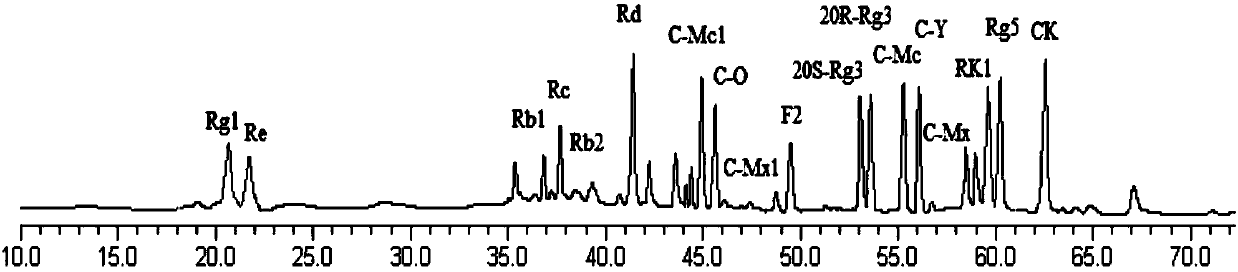
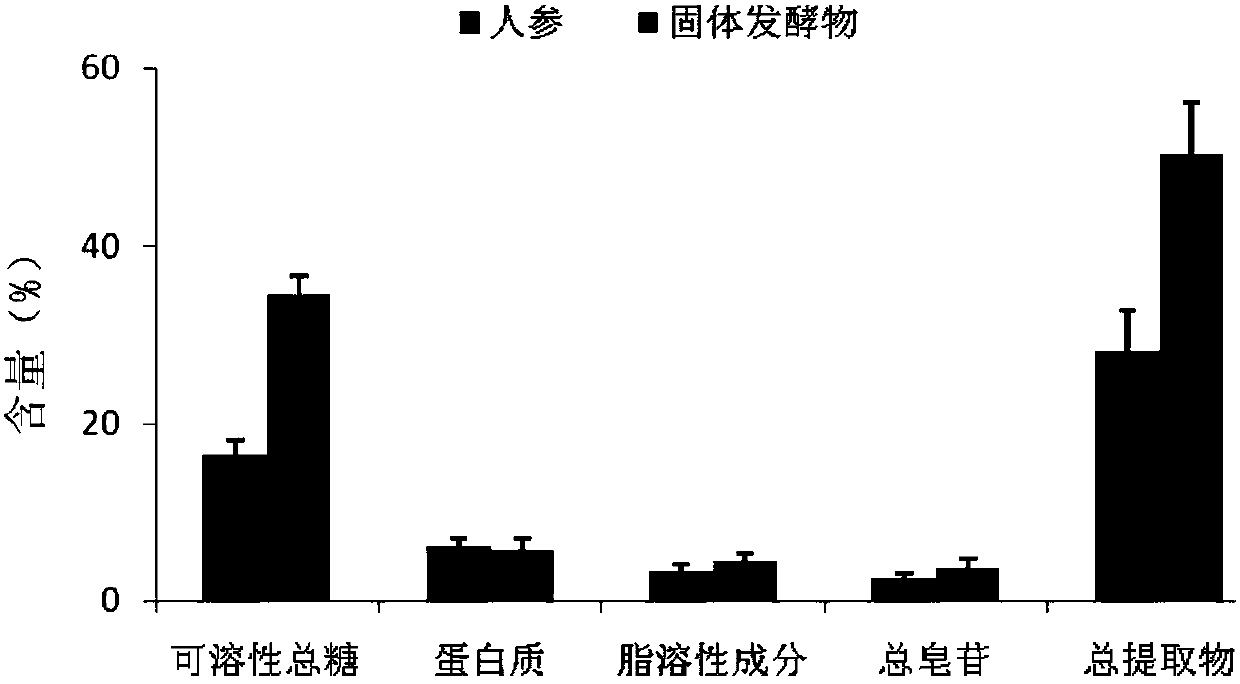
[0037] The whole root of fresh ginseng was used as the solid fermentation substrate, and the water content of fresh ginseng was 40%. After sterilizing at 121°C for 30 minutes, the cultivated Schizophyllum ferment strain was inoculated into the solid fermentation medium at an inoculation amount of 10%. Cultivate in the dark at 25°C for 20 days; the fermented product after fermentation is dried at 40°C. The original ginsenosides in the fermentation product were degraded, and a large amount of rare ginsenoside 20R-Rg was produced 3 、20S-Rg 3 , Rg 5 , Rk1, F 2 , compound K, compound O, compound Y, compound Mc1, compound Mc, C-Mx1 and C-Mx (see figure 1 with 2 ); at the same time, the contents of soluble total sugar, protein, fat-soluble components, total saponins and total extracts in the fermented product all increased significantly (see image 3 ).
Embodiment 2
[0039] Use undergrowth ginseng powder as the solid fermentation substrate, add an appropriate amount of water to make the water content 60%, and after sterilizing at 121°C for 30 minutes, inoculate the cultured Schizophyllum fermentation strains into the solid fermentation with an inoculum of 15%. In the culture medium, it is cultivated in the dark at 28°C for 10 days; the fermented product after fermentation is dried at 50°C.
Embodiment 3
[0041] The whole fresh American ginseng was used as the solid fermentation substrate, and the water content of American ginseng was 50%. After sterilizing at 121°C for 30 minutes, the cultured Schizophyllum ferment strain was inoculated into the solid fermentation medium at an inoculation amount of 20%. Cultivate in the dark for 25 days under the condition of ℃; the fermented product after fermentation is dried at 60 ℃. The original ginsenosides in the fermentation product were degraded, producing a large amount of rare ginsenoside F 2 and compound K (see Figure 4 with 5 ); at the same time, the contents of soluble total sugar, protein, fat-soluble components, total saponins and total extracts in the fermented product all increased significantly (see Image 6 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com